1. 引言
温度反映了一个区域气候特征,常用来表示热量资源及冷暖程度,由于气温的不同,四川省各地有着多种多样的丰富气候资源。气温也直接或间接地影响工业生产和产品质量,气温同样直接影响人们劳动、工作和学习的效率和生活上的是否舒适[1] 。大气热量的平衡受纬度和季节等因子的影响,所以气温的分布具有明显的地带性规律。同时,天气条件、下垫面性质等也会影响热量及热交换方式,所以气温也有一定的非地带性特征。因此,不同地点,影响因子不同,气温空间分布呈现出不均匀性。
近年来全国地震频发,对人们的生活造成了极大的影响。四川汶川发生地震后的两天出现了降雨甚至是暴雨,给救灾工作带来了极大不便,似乎是“天公不作美”[2] [3] 。但是,一些学者看来,地震本身就和旱涝息息相关。长期从事地震对旱涝影响研究的中科院寒区旱区环境与工程研究所研究员汤懋苍[2] 解释说,地球覆盖着厚约100公里的岩石圈,岩石圈的内部布满裂隙,积蓄着空气、水等流体,其中气体的总量达到大气圈中气体总量的10%~15%。这些流体并非静止不动,流体上升时,会给天气带来影响[4] 。
四川省位于中国西南部[5] ,属典型的亚热带季风气候(川西高原为高原季风气候),四季分明,降水丰沛,亚洲第一大河长江穿省而过,地处青藏高原向四川盆地过渡地带,地形类型复杂多样,加之2008年汶川大地震(继1976年唐山大地震以来中国遭遇的最大的一次地震)的发生,因此,地震对温度影响研究一个很好的区域,故本文选四川省作为研究对象。
2. 数据和方法
2.1. 数据
四川省(简称川)介于东经97˚21'~108˚31',北纬26˚03'~34˚19',位于中国西南腹地,地处长江上游,东西长1075公里,南北宽921公里。与7个省(区、市)接壤,北连青海、甘肃、陕西,东邻重庆,南接云南、贵州,西衔西藏。四川省地形西高东低,大致西部为高原、山地,海拔多在4000米以上;东部为盆地、丘陵,海拔多在1000~3000米之间。全省分为川西高原和四川盆地两大部分。
本文所采用的气温资料是由国家气象信息中心提供的时间序列为1963年1月1日至2013年12月31日,四川省48个地面气象观测站记录下来的日平均气温、日最高气温和日最低气温资料。先将原始文件为TXT格式的气象数据导入到SPSS软件中进行数据初始处理。剔除掉其中连续性不好的观测数据,最终选用40个气象台站资料作为主要分析对象。如图1所示表示1976年松潘和2008年汶川大于4级以上的地震及其余震,气象站台的分布。
2.2. 方法
克里金(Kriging)插值方法是一种以变异函数理论和结构分析为基础,在有限区域内对区域化变量进行无偏最优估计的地统计方法[6] -[9] 。该方法认为空间连续变化的属性是不规则的,不能用简单是平滑数学模型来模拟,应该用随机表面恰当地描述。其使用条件是研究区变量存在空间相关性,考虑测点的相互关系和空间分布位置等几何特征,对每个测点赋予一定的权重系数,最后用加权平均方法来估计未知的变量值。克里格方法是根据未知样点有限邻域内的若干已知样本点数据,在考虑了样本点的形状、大小和空间方位,与未知样点的相互空间位置关系,以及变异函数提供的结构信息之后,对未知样点进行的一种线性无偏最优估计[10] -[12] 。
计算公式一般形式可表示为公式(1):
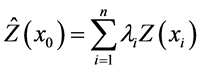 (1)
(1)
其中 ,
,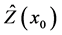 是
是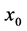 处的预测值,
处的预测值,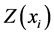 是
是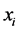 处的测量值。而本文所用的OK方法——克里金方法中的一种,还须满足以下条件:权重
处的测量值。而本文所用的OK方法——克里金方法中的一种,还须满足以下条件:权重 的选取必须使
的选取必须使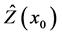 无偏估计。且估计方差
无偏估计。且估计方差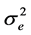 小于观测值的其他线性组合的方差。计算公式为(2)式和(3)式:
小于观测值的其他线性组合的方差。计算公式为(2)式和(3)式:
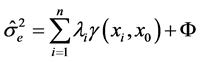 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
其中,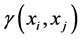 是Z在采样点
是Z在采样点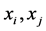 之间的半方差;
之间的半方差;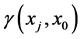 是采样点
是采样点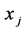 和位置点
和位置点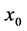 之间的半方差。
之间的半方差。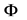 为计算最小方差需要的拉格朗日算子。
为计算最小方差需要的拉格朗日算子。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1. 四川省1963年-2013年气温时空变化特征分析
通过平均气温变化图和平均气温距平变化图,来分析四川省1963~2013年平均气温的变化情况。如图2、图3。
通过对图2、图3的分析,我们可以看到,四川省的过去50年年平均气温为11.60℃,平均气温在19世纪80年代以前气温偏低,1990年以前,仅仅5(5/27)年的平均气温超过平均值,从1976年开始,气温数据持续走低平均气温距平连续10年跌出−0.5℃,从1990年开始,有15(15/23)年的平均气温超过平均值,有八年的气温距平超过+0.5℃,2005、2006、2007、2008连续4年平均气温距平超出+1℃,2008年是最暖年份,气温距平(1.55),这与其他的地方的研究数据和世界范围内的研究数据有一定偏差,全球范围内最暖年份为2007年,这可能与四2008年汶川大地震有一定联系。
总体来看,平均气温呈上升的趋势,1963~1975年,气温上下波动幅度较小,相对稳;1976~1988年,整体气温偏低,都低于过去50年间的平均气温。但是气温的变化趋势是逐渐上升的。1988~2001年,这几年的气温在平均气温附近变化,波动幅度非常小。从2001年开始,气温开始大幅度的升高,气温的年平均值均在过去50年的平均气温之上,可以说是全球变暖最严重的几年。2013年的平均气温相对于

Figure 1. Spatial distribution of meteorological stations and earthquake event in Sichuan Province
图1. 四川省气象台站以及地震分布图
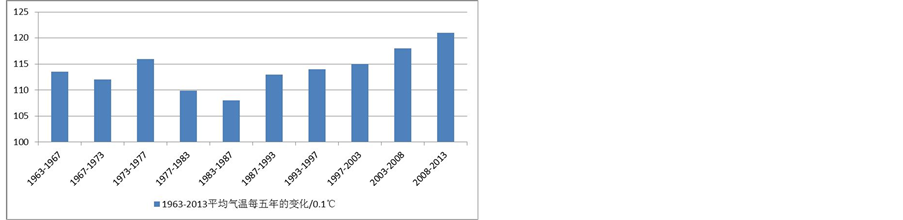
Figure 2. The average temperature variation of 1963-2013 in Sichuan
图2. 四川省1963~2013年平均气温变化图
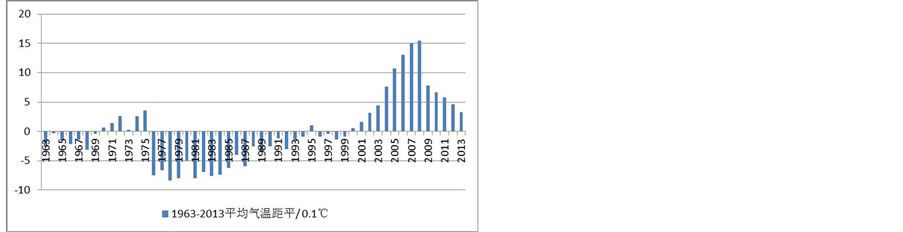
Figure 3. The average temperature departure of 1963-2013 in Sichuan
图3. 四川省1963~2013年平均气温距平变化图
1963年的平均气温,上升的幅度为0.6℃,但是平均气温最大浮动值(平均气温最高年份气温 − 平均气温最低年份气温)为2008年平均气温的与1978年平均气温的差值为2.38℃。
如图4所示为根据四川省40个气象站点的年平均气温生成的平均气温空间分布图,通过图可以大致地了解四川省过去五十年平均气温的分布情况。
总体上来说,四川省过去50年里,平均气温由西向东逐渐升高,当然川南地区的攀枝花市气温情况比较反常,这是由于该地区所在位置及地形地貌特征所导致的。从方位分析来看,气温的变化情况是由北向南,由西向东逐渐升高。东西温差达20.5℃,南北温差15℃左右。
3.2. 松潘大地震对气温影响分析研究
3.2.1. 松潘大地震对平均气温影响分析
本文为了对比分析,特地将1976年前后一年即1975、1977年的气温做对比分析,以下分别作了1975、1976、1977三年的平均气温空间分布图,让我们看图分析。
从图5可以看出,三年的气温分布布局大体一致,1975年的气温变化区间是−0.84~18.4℃,1976年的气温变化区间−1.55℃~17.3℃,1977年的气温变化区间为−2.47~17.9℃。总的来说,1976年相对于1975年最低气温降低了0.71℃,1977年相对于1976年来说,最低气温降低0.92℃。而从最平均高气温值来看,1976相对于1975下降了1.2℃,1977则有回升趋势,最高值增加了0.7℃。
因为1976松潘大地震发生在1976年8月的,为了更好地体现地震对气温的影响,现将1975、1976、1977年的平均气温空间变化分布图放到此处,做详细分析。如图6。
从图6的数据可以看出,75年8月的年平均气温变化区间为8.53~28.0℃,76年8月的平均气温变化区间为6.0~26.9℃,77年8月的平均气温变化区间为8.58~28.2℃。单单从地震月来看,地震月的平均气温相对于前后一年同比最低气温近2.5℃,平均气温的最高温度下降了1.2℃,变化比较明显。
从1976年大地震的分析我们大概可以对地震对气温的影响做出判断,因松潘地震的震级为7.2级,影响肯定不那么显著,为了更好地研究地震对气温影响,本文特地选了2008年四川8级汶川地震为例,研究地震对气温的影响,基于1976年的数据分析,我们知道研究地震年度气温前后变化效果不够明显,而对地震月前后年同比分析,得出的结果则比较明显,因此,对2008年四川汶川大地震的研究,我们只对地震月作研究分析。

Figure 4. The average temperature spatial variation of 1963-2013 in Sichuan
图4. 四川省1963~2013平均气温空间变化分布


 (a) 1975年 (b) 1976年 (c) 1977年
(a) 1975年 (b) 1976年 (c) 1977年
Figure 5. The average temperature spatial distribution in 1975-1977
图5. 1975年~1977年平均气温空间分布


 (a) 1975.08 (b) 1976.08 (c) 1977.08
(a) 1975.08 (b) 1976.08 (c) 1977.08
Figure 6. The mouth average temperature spatial distribution in 1975.08-1977.08
图6. 1975~1977年8月平均气温空间分布
3.3. 2008年四川汶川大地震对平均气温影响研究分析
为了对比分析,本文特地将2008年前后一年即2007、2009年的气温拿出来做对比分析,以下分别作了2007、2008、2009三年的5月份的平均气温空间分布图,让我们看图7分析。
总体上,从图7来看,平均气温的最低气温2008年5月偏高,平均气温的最高气温2007年5月偏高。从数据上看2007年5月平均气温空间差异区间为4.87~25.04℃,2008年5月平均气温空间差异区间为5.05~24.13℃,2009年5月平均气温空间差异区间为3.74~22.49℃。而从收集整理数据来看,对于平均气温,2007年5月,全省平均气温为18.29℃,2008年5月,全省平均气温为17.93℃,2009年5月,全省平均气温为16.39℃。可以看到,全省范围,平均气温在07,08,09三年的5月同比均在下降,07-08年的下降幅度小一些,08-09年的下降幅度则非常大。
4. 结论
(1) 从平均气温的变化趋势及距平变化趋势图,可以看出,不管是日最低气温、日最低气温还是日最高气温,过去五十年的整体趋势呈上升状态,温度上升趋势在2003年之后异常迅速。而在1975年发生过气温的突变,全省气温在1975年之后的10多年处于比较低的水平。根据统计结果,2007年为过去50


 (a) 2007.05 (b) 2008.05 (c) 2009.05
(a) 2007.05 (b) 2008.05 (c) 2009.05
Figure 7. The mouth average temperature spatial distribution in 2007.05-2009.05
图7. 2007~2009年5月平均气温变化图
年的最热年,在其之后,气温开始呈缓慢的降低趋势。
(2) 地震会对气温产生一定的影响,从1975年~1977年及2007年~2009年气温数据对比结果来看,1976年和2008年地震发生时,气温都发生了突变下降,在1976年气温发生突降后,1977年气温又迅速上升到与1975年的相似水平;而2008年地震发生,气温相对于2007年发生了突降,在之后的几年,气温总体都呈下降趋势。总的来说,地震的发生,会引起气温的突变下降。
(3) 对于空间变化来说,四川省的总体气温分布情况为由西向东,由北向南气温逐渐降低的趋势,最冷地区为甘孜、阿坝地区(这些地区海拔较高),而最热的地区为川东地区及川南的一部分地区。而地震之后,高温区域面积虽然有扩大趋势,但是最高低温却在下降。
致谢
本文为2014年苗子工程《基于3S的西南地区泥石流应急预警技术研究》,2014年中央高校项目(A030 11023401092)《潜在泥石流灾害遥感解译与危险性预警系统研究》,国家自然基金(G0501220141371398)《泥石流灾害危险性遥感评估模型》阶段成果。