1. 引言
光热疗法是临床医学上一种重要的治疗手段,因此激光辐照下生物组织中的光热传输问题一直是生物医学光子学中的重点问题。由于活体侵入式温度测量受到机体承受能力的限制,而且温度传感器的传导将影响测量结果的准确性,也限制了测试点的个数,而准确的组织光热效应数值模拟可以为激光临床运用提供更全面的信息,可以预测热效应的范围和程度,所以数值计算是光热效应研究的有力工具。利用计算机技术进行生物组织体内温度场的实时模拟和重构一直是当前生物医学工程领域研究的热点。数值模拟时,准确选取生物组织的光学和热学参数是一个重要问题,将直接影响模拟结果。有研究表明[1] -[4] ,生物组织的光学和热学参数会随着温度、含水量等动态变化,因此采用静态参数将导致模拟与测量结果之间存在误差。但已有的光热响应研究中要么没有考虑光热参数随温度的变化情况或只考虑了热学参数随温度的变化或虽给出动态光热参数下的温度分布,但未能同时报道动态光热参数下光分布的变化 [3] - [11] 。本文基于有限元分析方法,使用COMSOL Multiphysics 4.4软件,将生物组织光传输的物理场与热传输的物理场相耦合,模拟了分别使用不同温度的静态光热参数情况下,以及使用随温度变化的动态光热参数情况下,牛肌肉组织在加热过程中某一时刻空间的某一截面的光分布和温度分布、光入射点上光通量密度和温度随加热时间的变化,并对结果进行分析讨论。
2. 理论基础
2.1. 生物组织光传输
描述生物组织光传输的漫射方程为 [2] [12] [13]
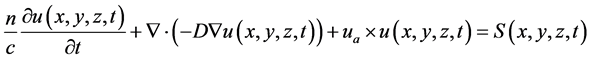 (1)
(1)
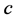 为光在真空中的传播速度,
为光在真空中的传播速度,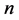 为组织的折射率,
为组织的折射率, 为辐射光通量密度,
为辐射光通量密度, 为吸收系数,
为吸收系数,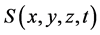 为漫射方程的源函数,
为漫射方程的源函数,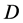 为漫射系数,其表达式为
为漫射系数,其表达式为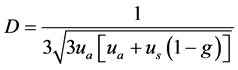 。
。
对于牛肌肉组织各项异性因子g取0.9 [2] ,折射率n取1.4 [2] ,并根据文献 [1] [4] 报道,在温度范围为30℃到80℃内,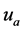 和
和 与温度的关系有如下形式:
与温度的关系有如下形式:
 (2)
(2)
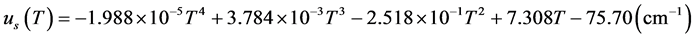 (3)
(3)
以上两式中 为温度,单位为℃,吸收系数、散射系数的单位均为cm−1。
为温度,单位为℃,吸收系数、散射系数的单位均为cm−1。
2.2. 生物组织热传导
描述生物组织热传导的方程为 [2] [3]
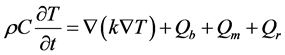 (4)
(4)
其中, 为组织温度,
为组织温度,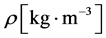 为组织密度,
为组织密度,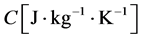 为组织比热,
为组织比热,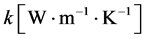 为组织热导率,
为组织热导率,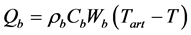 为血液灌注引起的热量变化,
为血液灌注引起的热量变化,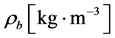 为血液密度,
为血液密度, 为血液比热,
为血液比热, 为血液灌注率,
为血液灌注率,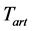 为血液温度,
为血液温度,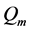 为代谢产热,对于离体组织有
为代谢产热,对于离体组织有 、
、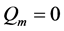 ,
, 为外加热源,在激光加热过程中
为外加热源,在激光加热过程中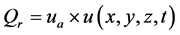 。
。
根据文献 [3] ,热学参数与温度的关系为:
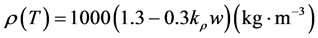 (5)
(5)
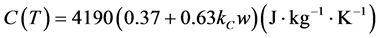 (6)
(6)
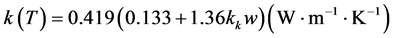 (7)
(7)
 分别为组织的密度、比热、热导率随温度变化的比例系数,其中
分别为组织的密度、比热、热导率随温度变化的比例系数,其中
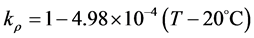 (8)
(8)
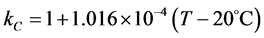 (9)
(9)
 (10)
(10)
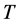 为温度,单位为
为温度,单位为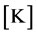 ,
,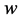 为组织的含水率,对于牛肌肉组织
为组织的含水率,对于牛肌肉组织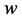 取0.75 [2] 。
取0.75 [2] 。
2.3. 参数设置
本文使用的模拟工具为COMSOL Multiphysics 4.4软件,模拟对象为牛肌肉组织,设置其为半径5 cm
高10 cm的圆柱体,激光从上底面正中央照射。模拟中从外部照射的激光表达式为 ,
,
其中激光功率 ,界面处的光束半径
,界面处的光束半径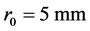 。对其进行光分布模拟,模拟中设置组织与环境是折射率匹配的,将模拟后的光通量密度乘以吸收系数得到光能量,把光能量作为热源对组织体进行加热,并设置组织的初始温度为35℃,所有边界都与外界绝热。
。对其进行光分布模拟,模拟中设置组织与环境是折射率匹配的,将模拟后的光通量密度乘以吸收系数得到光能量,把光能量作为热源对组织体进行加热,并设置组织的初始温度为35℃,所有边界都与外界绝热。
静态模型中当T为35℃、45℃、55℃、65℃时由式(2)、(3)、(5)、(6)、(7)分别得到四组光热参数:
35℃:吸收系数为0.1054 cm−1,散射系数为4.0316 cm−1,组织体热导率为0.4946 W/(m∙K),密度为1076.7 Kg/m3,比热为3533.4 J/(kg∙K)。
45℃:吸收系数为0.0883 cm−1,散射系数为6.5616 cm−1,组织体热导率为0.5022 W/(m∙K),密度为1077.8 Kg/m3,比热为3535.5 J/(kg∙K)。
55℃:吸收系数为0.0697 cm−1,散射系数为12.1936 cm−1,组织体热导率为0.5098 W/(m∙K),密度为1078.9 kg/m3,比热为3537.5 J/(kg∙K)。
65℃:吸收系数为0.0489 cm−1,散射系数为19.7756 cm−1,组织体热导率为0.5174 W/(m∙K),密度为1080.0 kg/m3,比热为3539.5 J/(kg∙K)。
用这四组光热参数分别进行模拟,这一过程中光分布单向地影响温度分布,在加热过程中光热参数的值在空间上各个点都是相同的,并且不随时间而变化。
动态模型中光热参数的值由表达式(2)、(3)、(5)、(6)、(7)表示,光分布影响温度分布,温度分布又对光分布有一个反馈作用,在加热过程中光热参数的值随空间和时间而变化。
3. 结果分析
3.1. 静态光热参数下的光热响应
使用35℃、45℃、55℃、65℃时的光热参数进行模拟,加热200 s后,中心纵向切面的同一区域上光分布如图1所示,温度分布如图2所示。
由图1可以看出,依次对应于35℃、45℃、55℃、65℃的静态光热参数情况下,光分布的范围在逐渐变大,入射点处最大光通量密度的值也在逐渐变大。这是由于与35℃、45℃、55℃、65℃相对应的吸收系数在依次减小,散射系数在依次增大。这就导致光在组织中被吸收的几率减小,被散射的几率增大,因此光分布范围就有所增大。
由图2可以看出,在加热200 s后,对应35℃、45℃、55℃、65℃时的静态光热参数下,被加热的范围在逐渐减小,入射点处温度的最大值也在逐渐降低。200 s时被加热范围随35℃、45℃、55℃、65℃时的静态光热参数依次变小的趋势与光分布范围随其依次变大的趋势正好相反。因为温度是受热源与热学参数影响的,热源数值上等于光通量密度的值乘以吸收系数,与35℃、45℃、55℃、65℃时的静态光热参数对应的光分布范围和光通量密度的最大值在依次变大,吸收系数在依次减小,热学参数组织密度、比热、热导率的值在依次变大,它们共同导致了图2所示的被加热范围随不同温度下光热参数的变化趋势。
由图1、图2可以直观看出使用各个温度下的静态光热参数时,加热200 s后空间某一截面上光分布与温度分布的情况,并得出结论:在温度范围为30℃到80℃内,使用两个不同温度下的静态光热参数模拟牛肌肉组织的光热响应时,使用较高温度的静态光热参数时光分布范围和光通量密度的最大值大于使用较低温度的静态光热参数时光分布范围和光通量密度的最大值,而加热200 s后温度的改变量,则小于使用较低温度的光热参数时加热200 s后温度的改变量。从而可以推测真实组织在加热过程中光分布范围和光通量密度的值会逐渐增大,而温度变化的速度随加热时间的变长则会减慢。
3.2. 动态光热参数下的光热响应
使用表达式(2)、(3)、(5)、(6)、(7)表示的动态光热参数时,在加热200 s的过程中,加热50 s、100 s、150 s、200 s时中心截面同一区域的光分布如图3所示,温度分布如图4所示。
由图3可以看出使用动态光热参数时,在加热过程中,入射点处最大光通量密度随着加热时间在逐渐增大,光分布范围也在逐渐变大。这是组织在加热过程中温度升高,导致吸收系数变小,散射系数变

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 1. The distribution of light in statically photothermal parameters: (a) The distribution of light in statically photothermal parameters of 35˚C; (b) The distribution of light in statically photothermal parameters of 45˚C; (c) The distribution of light in statically photothermal parameters of 55˚C; (d) The distribution of light in statically photothermal parameters of 65˚C
图1. 静态光热参数下的光分布:(a) 35℃时的光热参数下光分布;(b) 45℃时的光热参数下光分布;(c) 55℃时的光热参数下光分布;(d) 65℃时的光热参数下光分布

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 2. The distribution of temperature in statically photothermal parameters: (a) The distribution of temperature in statically photothermal parameters of 35˚C; (b) The distribution of temperature in statically photothermal parameters of 45˚C; (c) The distribution of temperature in statically photothermal parameters of 55˚C; (d) The distribution of temperature in statically photothermal parameters of 65˚C
图2. 静态光热参数下的温度分布:(a) 35℃时的光热参数下温度分布;(b) 45℃时的光热参数下温度分布;(c) 55℃时的光热参数下温度分布;(d) 65℃时的光热参数下温度分布

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 3. The distribution of light in dynamically photothermal parameters at different times: (a) The distribution of light in dynamically photothermal parameters at 50 s; (b) The distribution of light in dynamically photothermal parameters at 100 s; (c) The distribution of light in dynamically photothermal parameters at 150 s; (d) The distribution of light in dynamically photothermal parameters at 200 s
图3. 动态光热参数下不同时刻光分布 (a) 动态光热参数下50 s时的光分布;(b) 动态光热参数下100 s时的光分布;(c) 动态光热参数下150 s时的光分布;(d) 动态光热参数下200 s时的光分布

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 4. The distribution of temperature in dynamically photothermal parameters at different times; (a) The distribution of temperature in dynamically photothermal parameters at 50 s; (b) The distribution of temperature in dynamically photothermal parameters at 100 s; (c) The distribution of temperature in dynamically photothermal parameters at 150 s; (d) The distribution of temperature in dynamically photothermal parameters at 200 s
图4. 动态光热参数下不同时刻温度分布 (a) 动态光热参数下50 s时的温度分布;(b) 动态光热参数下100 s时的温度分布;(c) 动态光热参数下150 s时的温度分布;(d) 动态光热参数下200 s时的温度分布
大所造成的结果。通过图3可以知道组织在加热过程中空间光分布的变化趋势。这与前述的组织在加热过程中光分布范围和光通量密度的最大值会逐渐增大的结论相一致。
由图4可以看出,在加热过程中各个位置的温度随着时间在逐渐增大。我们可以根据前面的结论分析这一现象,与高温相比低温的时候光分布范围比较小光通量密度的最大值也比较小,吸收系数较大,热学参数较小,它们共同导致组织升温。组织升温后光分布范围变大光通量密度最大值变大,吸收系数变小,热学参数变大,接着组织又继续升温只是升温的速度比上一步慢一些,然后又导致光热参数的变化规律跟上一步一样,如此循环得到的温度随时间的变化就如图4所示。
图3、图4直观的反映了使用动态光热参数时,组织的光分布与温度分布随时间的变化情况,得出结论:在加热过程中,组织的光分布范围、光通量密度的最大值、被加热范围和温度的最大值都在随着加热时间的增加而变大。然而使用动态光热参数模拟时,光热参数随时间和空间而变,所以空间各个位置光通量密度和温度随时间的变化规律必定不一致。
3.3. 入射点光热响应随时间的变化
在35℃、45℃、55℃、65℃的静态光热参数下和动态光热参数下光入射点z = 0 m的光通量密度和温度随时间的变化分别如图5和图6所示。

Figure 5. Light flux density of incident point changes with time
图5. 光入射点的光通量密度随时间的变化
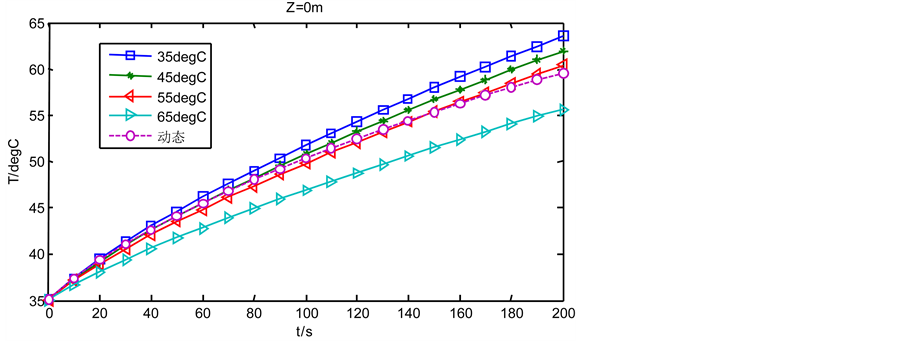
Figure 6. Temperature of incident point changes with time
图6. 入射点的温度随时间的变化
由图5可以看出35℃、45℃、55℃、65℃时的静态光热参数下入射点z = 0 m的光通量密度在整个加热过程中保持不变。动态光热参数下光通量密度的初始值与35℃时的静态光热参数下光通量密度值相同,加热到200 s时光通量密度值介于45℃与55℃时的静态光热参数下光通量密度值之间,整个过程中光通量密度的值随加热时间的增加而增大。引起这一现象的原因是动态光热参数的情况下光热参数随空间和时间变化。
由图6可以看出,在整个加热过程中,使用静态光热参数时,使用低温时的光热参数较使用高温时的光热参数时,温度升高的速度快一些。使用动态光热参数时,温度变化趋势刚开始与35℃时的静态光热参数下温度的变化趋势基本上相同,但随着加热时间的变长温度随时间的变化速度开始小于35℃时的静态光热参数下温度变化速度,之后又小于45℃、55℃时的静态光热参数下温度变化速度,加热到200 s时,动态光热参数下的温度介于55℃、65℃时的静态光热参数下的温度值之间。
4. 结论
本文基于有限元分析方法,将生物组织光传输的物理场与热传输的物理场相耦合,使用COMSOL Multiphysics 4.4软件分别模拟了牛肌肉组织在使用静态光热参数和动态光热参数时的光分布和温度分布,得出以下结论:在温度范围为30℃到80℃内,使用不同温度下的静态光热参数时,低温的静态光热参数下较高温的静态光热参数下光分布范围、光通量密度的最大值会要小一些,但是加热相同的时间温度升高的值却会要大一些。使用动态参数时,在加热过程中光分布范围和光流通量密度的最大值都在逐渐变大,入射点温度的最大值也一直在随时间变大,但温度随时间的变化率在慢慢变小。激光入射点在加热0 s时,动态光热参数下光通量密度值与35℃时的静态光热参数下光通量密度值一样,温度为初始温度35℃,加热200 s后动态光热参数下光通量密度值介于45℃和55℃时的静态光热参数下光通量密度值之间,温度介于55℃和65℃时的静态光热参数下的温度值之间。因此,使用常温下的静态光热参数对牛肌肉组织进行模拟时将会高估激光入射点的温度。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(Nos: 61178089, 81571726, 81201124)、福建省自然科学基金项目(Nos: 2014J01226, 2015J01006)、福建省教育厅项目(Nos: JA15125, JA14093)资助。