1. 引言
2013年,中国吸引外国直接投资3478亿美元;芬兰、新西兰、瑞典等国家外国直接投资净流入量为负。为什么不同国家吸引的外国直接投资的数额有如此大的差别?毫无疑问,这与东道国的市场规模、市场增长潜力和市场机会等经济因素有着密切联系。但是,我们也不能忽略文化对于吸引外国直接投资的影响。随着经济全球化的不断深入,不同文化之间的碰撞正在以惊人的速度增长。对外直接投资的主体是跨国公司,而跨国公司的运作以文化间的交流和合作为轴心。一次对外直接投资要想取得成功,跨国公司必须对东道国的文化环境进行考察。全球商业种一个日益增长的趋势是,关税和技术优势正在逐渐消失,它很自然地会过渡到经济条件地竞争以及文化优劣条件的竞争(Hofstede, 2004) [1] 。因此文化因素对于一国吸收的直接投资的量是有一定影响的。
2. 文献综述
为了更好的研究文化吸引外国直接投资的影响,首先必须确定哪几个因素可以比较全面的体现不同文化之间的差异。在根据纬度来划分国家文化的学者中,荷兰学者Hofstede无疑是先驱者。在其1980年出版的Culture’s Consequences一书中,他首先使用了这种方法,这在文化研究中代表着一种新的范式。Hofstede (2004) [1] 通过长时间反复的调查研究,在Cultures and Organizations一书中提出了文化的五个纬度:权利距离、集体主义-个人主义、阴柔气质-阳刚气质、不确定性避免和长期导向-短期导向。其中第五个纬度是在其早期著作Culture’s Consequences基础上,新加入的一个纬度。
除了Hofstede外,其他学者也根据自己的调查,提出了不同的划分文化纬度的方式。以色列心理学家Schwartz区分出了七个纬度:保守、等级、掌控性、情感自主性、智力自主性、对平等的认同、和谐(Hofstede, 2004) [1] 。Trompenaars (1993) [2] 区分了普遍主义与特殊主义、个体主义与集体主义、情感性与中立性、专一行与扩散性、成就地位与因袭地位、时间导向、以及人与自然的关系。House (2004) [3] 在他的课题全球领导与组织行为有效性(GLOBE)中提出了九个纬度:权力距离、不确定性规避、社会集体主义、内群体集体主义、性别平等主义、自信、未来导向、绩效导向以及人本导向。美国政治科学家Ronald Inglehart领导的世界价值观调查(World Value Survey, WVS)发现了两个关键的文化纬度:主观幸福——基本生存纬度和世俗理性——传统权威纬度(Hofstede, 2004) [1] 。
由于以上学者所做的研究结果或者与Hofstede (2004) [1] 的测量结果存在显著的相关关系,或者存在一定缺陷,因此本文采取Hofstede (2004) [1] 对文化纬度的划分方式。此外,大量的检验表明,这些相关关系并不随着时间的流逝而减弱。因此国家纬度的得分(或至少是其相对位置)现在还是有效的,这表明它们刻画的是这些国家的社会中一些相对持久的方面(Hofstede, 2004) [1] 。因此,本文将直接使用Hofstede (2004) [1] 的研究中对国家文化纬度的得分。
这些不同的文化对直接投资规模有何影响?一国经济对外扩张的方式主要有对外出口和直接投资两种。Dermott和Mornah (2015) [4] 根据House (2004) [3] 提出的文化纬度划分方式,从九个方面分析了东道国的文化对于企业在对其出口和直接投资之间做出选择时的影响;并且指出,这九个文化纬度对于企业的影响力是不同,其中绩效导向的影响是最大的。辉侠、董超和冯宗宪(2007) [5] 运用引力模型对文化因素在中国吸引外商直接投资中的影响进行的实证分析结果表明,投资来源国(地区)蕴涵的中国文化强有力地推动了额其对中国的直接投资。黄艳艳(2008) [6] 以2000~2005年对华投资较多的52个国家(地区)为研究对象,建立含有文化因素的计量经济学线性模型,采用面板数据对建立的模型进行回归。结果表明,文化是影响FDI的重要因素之一;同时,投资国与东道国的文化差异越大,其投资额越小。殷华方、鲁明泓(2011) [7] 研究显示1993~2006年49个世界重要经济体在29个OECD成员国的国际直接投资数据表明,文化距离和国际直接投资流向之间存在着水平S型曲线关系,即当文化距离较小时,文化距离和国际直接投资流向有负向关系;当文化距离在中间水平时,文化距离和国际直接投资流向有正向关系;当文化距离较大时,文化距离和国际直接投资流向又有负向关系。此外,易江玲和陈传明(2014) [8] 基于缘分视角,测量了国家之间的心理距离和其对于中国的国际直接投资的影响。周经和张利敏(2014) [9] 以及冀相豹(2014) [10] 从制度的视角,研究了中国对外直接投资影响因素分析。
上述研究中,有些仅仅止步于定性分析;其余的进行了实证分析的研究中,加入的文化变量均不全面。本文将运用Hofstede (2004) [1] 归纳的五个文化纬度,从定性和定量两个方面,研究文化对于一国吸引外国直接投资规模的影响。但本文仍存在一定缺陷:实证分析结果与经验分析结论出现分歧时,即在不确定性避免指数相似性对吸引外国直接投资规模的影响方面出现分歧分歧时,由于笔者能力有限,并没有给出完成系统的理论解释。
3. 文化对吸引外国直接投资规模影响的经验分析
3.1. 权利距离对吸引外国直接投资的影响
权力距离指在一个国家的机构和组织中,弱势成员对于权力分配不平等的期待和接纳程度。在这里,机构是指社会的基本单位,例如家庭、学校、社区等;组织是指人们的工作场所。权力距离指数得分能够告诉我们一个国家中人们之间的依赖关系。在低权力距离国家中,下级对上级的依赖性较小,上下级之间更喜欢协商方式。而在高权力距离国家,下级对上级有相当大的依赖性,下级不太可能直接与上级商讨问题,更不可能直接反驳他们的上级(Hofstede, 2004) [1] 。
在其他条件一定时,低权力距离的国家更倾向于对其他低权力距离国家进行直接投资;高权力距离的国家更倾向于对其他高权力距离国家进行直接投资(Dermott and Mornah, 2015) [4] 。若权力距离相差太大的两个国家相互进行直接投资,会由于文化上的巨大差异而导致跨国公司在组织上的困难。
3.2. 集体主义–个人主义对吸引外国直接投资的影响
个体主义指的是人与人之间松散联系的社会:人们只照顾自己及其核心家庭。相反,集体主义指的是这样的社会:人们从出生起就融入到强大而紧密的内群体当中,这个群体为人们提供终身的保护以换取人们对于该群体的绝对忠诚(Hofstede, 2004) [1] 。
个体主义指数得分低表示这个国家(地区)的公民具有高的集体主义精神。职工更倾向于与雇主保持长期的关系,为了完成组织上的责任,他们愿意做出自我牺牲(Dermott and Mornah, 2015) [4] 。忠诚度高的职工总是收到欢迎的,这可以降低企业在培养新员工上的支出。因此,在其他条件一定时,跨国公司更倾向于向个体主义指数得分低的国家进行直接投资。
3.3. 阴柔气质–阳刚气质对吸引外国直接投资的影响
一般情况下,男性被认为更具有阳刚气质,女性更具有阴柔气质。实际上,一名男性可能行为举止上有阴柔气质,一名女性的行为也可能具有阳刚气质,这只意味着他们的行为偏离他们所处的特定社会的习俗。具有阳刚气质的人更注重:收入——有机会取得高收入;赏识——干好工作时,能够得到肯定和认定;提升——有机会提升到更高的职位;挑战——拥有挑战性的工作,从中获得个人成就感。具有阴柔气质的人更注重:管理者——和直接上司有着良好的工作关系;合作——与善于合作的人一起共事;居住地区——居住在自己和家人喜欢的地方;雇佣保障——工作有保障,在这个企业中你愿意干多久都可以。
若一个国家国家(地区)阳刚气质指数得分较高,说明该国员工和管理者很注重规模经济和效率,该国更易吸引下列行业的外国直接投资:重工业、化学、天体化学等。若一个国家国家(地区)阳刚气质指数得分较低,说明该国员工和管理者更注重个人服务,该国更易吸引下列行业的外国直接投资:农业、食品、生物化学等。
3.4. 不确定性避免对吸引外国直接投资的影响
不确定性规避是指某种文化中的成员在面对不确定的或未知的情况时感到威胁的程度。这种感觉经常通过紧张感和对可预测性的需求(对成文的和不成文的规定的需求)表现出来(Hofstede, 2004) [1] 。一些文化中的员工非常乐意接受主管的具体指令,欢迎完整体系的规章制度,即使许多规则并不切实可行。这些员工具有较高的不确定性避免,偏好于回避工作中模棱两可的情况。对于不确定性避免较低的员工来说,刻板的规章制度会令他们不适,他们更希望有一些自己发挥的空间。
很显然,跨国公司更愿意向同自己国家(地区)不确定性规避指数得分相近的国家进行投资,这样可以减少不同文化间的摩擦,更快的适应东道国的环境。
3.5. 长期导向–短期导向对吸引外国直接投资的影响
长期导向意味着培育和鼓励以追求未来回报导向的品德——尤其时坚韧和节俭。与之相对的另一端,短期导向,意味着培育和鼓励关于过去和当前的品德——尤其时尊重传统、维护面子,以及履行社会义务。在长期导向指数得分较高的国家,相对于目前的盈亏状况,管理者更关注市场地位和未来的利润;人们投资与终生的人际关系网络,储蓄率很高。在长期导向指数得分较低的国家,管理者重点关注目前的盈亏状况;个人的忠诚度随着企业需求的变化而改变,储蓄率很低。
在长期导向指数得分较高的国家,人们倾向于使出口最大化,使进口最小化。因此,为了更好的占有该国市场,跨国企业更愿意在该国进行直接投资。相反,对于短期导向的国家,贸易可能使更好的方式。短期导向的国家不会采取方式减小进口,并且相对于直接投资,贸易的风险更小。
4. 文化因素对吸引外国直接投资规模影响的实证分析
从以上的分析可以看出,五个文化维度对于直接投资规模的影响方式是不同的。其中,权力距离指数和不确定性避免指数对于东道国吸引直接投资规模的影响是双向的:与东道国指数得分相近的国家会加大对东道国的投资,与东道国指数得分相差大的国家则会减小其对东道国的投资。个人主义指数和长期导向指数对于吸引直接投资规模的影响是单向的:随着个人主义指数得分的降低和长期导向指数得分的上升,一国吸引直接投资的总量会上升。最后,阳刚气质指数对于一国吸引直接投资总量的影响是不确定的,其指数得分的变化会造成吸引的直接投资的重点领域发生变化。
为了更准确的分析文化因素对于吸引外国直接投资规模的影响,笔者将实证研究分为两大部分。第一部分研究文化因素对吸引外国直接投资总量的影响,验证个人主义指数和长期导向指数对于吸引直接投资规模的影响。第二部分以中国作为东道国,探究当其它国家与中国在权力距离指数和不确定性避免指数相近时,其对中国的直接投资额是否会更大。本文并没有将阳刚气质指数对于吸引直接投资的影响纳入实证研究,因为无法很明确的区分开,哪些行业更注重规模经济和效率,而哪些行业又更注重服务;此外一些国家的行业数据也是不可获得的,所以对于阳刚气质指数的分析仅止步于经验分析。
4.1. 五个文化变量指数对吸引外国直接投资总量的影响
4.1.1. 模型建立
为研究文化因素对于一国吸引外国直接投资规模的影响,显然被解释变量为外国直接投资净流入(Foreign Direct Investment, net inflows, FDI)。模型中最重要的就是文化变量的选择。正如前文所言,本文将选择的文化变量为:权利距离指数(power distance index, PDI)、个人主义指数(individualism index, IDV)、阳刚气质指数(masculinity index, MAS)、不确定性避免指数(uncertainty avoidance index, UAI)、长期导向指数(long-term orientation index, LOI)。
除文化变量以外,必须加入其他控制变量使模型更加完整。在参考了其他研究文化对直接投资规模影响的文章的基础上(孙炎林、胡松,2004) [11] ,我们选择的变量为:国内生产总值(Gross Domestic Product, GDP)、人均国内生产总值(GDP per capita, PGDP)和国内生产总值增长率(GDP gorwth, GDPGRO)。
本文所使用模型为:
4.1.2. 模型数据的选择
Hofstede (2004) [1] 在Cultures and Organizations中对74个国家(地区)的前四个文化纬度以及39个国家(地区)的第五个文化纬度进行了评分。本文关于文化纬度变量的数据全部来源于Hofstede。此外,各国2013年GDP、PGDP、GDPGRO及FDI的数据全部来源于世界银行数据库。
4.1.3. 计量结果及分析
由回归结果(见表1)可以看出,五个文化维度中,对外国直接投资净流入量最大的是不确定性避免指数,并且只有该文化变量的系数是显著的。不确定性避免指数上升,即面对未知情况的紧张程度增加,会使外国直接投资净流入减少。其他四个文化维度变量,虽然在不同的回归方程中的符号不变,但是其系数都不是显著的。权利距离指数和个人主义指数与外国直接投资净流入是负相关的;阳刚气质指数与长期导向指数与外国直接投资净流入是正相关的。个人主义指数以及长期导向指数的符号与预期的结果是一致的:跨国公司倾向于在个体主义指数得分低和长期导向指数得分高的国家进行直接投资。
虽然除了不确定性避免指数外,其余四个文化纬度指数对于外国直接投资净流入的影响不是显著的,但是并不能说明其对于吸引外国直接投资规模是没有影响的。正如上文所述,文化纬度得分不同可能吸引的直接投资的产业和国家来源不同。因此,回归结果只能说明,不确定性避免上升,总体上会导致外国直接投资净流入量减少;其他文化纬度对吸引外国直接投资的影响在总体的量上并没有体现出来。
表1. 回归结果
4.2. 权力距离指数与不确定性避免指数相似性对吸引外国直接投资的影响——以中国为东道国的分析
4.2.1. 权力距离指数相似性对中国吸引外国直接投资规模的影响
与上述模型相比,该模型并没有太大变化,只是将权利距离指数(PDI)换成了权利距离相似指数(similarity of PDI, SIPDI);被解释变量由各国吸引的外国直接投资额变为不同国家对中国的直接投资额。权利距离相似指数的计算采用Kogut and Singh (1988) [12] 提出的公式:
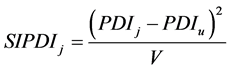
SIPDIj代表j国与东道国中国的权利距离相似指数;PDIj代表j国的权力距离指数;PDIu代表中国的权利距离指数。V表示各国权利距离指数的方差。下文中关于不确定性避免相似指数(similarity of UAI, SIUAI)同样用这种方法得出。回归方程为:
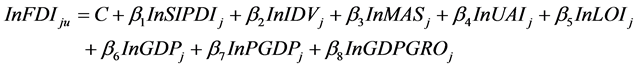
其中,FDIju表示2013年j国对中国的直接投资额,其数据来源于CEIC数据库。
从结果(见表2)中可以看出,权利距离相似指数与母国对东道国的直接投资流量是正相关的,这与经验分析结论一致。但是根据P值显示,这种正相关性并不是十分显著。加入其他文化维度指标后,权利距离相似指数对直接投资的影响增强,其显著性有所上升,但仍旧不是十分显著。
4.2.2. 不确定性避免指数相似性对中国吸引外国直接投资规模的影响
回归方程为:
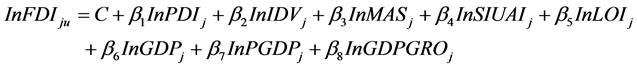
回归结果(见表3)与经验分析结论大相径庭。经验分析表明,跨国公司更愿意向同自己国家(地区)不确定性规避指数得分相近的国家进行投资。但是根据回归结果,不确定性避免指数相似性与母国对东道
表2. 回归结果
表3. 回归结果
国的直接投资流量是呈负相关的。并且,根据P值可以看出,该指数的系数是显著的。为什么会出现截然不同的结论?可能有以下原因:首先,可能受到个别样本的影响。由于地理、文化和历史等原因,韩国和日本与中国的经济交往非常密切:2013年其对中国的直接投资分别为30亿和70亿美元,仅次于香港和新加坡。但是,其不确定性避免指数与中国差距很大:韩国和日本的不确定性避免指数分别为85和92;而中国的不确定性避免指数得分仅为30。其次,Hofstede仅对一部分国家的文化维度进行了评分,统计样本的不完整性可能会使回归结果出现一定偏差。
5. 结论
不同的国家的文化纬度指数得分或多或少存在一些差异。但是,本文的实证结果显示,除了不确定性避免会对吸引外国直接投资总量产生影响外,其余的四个纬度对对总量的影响是不明显的。也就是说,没有一个国家擅长所有的东西,文化优势中同时包含着弱势。为了能吸引更多的外国直接投资,降低不确定性避免指数是有效的,但是其他四个文化纬度指数的改变,不会对所吸引直接投资总量产生显著影响,或者说只会引起直接投资从一个行业转移到另一个行业,投资国从一个国家变为另一个国家。从文化相似性的角度来看,中国权利距离指数得分相近的国家更倾向于对中国进行直接投资;而与中国不确定性避免指数得分差距较大的国家更倾向于对中国进行直接投资。
致谢
对给予转载和引用权的资料、图片、文献、研究思想和设想的所有者,表示感谢。