1. 引言
社会经济的快速发展带来了人口老龄化、空巢家庭 [1] 的数量急剧增加等诸多问题,人们开始对家庭环境中老年人的安全问题越来越重视,这就需要一种能够自动检测到危险行为的方法,在老年人遇到危险的时候能够及时判断出来并发出警报。随着计算机技术和通信技术的迅速发展,服务机器人开始被广泛地应用于安全监控、医疗卫生等多种领域,其中,基于视觉的人体动作行为分析技术显得尤为重要 [2] 。利用家庭医疗服务机器人检测人体的危险动作,可以在不影响老年人日常生活的情况下对当前人体姿态进行视觉分析,及时发现危险情况并发出警报,从而确保老年人的人身安全,为提高老年人的生活质量提供了有效的途径。
目前对于危险动作的检测主要体现在跌倒检测上。文献 [3] 通过安装在地板上的压电传感器获取震动信号来分析地板的震动模式,从而实现人体跌倒检测。文献 [4] 利用安装在墙上的红外线传感器阵列来监测人体的运动状态和速度,并基于多层感知器网络进行人体跌倒检测。文献 [5] 将三轴加速度计和陀螺仪组合在一起分别穿戴在胸前和腿部,通过检测加速度的数据变化对跌倒和正常行为进行分类。文献 [6] 将一个顶棚广角摄像机部署在房间的天花板上来测量人体朝向、位置等数据,采用高斯混合模型和最大后验估计来构建空间环境的学习模型,判断是否有人在不适当的位置时间过长,从而根据人体的移动轨迹来进行跌倒检测。
在实际生活中,还有一种常见的危险动作是老年人突发疾病或身体不适时捂住胸口或是扶着墙缓慢倒下。这种情况下,老年人在发病过程中逐渐失去行动能力,无法自主站立,最终很可能也会造成“长躺不起”的后果,但由于倒下的过程比较缓慢,人体没有产生较大的速度和加速度变化,往往无法被跌倒检测系统识别出来。
针对以上两种危险情况,本文利用Kinect传感器 [7] [8] 对人体头部进行跟踪,分析不同动作时人体头部位置的变化趋势,从而实现危险动作检测。该方法可以在检测过程中直接输出骨骼信息而不显示当前场景的RGB图像,防止被检测者的隐私泄露。
2. 危险动作模式
人体在日常生活中的静态姿势主要包括以下几种:直立、前顷立、后仰立、仰卧、俯卧、左侧躺、右侧躺、直坐、前倾坐、后仰坐等,这些静态姿势间的相互转换构成了人体的基本动作行为。日常活动主要包括以下几种基本动作行为:行走、奔跑、跳跃、坐下、蹲下、起立、躺倒等。其中一些基本动作还可以进一步进行划分:行走根据路面情况不同可以分为平地走、上楼梯和下楼梯;起立根据初始姿态不同可以分为从坐姿到站立和从下蹲到站立;躺倒根据动作时间长短的不同可以分为缓慢躺下和跌倒。这些动作行为在实际生活中还存在着更多的复杂情况。
在人体日常活动中,一些动作行为会对人体直接造成伤害,还有一些动作行为预示着人体即将会受到伤害,本文将以上两种动作统称为危险动作。根据危险动作的定义,可以将人体日常活动分为正常日常动作(非危险动作)和危险动作两大类。
日常活动中会给人体直接造成伤害的动作主要体现在跌倒动作上。跌倒是由于身体对平衡失去控制所引发的动作,主要发生在婴幼儿和老年人身上。跌倒动作发生的过程中,人体会在一个极短的时间内(通常为1~2秒)向不可预知的方向发生倾倒动作,给人体造成伤害,其中对老年人造成的伤害更为严重。引发跌倒的因素有很多,既包括生理因素、心理因素、疾病因素、药物因素等内在因素,又包括社会因素、环境因素 [9] 等外在因素。
针对老年人行动缓慢的特点,本文不考虑奔跑、跳跃等剧烈运动,重点研究行走、坐下、蹲下三种动作模式与以上两种危险动作的区别。
3. 头部位置特征提取
3.1. 基于头部位置特征的危险动作描述
人体动作的识别是危险动作检测中的关键部分,其首要任务就是选择合适的特征来描述人体动作。根据特征性质的不同,人体动作的描述方法能够分成基于低层图像信息的动作描述和基于高层人体结构信息的动作描述两大类:低层的图像信息包括运动目标、运动轨迹、运动速度、光流、人体轮廓、侧影等 [10] ,由于这些特征比较容易获取,使得这种方法成为了主要的动作描述方法;高层的人体结构信息指人体姿态特征,能够更加精确地描述人体动作,但这种方法需要更多的参数,运算量大且训练复杂。
基于视觉传感器的检测方法与穿戴式传感器和环境布设传感器的检测方法相比具有很多优势,使用摄像机可以同时检测到多个事件,具有较高的检测准确性且不会给人体带来负担。随着摄像机价格的大幅度下降和计算机处理速度的不断上升,这种方法的应用价值越来越大。
危险动作发生时,利用视觉传感器检测到的人体往往存在自遮挡现象,这就妨碍了检测系统对人体动作的识别。而相对于整个身体,头部很少会被遮挡,更利于获取,其运动特征与危险动作的关联性更高,计算量少,因此,通过对头部运动信息的分析可以有效地检测出危险行为。利用视觉传感器进行头部跟踪通常需要先将真实的三维场景映射到摄像机的二维坐标系下,再通过分析获取到的头部运动信息来判断人体的运动情况 [11] 。
危险动作发生后,人体在地面躺倒,头部位置明显低于正常日常活动中的水平,但由于弯腰、下蹲等非危险动作也有可能导致头部位置降低,所以基于规则的方法会产生误判现象。
头部在危险动作中的位置变化规律与正常日常动作中的位置变化规律存在着比较明显的区别,危险动作发生时,头部在竖直方向上会产生明显的位置变化,而在水平方向上的运动并不明显。
本文采用人体头部在竖直方向上的位置变化作为特征向量描述危险动作。利用Kinect传感器获取当前帧中的人体头部位置,通过分析运动序列中连续帧之间的头部位置变化得到运动过程中竖直方向上的头部位置变化特征,利用支持向量机分类器基于该特征进行分类,从而检测出危险动作。
3.2. 基于Kinect的头部位置特征提取
Kinect是一款集合了机器学习技术、语音识别功能和身份识别能力的外接体感传感器,能够以30帧每秒的传输速率同时提供彩色图像数据流和深度图像数据流。Kinect其最关键的核心技术在于骨骼跟踪,利用机器学习的方法通过捕捉到的深度图像来识别出人体的20个关节点,从而构建人体骨骼。通过Kinect提供的骨骼数据可以得到人体不同部位的实时位置 [12] 。
根据上文对日常生活中人体运动模式的分析,考虑到老年人行动缓慢的运动特点,本文只对行走、坐下、蹲下、跌倒和缓慢倒下五种动作模式进行分析,其中行走、坐下、蹲下三种动作视为日常正常动作,跌倒和缓慢倒下两种动作视为危险动作。图1给出了这五种动作发生时Kinect分别从被检测者正面(左)和侧面(右)提取到的人体骨骼图像,可以看出在危险动作发生时人体四肢存在比较严重的自遮挡现象,但仍可以准确检测到头部位置。
将运动过程中连续180帧人体骨骼的头部关节点三维坐标作为研究对象,可以得到人体头部位置在竖直方向下6秒内的变化趋势。图2中是行走过程中人体头部位置的正面(左)和侧面(右)变化趋势。可以看出在正对着Kinect行走时,人体头部在竖直方向上的坐标随着人与传感器距离的减小而增大,但是这种增长幅度很小,基本维持在0.6 m~0.8 m;在侧对着Kinect传感器行走时,人体头部在竖直方向上的坐标在0.6 m~0.8 m内上下波动,基本保持不变。
图3中是坐下时人体头部位置的正面(左)和侧面(右)的变化趋势。可以看出开始坐下时人体的头部位置在竖直方向上会产生一个急剧下降的过程,随着人体坐到椅子上之后直起身,头部位置在降低到一定程度后又会小幅度地提高,坐标值最终停留在0.2 m左右。
图4中是蹲下时人体头部位置的正面(左)和侧面(右)的变化趋势。可以看出蹲下时人体头部位置在竖直方向上会产生一个急剧下降的过程,坐标值最终在0 m左右保持稳定。
图5中是跌倒时人体头部位置的正面(左)和侧面(右)的变化趋势。可以看出跌倒时人体头部位置在竖直方向上会产生剧烈的下降,坐标值最终保持在−0.5 m左右,最终躺倒后的头部位置停留在一个正常日常行为中不可能出现的极低位置。
图6中是缓慢倒下时人体头部位置的正面(左)和侧面(右)的变化趋势。可以看出缓慢倒下时人体头部位置在竖直方向上缓慢地下降,直至最终坐标值维持在−0.5 m左右。此时人体已经躺倒不起,头部停留在一个极低的位置,与跌倒发生后的情况一样。
通过对以上五种动作模式中头部位置在竖直方向上变化规律的分析,可以发现危险动作与日常正常
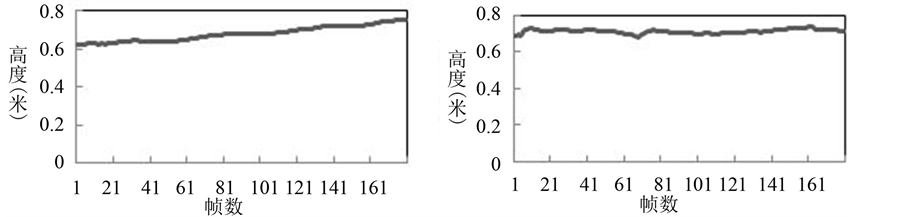
Figure 2. Head position changes while walking
图2. 行走时的头部位置变化
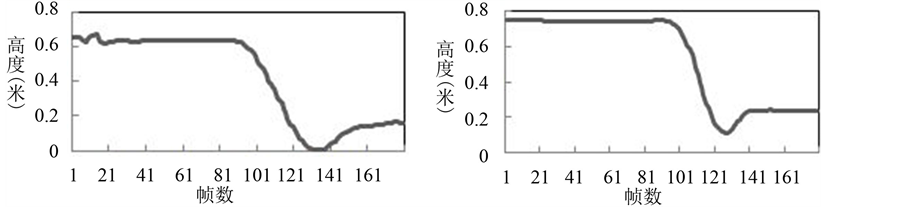
Figure 3. Head position changes while sitting down
图3. 坐下时的头部位置变化
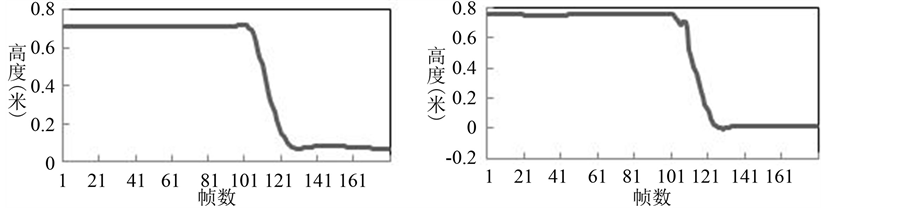
Figure 4. Head position changes while squatting
图4. 蹲下时的头部位置变化
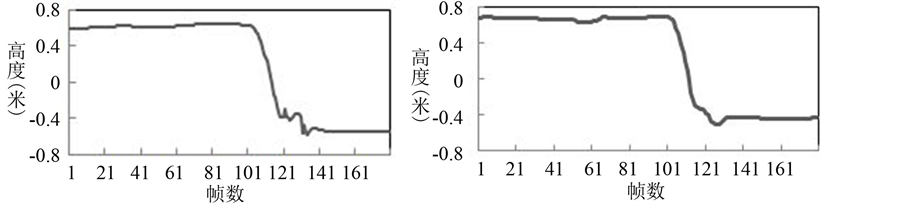
Figure 5. Head position changes while falling
图5. 跌倒时的头部位置变化
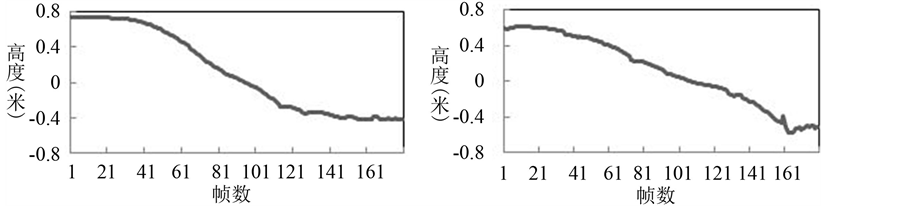
Figure 6. Head position changes while falling slowly
图6. 缓慢倒下时的头部位置变化
动作具有很明显的区别。危险动作发生时,由于人体开始与地面接近,头部位置坐标值会出现明显的下降。动作结束后,人体处于长躺不起的状态,头部位置坐标值保持在一个明显低于正常情况的水平上。通过对以上两点变化趋势的检测,可以有效地区分危险动作与正常动作,从而实现危险动作的检测。
3.3. 分类器及参数选择
相比其他的机器学习算法,支持向量机最大的优势在于其良好的泛化性,即由有限训练样本得到的决策规则对独立的测试集仍能保持较小的误差。支持向量机的泛化性主要体现在其处理非线性问题时所采用的核函数思想,核函数及其参数的选择会对分类结果造成很大的影响。RBF核函数对任意的训练样本集都能取得准确的分类结果,具备良好的局部调节特性,被广泛应用于各个领域。基于交叉验证的网格搜索方法利用支持向量机得到基于不同函数参数值的多组分类模型,然后用交叉验证的方法分别计算这些分类模型的预测准确率,选取预测准确率最高的分类模型,这个分类模型对应的参数值就是优化后的模型参数。综上所述,本文选用支持向量机作为危险动作检测的分类器,并通过基于交叉验证的网格搜索方法来获取RBF核函数的最优参数。
4. 危险动作检测实验
为了更好地模拟真实场景中老年人发生危险动作的情况,本文将实验安排在卧室和客厅两处老年人日常生活中经常进行活动的场所,对人体的运动模式进行分析。为了避免测试者独特的运动习惯影响提取到的动作特征的准确性,一共安排了三名志愿者来完成全部的运动行为。Kinect传感器被安置在距离人体约2~3米远的水平位置上,距离地面约1米高,以每秒30帧的帧率实时获取运动中的人体骨骼信息,保证对短时间内发生的人体动作也能很好地检测到并完整地记录下来。
实验数据集中总共包含了300个样本,每个样本记录了人体在连续的180帧中头部位置的变化规律,分别描述了行走、坐下、蹲下、跌倒和缓慢倒下五种动作。实验从数据集中选取60组数据作为训练样本来训练支持向量机分类器,再将其余的240组数据作为测试样本,利用分类器进行分类,从而实现危险动作的检测。
为了验证头部位置特征对危险动作检测的有效性,提取该数据集的竖直方向上头部运动速度特征进行对比实验,结果如表1所示。可以看出分类器对于坐下和蹲下两种动作之间的区分度不是很理想,这两种动作中都存在被误判成缓慢倒下的情况,跌倒和缓慢倒下两种动作之间存在误判现象,跌倒还有可能被误判为坐下。分类器对该测试数据集的分类准确率为88.75%。如果将这五种动作分为危险动作和正常动作两大类,那么分类器对危险动作的检测率达到了98.96%,存在误判、漏判现象。
利用头部位置特征进行危险动作检测实验,结果如表2所示。可以看出在所有测试数据中存在1例

Table 1. Classification results based on the velocity of head motion
表1. 基于头部运动速度特征的分类结果

Table 2. Classification results based on the position of head motion
表2. 基于头部位置特征的分类结果
缓慢躺倒误判成跌倒、1例蹲下误判成跌倒和1例蹲下误判成坐下,分类器对该测试数据集的分类准确率为98.33%。如果将这五种动作分为危险动作和正常动作两大类,那么分类器对危险动作的检测率达到了100%,但存在误判现象。
从实验结果可以看出,基于头部位置特征的分类准确度明显高于基于头部运动速度特征的分类准确率,而且基于头部位置特征的危险动作检测不存在漏判现象,能够更有效地保障老人的人身安全。实验证明本文提出的这种以头部位置为特征,基于Kinect的危险动作检测方法具有较高的准确率,能够有效检测出家庭环境中人体危险动作的发生。
5. 结束语
本文提出了一种基于Kinect的危险动作检测方法,通过Kinect传感器获取的骨骼信息得到人体头部的位置并分析其在危险动作模式中的变化规律,再利用训练好的支持向量机分类器检测危险动作。对日常生活中人体的运动模式进行分析,将对人体直接造成伤害和预示着人体即将受到伤害的两种动作定义为危险动作。由于人体头部在危险动作发生时具有明显的位置变化并且不容易被遮挡,提出了一种基于头部位置的危险动作特征描述方法。
在居家环境中利用Kinect提供的人体骨骼数据获取头部位置,分析不同动作模式下头部位置在竖直方向上的变化规律来区分危险动作与正常日常动作。用支持向量机分类器基于头部位置特征对人体动作进行划分,取得了很好的分类准确率。实验结果证明本文提出的危险动作检测方法具备良好性能,能够有效检测出危险动作的发生。