1. 引言
快速发展的城市化进程,城市规划方案的不稳定及长官意志和政绩观的突出导致片面追求城市的建设速度,与此同时也带来了一系列影响人类生活与城市可持续发展的突出性城市问题,例如人口拥挤、交通拥堵、环境污染、住房困难、半城镇化、城市居民幸福感缺失、城市贫困等问题在我国城市中广泛存在 [1] ;其次,多数城市发展产业结构雷同,使我们的城市缺乏经济特色,不重视城市历史文脉的挖掘与保护,使我们的城市文化内涵缺失 [2] [3] 。
诸多的城市问题影响着城市的可持续发展,而这些问题凸显的原因主要来自于两方面,一是各级行政官员的干预,二是各高校培养的规划设计师以及相关从业人员本身的知识结构、培养技能方面存在问题 [4] 。
目前,众多学者对前者的讨论研究较多,而对后者的研究相对比较欠缺,因此,本文对我国高校城市规划专业的课程设置、培养目标、发展趋势进行研究,以期为新型城市规划人才培养提供一定的指导,适应时代的需要 [5] 。
2. 研究材料及方法
2.1. 高校选取
首先通过搜索罗列出所有设置城市规划专业的综合性高校,根据各高校的资料可得性及地区代表性,我们分别选取了部分“985”、“211”高校进行分析对比(表1)。
2.2. 数据收集
主要通过搜索各高校院系网站、高校招生简章、发送电子邮件等途径,收集关于城市规划专业的设置课程及相应的课时。
2.3. 资料分析
整合并分析通过上述方式所取得的相关数据资料,主要通过Excel列表及制图的方式,重点分析所选取高校的培养目标、课程设置、总课时及分类课时、专业设立背景的特点及相关问题,进行比较和归纳。
3. 结果分析
3.1. 培养目标
本文选取了具有代表性的开办有城市规划专业的“985”及“211”高校,它们或者是以建筑学为核心或者以地理学为核心的培养模式,对其培养目标、培养方案、地理学和生态学课程的开设情况进行了对比和分析(表2、表3)。
通过对以上12所比较有代表性的“985”高校的城市规划专业的培养目标及主干学科等方面进行对比分析,不难发现其中大多数院校如:清华大学、同济大学、四川大学等院校的城市规划专业是以建筑学科为主要培养模式,注重城市形体规划,培养具有城市规划学科高级技术人才。而少数的院校如:北京大学、中山大学等是以经济地理为主要培养方向,注重区域与城市规划,培养具有地理学理论素养的科研、管理等专业人才。
由此可见,大部分985高校的城市规划专业是以建筑学为核心的培养模式,以城市物质形体规划为导向,培养学生的手工绘图能力,快速构图能力、空间思维以及空间形体设计能力 [6] 。而对于地理学和生态学学科的忽视较明显,有的仅仅只开设一门课程,有的甚至没有开设这两类学科及相关的课程。
在该培养模式的导向下,直接导致了学生在实际的规划中扮演的只是绘图员的角色或是在实际规划工作中,不能很好的分析规划对象,理解大空间尺度的区域分异,导致“只见树木,不见森林”的弊端 [7] 。因此,我们应该增加地理学和生态学课时,并通过必修和选修及实践教学相结合的多种形式,将地理学和生态学思想融入到城市规划专业教学中来,既重视物质空间规划的培养,又重视宏观理论的学习,培养出既是城市系统分析师又是城市设计师的城市规划人才 [8] 。
根据表3可知:
3.1.1.
学校类型差异
工科型大学的培养目标主要是培养高级技术应用型人才,如北京工业大学及河北工业大学的城市规划专业,主要采取的是以建筑学为核心的培养模式,因此注重技能培养,主要输送的是应用型人才。
综合型大学如云南大学、福州大学则是注重培养科研及管理人才。
师范类院校如湖南师范大学、东北师范大学则是注重培养从事教学、研究与管理的专门人才。
农学型院校如东北农业大学、四川农业大学则注重培养乡镇规划、园林规划方面的人才,原因归于农学类院校比较注重新农村建设、土地资源、园林规划等方面的发展。
3.1.2. 地区差异
东部高校的目标主要是培养与城市规划特点相结合的,掌握城市规划、城市设计及建筑设计专业技

Table 1. Representative college selection results
表1. 代表性高校选取结果

Table 2. The training objectives and geographical, ecological curriculum setting of “985 Colleges” list
表2. “985高校”培养目标及地理、生态课程设置一览表

Table 3. The training objectives and geographical, ecological curriculum setting of “211 Colleges” list
表3. “211高校”培养目标及地理、生态课程设置一览表
能,了解城市规划及建筑设计相关知识的高级专门人才 [9] ;如北京工业大学的培养目标是主要突出北京城市建设规划相结合的特点,立足北京,面向全国,向各单位企业提供熟练掌握城市规划与设计的技术型实践性人才。
中部高校主要是培养城乡规划与管理、区域规划、城镇规划方面的人才;如东北师范大学的培养目标是培养能在科研机构、企事业单位和行政管理部门从事城乡规划与管理、区域规划与管理、土地规划与管理、资源与环境管理等科研、教学与管理的专门人才。
西部高校主要是注重培养新农村建设中各级乡镇对国土资源管理与城乡规划方面的人才需求。如西藏大学的培养目标是培养面向西藏城乡建设、新农村建设第一线的高素质应用型人才,满足西藏城乡建设、新农村建设中各级乡镇对国土资源管理与城乡规划方面的人才需求 [10] 。
从各大高校的培养目标来看,一方面,城市规划专业培养的毕业生是具有制图、建筑设计、计算机应用等基本技能,掌握对城乡空间组织进行研究和规划设计,对建设项目进行规划管理的方法和技术,熟悉有关城乡资源与环境、城镇建设及规划管理的政策法规的专门人才 [11] 。
另一方面,该专业要求学生德、智、体全面发展,同时城市规划学也是一门知识系统涵盖面极广的综合性学科,要求学生广泛了解并深入挖掘历史、人文、科技、环境和经济等学科知识。
因此,各高校培养目标的设定与实际是相符的,本专业的学生既是全才,更是专才。所以各高校课程的设置应该与培养目标相一致。通过课程设置等措施培育全面综合型城市规划人才。
3.2. 课程设置
本文主要通过分析各高校的自然地理学、人文地理学、生态学课时来分析目前各高校城市规划专业的课程设置是否合理。
3.2.1.
总课时比较
图1是对一些有代表性的“985”高校城市规划专业的课程设置即建筑学、城市规划学、地理学以及生态学的总学时设置进行对比分析。我们可以看出大多数院校城规专业的课程设置中建筑学和城市规划
学的课程总学时比重大,占绝对优势,而地理学和生态学的课程总学时比重极小,部分院校甚至没有开设地理学及生态学;只有少数院校城规专业的地理学和生态学的课程设置比重大。因此,我们应该增加地理学和生态学课时,将地理学和生态学思想融入到城市规划专业教学中来,合理地平衡技能训练和地理学及生态学思维。
通过图2四类课程总课时设置的对比分析可知:“211”高校的课程设置中,建筑类和规划类两类课程总课时所占的比重较大,而地理类和生态类两类课程的总课时所占比重很小,有的院校甚至都未涉及两类课程的设置。其中,明显可以看到图中的河北工业大学城市规划专业的建筑类总课时明显高于其他院校,主要是因为河北工业大学的城市规划专业是在土木建筑系的基础上发展而来的,比较注重建筑学技能的培养,因此,建筑类总课时明显高于其他院校。
因此,我们不难发现,大部分高校在城市规划专业的课程设置中,建筑学和城市规划学的设置学时比重很大,而地理学和生态学的设置学时比重小,有的甚至为零,城市规划理论学习中存在地理学和生态学的缺失。
3.2.2.
类型比较
以下各图分别是对以地理学、建筑学为核心的相关院校的城市规划专业所设置课时进行的比较分析,并结合各城市规划专业的发展基础来分析对四类课程的课时设置的影响。表4列举了相关“985”和“211”院校的城市规划专业的发展基础。
图3对比了以经济地理为培养模式的有代表性的985高校的城市规划专业的人文地理学、自然地理学和生态学开设课时。其中,北京大学仅以必修的形式开设了人文地理学,武汉大学以必修的形式开设了自然地理学和生态学,而以选修的形式开设了人文地理学,其中生态学课时比重大;中山大学以必修的形式开设了人文地理学、自然地理学,两者开课课时相同;北京师范大学以选修的形式开设了自然地
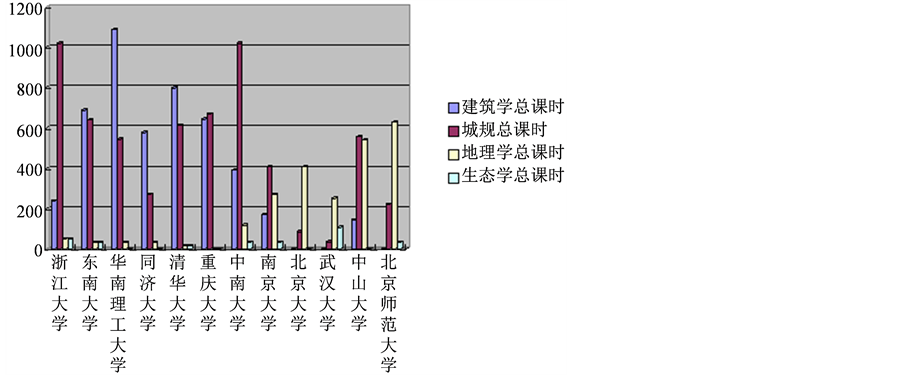
Figure 1. Four categories courses’ total hours of “985 Colleges” comparison chart
图1. “985高校”四类课程总课时比较图

Figure 2. Four categories courses’ total hours of “211 Colleges” comparison chart
图2. “211高校”四类课程总课时比较图

Figure 3. In the geography core of “985 Colleges” course hours comparison
图3. 以地理学为核心的“985高校”课时比较

Table 4. The basic of department including urban development planning profession list
表4. 城市规划专业所在学院的发展基础一览表
理学和生态学,没有开设人文地理学。因此,可以看出这四所高校,开设地理学和生态学的侧重点不同,课时设置比重也有所差异。但总的来说,都没有形成一个完整的、全面的地理学和生态学课程系统。
图4描述了以地理学为核心的有代表性的“211”高校城市规划专业的人文地理学、自然地理学和生态环境学的开设课时。其中,中国矿业大学有以必修课的形式开设自然地理学,人文地理学、生态环境学,并且课时安排合理。缘由便是该校本专业所在的资源与环境科学学院的发展前身是煤田地质系,学院的主要组成包括应用地球物理研究所。东北师范大学有以必修课的形式开设地理学相关课程,但是未涉及生态学课程的开设。这其中重要的原因是该校本专业所在的地理科学学院的发展基础为1949年建立的地理系。湖南师范大学以必修课的形式对三门课程均有开设,并且课时安排较合理。主要是因为该校本专业所在的资源与环境科学学院是在原地理系基础上整合发展相关学科、拓展新专业于2001年12月建立的。

Figure 4. In the geography core of “211 Colleges” course hours comparison
图4. 以地理学为核心的“211高校”课时比较
云南大学资源环境与地球科学学院由原地球科学系、云南省地理研究所以及云南大学澄江动物群研究中心共同组成,因此地理类课程均有开设;宁夏大学以必修课的形式开设三门课程,并且课时安排较合理。原因归于该校本专业所在的资源环境学院的前身是宁夏大学地理系,所以在地理课程的设置上比较注重。五所高校的规划专业所在的学院均是在地理系的基础上发展而来的,因此比较注重地理方面的课程设置。其中东北师范大学并没有涉及生态环境学课程的开设。结果表明,五所高校的课程设置比较偏重于地理学课程的开设,但是忽视了生态学课程的合理设置,因此,没有形成一个完整的、系统的课程体系。
可以看出的是所选取的具有代表性的“985”与“211”高校中该专业并没有形成一个完整的地理学和生态学课程设置系统。
图5对比了以建筑学为培养模式的“985”高校的城市规划专业的人文地理学、自然地理学和生态学的开设课时,不难发现,大部分院校开设了生态学,但仅仅是设置一门课程而已,几乎没有相关先修课程,而且相比建筑学课程来说,该课程课时设置较少,而人文地理学和自然地理学的课程开设很少,甚至很多高校都没有开设这类课程。因此,可以看出大部分工科院校的城市规划专业都忽视了自然地理学和人文地理学的重要性,关于生态学课程的开设,也没有形成一个体系,而是单一的开设一门课程。
图6描述了以建筑学为核心的有代表性的“211”高校城市规划专业的人文地理学、自然地理学和生态环境的开设课时。其中,河北工业大学与北京工业大学是以选修课的形式开设了自然地理学和人文地理学,并且课时安排较少。主要是因为两所学校的本专业所在的学院是在建筑系的基础上发展而来的,所以比较注重建筑课程的设置,而忽视了对规划起着重要作用的地理学方面课程的设置。而贵州大学则未以任何形式开设三门课程,原因主要归于该校本专业所在的建筑与城市规划学院的前身是贵州工业大学建筑系,所以难以避免的出现了同样的忽略地理学科学习的问题。
结果表明,所选取的三所高校是以建筑学为核心的代表性高校,存在着忽视地理学及生态学课程的开设,未以任何必修的形式开设此课程,因此,形成了一个不合理的以建筑学为核心的单一的课程设置体系。
通过对“985”及“211”高校的课程设置及学院发展基础的分析发现二者都出现了同样的问题:其一,在以地理学为核心的高校中,很重视地理课程的设置,但是没有注意到地理学的先修课程的设置以及地理学和生态学体系的形成,如东北农业大学仅以必修的形式开设人文地理学,与之密切联系的自然
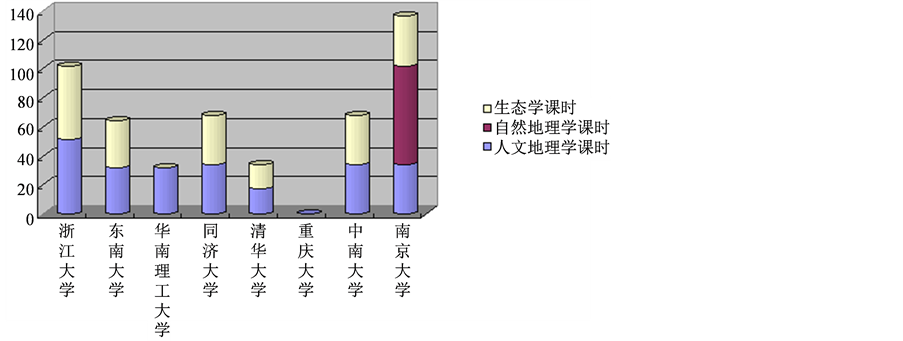
Figure 5. In the architecture core of “985 Colleges” course hours comparison
图5. 以建筑学为核心的“985高校”课时比较

Figure 6. In the architecture core of “211 Colleges” course hours comparison
图6. 以建筑学为核心的“211高校”课时比较
地理则未以任何形式开设,生态环境学的课程设置相对而言没有与地理学形成一个完整的系统;北京大学仅开设了人文地理学,而没有开设自然地理学和生态学的课程;其二,以建筑学为核心的高校中,十分重视建筑学科课程的设置,地理学科变得可有可无,出现了忽略地理学和生态学课程设置的问题。如华南理工大学和重庆大学,在课程设置中并未开设地理学和生态学的课程。
4. 结论与建议
4.1. 结论
1) 通过对各高校的城市规划专业课程设置中的课时分析可知,建筑学和城市规划学的课程总学时比重大,占绝对优势,而地理学和生态学的课程总学时比重极小,有的甚至未开设地理学及生态学课程。
2) 通过对各院校的发展前身进行分析,大部分院校的城市规划专业是在建筑学与土木工程的基础上发展起来的,受建筑学和土木工程的影响较深,直接导致各高校城市规划学习中存在着地理学和生态学的理论缺失问题,并没有形成一个完整的地理学和生态学体系。
3) 目前各高校城市规划专业大多数是以建筑学为核心发展起来的,培养出来的学生对城市空间形态的规划能力强,而缺乏对城市地理和生态等宏观城市问题的分析。这其中重要的原因便是师资队伍的中坚力量主要是原建筑学专业的教师,缺乏地理学和生态学专业教师。
4.2. 建议
1) 针对不同高校的优劣势,各高校应该在课程设置上取长补短,注重学科优化组合,改变单一的偏重于建筑学的课程设置模式,即在总课时不变的情况下,适度减少建筑学专业课的数量和课时,适当增加生态学和地理学的开设课时。
2) 在保证城市规划基本教育和统一规格要求的基础上,作为必修课独立开设地理学和生态学课程,同时要增加地理学和生态学的先修课程、选修课程以及系列课程加以辅助,如地理学中不仅是人文地理学还要有自然地理学、地图学、第四纪地质学基础等,生态学中包括植物生态学、环境生态学等。注重各类课程的合理配置,使之形成一个完整的地理学和生态学课程体系。
3) 城市规划之前最重要的是对规划地区的人文环境、自然条件、生态环境等进行调查研究 [12] ,这对教师的知识背景及实践经验具有很高的要求,因此,高校可以从外系或外学院聘请具有扎实专业知识背景和实践经验的专业教师,使得教师的专业基础和知识背景多元化。
基金项目
长沙地区农田主要土壤营养物质收支平衡的定量分析(K1303028-21)。
*通讯作者。