摘要:
目的:总结乳腺癌乳房切除术后的放疗效果,并探讨相关预后影响因素。材料与方法:2005年1月至2012年12月共有241例入组,中位年龄51岁,最小27岁,最大75岁。0期1例,IA期11例,IIA期51例,IIB期41例,IIIA期82例,IIIB期3例,IIIC期42例,IV期10例。全组患者均接受乳房切除术,其中改良根治术210例,根治术29例,扩大根治术2例。除3例不详,其余患者均接受术后化疗,其中有50例接受新辅助化疗。全组患者均接受放射治疗,中位剂量50 Gy (30~60 Gy),照射部位包括同侧胸壁、淋巴引流区(锁骨上和/或内乳),147例照射同侧胸壁、锁骨上和内乳(61.0%),47例照射胸壁和锁骨上(19.5%),39例未照射胸壁,仅照射锁骨上和/或内乳(16.2%),6例仅照射胸壁(2.5%),2例照射胸壁和内乳(0.8%)。结果:中位随访5.5年(0~10年),全组5年OS为87.5%。单因素分析显示肿瘤分期是影响OS的重要因素(P = 0.002),I、II期的5年OS为95.9%,III、IV期的5年OS为81.0%。LRR有14例(5.8%),DM是主要失败原因,有49例(20.3%)。死亡36例,均死于肿瘤。结论:仅5.8%的复发,提示乳房切除术后的放射治疗仍是乳腺癌术后规范治疗标准,5年OS接近国内外先进水平。
Abstract:
Objective: To summarize the outcome of radiotherapy in breast cancer after mastectomy, and to explore the relevant prognostic factors. Material and Methods: From January 2005 to December 2012, a total of 241 women who had undergone mastectomy were analyzed. The median age was 51 years old, with minimum 27 years old and maximum 75 years old. The pathological stage 0 were 1 case, IA of 11 cases, IIA of 51 cases, IIB of 41 cases, IIIA of 82 cases, IIIB of 3 cases, IIIC of 42 cases, IV of 10 cases, which performed in all patients by using AJCC 7th. All patients underwent mastectomy, which 210 cases of modified radical mastectomy, 29 cases of radical mastectomy, and 2 cases of extended radical mastectomy. In addition to three cases were unknown, the remaining patients received postoperative chemotherapy, while 50 patients received neoadjuvant chemotherapy. All patients were treated with radiation therapy, the median dose 50 Gy (30 - 60 Gy), irradiated sites included ipsilateral chest wall, lymph drainage area (supraclavicular and/or internal mammary). 147 cases were treated with chest wall, ipsilateral supraclavicular and internal mammary nodes irradiation (61.0%), 47 cases were treated with chest wall and supraclavicular irradiation (19.5%), 39 cases were treated with non-irradiated chest wall, only supraclavicular and/or internal mammary nodes (16.2%), 6 cases were only irradiated to chest wall (2.5%), two cases to chest wall and internal mammary irradiation (0.8%). Results: The median follow-up was 5.5 years (0 - 10 years), the 5-year OS was 87.5%. Univariate analysis showed that tumor stage was an important factor affecting the OS, 5-year OS of the pathological stage I and II was 95.9% while the OS of stage III and IV was 81.0% (P = 0.002). LRR in 14 cases (5.8%), whereas DM was the main causes of failure, which included 49 cases (20.3%). 36 patients died, all died of cancer. Conclusions Only 5.8% patients have locoregional recurrence, suggesting that radiation therapy after mastectomy is still the standard treatment in breast cancer. 5-year OS is approaching the world advanced level.
1. 引言
乳腺癌是女性最常见的恶性肿瘤,美国癌症协会预计2014年有235,030人被诊断为浸润性乳腺癌,40,430人将死于乳腺癌。另外2013年有64,640人被诊断为导管原位癌或小叶原位癌[1] 。在我国,无论城乡,乳腺癌同样是女性最常见的恶性肿瘤[2] 。在过去的几十年内,美国的乳腺癌发病率仍在稳步上升,但死亡率却在下降。其中的原因应归功于早期的发现和越来越有效的治疗手段。
EBCTCG1995年对36组随机实验的荟萃分析显示:乳腺癌根治术或改良根治术后放疗和未放疗组局部和区域淋巴结复发率分别为6.7%和19.6% (P = 0.001)。术后放疗使局部和区域淋巴结的复发率减少了2/3 [3] 。随着化疗和内分泌治疗的进展,全身治疗不但能提高总生存率,还能降低局部和区域淋巴结的复发。在这种背景下,术后放疗的地位和作用如何?本文通过对我院2005年1月至2012年12月的乳腺癌根治术或改良根治术后放疗的资料分析,总结本单位的术后放疗效果,并探讨相关预后影响因素。
2. 材料与方法
1) 入组条件:① 手术方式为根治术或改良根治术;② 均为病理明确。
2) 临床资料:2005年1月至2012年12月共有241例符合入组条件,中位年龄51岁,最小27岁,最大75岁。肿瘤分期均为术后病理分期,采用AJCC第7版分期标准。其中T分期为T1期82例,T2期142例,T3期13例,T4期4例。两侧乳房发生肿瘤比例为左侧51.0% (123例),右侧47.7% (115例),双侧同时发生1.2% (4例)。肿瘤分布部位最多为外上象限105例(占43.6%),其次为内上象限36例(占14.9%)。N分期为N0期32例,N1期79例,N2期85例,N3期45例。解剖淋巴结数目中位15枚,最少0枚,最多34枚,阳性淋巴结数目中位4枚,最少0枚,最多26枚。M分期为M0期231例,M1期10例(转移部位为肺1例,骨7例,胸膜1例,腹直肌鞘1例)。0期1例,IA期11例,IIA期11例,IIB期41例,IIIA期82例,IIIB期3例,IIIC期42例,IV期10例。病理类型中浸润性导管癌178例(73.9%)。在可进行肿瘤分级的173例中1级9例,2级92例,3级72例。血管内是否见癌栓:阳性34例(14.1%),阴性84例(34.9%),未记录或不详123例(51.0%)。淋巴管内是否见癌栓:阳性84例(34.9%),阴性32例(13.3%),未记录或不详125例(51.8%)。神经是否见癌累及:阳性21例(8.7%),阴性81例(33.6%),未记录或不详139例(57.6%)。
3) 治疗方法:全组患者均接受乳房切除术,其中改良根治术210例,根治术29例,扩大根治术2例。除3例不详,其余患者均接受术后化疗,其中有50例接受新辅助化疗。全组患者均接受放射治疗,中位剂量50 Gy (30~60 Gy),照射部位包括同侧胸壁、淋巴引流区(锁骨上和/或内乳),147例照射同侧胸壁、锁骨上和内乳(61.0%),47例照射胸壁和锁骨上(19.5%),39例未照射胸壁,仅照射锁骨上和/或内乳(16.2%),6例仅照射胸壁(2.5%),2例照射胸壁和内乳(0.8%)。
4) 研究终点:主要为OS,OS定义为从放疗结束到任何死亡的时间。次要为LRR和DM,LRR定义为同侧胸壁、同侧、锁骨上、腋窝、内乳淋巴结复发;DM定义为临床检查和影像学检查和/或病理学证实的远处转移。
5) 统计方法:使用SPSS19.0行Kaplan-Meier法计算生存率,Logrank法检验和单因素预后分析,分析因素包括年龄、肿瘤分期、脉管癌栓、神经累及、新辅助化疗等,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
3. 结果
1) 生存情况:中位随访5.5年(0~10年),失访21例,随访率91.7%。随访满5年142例,全组5年OS为87.5% (见图1)。单因素分析显示肿瘤分期是影响OS的重要因素(P = 0.002),I、II期的5年OS为95.9%,III、IV期的5年OS为81.0% (见图2、表1)。
2) 复发与失败分析:LRR有14例(5.8%,复发部位见表2),DM是主要失败原因,有49例(20.3%),另有1例病理证实为第二原发。死亡36例,均死于肿瘤。
4. 讨论
多个指南均推荐对4个以上淋巴结转移的乳腺癌术后除照射胸壁外需照射锁骨上下区淋巴结[4] -[6] ,其证据来自3项大型随机临床试验:丹麦乳腺癌协作组82b试验(Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group, DBCG 82b)、丹麦乳腺癌协作组82c (DBCG 82c)和英国哥伦比亚随机临床试验(the British Columbia randomized trial) [7] -[9] 。
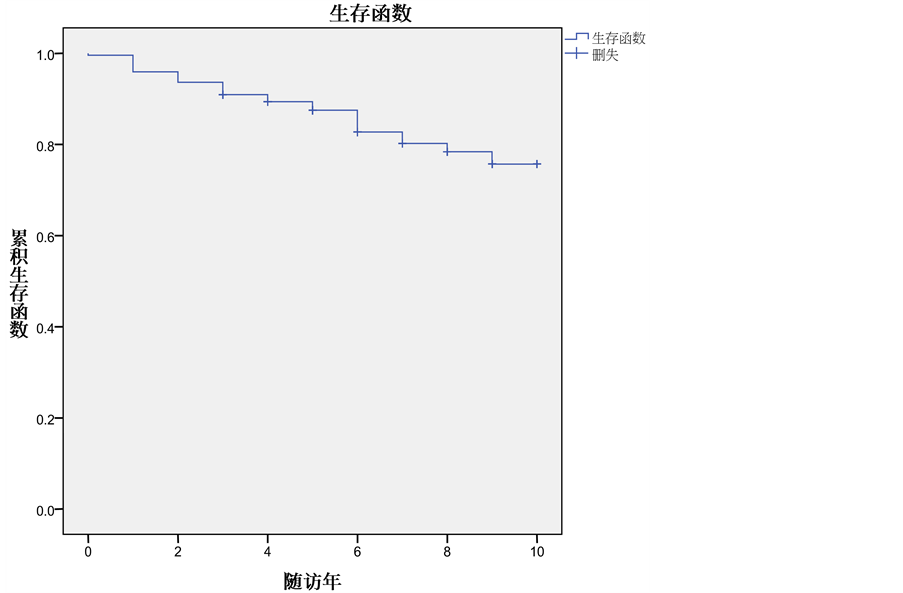
Figure 1. Overall Survival at 5 years in the whole group
图1. 全组的5年OS曲线
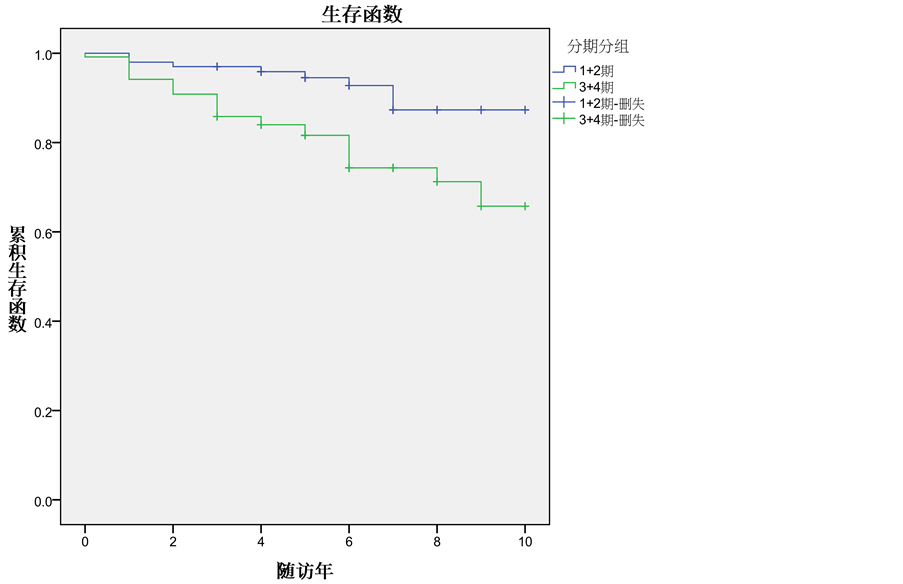
Figure 2. Overall Survival at 5 years among the patient of I + II and III + IV stage
图2. I + II期和III + IV期病人的5年OS曲线比较

Table 1. The univariate analysis of overall survival in the whole group
表1. 全组OS单因素分析

Table 2. The distribution site of local relapsed (14 patients in the whole group)
表2. 全组14例复发分布部位
DBCG 82b试验共入组1708例乳房切除术后病理分期为II或III期的绝经前乳腺癌患者随机分成术后放疗加化疗组和单纯化疗组,放疗照射胸壁和区域淋巴结,化疗为CMF方案。中位随访114个月,联合治疗组局部失败及远处转移率为9%,而单纯化疗组为32% (P < 0.001);10年无病生存率联合治疗组为48%,单纯化疗组34% (P < 0.001);10年OS联合治疗组为54%,单纯化疗组45% (P < 0.001)。DBCG 82c试验则入组1375例乳房切除术后病理分期为II或III期的绝经后乳腺癌患者随机分成术后放疗加内分泌治疗组和单纯内分泌治疗组,放疗照射范围同DBCG 82b,内分泌药物采用三苯氧胺。中位随访123个月,局部失败在联合治疗组有8%,而单纯内分泌治疗组达35% (P < 0.001);无病生存率联合治疗组为36%,单纯内分泌治疗组24% (P < 0.001);10年OS联合治疗组为45%,单纯内分泌治疗组36% (P < 0.001)。英国哥伦比亚随机临床试验随访时间更长(中位随访249个月),入组380例改良根治术患者,随机分为放疗加化疗组和单纯化疗组,放疗照射剂量为37.5 Gy/16次。联合治疗组与单纯化疗组无局部失败率分别为90%和74% (RR = 0.36, P < 0.001);OS分别为47%和37% (RR = 0.73, P = 0.03)。我们的研究也显示术后采用放射治疗,局部复发仅5.8%,虽然我们的随访只有中位5.5年,但5年OS接近90%,而来自上海疾病预防控制中心2013年的报道显示上海乳腺癌5年的相对生存率已接近90%,接近美国水平[10] 。说明本研究的数据与国内外先进水平接近。
近年来MA20研究的结果强烈支持对1~3个淋巴结转移的患者也应照射锁骨上下区,不仅显著提高了局控(HR 0.59, P = 0.02)和无病生存率(HR 0.68, P = 0.003),而且有提高总生存的趋势(HR 0.76, P = 0.07) [11] 。我们的资料显示61.0%的患者接受了胸壁加区域淋巴引流区照射,虽然OS不及MA20研究的结果,但我们的资料来自于乳房切除术后患者,而且III期以上病例占56.8%。
本组资料中局部复发最常见部位为胸壁和锁骨上,中华医学会肿瘤放疗分会对国内1999~2008年间根治术后放疗部位的流行病调查显示这两个部位是大多数单位最常照射的部位,腋窝和内乳的照射在减少,符合国际临床指南,体现了国内放疗的规范性[12] 。我们病例相对分期较晚,且多数内乳也在照射范围,故我们的研究中仅1例内乳复发,而该患者术后按照指南标准未照射内乳区。
当然,我们的研究属回顾性研究,随访多为电话随访,存在着不少偏倚和不足,有待前瞻性研究进一步证实。
5. 结论
总之,我们的资料显示仅5.8%的复发,说明乳房切除术后的放射治疗仍是规范治疗标准,且我们的5年OS接近国内外先进水平。
*通讯作者。