1. 引言
如今,随着社会的发展,生活水平的提高,人们的生活节奏越来越快,生活压力也越来越大。在这种情况下,面对日常的生活、学习和工作,人们经常会感到疲劳。这不仅对我们的生活、学习、工作产生了影响,还损害了我们的身心健康,给学习和工作造成了一定的困扰。同时在这种快节奏的生活中,因为压力大,睡眠不足等原因,也加速了我们的衰老,降低了身体的机能。为了缓解日常生活中所产生的疲劳,提高我们的健康水平,提高运动员的运动成绩,通过对一些传统的中药进行了研究,以探索它们对疲劳的缓解作用及抗衰老的作用。中医因擅长对人体进行整体调理,综合调整人体免疫机能,平衡机体阴阳气血内环境,促进人体阴阳平衡、气血调和,在治疗疲劳方面有其独特优势。近年来,随着现代药理学理论及现代生物技术的更新,消除疲劳的机制及方法研究不断深入,传统中药凭借其疗效确切、副作用小等独特优势,成为了抗疲劳研究的热点[1] 。在以上的基础上,我们采用泰山四叶参、楤木、黄芪、黄精这四种中药组方进行了抗疲劳及抗衰老的研究。
四叶参(Radix Codonopsis Lanceolatae)又名奶参、羊乳、山海螺、白蟒肉、狗头参、乳头薯、乳薯,是桔梗科党参属植物四叶参的根,与泰山何首乌、黄精、紫草并称为泰山四大名药。有研究显示其提取物具有镇咳、镇痛抗炎、抗疲劳、抗氧化及抗衰老等作用 [2] 。黄精(Polygonatum sibiricum Delar)又名老虎姜、鸡头参。为百合科植物滇黄精、黄精或多花黄精的干燥根茎。黄精是药食两用中药,在我国应用历史悠久,分布广泛。具有补气养阴、健脾、润肺、益肾、抗疲劳之功效,可用于治疗脾胃虚弱,体倦乏力,口干食少,肺虚燥咳,精血不足,内热消渴等症 [3] 。黄芪(Leguminosae)是豆科植物,是一种常用的补益中药,具有补气表固,益气活血,排毒,抗疲劳等增强机体抵抗力的作用 [4] 。用于气虚乏力,食少便溏,中气下陷,久泻脱肛,便血崩漏,表虚自汗,痈疽难溃等症。楤木(Aralia chinensis L)为五加科楤木属植物,该属植物主要以根及根皮入药,有祛风除湿、抗疲劳、利尿消肿、活血止痛的作用。
目前国内有一些对黄精、黄芪抗疲劳及抗衰老的研究,也取得了一定的成果。金英子,曲香芝等 [5] 研究复方黄精对小鼠耐缺氧及抗疲劳能力的影响,得出复方黄精可明显提高小鼠心脑耐缺氧能力,降低组织耗氧量,4.2 g/kg复方黄精可不同程度地提高小鼠抗疲劳能力。吴晓岚,王玉勤等 [6] 研究黄精和玉竹二种中药对小鼠抗疲劳作用的影响及其可能的作用机制。吴铭,周桃英等 [7] 进行了黄芪多糖抗疲劳作用研究,黄芪多糖可延长小鼠负重力竭游泳时间,降低机体血乳酸的积累,增加肝糖原的储备,起到延缓疲劳发生、提高运动能力的作用。但是对楤木在这方面的研究几乎没有,对四叶参的研究也比较少。同时,利用中药的协同原理,将这四种中药联合起来对小鼠抗疲劳及抗衰老的研究还未见报道。因此,我们研究四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木这四种中药提取液对小鼠抗疲劳能力及抗衰老能力影响。
2. 实验材料与方法
2.1. 实验材料与仪器
2.1.1. 实验药材
四叶参 购自泰安市泰山四大名药科技有限公司
黄精 购自泰安市泰山四大名药科技有限公司
黄芪 购自泰安市药材批发公司
楤木 采自泰山北麓
2.1.2. 实验动物
昆明种雄性小鼠30只,体重18~22 g,由山东鲁抗股份有限公司提供。
2.1.3. 实验仪器
游泳箱 规格:50 cm × 50 cm × 40 cm,水温(26 ± 1)℃。
离心机:LD5-2A型 北京医用离心机厂
电子分析天平:FC104 上海恒平科学仪器有限公司
电热恒温干燥箱:DHG-9147A 上海精宏试验设备有限公司
单列八孔水浴锅:HH.SY11.N 北京市长风仪器仪表公司
中草药粉碎机:FW-177 天津市泰斯特仪器有限公司
丙二醛(MDA)测试盒:南京建成生物工程研究所
肝/肌糖原测试盒:南京建成生物工程研究所
微波炉:WD750ASL23 广东格兰仕微波炉电器制造有限公司
旋转蒸发仪:RE-52A 上海亚荣生化仪器厂
紫外分光光度计:上海美谱达仪器有限公司
2.2. 实验方法
2.2.1. 四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木提取液的制备
烘干:将四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木切片,在60℃烘干箱内烘至恒重。
粉碎:将烘干后的四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木在粉碎机中分别进行粉碎。
浸泡:分别称取粉碎好的四叶参450 g、黄精360 g、黄芪135 g、楤木180 g,所占比例分别为40%、32%、12%、16%。按照药、水比为1:20的比例分别加水9000 ml,7200 ml,3600 ml,2700 ml,共加水22,500 ml,分别放入烧杯内,浸泡6~8小时。
提取:用微波炉进行提取,提取10分钟。
过滤:微波炉提取后,用四层纱布进行过滤,楤木过滤后还需要用无水乙醇进行再提取、过滤。
浓缩:将滤液用旋转蒸发仪蒸发浓缩,浓缩浓度为0.5 g/ml。
将浓缩液装瓶,存放于4℃冰箱备用。
2.2.2. 小鼠负重游泳实验
将30只雄性小鼠随机分成3组,每组10只,分别为高浓度组、低浓度组和对照组。高浓度的提取液浓度为0.25 g/ml,低浓度的提取液浓度为0.125 g/ml。高浓度组和低浓度组分别灌胃0.2 ml/10g的提取液,对照组灌胃0.2 ml/10g的生理盐水,每天一次,连续灌胃四周。末次灌胃给药30 min后,在小鼠尾根部负荷8%体重的铅丝,置于游泳箱内进行游泳,从放入水中开始计时,观察小鼠游泳至力竭下沉的时间(在水下10 s不能游出水面),记录时间,这段时间为小鼠的游泳时间。
2.2.3. 肝糖原和肌糖原含量的测定
分组与给药同上,对小鼠肝糖原和肌糖原含量进行测定。取新鲜肝脏、肌肉样本用生理盐水漂洗后用滤纸吸干,称重。按样本重量:碱液体积 = 1:3一起加入试管中,沸水煮沸20 min,流水冷却。然后将糖原水解液进一步制备成糖原检测液。按照要求配置空白管、标准管、测定管,最后混匀后煮沸5 min,冷却后于620 nm波长,1 cm光径,空白管调零,测各个管OD值,计算出肝糖原和肌糖原含量。
2.2.4. 血清MDA含量的测定
分组与给药同上,对小鼠MDA含量进行测定。小鼠眼球取血,离心分离血清。按照要求配置好空白管、标准管、测定管后,用旋涡混匀器混匀,试管口用保鲜薄膜扎紧,用针头刺一小孔,95℃水浴(或用锅开盖煮沸) 40分钟,取出后流水冷却,然后3500~4000转/分,离心10分钟(3000转/分以下离心时间需延长,目的使沉淀完全)。取上清,532 nm,1 cm光径,双蒸水调零,测各管吸光度值,计算出MDA的含量。
2.3. 统计学处理
运用SPSS13. 0统计软件进行统计,实验数据用均数±标准差(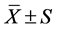 )表示,采用方差分析处理数据。
)表示,采用方差分析处理数据。
3. 结果
3.1. 四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木提取液对小鼠负重游泳能力的影响
结果见表1,表1结果表明,与对照组比较,高浓度组和低浓度组均能延长小鼠的游泳时间,且高浓度组的效果更明显。
3.2. 四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木提取液对小鼠肝糖原和肌糖原含量的影响
结果见表2,表2结果表明,与对照组相比,高浓度组和低浓度组小鼠的肝糖原和肌糖原含量均增多,且高浓度组增多明显。
3.3. 四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木提取液对小鼠血清MDA含量的影响
结果见表3,表3结果表明,与对照组相比,高浓度组和低浓度组小鼠血清MDA含量均减少,且高浓度组减少明显。
4. 讨论
四叶参是泰山特有的一种中药,是泰山四大名药之一,具有清热解毒、止咳祛痰、补虚通乳、健身补气等功效,可用于肺痈咳嗽、病后虚弱、产后缺乳等症,具有很高的药用价值,对小鼠抗疲劳及抗衰老具有重要作用。楤木对小鼠抗疲劳及抗衰老也具有重要作用,此外,国内外一些专家、学者对黄精、

Table 1. The effects of the lance asiabell root, rhizoma polygonati, astragalus membranaceus, Cong wood extract on swimming ability in mice (n = 10,)
表1. 四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木提取液对小鼠负重游泳能力的影响(n = 10,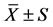 )
)
注:与对照组比较,*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01

Table 2. The effects of the lance asiabell root, rhizoma polygonati, astragalus membranaceus, Cong wood extract on liver glycogen content and muscle glycogen content in mice (n = 10,)
表2. 四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木提取液对小鼠肝糖原和肌糖原含量的影响(n = 10,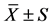 )
)
注:与对照组比较,*P < 0.05,**P < 0.05

Table 3. The effects of the lance asiabell root, rhizoma polygonati, astragalus membranaceus, Cong wood extract on serum MDA content in mice (n = 10,)
表3. 四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木提取液对小鼠血清MDA含量的影响(n = 10,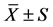 )
)
注:与对照组比较,*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01
黄芪抗疲劳及抗衰老的研究已经取得了一定的成果。在这些基础上,我研究了四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木这四种中药提取液对小鼠抗疲劳能力及抗衰老能力影响,并取得了较理想的研究结果。
疲劳是机体在一定环境条件下,因长时间过于繁重、紧张的劳动(包括脑力和体力)而引起的工作效率暂时性明显降低的一种生理现象 [8] 。疲劳可分为体力疲劳和精神疲劳。体力疲劳即运动性疲劳,指在运动过程中,当机体生理过程不能继续保持在特定水平上进行和/或不能维持预定的运动强度时出现的现象。精神疲劳指脑力劳动在一定条件下产生的疲劳,主要表现为厌倦、心情烦躁、记忆力下降、思维迟钝、反应迟缓 [9] 。疲劳不是一个简单的生理过程,而是一个多方面因素综合起来的生理过程,是人体脑力或体力活动到一定阶段时必然出现的一种正常的生理现象,它既标志着机体原有工作能力的暂时下降,又可能是机体发展到伤病状态的一个先兆 [10] 。中医学对疲劳的解释,认为主要是由于强力的劳动导致人体经络脏腑、气血、阴阳的平衡失调,特别是精、气、神因劳而发生,乃至衰弱的多因素综合结果 [11] 。疲劳最直接和最客观的表现是运动耐力的下降,而力竭游泳时间一直以来被作为反映运动耐力的重要指标 [8] 。有研究显示黄芪多糖有明显的抗疲劳作用,能显著延长耗竭小鼠的游泳时间和增加肾上腺素分泌量,对小鼠多种缺氧模型均具有显著的耐受能力,可明显减少全身性耗氧以及增加组织耐缺氧能力 [12] 。通过对小鼠负重游泳实验的研究,发现高浓度组和低浓度组的小鼠游泳时间都比对照组的时间长,说明了四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木的提取液对促进小鼠缓解疲劳具有一定的作用。
在正常情况下,机体内糖的分解与合成代谢是在一动态平衡下进行的,糖是机体最重要的能源,主要分为肌糖原和肝糖原。其中肌糖原是骨胳肌中可以随时动用的贮备能源,肝糖原主要作用是维持血糖的相对稳定 [13] 。肌糖原既是高强度无氧运动时机体的重要能源,又是大强度有氧运动时的主要能源。运动时,机体能量平衡被打破,肌细胞对能量的需求量猛增,体内的糖原和脂肪是能量的主要来源。随着运动时间的延长,血糖利用占肌肉总能耗的比例上升。为补偿血糖的消耗,肝糖原分解和糖异生作用增强,肝脏释放葡萄糖加速。正常情况下,运动使肌糖原消耗,血糖降低,蛋白质及氨基酸的分解代谢加强。有研究发现人体的碳水化合物储备量有限,大强度体力活动1~2 h可发生疲劳,同时伴有低血糖、肌糖原和肝糖原耗竭 [14] 。肌糖原是骨骼肌中的重要能源物质,是运动时能量的主要来源,肌糖原储备充足,供应的能量就较多,耐力就越好 [15] 。糖原是运动时能量的重要来源,它的含量直接影响运动能力。因此,提高糖原的储备可维持运动时血糖水平,在一定程度上能提高运动能力,延缓疲劳的发生。通过对小鼠肌糖原和肝糖原含量的检测,结果显示高浓度组和低浓度组的小鼠肝糖原和肌糖原含量均比对照组的高,说明四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木的提取液可以提高小鼠肌糖原和肝糖原的含量,使运动时可动员和利用的糖原的量增加,从而维持运动时所需的能量,延缓疲劳的发生,起到了较好的抗疲劳作用。
自由基,是机体氧化反应中产生的有害化合物,具有强氧化性,可损害机体的组织和细胞,进而引起慢性疾病及衰老效应。机体通过酶系统与非酶系统产生自由基,后者能攻击生物膜中的多不饱和脂肪酸,引发脂质过氧化作用,并因此形成脂质过氧化物。氧自由基不但通过生物膜中多不饱和脂肪酸的过氧化引起细胞损伤,而且还能通过脂氢过氧化物的分解产物引起细胞损伤。自由基学说认为,生物体的衰老过程是机体的组织细胞不断产生的自由基积累的结果。因此,清除过多的自由基能够延缓衰老。MDA是脂质过氧化物,是自由基作用于脂质发生过氧化反应产生的一类具有细胞毒性的物质,能使蛋白质、核酸、脂类发生交联,导致生物膜变性、细胞突变或衰老甚至死亡 [16] 。其含量可反映机体内脂质过氧化程度,又间接反映了机体细胞受自由基攻击的严重程度。因此,通过检测MDA的含量,能够反映出机体的衰老程度。刘小阳 [17] 对黄精有效成分的氧化活性进行检测,得出乙酸乙酯相和正丁醇相提取物对DPPH产生的自由基有清除作用,活性呈剂量依赖性增强,石油醚提取物和乙酸乙酯提取物对黄嘌呤/黄嘌呤氧化酶体系所产生的自由基均没有清除效果。卞云云,李萍 [18] 研究显示黄芪中黄酮类成分具有较好的清除自由基能力和抗氧化活性。本研究通过对小鼠血清MDA含量的检测,结果显示高浓度组和低浓度组的小鼠血清MDA含量均比对照组低,体内更多的自由基被清除,说明四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木的提取液能够降低MDA的含量,对小鼠的抗衰老有一定的作用。
5. 结论
本实验研究结果表明,高浓度组和低浓度组的小鼠负重游泳的时间比对照组长,肝糖原和肌糖原的含量比对照组的高,血清MDA的含量比对照组低。这些结果均表明四叶参、黄精、黄芪、楤木的提取液对小鼠的抗疲劳和抗衰老具有一定的作用。提示该中药组方有较高的开发应用价值。