摘要:
根据2003年至2014年景德镇市农业、工业、生活、生态环境等行业的用水量资料,分析景德镇市近12年来行业用水的变化发展,结合SPSS统计软件对引起行业用水变化的主要驱动力因子进行分析和说明。结果表明:景德镇市的水资源利用以农业用水为主,占用水总量的50.6%,工业用水占用水总量的34.5%,比重相对较大,生活用水和生态环境用水所占用水总量的比重较小,分别为13.9%和1.0%;景德镇市用水总量基本稳定,无整体上升或下降趋势,农业用水量及其所占用水总量的比重呈现整体上升的趋势,工业用水量及其所占用水总量的比重呈现出先上升而后下降的趋势,生活用水量及其所占用水总量的比重近10年来呈现逐年攀升的趋势,生态环境用水量及其所占用水总量的比重呈现略微上升的态势;因子分析的结果显示人口因素、经济发展因素和农田灌溉因素是景德镇市行业用水演变的主要驱动力。
Abstract:
According to the agricultural, industrial, life, public and ecological environment water use data of Jing-dezhen city from 2003 to 2014, the paper analyzes the change of water use in various industries in Jing-dezhen city during the last 12 years, and analyzes and explains the main driving factors of the develop-ment of water use in various industries by using SPSS statistical software. The results show that the water resources utilization in Jingdezhen city is mainly agricultural water use, which accounts for 50.6% of the total amount; the proportion of industrial water use is relatively larger, which accounts for 34.5% of the total amount; the proportion of water used for life, public and ecological environment is small, which accounts for 13.9% and 1.0% of the total amount. The total amount of water use in Jingdezhen is basically stable, and there is no overall rise or fall, agricultural water use, water use of the ecological environment are showing an overall upward trend and the proportion of total water use in agriculture and ecological environment is also increasing; industrial water use and its proportion of the total water use showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing trend; water use for life and public and their proportion of the total water use in the past 10 years has been rising year by year. Factor analysis results show that the main driving force of the development of water use in various industries in Jingdezhen city is the population, economic development and farmland irrigation.
1. 区域概况
1.1. 城市概况
景德镇市位于江西省东北部,江西、浙江、安徽三省交界处,居东经116˚57'~117˚42',北纬28˚44'~29˚56',坐落在黄山、怀玉山余脉与鄱阳湖平原过渡地带,地势四周高中间低,属于亚热带季风气候,四季分明,日照充足,雨量充沛。全市面积5256 km2,人口162.98万人。
1.2. 水资源及其开发利用状况
景德镇市所在的流域属于长江流域鄱阳湖水系。昌江和乐安河分别是鄱阳湖水系五大河流之一饶河的北支和南支,二者贯穿景德镇市全境。景德镇市水资源公报的数据显示,景德镇市多年平均降水量1816.1 mm,多年平均水资源量53.40亿m3。2014年,景德镇市年平均降水量1919.9 mm,水资源总量54.27亿m3;供水量8.45亿m3,其中地表水源供水量7.89亿m3,地下水源供水量0.56亿m3;用水量8.45亿m3,其中农田灌溉用水量4.50亿m3,林牧渔畜用水量0.12亿m3,工业用水量2.63亿m3,城镇公共0.21亿m3,居民生活0.86亿m3,生态环境0.13亿m3,全市人均综合用水量518 m3。
2. 行业用水演变分析
用水行业是指凡生产、生活和环境等用水行业或产业统称为用水行业 [1] 。根据《水资源公报编制规程》,考虑不同统计口径的需要,按照生产、生活(仅指居民生活)、生态环境三大类用水统计,也可按农业、工业、生活(含公共用水)、生态环境四大类用水统计。本文按照农业、工业、生活和生态环境四大类行业用水进行统计分析,其中林牧渔畜用水量归类到农业用水量,城镇公共用水量归类到生活用水量。
根据2003~2014年景德镇市水资源公报用水量数据,绘制2003~2014年景德镇市行业用水比重表和2003~2014年景德镇市用水变化情况图,见表1和图1。由表1可知,从2003年到2014年的12年中,农业用水和生态环境用水各自占用水总量的比重整体都呈现出逐年增长的趋势,工业用水所占比重随着时间推移呈现出先上升再下降的趋势,生活用水所占比重则呈现出先下降再上升的趋势,其中近10年来稳步上升。景德镇市农业用水、工业用水和生活用水三者之和达到用水总量的98%以上,可见景德镇市水资源主要利用在农业、工业和生活上面。

Table 1. Proportion of water use in various industries in Jingdezhen city (2003-2014)
表1. 2003~2014年景德镇市行业用水比重
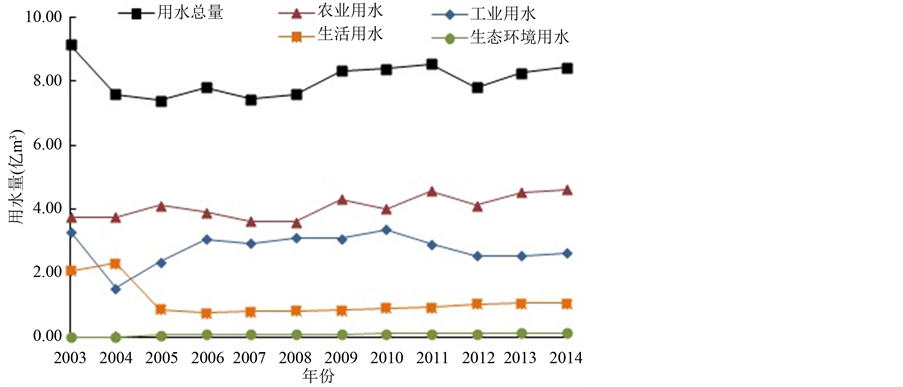
Figure 1. Change of water use in Jingdezhen city (2003-2014)
图1. 2003~2014年景德镇市用水变化情况
农业、工业、生活用水比重可以从一个侧面反映一个国家或地区经济与文明的程度,也是科技水平的标志之一。一般来讲,工业用水比重大,说明工业化程度发达;生活用水比重大,说明文明程度较高;而农业用水量比重大,不仅说明是以农业为主要产业,而且也从侧面反映农业科技较为落后[2] 。由表1可知,农业是景德镇市的主要产业之一,占全市国民经济的较大比重,景德镇市的工业化程度相对较高,而文明程度相对稍低[3] 。
用水量数据来源于景德镇市水资源公报,由于编制单位从2006年之后变动,编制方法、用水定额、指标选取等各方面存在一定差异使得用水量数据前后的衔接和趋势性等存在一定的不协调,反映在图1中2003年到2005年用水总量的急剧变化以及工业用水量和生活用水量的点据跳跃。
从图1可知,从2003到2014年的12年中景德镇市用水总量的平均值为8.07亿m3,用水总量的变化基本上在8.00亿m3上下波动,没有明显的整体上升或整体下降趋势。农业用水量整体呈现震荡上升趋势并于2014年达到12年中的最大值4.62亿m3,其逐年走势与用水总量走势相近,这和农业用水占用水总量比重较大密不可分,12年中农业用水的平均比重达到了50.61%,大于其他三类行业用水平均比重之和。工业用水量呈现出先上升而后下降的趋势,12年中的最大值是2010年的3.37亿m3。生活用水量去除2003年和2004年两个跳跃点后呈现逐年略增的趋势。生态环境用水量的逐年趋势是略微上升的。
3. 行业用水演变的主要驱动力分析
3.1. 基于SPSS统计软件的驱动力因子分析
SPSS软件中的因子分析属于多元分析中处理降维问题的一种常用的统计方法,它是将具有一定相关关系的多个变量综合为数量较少的几个因子,研究一组具有错综复杂关系的实测指标是如何受少数几个内在的独立因子所支配的[4] 。运用SPSS因子分析处理数据,就是将为数较多的变量综合成较少的若干综合指标,这些综合指标即为因子,因子个数少于变量,却能够有效地解释原始变量,反映原始变量的大部分信息,同时,因子之间不具有显著的相关性。
根据《水资源公报编制规程》和《用水总量统计方案》,用水量数据是综合相关社会经济指标以及调查统计等汇总得来的。各行业用水也会受到各方因素的影响。行业用水的逐年变化是社会经济因素影响因素和自然环境因素共同作用的结果,行业用水量受到各种因素变化的影响[5] 。
依据因子分析的基本概念和原理,结合景德镇市的用水情况和特点,选取农业产值、年降水量、有效灌溉面积、工业产值、万元工业增加值用水量、人口数量、城市化率(城市人口占总人口的比例)、第三产业产值和城镇居民人均可支配收入等9项指标作为影响景德镇市行业用水演变的变量,运用SPSS统计分析软件进行因子分析[5] -[7] ,分析驱动景德镇市行业用水演变的因子。资料及数据来源于2003~2014年景德镇市国民经济和社会发展统计公报和景德镇市水资源公报。
因子分析的前提是进行样本充足度(KMO)检验,KMO的取值范围是0~1,0~0.5表示不可接受[4] ,越接近1样本数据越适合进行因子分析。本次分析计算得出的KMO值为0.713,适合进行因子分析。运用SPSS因子分析的主成分分析法,提取出特征值大于1的前两个成分,两个成分与9个初始变量的旋转载荷矩阵见表2,同时,得到成分特征值及矩阵旋转贡献率见表3 [4] -[7] 。
由表2可知,成分1中人口数量、万元工业增加值用水量、农业产值、城镇居民人均可支配收入、工业产值和第三产业产值等因子的载荷相对较大,对成分1的贡献大,把它们综合定义为社会经济因子。成分2中,有效灌溉面积的载荷对相对较大,对成分2的贡献大,把它定义为农田灌溉因子[7] 。
从表3可以看到,成分1社会经济因子和成分2农田灌溉因子分别占全部分类贡献率的63.05%和24.30%,它们二者的累积贡献率占全部分类贡献率的87.35%。由此可见,选取前两个成分即成分1和成分2能够代表9个初始变量,几乎涵盖初始变量的全部信息[4] 。因此,社会经济因子和农田灌溉因子能够较好的反映出影响行业用水演变因子的信息。

Table 2. Rotated component matrix in factor analysis
表2. 驱动力因子分析旋转载荷矩阵

Table 3. Component characteristic value and its total variance explained in factor analysis
表3. 成分特征值及其贡献计量值
根据以上分析,将景德镇市行业用水演变的主要驱动力归纳为人口数量、经济指标和农田灌溉因素。
3.2. 主要驱动力因子与行业用水的关系说明
生活用水包括居民生活用水和公共用水。居民生活用水量与用水定额和人口数量等息息相关,用水定额与水资源和气候条件、人民的生活水平、生活习惯、收费标准及办法、管理水平、水质和水压等因素有关[1] ,年际变化不大。2006年至2014年,景德镇市的人口从153.62万人增加至162.98万人,生活用水从0.75亿m3增加至1.03亿m3。可见,人口数量的变化直接驱动生活用水的演变。
工业用水按照火(核)电用水、国有及规模以上用水和规模以下用水三部分来统计,三者与各自的工业增加值、用水定额、用水的重复利用率、工业节水情况、结构调整、用水技术改进等密切关联。工业用水的演变受到国内生产总值、工业增加值等经济指标的正驱动以及重复利用率、工业节水等因素的负驱动。
农业用水包括农田灌溉用水和林牧渔畜用水。农田灌溉用水占农业用水的绝大部分,它受到农田灌溉面积、节水灌溉面积、降雨量数量和时空分配情况、农业产业结构调整等因素影响[8] 。农田灌溉因素对农业用水的驱动显而易见。
4. 结语
2003~2014年,景德镇市的水资源利用是以农业用水为主,工业用水占用水总量的比重相对较大,生活用水和生态环境用水所占用水总量的比重较小。景德镇市用水总量保持基本稳定,农业用水量、生态环境用水量及其各自占用水总量的比重均呈现整体上升的趋势,工业用水量及其所占用水总量的比重均呈现出先上升而后下降的趋势,生活用水量及其所占用水总量的比重近10年来呈现逐年上升的趋势。人口因素、经济发展因素和农田灌溉因素为景德镇市行业用水演变的主要驱动力。因此,分析景德镇市行业用水演变及其驱动力,可以认清各行业水资源利用的变化发展,为区域水资源管理、合理配置水资源、协调水资源供需关系等提供参考。