1. 引言
互动创新(Co-creation)描述了价值创新的演变过程,创新过程是由以公司为中心完成过渡到了在多方互动,特别是与客户的互动下来完成[1] 。互动创新大师Venkat Ramaswamy和Kerimcan Ozcan认为在一个互联网的时代、个人相对于体系,更是站在了价值创造的中心。为适应这种构造的转变,组织不再单方面制定产品和服务,他们必须促使利益相关者从客户和员工到供应商、合作伙伴和多数公民作为互动创新的参与者[2] [3] 。Co-creation也有学者直译为合作创新、共同创造等,但笔者认为合作创新是比互动创新更高的层次,属于契约式;而交互技术的发展,使得互动创新更多的走向非契约。因此,本文认为译为互动创新更确切。随着社交媒体的兴起及信息技术的发展,把互动创新应用于营销、管理和生产等方面将为定制企业带来机遇和挑战,成为越来越多定制生产企业未来的发展方向。而随着大规模生产逐渐转移到发展中国家,欧美国公司已经转向小批量生产更多创新的、定制化的、可持续的,具有高附加值的产品。为了在这个激烈的环境中获得竞争优势,制造型企业必须寻求新的制造技术来应对客户不断变化的动态需求,并做到经济生产,做到“智造”。随着客户需求的不断个性化与社会化媒体交互技术的发展,制造模式在不断演化、深化,从大规模生产–大规模定制生产–大规模个性化定制生产–完全个性化定制,如图1所示。图1中,在第3象限,以工程师设计的产品为主,是大规模生产模式;在第1象限右上角,工程师以客户为主,为客户设计产品,是完全个性化定制;在第4象限,在工程师引导下,实现产品的部分合作设计,是大规模定制模式;而在个性化需求与信息技术不断发展下,在第4象限开始向第1象限左下角发展,由客户需求引导工程师设计的产品,出现了互动创新驱动的大规模个性化定制。
大规模定制(Mass Customization, MC)是综合提升客户个性化需求满意度、企业生产或服务效率的有效生产模式。大规模定制的市场目标是小众市场,或多个细分市场。完全个性化定制(personalization)可
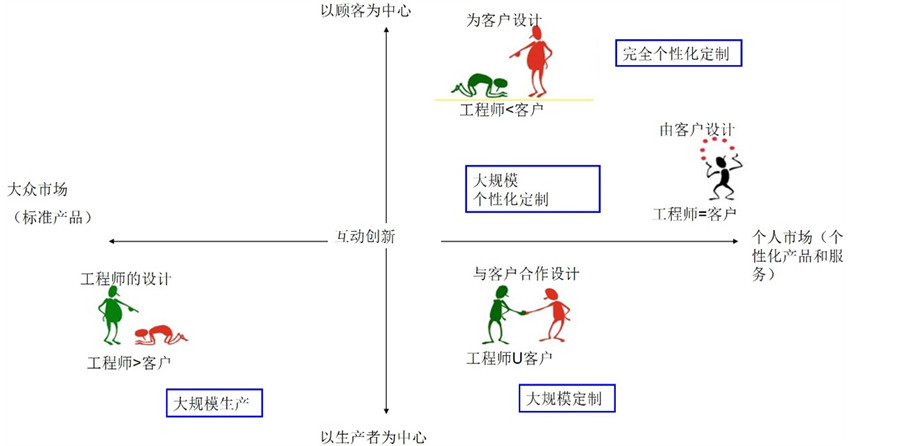
Figure 1. Customized manufacturing mode evolution chart [8]
图1. 定制模式演化图[8]
以满足消费者的特定需求,是根据客户的个性化和偏好,为单个客户生产或提供的产品和服务。(完全)个性化定制的目标是针对单个个体的细分市场。出现的“大规模个性化定制(mass personalization, MP)”生产模式,可称为一种“智造”新模式。是指以相对低的成本、相对快的交货期为单一客户生产或提供产品与服务,是提升客户个性化需求满意度与企业生产或服务效率的新模式,使得实现面向单一客户的市场得于实现。对于顾客,可以更快拿到高质量、符合要求、实时服务的个性化产品。对于生产商,可以通过提供价格稍高的个性化产品,来获得差异化和提高客户的忠诚度和满意度。Michael Fink, et al. (2006) [4] 介绍了大规模个性化定制的四个应用程序:个性化的内容层、Ad Hoc网络社区、实时评分和虚拟的媒体库服务。Ashok Kumar (2008) [5] 认为大规模定制战略正转变成为一个大规模个性化定制的策略,使一个人的市场成为现实,至少在某些行业上已经实现。M.M. Tseng (2010) [6] 从产品设计角度研究了大规模个性化定制,设计了一个基于设计平台和客户主动参与制定的产品生态系统来实现MP。认为达到规模化个性化定制的目的是通过提供个性化产品设计,获得用户良好的用户体验,有效和高效地满足客户的需求。Wang,J;Lu,GD (2011) [7] 提出了大规模个性化客户参与的3D服装设计方法。Feng Zhou等(2012) [8] 认为大规模个性化定制需要一个超越客户和生产商的成本价值的战略,来满足个性化客户的潜在需求,并从互动创新角度分析了定制生产的发展。Vladimir Zwass (2010) [9] 认为目前定制企业对互动创新的应用形式以虚拟社区、开放创新和众包为主。
总之,从目前的研究来看,把互动创新与定制生产结合起来的研究不多。2012年,著名大规模定制专家Dominik Walcher和Frank Piller评选出的国际定制电商网站500强中,没有强调互动创新的作用[10] 。Celestine C (2012) [11] 互动创新是企业未来竞争的趋势,在以“客户为中心——customercentric”的时代,定制企业对互动创新更是重视。目前的研究主要是从开放创新的角度去研究定制模式,较多的文献的重点集中在如何设计提供给客户做选择的“工具包”方面。随着交互技术的不断增多,也有不少文献重视与客户的交互,但没有从互动创新双驱动下,结合大规模定制与完全个性化定制的优势去建立“基于互动创新的大规模个性化定制供应链模式”。综上所述,“互动创新驱动的大规模个性化定制生产模式”是未来生产的发展趋势,可以说是“智造”的新模式,在客户动态需求下,如何建立这种模式、供应链上各方如何使用互动创新驱动技术,提升客户满意度与企业生产效率,面临不少的困难和问题,亟待从理论和实践层面研究和探索解决之道。
2. 互动创新驱动的大规模个性化定制生产模式提出的必要性
2.1. 大规模定制与完全个性化定制的存在不可避免的局限性
大规模定制是实施个性化定制的过程。在某些方面,个性化定制是一个目标,而大规模化定制是实现这个目标的过程。个性化定制和大规模定制都能使企业更适应市场变化,从而变得更灵活,更有效地应对市场波动。但面对复杂多变的市场环境,大规模定制与个性化定制的弊端也越来越明显。
2.1.1. 大规模定制的局限性
理想中的大规模定制是一种根据每一位客户的特殊需求,以大规模生产的效益提供定制产品的生产方式。然而在实际当中,应用大规模定制生产方式的企业,并非所有的生产环节都是按客户定制化的需求来生产,通常客户订单分离点(customer order decoupling point, CODP)位置的确定,也就决定了该企业的可定制程度和客户定制可选范围。在动态环境下,客户个性化多样化需求不断增加且变化,传统MC方式提供的既定选择及其生产系统,不能适应市场的变化,不能实现不同层次、不同程度的定制,不能区别对待不同定制深度的客户,对客户复杂需求响应慢,这样其占有的细分市场和目标客户群范围也较小。虽然与大规模生产模式相比,大规模定制增加了对差异化产品需求的一部分客户,细化了客户群,但是这类客户群的范围还是有限的,无法把产品渗透到更多细分的市场里。而且,当大规模定制提供多款品种给消费者选择的时候,品种增加也造成了装配系统的复杂性,从而影响系统的性能。另外,消费者的作用仅仅局限于选择固定的模块组合,消费者并没有获得完全按照其意愿生产的产品。而追随包括价格和客户等待时间等参数、占有具有多样化需求的细分市场、并尽量满足这些细分市场中不断变化的需求,是大规模定制企业进一步发展的方向。
2.1.2. 大规模定制正朝着完全个性化定制方向迈进
Monetate公司2013 [12] 在针对1100多个数字化公司和电子商务的专业品牌和机构调查基础上,在Econsultancy发表了一份关于个性化在线定制的报告。报告中提到“个性化的网络体验是当前和未来成功的关键”,这句话得到了61%的网络用户和94%的公司肯定。在21世纪,信息和通信技术的广泛运用使得个性化定制战略在与客户的互动关系更加多样化,实现个性化化定制也趋于容易。越来越多的个性化定制电子商务网站不断涌现,很多企业都开始创办公司或扩展业务来提供个性化产品,如Chip N Dough (个性化饼干罐)、Zyrra (个性化内衣)、Choiceshirts (附个性化标志的鞋设计)、Namemaker (附独特标语的礼品包装)和American Art Resources (定制的健身设备工艺品)。一些公司为迎合个性化并获利,也在重塑他们的定制化生产战略,如Spreadshirt (T恤自主设计)、Zazzle (定制鞋和邮票)、CafePress (可定制多种产品,包括T恤、杯子、邮票、CD、书等)。CafePress代表着一种超越简单个性化的新趋势,你可以在繁多的产品中挑选并管理自己的客户服务,因此它是一站式的个性化。这些公司反映了生产商正往个性化生产发展,定制化生产已经在前往经济实惠的个性化生产的道路上取得了显著的进步。
2.1.3. 个性化定制存在的局限性。
Monetate公司的调查也显示:56%企业没有实现对客户的个性化定制的网络经验。个性化被看作是在线业务成功的关键任务,但国际国内定制成功的企业较少,没有一个标杆与运作参考模式。总之,目前没有一个指导定制客户需求变化快、生命周期短的定制电商运作的模式,有必要去进一步深入研究。而且,动态环境下,完全个性化定制方式往往存在价格高、交货期长、质量不稳定等问题。个性化定制虽然满足了用户某种程度的个性化需要,但由于需要根据用户的特殊需求组织生产,由此带来生产周期长、产品价格高与质量不稳定等问题。生产周期长,是因为对定制产品的设计和制造过程相对复杂;生产成本高,是因为产品品种多、批量小,需要大量的人力和物力,无法通过规模生产方式降低成本;质量不稳定,是因为面对的是层出不穷的新产品,员工的知识和经验往往跟不上产品的发展,导致产品质量波动较大。目前的客户希望产品能具备高质量、快速的交货期、高水平的定制,却不希望付出过高的价格。因此在动态复杂需求环境下,如何以较低成本、较快速度,满足客户的高度个性化需求水平,是影响个性化定制发展亟待解决的问题,其不仅影响了客户满意水平的提升,也限制了企业的进一步发展。
2.2. 互动创新驱动的大规模个性化定制是企业竞争的新范式
2.2.1. 互动创新是当前企业竞争的发展趋势
未来竞争的基本思想是,在新的竞争格局,价值越来越将由公司和客户互动交互决定。苹果公司利用互动创新方式来提高其创新的速度和范围,两年里与参与创新的实体共同创造的价值超过10亿美元,使它在市值上超过了微软公司。星巴克推出了在线平台MyStarbucksIdea.com去挖掘客户的想法和引导转变。联合利华转向共同创造等重新设计促使重构产品线,例如Sunsilk公司洗发水,恢复增长等。耐克的“Nike + 互动创新”行动也取得了非凡的成功。互动创新实践的例子充分说明了,互动创新范式为个人、组织、社会提供了一个蓝图,同时提出一个概念性的框架,引导组织跨部门采用这种转换的方法。Venkat Ramaswamy和Kerimcan Ozcan [3] 呼吁企业要注意生活经验,建立接触平台和管理系统以作为创造性的合作,设计和开发“win more-win more”战略,强化财富、福利和幸福感。
互动创新重新定义了组织,把客户、员工、供应商、合作伙伴和其他利益相关者引入到价值创造的过程。目的是为了:规划新的突破策略;执行设计引人注目的新产品和服务;转变管理过程;减少风险和成本;增加市场份额、忠诚和回报等。企业再也不能视定制客户和其他利益相关者作为产品和服务的被动接受者,而必须学会进行重新定义和交付附加价值。在未来竞争中,价值越来越将由公司和客户交互去共同创造,传统的以公司为中心、以产品为中心的价值创造,迟早会被超越。目前更需要关注消费者和他们的经验,来更积极参与价值的创造。
2.2.2. 信息技术的新发展使得实现大规模个性化定制成为可能
由于市场压力,客户参与产品设计所需技术的发展(如web2.0、P2P、B2C、B2B,通信技术、搜索和推荐引擎),CRM战略的发展,ERP软件随个性化需求的进一步改进,数据库和数据挖掘技术的发展等,使大规模个性化定制生产已经成为可能。大规模个性化定制将会为客户和生产商带来高于成本的价值,因此它是可行的战略。在连续的细分市场,大规模个性化定制强调单个市场,它是大规模定制的极端。相对于大规模定制中有限的客户参与,大规模个性化定制需要客户积极参与产品设计过程。
互动创新范式是目前的发展趋势,信息技术使大规模个性化定制成为可能,在线定制企业为了获得客户动态需求,不断通过各种互动创新技术与方式,如社交网站、开放创新、众包等作为主要的交互信息渠道,与客户进行合作创新。如今,在实施互动创新战略过程中,很多公司已经采纳如博客、社交网络等社交媒体应用来找到与客户、商业伙伴和供应商合作的新方式,公司的价值不仅仅来自平台自身,还来自于社交媒体的使用方式和平台产生或分享的信息。大规模个性化定制是客户“互动创新”新范式,把两者结合的互动创新驱动的大规模个性化定制是企业未来发展趋势。
3. 互动创新驱动的“大规模个性化定制生产模式”提出
“互动创新驱动的大规模个性化定制生产”模式的基本设计思路是:在客户动态需求驱动下,充分发挥“互动创新”的驱动作用,开发利用互动创新知识,促进客户、电商商户、生产商、供应商等供应链上的各方实现双向推拉结合的“互动创新”,从而实现产品创新、市场策略创新、服务创新的新模式。其基本生产流程见图2。

Figure 2. The process of mass personalization driven by co-creation
图2. 互动创新驱动的大规模个性化定制模式流程图
首先,从物质实体的角度上看,从互动创新的渠道与途径出发,用户通过社会化电商社区、工具包、众包等方式提出自己的想法或评价或交流。定制电商商户可从这三种方式获得并收集用户信息交流的知识,并对其进行分类,然后把客户知识交给生产商。生产商通过了解筛选客户知识信息,进行产品、服务以及市场策略的设计和改进,产生新的3D原型,交给电商用户。在线定制电商进而通过网站将产品原型交给用户进行访问与虚拟体验。用户则通过网站的交流平台对产品进行意见反馈。在线定制电商重新获得用户反馈知识,并将其整理分类交给生产商。生产商通过反馈知识再做改进,并向供应商等采购生产该产品的原材料等,生产该产品,将改进后的产品交由电商,以此结束和用户互动创新的过程。
其次,从知识流的角度,互动创新主要有三种途径:社会化电商社区例如facebook、twitter;工具包例如建议包、心愿包等;众包形式例如威客、人人猎头等。用户在这些网站中对产品服务等进行知识交流,留下用户的声音(各种需求知识)。紧接着,定制电商和生产商把客户知识从网站中被提取,将收集的信息通过大数据挖掘技术进行整理加工后,建立互动创新知识库,并与企业自身的产品、服务知识库进行优化存储,最终形成客户知识。其中包括用户对产品的使用体验、产品评价、改进创意,包括售后服务的评价、服务满意度评价,也包括用户对现下潮流趋势的分享、市场价格的讨论、用户的偏好信息等。这些信息都为各类企业后续的生产服务推广方面提供了非常有用的价值。这一阶段,客户知识是数据挖掘的结果,信息价值不断增值的过渡阶段。分类优化后的客户知识开始进入企业内部,进行知识应用。从信息知识库中提取出对应产品、服务和市场创新的有价值的用户知识数据,进行信息优化,制定产品创新、服务创新及市场创新。这一阶段企业处于信息价值的“高端”,是信息充分实现其价值的阶段,是客户知识的创新与应用阶段,达到信息价值最优化。
从实现大规模个性化定制的角度,主要体现在如何实现既能满足客户个性化需求,又能实现相对低的成本与相对快的交货期上。在互动创新知识上产生新的3D模式产品原型,是一个改进组合或增加其它元素的原型,在提供给客户网络选择与体验时,生产商就会规定每件组合产品保证全球限量生产,这样就满足了客户的个性化定制;但由于生产商已对产品属性分解,因此,在根据客户需求挖掘、提供给的组合选择中,生产商就已经测算出最大组合量,及不同数量生产的成本,生产商通过共性组合,已经降低了成本。而为了尽量满足生产商的最大组合数量,达到组合批量,降低成本,在线定制企业也可以通过聚需求的方式,如团购等来汇聚达到最大组合量,这样,就实现了价格相对低、交货期相对快的个性化定制产品,提高了客户的个性化满意度,也使生产商降低了生产成本,提高了生产效率。总之,通过对互动创新知识的挖掘应用,可以实现产品、服务与市场的创新,促进客户、定制电商、生产商、供应商等参与到互动创新过程,企业与客户共创价值,实现互利共赢。
4. 案例应用
大多数定制企业的鞋子定制都是从鞋面、鞋底、鞋跟、鞋帮等方面定制。运动鞋的定制还会涉及到鞋舌、鞋带的定制。女鞋的单鞋主要由鞋头、鞋面、鞋跟、鞋垫、鞋底、鞋帮、装饰物等组成。如图3所示。下面用美国一女鞋定制企业Ninashoes做案例分析。Nina由两兄弟Mike和Stanley Silverstein于1953年在纽约成立,随着电商的兴起,Nina也推出了个性化的在线定制服务,用户在该企业的定制网站通过对材料、皮质、颜色的选择可形成超过两百万的定制属性组合。图4表示了Nina网上的女鞋定制流程。Nina的个性定制采用组合产品的设计原理,用“选择款式–选择颜色花纹–选择大小”的流程,将女鞋各个组成部分拆开使用户能进行颜色、材料的个性组合选择。
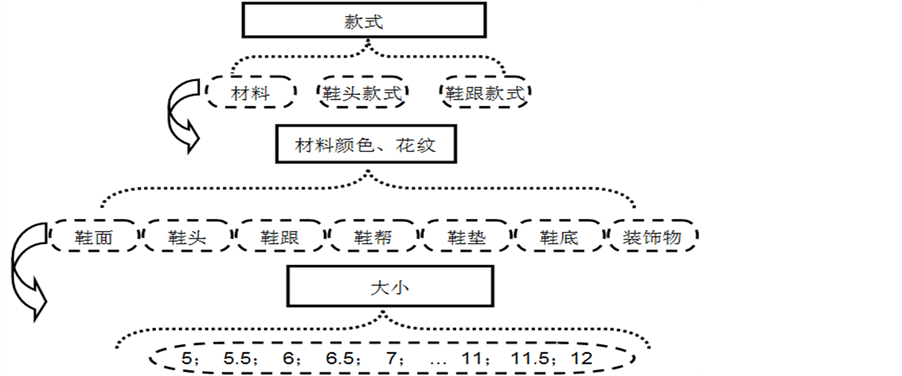
Figure 4. Flow chart of online customization shoes
图4. 在线定制鞋流程图

Figure 5. Nina mass personalization model driven by co-creation
图5. 互动创新驱动的Nina大规模个性化定制模式
Nina定制平台上的互动创新的方式主要是两种,一种是工具包,就是她的“Wish List”,客户可以通过给Nina发送留言的方式表达自己的想法;另一种就是“Design Your Own”,就是直接在定制页面上进行定制属性组合的选择。当订单发送到Nina后台时,Nina可以通过自建的知识库对定制产品的信息进行知识分类与数据挖掘,最后将知识应用到产品创新中。知识库建立后由生产商对产品进行3D原型设计开发,原型出炉后交由客户做产品体验和反馈,Nina将客户反馈的知识挖掘分析得出聚需求等数据,接着给生产商进行改良设计,供应商提供原料生产,最后物流商将产品配送到客户手上。具体流程如图5所示。
总之,在互动创新驱动下,互动创新驱动的Nina大规模个性化定制模式协助消费者挖掘更多隐性需求,增强消费者的个性化设计体验以及对定制产品的满意度,进而提升客户忠诚度。另外通过聚需求手段扩大需求规模,形成大规模生产,降低制造商生产成本,从而降低定制鞋价格,这样,企业与客户共创价值,实现多方共赢。
5. 结论
模式实践的关键因素。在互动创新驱动的大规模个性化定制模式中,每个环节都发挥重要的作用,环环相扣。但要让在线定制企业的交流知识得以运用到企业生产经营中,对信息的大数据挖掘技术是一大关键因素。另一关键因素,就是信息在供应商、生产商、在线定制企业、物流商之间的紧密联系下如何发挥作用,以及发挥什么样的作用。因为单从社区用户来讲,他们的角色任务只需制造信息、生产知识,而企业则需要采取数据挖掘技术从这庞大的信息量中提取自身所需的客户知识,运用至产品、服务、市场策略中,同时企业与企业之间、企业与部门之间如何更好的聚合信息,增加信息与企业的粘度。可见,整个模式的有效运行主要依赖大数据挖掘技术和企业之间的信息聚合、共享和管理。总之,推行大规模个性化定制战略,对于传统定制企业而言有了更高的要求。互动创新应用需要依赖先进的信息技术,通过IT技术吸引消费者参与到个性产品的互动创新当中(包括Web 2.0、P2P交流技术,引擎搜索和推荐引擎等),另外相应的客户关系管理战略,ERP软件在个性需求、数据仓库以及数据挖掘方面的改进发展等也需相应地给予重视。
模式实践的局限性。首先,这个模式是基于互动创新的在线定制平台之上,知识的增值前提是有知识的产生,所以模式依赖于用户所发表的信息。这就要求了在线定制企业需要加强网站建设力度,更好的聚合社区用户,增加忠实用户数量,一旦失去了用户的信息,大规模个性化定制也失去了互动创新的意义。我国多数企业已经接入了Internet,并利用其进行管理和商务活动,但总体上我国企业信息化竞争力有限,技术水平较低,大数据挖掘技术对于多数企业而言也是可望而不可即,所以,大数据挖掘技术的不够成熟也会对此模式的实践造成一定局限性。此外,该模式的实现还存在行业问题,比如农产品行业应用较少。在对全球在线定制与国内在线定制企业对互动创新的应用等调查时,由于涉及的企业全球各个国家都有、成本等限制,我们仅能从在线定制网站上分析各个在线定制企业的情况,至于这些在线定制企业是否成功运营、成功运营的要素是哪些等尚有待研究,但无疑这是未来竞争的趋势。
基金项目
中国博士后特别资助项目(2014T70838);国家自然科学基金资助项目(71302153);广东省自然科学基金项目(2014A030313608)。