1. 引言
位于云南省大理白族自治州的洱海,被大理州350万人民亲切地称之为“母亲湖”,它是云南省第二大高原淡水湖,是著名的“高原明珠”。然而随着社会经济的发展,人类活动的影响,洱海水质不断下降,水体富营养化加剧,多次暴发大面积的蓝藻水华现象引发了社会的强烈关注 [1] 。叶绿素a是水体初级生产力的重要指标,可以反映浮游植物生物量状况及其变化趋势,其浓度被广泛应用于评价水体富营养化和预警水华 [2] 。因此,对叶绿素a浓度的动态变化监测对于了解湖泊富营养化程度及其变化趋势以及制定有效的治理决策具有重要意义。
传统的对湖泊监测和调查的方法是通过实地考察获取样本提取有关数据,需要耗费巨大的人力、物力和时间,对于地形较为复杂地区或面积广阔的湖泊而言,不能全面其叶绿素分布情况。而遥感技术具有观测宏观、数据更新周期短、速度快、连续、包含的信息量大、可视化程度高、便于动态监测等特点,并且能够很好地反映环境变化的连续性、空间性和规律性可以在很大程度上解决由于人类对湖泊的考察和定点观测范围的有限性所带来的问题。
国内外许多学者对在运用遥感技术监测对湖泊叶绿素进行监测已经进行了大量的研究工作。谢杰等在基于TM/ETM+数据上利用已有模型对巢湖提取叶绿素a相对浓度信息的基础上获取了叶绿素a相对浓度分布图,有效地反映了1995~2007年年巢湖叶绿素a各浓度等级在7~9月份的空间分布变化情况 [3] ;张玉超等确定了一个基于MODIS数据的叶绿素a指数,并以此为基础构建出一个具有普适性的、反映太湖叶绿素a时空分布动态变化的反演模型 [4] 。这些研究表明通过遥感技术进行叶绿素a浓度动态监测具有一定的可行性。
郑国强等根据1971年至2000年的洱海水质实地监测数据,研究洱海水质的演变过程及趋势 [5] 。杨威等使用2010年5月至2011年4月洱海实地采样调查数据,对洱海叶绿索a的季节动态、空间分布及其与环境因子的关系进行研究 [6] 。目前对洱海的水质监测大多还是使用的传统采样的方法,效率低且不能全面其叶绿素分布情况。本文选取了多时相的洱海湖区Landsat TM/ETM+数据,在通过已有的效果较好的模型进行叶绿素a浓度反演的基础上,探寻洱海湖区叶绿素a浓度动态变化趋势,并通过实测数据进行对比,验证通过Landsat TM/ETM+数据进行洱海湖区叶绿素a浓度动态监测的有效性。
2. 研究区域与数据
研究选取位于云南大理的洱海作为研究区,是云南省第二大淡水湖。地理坐标位于N25˚36'~25˚58',E100˚06'~100˚18'之间。总径流面积2565 km2,湖泊面积约251 km2,蓄水量30亿m3,平均水深约11.5 m,最深为20 m [4] 。选取2009年5~6和8~11月共六景Landsat TM/ETM+遥感数据,均来源于地理空间数据云(Geospatial Data Cloud)。
3. 研究方法
3.1. 遥感影像预处理
3.1.1. 辐射定标与大气校正
辐射定标的目的是将传感器记录的电压或数字量化值(DN)转化成绝对辐射亮度值(辐射率)的过程,或者转换与地表(表现)反射率、表面温度等物理量有关的相对值得处理过程 [5] 。本文使用ENVI5.1中提供的radiometric calibration工具进行辐射定标。地物反射辐射在到达传感器前在大气中会经历吸收、散射、投射、反射、折射等物理过程,使能量衰减,导致光谱发生变化。大气的衰减作用受多种因素控制,例如波长、传感器参数、地区差异、时间差异等。为了消除大气的影响,需要对遥感影像进行大气校正,即获得地表辐射率、地表温度、反射率等真实物理参数 [7] 。本次采用FLAASH模型进行大气校正,它是一种绝对大气校正方法,适用于精细定量遥感 [8] 。
3.1.2. 条带修复
2003年5月31日(21:42:35 GMT),Landsat-7ETM+机载扫描行校正器(Scan Lines Corrector,简称SLC)突然发生故障,导致获取的图像出现数据重叠和大约25%的数据丢失,因此2003.5.31日之后Landsat 7的所有数据都是异常的,需要进行条带修复。一般去条带有两种方法:1) 差值修复:利用同一景影像完好的数据部分对数据缝隙进行差值;2) 回归修复:利用故障前的正常数据对数据缝隙进行填充。本次研究使用了landsat_gapfill去条带补丁中单个文件缝隙填充(三角剖分)的功能,运用三角插值对条带进行填充,得到了较好的效果。
3.2. 叶绿素a信息提取
叶绿素a是湖泊水质遥感监测中研究最多的水质参数,广泛的应用于湖泊中叶绿素a的遥感监测研究。半经验方法、经验方法、分析方法是实际应用中使用最多的方法。经验和半经验方法是目前研究中使用较多的方法,反演效果也比较好,经验方法比较简单、易用,可以通过选择适当的波段组合或建立相对复杂的回归方程来提高二类水体的水质参数的反演精度。因此选取由经验方法所得出的模型进行叶绿素a浓度的反演具有较高的可靠性和精确性 [9] - [11] 。
经过大量对比,在李苗等对克钦湖的叶绿素a浓度反演中,通过对叶绿素光谱特征研究的基础上,选取了TM2、TM3、TM4单波段和多种波段组合与叶绿素a浓度进行相关性分析,最终获得了精度较高的模型Y = 41.57 × (TM3 + TM4) − 0.697。其中TM3对应的波长范围为620~690 mm,是叶绿素的主要吸收波段,可以反应不同植物叶绿素吸收;TM4对应的波长范围为760~960 mm,是绿色植物类别差异的敏感区,为植物通用波段 [12] 。利用ENVI5.1中band math工具根据该模型得到洱海叶绿素a分布结果,总体上效果较好,满足监测研究的需要。
4. 结果分析
4.1. 叶绿素a浓度信息提取结果分析
全湖共设置12个采样点,从北至南共四个断面,每个断面分为西、中、东3个采样点(图1) [13] 。通过模型反演最终得出各点5~11月的叶绿素a浓度值,并以将其逐月求取算术平均值代表全湖叶绿素a浓度水平(图2)。将其与实际采样结果对比分析可知,该模型在此区域内反演效果较佳,基本与实测数据吻合度高,E = −0.5152,D = 1.003。
4.2. 洱海叶绿素a浓度的时间变化趋势及分析
由反演出的叶绿素a浓度信息图(图3)可以看出,2009年5~11月洱海全湖叶绿素a浓度平均值变化范围为0 μg/L~45 μg/L,从遥感图像上可以看出,5月份全湖水质较好,湖区南北边缘地区叶绿素a浓度相对略高;6~9月份叶绿素a浓度不断上升,全湖受污染面积不断扩大,气温高,蒸发量大的气候条件有利于蓝藻的大量繁殖,因此随着水温的上升,浮游植物的生长加快,叶绿素a浓度值也逐渐升高。10月份时全湖叶绿素a浓度普遍偏高,蓝藻水华现象较为严重,洱海近60%的水量来自北部,且是洱海的主要污染源 [14] ,而北部区域农田面积约占流域面积的58%,高污染的作物种植比例较高,同时洱海秋季(10月)雨水较多,雨水冲刷农田使得大理氮、磷流入湖中,南部靠近城市,人口密集,大量的污水排放流入南部湖区,导致南、北湖区污染加重。同时湖水在南部地区形成了浓度高值区,这与洱海湖区秋季盛行大风现象有一定关系,水中的营养物质和浮游藻类的扩散迁移受风浪的影响较大,在风的作用下,藻类往往可以上下混合或者随风漂移而在某一区域形成堆积 [6] 。11月份开始,叶绿素a浓度有所下降,水质得到了改善。总体来说,总体上形成了从五月份开始逐渐增加,在10月份达到峰值,11月份开始下降的变化趋势(图4)。
在春季,北部与中部叶绿素a含量较低,南部稍高(图3(a));在夏季,整个湖区叶绿素a含量较明显升高,北部和中部超过南部(图3(c));在秋季,全湖叶绿素a含量均达到最大值,中部略低(图3(d)、图3(e));在冬季,叶绿素a含量明显降低(图3(f))。通过图3与图5对比后可以看出,遥感反演结果与实测结果基本一致。

Figure 1. Distribution of sampling sites in Erhai
图1. 洱海采样点分布
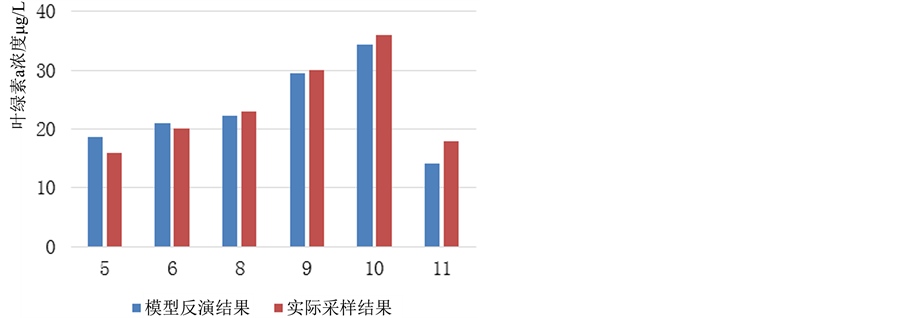
Figure 2. Inversion data comparison with the measured data
图2. 模型反演数据与实测数据对比
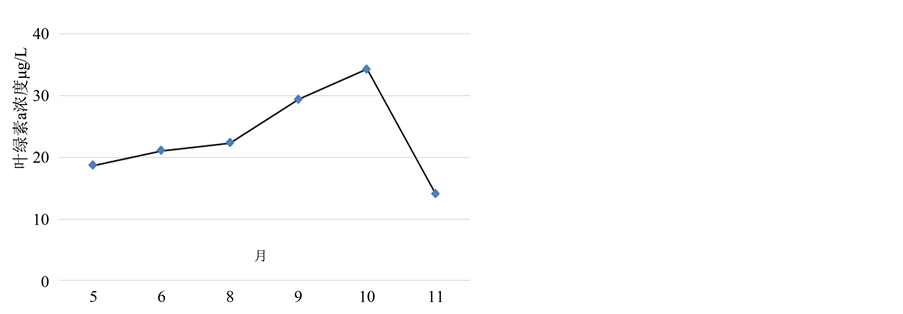
Figure 4. Seasonal variation of Chl. a concentration in Erhai from April to November in 2009
图4. 2009年5~11月洱海叶绿素a浓度变化

Figure 5. Spatial distribution of Chl. a concentration in Erhai in different seasons [6]
图5. 不同季节洱海叶绿素a浓度的空间分布 [6]
5. 结论
1) 通过多时相遥感图像得出不同时期洱海叶绿素a浓度分布图可以看出,洱海叶绿素a浓度呈现出明显的季节变化,即从春季开始上升,夏季增大,秋季达到峰值,冬季下降的变化规律。
2) 洱海湖区叶绿素a浓度的时空变化受到多方面因素的影响,气温、水温、降水、风等因素的共同作用造成了其随时间的动态变化。
3) 基于Landsat数据对洱海湖区进行叶绿素a浓度的监测基本可以反映出该地区叶绿素a浓度值随时间变化的趋势,可以进行有效的动态监测。并且Landsat数据具有周期短、信息丰富、现势性强、成本低等优势,为快速进行科学有效的决策提供了依据。
4) 基于卫星遥感技术对湖泊进行监测能够获取大范围、连续的叶绿素a浓度分布信息,相比起传统采样方法具有很强的优势,值得进一步探索与发展 [15] 。