摘要:
利用1957~2014年甘肃中北部4个台站逐日降水资料,分析了第一场透雨发生的气候特征及其影响因子。结果表明:第一场透雨出现日期在空间上从南向北推迟,区域性平均第一场透雨日期集中出现在5月,平均日期在5月中旬,也是出现频率最高的旬;区域性平均第一场透雨无显著的气候特征趋势,但有明显的年代际变化:1950年代末至1960年代初、1970年代中后期、1990年代初期至2000年代后期迟于6月以后;1960年代中期至1970前期、1980年代、2010年以后普遍偏早于4月下旬,有提前的趋势;透雨与春季降水有显著的负相关,透雨偏早,则春季降水偏多,特别是4月、5月降水偏多;前期1月亚洲中高纬500 hPa高度距平场呈“− + −”、甘肃中北部经向风距平场出现偏南风,则透雨偏早,反之偏迟;上年5~7月大西洋中北部、欧洲中西部、西西伯利亚OLR增强(减弱),对应的甘肃中北部透雨偏迟(早);透雨的年际变化从南向北增大,均方差会宁26 d,靖远31 d,景泰35 d,白银41 d,这就决定了其预测难度大,稳定性差。
Abstract:
In this paper, the first soaking rain climate characteristics as well as its influence factors are ana-lyzed statistically based on daily precipitation data of four stations in north-central region of Gansu from 1957 to 2014. The results show that: the first soaking rain has delayed from south to north and regional soaking rain which concentrated in May, frequently in mid-may, is insignificant in climate change trend but obvious in terdecadal changes: for example, from late 1950s to early 1960s, in the mid to late 1970s and from early 1990s to the late 2000, regional soakers are later than June, while from mid 1960s to early 1970s, in 1980s, and after 2010 they are generally before late April, with tendency of advance. It also shows that the soaker has significant negative correla-tion with the spring precipitation, that is, if the soaking rain is earlier, the spring precipitation es-pecially in April and May is more. If the anomaly field presented negative, positive and negative at 500 hPa of middle and high latitude areas in Asia of previous period in January, and the Radial wind anomaly field appeared southerly wind in north-central Gansu province, the soaking rain occurred early, or vice versa. OLR was enhanced in north central in the Atlantic, the west central Europe and west Siberia from May to July in the year before corresponded to soaking rain later in north-central Gansu province, or vice versa. And interannual variability of soaker increases from south to north, for example, mean square deviation of Huining is 26 d, Jingyuan 31 d, Jingtai 35 d, Baiyin 41 d, which means the soaker is difficult to predict and its result is unstable.
1. 引言
甘肃中北部位于青藏高原东北侧,属于干旱半干旱气候过渡区[1] [2] ,是中国西部雨季开始最迟的地方。春季4~5月,正值冬小麦返青、拔节、春小麦及大秋作物播种、出苗的关键生长期,特别是4月下旬至5月中旬,春小麦进入出苗以后的分蘖、拔节生长发育阶段,对水分的要求较高,而某些天气过程所带来的降水往往能满足这个要求,通常气象上把一次降雨能够将干土层全部淋透就叫透雨,透雨来临迟早与否对当年旱作农业丰收具有重要的基础作用。因此,第一场透雨受到许多地方气象服务的重视,被列为气候预测的一个专题项目。因其变化规律复杂,制约因素多,是气候预测的一个难点。目前,有关春季降水方面的研究比较多[3] -[6] ,对透雨的分析,大多数是对个别年份发生的第一场透雨的天气学特征分析,也有少数有关透雨的时空变化规律研究,如乜国妍等[7] 分析了青海省东部地区春季降水量、第一场透雨与雨季及春旱的关系;白玲等[8] 对宁夏中卫市2011年的首场透雨进行了成因分析;李辑等[9] 分析了辽宁省春播期第一场透雨的气候特征及其变化规律。然而,对于透雨前期影响因子的研究不多见。为此,我们使用白银市辖区4个台站近58年的逐日地面降水资料,分析甘肃中北部透雨的气候变化规律及其影响因子,对于气候预测、防灾减灾具有实际意义。
2. 资料方法
1) 白银市4个气象站1957~2014年逐日降水资料,资料由甘肃省气象局提供,已经进行了严格的质量控制;
2) 环流特征量资料,是间接利用高度场网格点的高度值组成的区域综合资料[10] ,来自国家气候中心网站,多年来一直在气候分析和气候预测中广泛应用[11] -[13] ;
3) NCEP/NCAR北半球2.5˚ × 2.5˚网格点500 hPa高度场、射出长波辐射(OLR)再分析资料,该资料数据可靠,在科学研究中已得到广泛的应用[14] -[16] 。
第一场透雨出现日期的定义:某站年内首次日降水量 ≥ 10.0 mm或连续2日降水量 ≥ 15.0 mm。区域性平均第一场透雨日期的定义:区域1/2或以上的站同时达到的日期,如果各站开始时间不一致,则取各站的平均值。
统计各站的第一场透雨日期序列,因为各站透雨最早出现在3月份,因此从3月开始,把3月1日记为1,3月2日记为2,……,依次类推,5月10日记为71,5月20日记为81……,建立各站第一场透雨日期序列。统计甘肃中北部1957~2014年区域性透雨时间序列,运用线性趋势分析,Mann-Kendall (M-K)突变分析、滑动T检验(MTT)、MHAT小波等方法[13] 分析透雨的分布特征和变化特点。
计算透雨与降水、环流特征量、500 hPa高度场、经向风、OLR的相关系数,分析影响透雨的因子。
3. 第一场透雨出现日期的空间特征
第一场透雨(表1)出现的平均日期,从南向北推迟,会宁出现在5月上旬,靖远出现在5月中旬、白银、景泰出现在6月上旬。区域内最早出现日期3月上旬至中旬,最晚到10月才出现。
甘肃中北部的4个站,在同一旬中,3站以上出现透雨的有11次占19%,2个站有38次占65%,4站都不在同一旬的有9次占16%。即出现2站以上的区域性平均透雨占84%
从3月下旬开始,统计各旬透雨出现的频率,从图1可见,北部的景泰、白银两站5月上旬至6月中旬出现的频率较高,一般旬频率在10%以上,5月中旬出现的频率最高;靖远的透雨主要出现在5月,其中上旬频率最高;南部的会宁4月中旬至6月上旬出现的频率较高,其中4月中旬最高。80%的透雨,景泰、白银、靖远出现在5月中旬以后,会宁则出现在3月下旬至5月中旬。
区域平均第一场透雨日期为5月17日,有1年(1967年)出现在3月,有12年出现在4月占21%,有13年出现在6月及以后占22%,集中出现在5月(32年)占55%,5月中旬频率最高。
4. 第一场透雨日期的时间变化
第一场透雨日期年际变化从南向北增大,景泰均方差41 d,白银、靖远均方差分别为35 d、31 d,而会宁透雨年际变化较小,均方差为26 d。符合降水少变率大的特点。

Table 1. The date of the first soaking rain in north-central region of Gansu province (1957~2014)
表1. 甘肃中北部第一场透雨出现的日期(1957~2014)




Figure 1. The frequency of the soaking rain occurred during each ten-day period of 4 stations in north-central region of Gansu province (unit: %)
图1. 甘肃中北部4站透雨出现在各旬的频率(%)
4.1. 年代际变化
用区域性平均第一场透雨日期序列分别与景泰、白银、靖远和会宁各站第一场透雨日期序列求相关,其相关系数分别为0.21、0.43、0.81、0.41,除景泰通过90%的显著性检验,其余各站都通过了99.9%的显著性检验,可见区域性平均第一场透雨日期具有较好的代表性。分析其年代际变化特征(图2(a)),可以发现,近58 a甘肃中北部第一场透雨日期的气候趋势不明显,平均开始日期在5月中旬。有明显的年代际变化:1950年代末至1960年代初、1970年代中后期、1990年代初期至2000年代后期迟于6月以后;1960年代中期至1970前期、1980年代、2010年以后普遍偏早于4月下旬,相对平均出现日期有提前的趋势。从较长周期演变来看(图2(b)),区域性透雨经历了3个“+ −”波动阶段,随时间波动周期变长,目前正处于偏早的阶段。
4.2. 气候突变
从M-K曲线图(图2(c))看出,甘肃中北部透雨表现出明显的突变特征,UF和UB在1981年之前围绕0线波动变化,起伏不大,1981年之后两者分开,UB急剧下降至1992年突破显著线,1995年以后又上升到显著线以内,但UF于2009年接近而未超过显著线,之后下降;用滑动T检验(MTT)方法检测的结果是1992年发生突变;从小波分析图(图2(b))上也可看出,1992年附近发生了突变。每一种统计方法都有其局限性,因此我们综合三种统计方法,确定区域透雨突变年份为1992年。但突变显著期较短(1992~2009年)。
进一步检测春季气温的变化,发现1992年开始春季发生突变增暖。因此,透雨发生突变的原因可能与气候变暖有关。
5. 透雨日期与降水量的关系
计算各站及区域透雨日期与3~5月降水量的相关系数,3月各站都是较弱的负相关,说明3月降水与透雨无关系;各站4月、5月、春季降水和透雨日期都是显著的负相关,都通过了99%的显著性检验,特别是南部的会宁,4月、5月、春季降水和透雨日期的相关系数分别达−0.51、−0.56、−0.70,通过了99.9%

Figure 2. The inter-annual variation (a), wavelet analysis (b) and M-K abrupt change analysis (c) of the first soaking rain in north-central region of Gansu province
图2. 甘肃中北部第一场透雨日期的年际变化(a)、小波分析(b)和MK突变分析(c)
的显著性检验。说明,透雨偏早,4月和5月的降水都偏多,春季降水也偏多,反之亦然。全区域最早平均透雨出现在4月上旬初,所以,如果4月出现了透雨,则4月、5月降水偏多;从图3也可以看出,对区域来说,透雨日期与降水的年际振荡方向相反,5月中旬前出现透雨,则5月区域降水偏多的可能就大,5月下旬后出现透雨,则5月降水偏少的可能就特别大。把透雨的年际振荡与出现日期相结合,可以作为一个预测指标。即透雨偏早,5月降水有可能偏多,反之,透雨偏迟,5月降水偏少。
6. 透雨的影响因子
6.1. 透雨与环流特征量的关系
计算甘肃中北部透雨序列与74项环流特征量的相关系数(为了建立预测方程,独立检验2007~2014年,用1957~2006年的透雨资料计算相关系数,N = 50 a),诊断影响甘肃中北部透雨的环流系统。通过计算发现,影响甘肃中北部透雨的环流特征量主要有副高、极涡和径向环流指数(限于篇幅,表1只列出相关最高的特征量)。
从表2可以看出,同期影响透雨的环流特征量,以4月最好,通过了99%的显著性检验。主要是与

Figure 3. The time series of regional average date of the first soaking rain and precipitation in May (a) and their relationship (b) in north-central region of Gansu province
图3. 甘肃中北部区域性平均第一场透雨日期与5月降水的时间演变(a)及其两者的关系(b)

Table 2. The correlation coefficients between the circulation indices and the first soaking rain in north-central region of Gansu province
表2. 甘肃中北部第一场透雨与环流特征量的相关系数
*:滞后时间101表示预测年的前1年1月,001表示预测年当年1月,……等等。
大西洋副高强度的正相关以及与极涡面积的正相关。当大西洋副高强度越强,极涡面积越大时,极区的冷空气就容易南下,甘肃中北部地区的透雨开始得就越早。
前期的高相关(相关系数 ≥ 0.50)主要有:北非副高、北美副高、北美区极涡强度、大西洋欧洲环流型和亚洲经向环流指数,通过时空遥相关影响甘肃中北部地区的透雨。对于透雨的气候预测具有指示性意义。
6.2. 透雨偏迟年与偏早年高度场的合成分析
在甘肃中北部区域透雨开始日平均序列中,挑取开始最迟的前10年依次是1961、1959、2001、1970、2000、1976、2009、1979、2007、1980年,均出现在6月以后,比常年(5月中旬)偏迟半月以上。透雨开始最早的前10 a依次是2002、1991、1989、2014、1968、1981、1983、2010、1958、1977年,均出现在4月,比常年偏早半月以上。以下做亚欧500 hPa高度场及其经向风场的合成分析。
同期4月,欧亚范围内,透雨偏早年(图4(a))与偏迟年(图4(b)) 500 hPa高度距平场呈相反分布,特别是在中国范围内,透雨偏早年高度距平场呈“西负东正”分布,500 hPa经向风距平场为大片的正距平(图4(c)),表明新疆脊减弱,东亚槽减弱,有利于甘肃中北部偏南风增强;透雨偏迟年高度距平场呈“西正东负”,我国中西部经向风距平场为大片的负距平(图4(d)),表明新疆脊增强,东亚槽加深,有利于甘肃中北部偏北风增强。
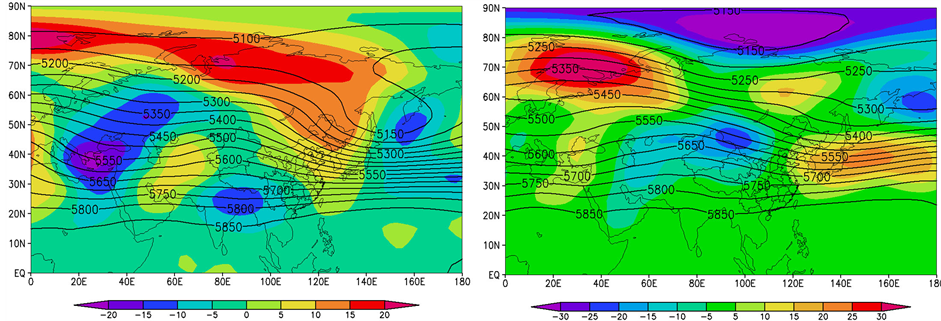
前期1月高度距平场、经向风距平场。欧亚范围内,透雨偏早年(图5(a))与偏迟年(图5(b))的环流有一定的差异,亚洲中高纬度距平场呈相反分布,透雨偏早年500 hPa高度距平场呈“− + −”分布,中国中东部500 hPa经向风距平场为大片的正距平(图5(c)),表明新疆脊减弱,东亚槽西部减弱,有利于偏南风增强;透雨偏迟年高度距平场呈“+ − +”分布,北疆–甘肃中北部经向风距平场为大片的负距平(图5(d)),表明新疆脊增强,东亚槽西部加深,有利于偏北风增强。
6.3. 透雨与OLR的关系
用1975~2006年北半球OLR资料(n = 32),与透雨序列进行前期至同期的相关分析,发现上年5月~7月存在连续、稳定的高相关区,相关系数在0.50以上。其中5月在大西洋中北部(32.5˚N~42.5˚N, 20˚W~40˚W),中心最高相关系数0.63 (图6(a));6月此高相关区东移到欧洲中西部(45˚N~55˚N, 20˚E~40˚E),中心最高相关系数0.63 (图6(b));7月此高相关区又东移到西西伯利亚(50˚N~60˚N, 80˚E~100˚E),中心最高相关系数0.61,另外在菲律宾以西有一个−0.52的相关中心(图6(c))。表明,当上述区域5~7月的OLR增强(减弱)对应甘肃中北部透雨来得迟(早)。
利用这一关系,预测2007~2014年透雨相对平均日期的变化,其准确率为7/8 = 87.5%,具有预测的参考价值。
 (a)
(a) 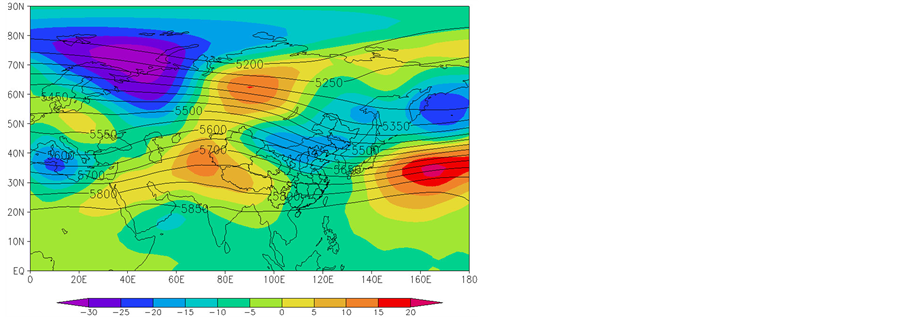 (b)
(b) 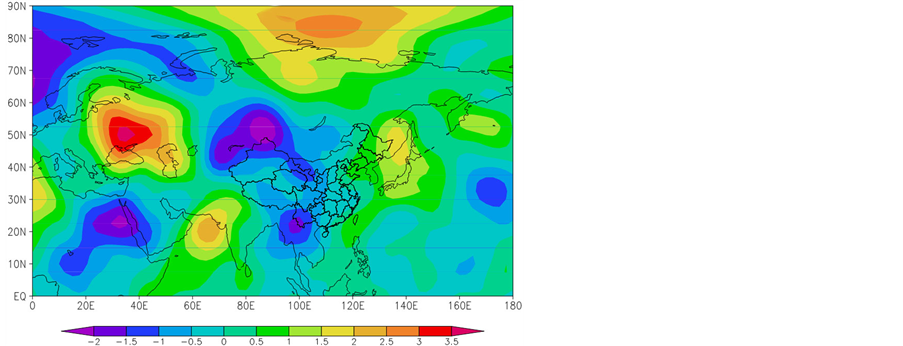 (c)
(c) 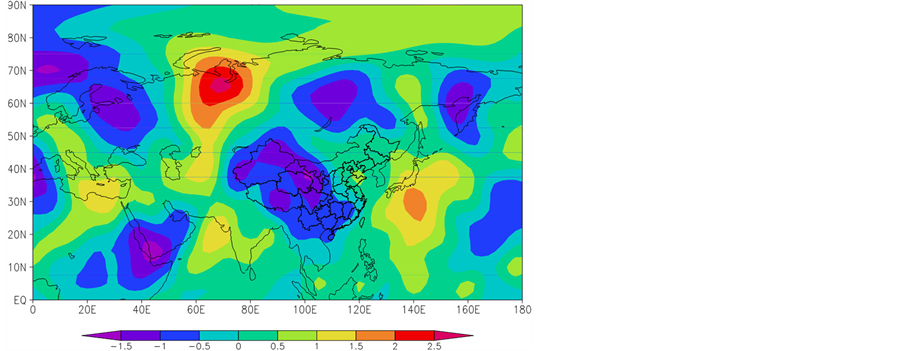 (d)
(d)
Figure 4. The synthetic of height field on the 500 hPa and its anomalies during the soaker earlier (a) and later (b) years (unit: gpm), and the longitude wind anomalies during the soaker earlier (c) and later (d) years (unit: m/s) in the same period of April
图4. 同期4月500 hPa高度场及距平的叠加(单位:gpm) ((a)偏早年、(b) 偏迟年)和经向风距平(单位:m/s)合成(c) 偏早年、(d) 偏迟年)
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)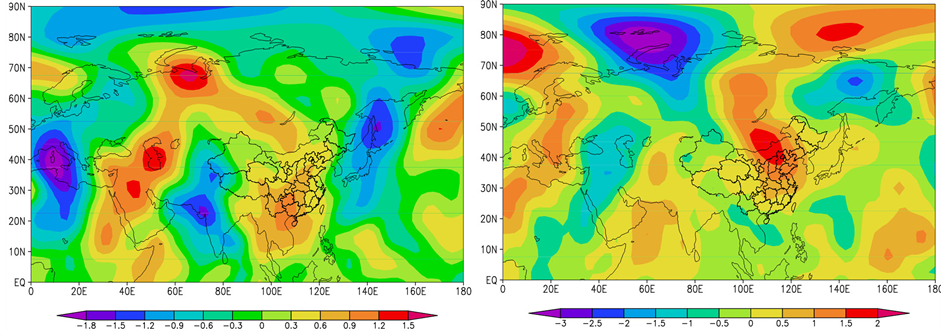 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 5. The synthetic of height field on the 500 hPa and its anomalies during the soaker earlier (a) and later (b) years and the longitude wind anomalies during the Soaker earlier (c) and later (d) years in earlier January
图5. 前期1月500 hPa高度场及距平的叠加(a) 偏早年、(b) 偏迟年)和经向风距平合成(c) 偏早年、(d) 偏迟年)

Figure 6. The correlation coefficients between the regional soaking rain in north-central region of Gansu province and the OLR field of earlier period ((a) May, (b) June, (c) July) (The correlation coefficients value are multiplied by 100)
图6. 甘肃中北部区域透雨与前期OLR的相关系数((a) 前期5月;(b) 前期6月;(c) 前期7月 (图中相关系数*100)
7. 结论
1) 甘肃省中北部第一场透雨,从南向北推迟,各地集中出现期也是从南向北推迟。区域性透雨集中
出现在5月。
2) 区域性透雨无显著的气候变化趋势,但有明显的年代际变化:1950年代末~1960年代初、1970年代中后期、1990年代初期~2000年代后期迟于6月以后;1960年代中期~1970前期、1980年代、2010年以后普遍偏早于4月下旬,有提前的趋势。受气候变暖影响,1992年出现了突变。
3) 透雨与春季降水有显著的负相关,透雨偏早,则春季降水偏多,特别是4月、5月降水偏多。
4) 前期1月亚洲中高纬500 hPa高度距平场呈“− + −”、甘肃中北部偏南风距平,则透雨偏早;反之偏迟。为透雨的预测提供了前期信号。
5) 同期影响透雨的环流特征量,以4月最好,主要是大西洋副高强度的正相关以及极涡面积的正相关。前期的环流特征量主要有:北非副高、北美副高、北美区极涡强度、大西洋欧洲环流型和亚洲经向环流指数等;另外,上年5~7月从大西洋中北部、欧洲中西部、西西伯利亚有显著的正相关区,表明这些关键区OLR增强(减弱),对应甘肃中北部透雨偏迟(早)。
基金项目
“国家重点基础研究发展计划资助”2013CB430200 (2013CB430206)。