摘要:
目的:探讨在河南上消化道癌高发地区开展内镜筛查和早诊早治项目的过程和结果。方法:选择河南上消化道癌高发地区的12个市县,将40~69岁设定为目标人群。除外胃镜检查禁忌症者,按照国家《癌症早诊早治技术方案》,对筛查对象的食管、贲门、胃进行内镜检查并以组织学诊断进行评价。结果:5年来共筛查9万多例,在进入分析的89,495例中,发现各类癌前病变以解剖部位食管、贲门、胃来分,依次为26,199例(29.27%)、23,337例(26.08%)和3248例(5.20%);共检出上消化道癌病例2095例,检出率2.34%,其中,食管1.38%,贲门0.73%,胃0.33%。早期病例1706例,占81.72%。对3000多例进行了近期随访筛查,对林州5年治疗情况做了简要报告。结论:在上消化道癌高发地区,对40~69岁高危人群开展内镜筛查和实施早诊早治是可行的,对各类癌前病变进行干预并对各类早期阶段癌变开展微创治疗,将会对防治上消化道癌,降低死亡率起到积极地作用。
Abstract:
Objective: To study the process and results of endoscopic screening and early diagnosis and treatment for the cancer of upper digestive tract in high-incidence areas in Henan. Methods: 12 high-incidence cities and counties of upper gastrointestinal carcinoma in Henan province were included in this study. People aged 40-69 were set to the target population. Except contraindications for endoscopy, in accordance with the national technical scheme of early cancer diagnosis and treatment, endoscopic screening and histologic diagnosis for human esophagus, cardia and gaster of the target people were carried out. Results: During the 5-year period, more than 90,000 cases had a total sieve check, and in the 89,495 cases which entered the analysis, various precancerous in anatomy parts esophagus, cardia and gaster were found: 26,199 subjects (29.27%) in esophagus, 23,337 subjects (26.08%) in cardia and 3248 subjects (5.20%) in gaster respectively. A total of 2095 cases were found to have cancers (2.34%), followed by anatomy parts for 1.38%, and 0.73% and 0.33% respectively, among them 1706 cases had early stage with an early diagnosis rate was 81.72%. More than 3000 cases have been followed-up screening in near future, and we made a brief report on the 5-year treatment in Linzhou. Conclusion: The results of this study demonstrate that endoscopic screening and early diagnosis and treatment for the target population aged at 40 - 69 is feasible in high-incidence areas of upper digestive tract carcinoma. We could intervene various types of precancerous lesions and have minimally invasive treatments to cancer developing in the early stages, which have positively effects on the prevention and treatment of upper digestive tract cancer and reducing mortality.
1. 引言
上消化道癌,在这里通指食管癌、贲门癌和胃癌,是我国最常见的恶性肿瘤之一[1] [2] 。2014年2月3日,IARC (国际癌症研究中心)发布的《世界癌症报告2014》指出,全球癌症负担目前正以惊人的速度不断加重,仅依靠治疗并无法遏制癌症危机的蔓延;无论在发达国家和发展中国家,癌症都是导致人们死亡的主要原因。有超过60%的癌症病例集中在非洲、亚洲等低中收入的发展中国家。《全球癌症报告2014》显示,以中国的食道癌、胃癌为代表的上消化道癌症威胁最为显著,中国的食管癌患者的死亡人数约占全球一半以上,胃癌病例中约35%发生在中国。在我国,食管癌、贲门癌、胃癌均呈现明显的地域性分布,高发区主要分布在农村和贫困山区。在农村开展对于上消化道肿瘤高危人群的大范围筛查,一次内镜检查,可同时发现食管、贲门和胃的病变,提高早诊早治效率,节约资源。工作结果表明,实施早诊、早治是降低上消化道肿瘤发病率和死亡率的关键措施之一。
从2009年起,河南启动了国家上消化道癌早诊早治项目,目前,已扩展至12个项目点(市县),先后完成9万多例筛查对象的内镜检查及其诊断和治疗。本文对89,495例筛查和早诊早治结果进行分析,并对相关问题展开讨论。
2. 资料与方法
2.1. 目标人群
按照《中国癌症筛查及早诊早治技术方案》[3] 的要求,筛查对象为河南省上消化道癌高发区内的12个项目市县的40~69岁自然人群,其地理分布如图1。依据《河南省肿瘤登记年报2014》,2011年,林州上消化道癌发病率最高,为161.50/10万,偃师最低为73.72/10万,其他10个项目市县发病率介于期间。

Figure 1. Geographic distribution of high-incidence area of upper digestive tract carcinoma in Henan
图1. 河南上消化道癌高发地区分布示意图
2.2. 方法
在目标人群中,排除有胃镜检查禁忌症者,根据自愿原则签署患者知情同意书后,经身份证验证后接受内镜检查,并保持必要的参加率。根据技术方案要求对每个筛查对象的食管、贲门、胃进行内镜检查。食管经用1.2%~1.5%碘液染色后指示性活检,贲门脊根部重点检查,胃部全面检查,对可疑病变咬取活体组织,经病理组织学确定诊断和分级分型。
3. 结果
3.1. 上消化道癌检出率
2009~2013年的5年间,12个项目市县应用内镜完成9万多例筛查,用于统计分析的89,495例中,共发现上消化道癌2095例,检出率2.34%,其中,食管癌1.38%,贲门癌0.73%,胃癌(非贲门) 0.33%。早期病例1706例,占81.72% (表1)。
3.2. 食管病变
在内镜检查89,495例中,食管粘膜正常者61,850人,占65.27%;各类食管癌前病变(包含炎症,轻度、中度异型增生) 26,199例,占29.27%;各类癌(包含重度异型增生和原位癌,粘膜内癌、粘膜下癌以及浸润癌) 1242例,占1.39%,其中,列入可干预的早期阶段病变者1057例,占1.18%,中晚期癌185例,占0.21%。其病变的金字塔结构如表2。
3.3. 贲门病变
在89,495例检查对象中,贲门部正常者64,755例,占72.36%;各类贲门癌前病变(包含非萎缩胃炎、萎缩性胃炎和低级别上皮内瘤变) 23,337例,占26.08%;各类癌(包含高级别上皮内瘤变、粘膜内癌、粘膜下癌和浸润癌) 653例,占0.73%;其中,可干预的早期病变515例,占0.58%,中晚期癌138例,占0.15% (表3)。
3.4. 胃病变
可用于非贲门胃病变分析的资料62,415例,显示胃黏膜正常者58,144例,占93.16%;各类癌前病变(包含重度萎缩性胃炎、重度肠上皮化生和低级别上皮内瘤变) 3248例,占5.20%;高级别瘤变93例,占0.15%,早期癌47例,占0.08%;浸润癌66例,占0.11% (表4)。
3.5. 随访筛查
按照技术方案[3] 的要求,2012年度完成内镜随访筛查1469例,2013年度完成1575例,共计3044例(随访率64.65%)。除去由于没有接受治疗而进行随访筛查的早期癌193例外,有2851例依解剖部位分为食管、贲门及胃,其转归如表5。其病例检出率4.77%,是一般人群2.04倍。
3.6. 治疗情况
以林州为例,说明治疗情况如下。短期内(一年内)未接受治疗者占29.20%,治疗者占70.80%;接受治疗者又分为两种情况。一种是内镜下微创治疗,包括内镜粘膜切除术(EMR, 30.75%)和氩离子束凝固术(APC, 8.46%),合计占39.21%;外科手术占30.04%;放疗1.55% (表6,图2)。
4. 讨论与结论
在中国,尤如在河南地区一样,食管癌、贲门癌和胃癌是最为常见的恶性肿瘤之一。同一地区,这

Table 1. Endoscopic examination of upper digestive tract carcinoma in 89,495 cases
表1. 89,495例目标人群内镜检查结果

Table 2. Endoscopic examination of esophageal Lesions and their distribution in 89,495 cases
表2. 89,495例筛查对象的食管病变分布

Table 3. Endoscopic examination of gastric cardia lesions and their distribution in 89,495 cases
表3. 89,495例筛查对象的贲门病变分布

Table 4. Endoscopic examination of gastric lesions and their distribution in 62,415 cases
表4. 62,415例筛查对象的胃部病变分布

Table 5. Follow-up outcome of screening analysis for upper digestive tract precancerous lesions
表5. 上消化道癌前病变筛查分析的随访结果

Table 6. Analysis of cases received treatment over the 5 years in Linzhou
表6. 5年期林州病人接受治疗情况分析
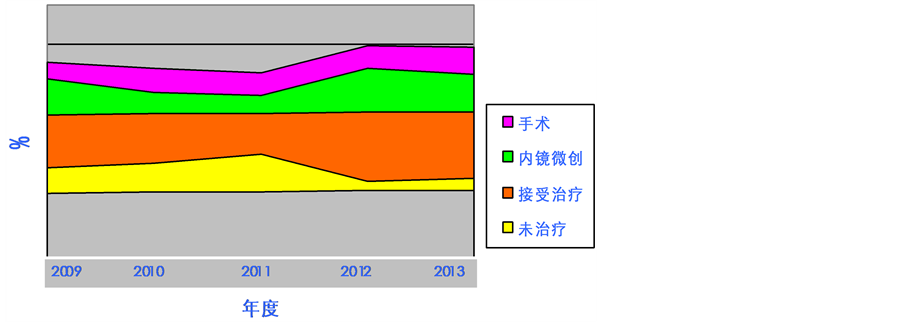
Figure 2. Percentage of distribution and dynamic variation of screening cases in Linzhou
图2. 林州筛查病人治疗情况分布及动态变化
三种肿瘤往往同时存在较高的发病水平[4] [5] 。河南12个市县5年来9万多例内镜筛查病例显示,这三种癌症依然高发。在40~69岁目标人群中,其病例检出率达到2.34%,依部位分别为,食管1.38%,贲门0.77%。胃0.33%。其中,处于早期癌症阶段病例占到80%以上,处于各类癌前病变阶段分别为29.27%、26.08%和5.20%,由于前两年重点检查食管和贲门部位病变,因此,胃的癌前病变可能会被低估。对近2%的早期病例积极治疗。并对60%左右的癌前病变进行干预,这无疑表明我国肿瘤防治战略的前移,开拓了我国上消化道癌早诊早治和现场防治的新思路、新方向[6] [7] 。
经过20多年的研讨,WTO在2006年正式公布癌症是一类慢性疾病。所谓癌症只是慢性病,基于两点:一、它发生、发展的过程缓慢,有一个长期渐进而累积的过程,一般需要5到20年;二、在这种情况下,为我们早期发现、早期治疗以及治愈提供了机会。有时它可以长期荷瘤生存,或逆转康复[8] 。
从对3000多例各类癌前病变的随访筛查来看,逆转者也主要是轻中度增生或低级别瘤变人群,重度增生和高级别瘤变仍然是我们关注的焦点[9] -[11] 。随访筛查数据表明,把食管重度异型增生/原位癌和贲门胃部的高级别瘤变作为危险癌前病变进行积极干预及微创治疗是合理的[12] 。对于未经治疗早期患者的随访结果提示,早期患者必须抓紧治疗,否则就会延误挽回生命的时机。食管重度异型增生患者一年后,29%维持原状,10%进展为早癌,2%进展为中晚期癌,丧失最佳治疗时机。而未经治疗的9例早癌,7例进展为中晚期癌,贲门和胃的情况类似,高级别上皮内肿瘤患者一年后,24%维持原状,11%进展为早癌,3%进展为中晚期癌。而未经治疗的14例早癌,7例进展为中晚期癌。
在高发区高危人群中,开展上消化道癌人群筛查,可以发现癌前病变或早期肿瘤病例,从而进行早期发现早期诊断和早期治疗。实践表明,对于上消化道癌,筛查不仅可以通过早诊早治提高癌症病人的生存率,而且可以降低其死亡率,因此,上消化道癌的二级预防也是减轻社会、家庭及个人疾病负担的重要措施,在癌症控制方面具有重要的公共卫生学意义。
林州现场资料表明,项目实施5年来,不愿接受治疗的人数逐年减少,而接受治疗者在逐年增加,主要是内镜下微创治疗。表明现场群众对于癌症防治知识的认知和积极的抗癌意识在逐步提高。然而,对于治疗措施的评价尚在进行之中,我们还需要积累更多的资料和时间,对早治效果做出更加科学合理的评价。
*通讯作者。