1. 引言
地表温度是研究城市热环境的重要参数之一,在生态、气象和地理学等领域的研究具有重要的意义 [1] 。近年来,随着自贡市城市高速发展,土地利用和土地覆盖类型发生了较大变化。城市周围大量的林地、农用地等自然表面被建筑、道路等不透水地表所代替,由于这些地表类型的太阳辐射吸收、热容量及传导率较高,导致城市地表温度不断升高,造成了城市热环境的空间格局发生了较大变化。城市热岛现象日益突出使得热岛效应的研究受到越来越多的关注 [2] 。不同下垫面类型具有不同的热容量,建筑、水体和植被等下垫面的变化对地表温度有着不同程度的影响。
城市热岛景观格局利用景观生态学方法和原理辩证城市热岛的分布、形状与组成等规律,可以在一定程度上反映城市化进程。基于土地利用/变化的景观格局指数研究室景观格局分析的重要方法,研究城市热岛景观格局指数可以为城市规划、缓解城市热岛效应等提供科学依据 [3] ,目前的城市热岛研究主要是针对城市热岛变化规律、城市热岛产生机理等方面,针对多尺度的城市热岛格局研究还是比较少的。本文研究的流程见图1。
近年来,随着城市高速发展和人口持续增长,自贡市城市发展与生态之间的矛盾日益加剧。本文利用5景Landsat遥感影像,基于空间尺度条件变化下景观格局指数研究,分析城市热岛景观格局的演变特征及趋势。

Figure 1. The process of landscape pattern index calculation
图1. 景观格局指数计算基本过程
2. 研究方法
2.1. 研究区概况
自贡市是川南区域中心城市,地处四川盆地南部,享“千年盐都”,“恐龙之乡”,“南国灯城”,“美食之府”之美誉。地理位置为北纬28˚55'N~29˚38'N,东经104˚02'E~105˚16'E,属亚热带波澜季风气候区,日照时间较短,四季分明,年平均气温17.0℃~18.0℃,极端最高气温40℃,常年日照1150~1200小时。自贡市全年雨量充沛,常年降水量平均为1000~1100毫米 [4] 。本文研究的区位图见图2。
2.2. 数据来源及预处理
本文选取2001年、2004年、2007年、2010年和2013年5幅Landsat影像对自贡城市热环境年际变化进行研究。根据研究需要对原始数据进行辐射定标、大气校正、几何精校正及裁剪等预处理。由于2004年和2010年数据来源于ETM,存在明显的条带,无法直接使用,因此对这两幅影像首先进行了条带修复工作使其满足研究的需要。
2.3. 陆地表面温度反演及归一化处理
由于选择的数据中2001年和2007年为Landsat-5数据,2004年和2010年为Landsat-7数据,以上数据都是单通道热红外数据,因此,可以根据辐射传输方程法对地表温度(LST)进行反演;而2013年的数据为Landsat-8数据,存在两个热红外波段,因此使用分裂窗算法对其地表温度进行反演。
一、辐射传输方程法计算地表温度:
首先将第6波段的像元灰度值DN值转换为传感器的辐射亮度值,公式如式(1)。
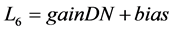 (1)
(1)
式(1)中:L6为第6波段辐射亮度值[w/(m2·sr·µm)];DN为遥感影像的像元灰度值[w/(m2·sr·µm))];gain和bias分别为辐射亮度值的增益量[w/(m2·sr·µm)]和偏移量[w/(m2·sr·µm)],gain和bias可以通过影像的头文件获得。
然后利用辐射亮度值对亮温进行计算,如公式(2)。
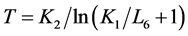 (2)
(2)
式(2)中:T为第6波段的亮温值;对于Landsat数据,Kl = 607.76 [w/(m2·sr·µm)],K2 = 1260.56 K。
物体比辐射率是指物体向外界辐射电磁波能力强弱,地表温度的反演需要比辐射率参数的计算,如公式(3)。
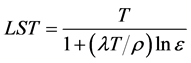 (3)
(3)
式(3)中,LST为地表温度(K);λ为第6波段的中心波长(11.5 µm);ρ = hc/σ = 1.438 × 10−2 m∙K,σ为玻尔兹曼常数(1.38 × 10−23 J/K),h为普朗克常数(6.262 × 10−34 J∙s),c为光速(2.998 × 108 m/s);ε为地表比辐射率(地表比辐射率ε直接与地表构成有关。本文中地表比辐射率根据ENVI中自带地表比辐射数据计算得到,植被覆盖区域为0.98,裸地区域为0.96,建筑为0.95,水体为0.99) [5] ,T为传感器处温度值。
二、针对双通道的热红外数据可以用分裂窗算法计算:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
式中,T10、T11分别为第10、11波段的亮度温度,εi、τi为第i波段地表反射率和大气透过率, 、
、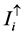 分别为大气向下、向上辐射。
分别为大气向下、向上辐射。
地表温度时间归一化处理:由于用到的五幅影像中所对用的月份不尽相同,因此不能直接运用所计算出的地表温度进行热岛等级划分,必须先对其进行时间归一化处理。这里选取2010年反演出的地表温度作为基准数据,将其余四幅影像反演出的地表温度分别进行时间归一化得到地表温度数据。
2.4. 地表温度降尺度操作
Landsat地表温度数据是由热红外波段数据计算出来的,而Landsat热红外波段分辨率较其他波段空间分辨率低。由于自贡本身城市较小,每个热红外像元多对应的空间范围较大,热红外波段影像效果不如别的高分辨率影像所呈现得清晰。因此结合归一化植被指数对原始的地表温度影像进行降尺度操作,得到在可见光空间分辨率下的地表温度影像,使影像包含空间分辨率较高的特点 [6] 。见图3、图4。
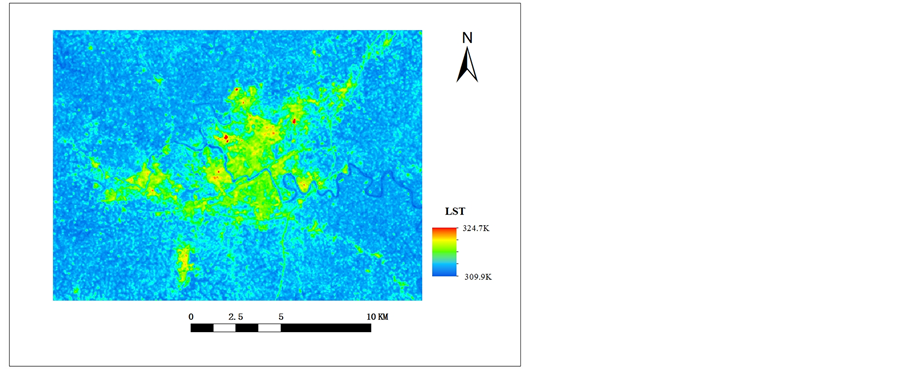
Figure 3. The figure image of surface temperature before the downscaling
图3. 降尺度前图像地表温度示例图
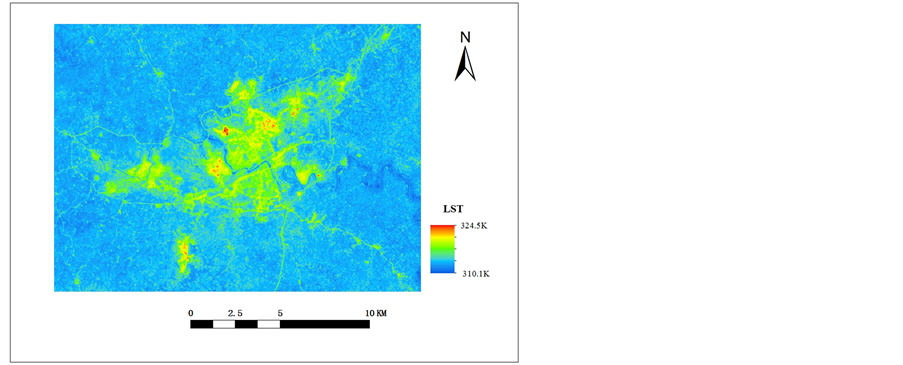
Figure 4. The figure image of surface temperature after the downscaling
图4. 降尺度后图像地表温度示例图
通过上面两张图对比可以看出,左侧降尺度前图像轮廓较为模糊,像元包含信息太多、太杂,不容易进行区分;右侧降尺度后图像轮廓较为清晰,降尺度后图像结合了空间分辨率高的特点。
2.5. 城市热岛等级划分
根据1.3、1.4操作后,在图像上随机分布250个像元点,求得这250个像元平均温度值作为基准值。利用归一化后的地表温度图像与平均值做差得到地表温度差值图像。利用ArcGIS软件中重分类工具中的几何间隔法对地表温度差值图像进行划分 [7] ,得到热岛强度等级,具体划分等级见表1。
2.6. 土地利用类型分类
本研究事先将地表划分为建筑、植被、水体和裸地四大类型。土地利用数据来源为各幅影像的432假彩色合成影像,由于不同地物在遥感影像上呈现出不同的色调。因此,可以通过目视解译的方法对其进行判别,在图像上随机分布250个像元点,然后利用Google Earth高分辨率图像逐点进行目视解译判

Table 1. The table of heat island intensity grade partition
表1. 热岛强度等级划分表
断其类别 [8] 。结果显示,分类总精度在86%~89%之间,Kappa系数在75%~82%之间,精度较高,符合研究需要。
2.7. 城市热岛景观指数
为研究城市热景观格局变化,定量分析其变化趋势。本文在研究中采用景观生态学中的景观格局指数来分析城市热岛景观的空间格局变化,本文主要从景观水平上选取相关的指数进行分析,采用Fragstats3.3分别计算斑块数(NP)、斑块密度(PD)、景观多样性指数(SHDI)、景观均匀性指数(SHEI)、景观聚集度指数(CONTAG)5种景观指数 [9] 。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 地表温度时空变化分析
由于图像数据获取时间不一致,因此对这五幅图像进行了时间归一化,使得地表温度(LST)具有一定的可比性。下表显示了这5幅影像的最高温度、最低温度和平均温度信息。详细参数见表2。
从表2可以看出2001~2013年自贡城市地表温度情况,自贡市地表最高温度、最低温度和平均温度都随着时间推移呈现出整体升高的趋势。说明随着城市不断发展,原来的自然地表逐步被人工地表所代替,由于人工地表的地表反射率较高,造成地表温度的升高。
3.2. 降尺度前后城市地表温度变化
自贡城市范围较小,Landsat热红外波段的空间分辨率较低导致像元所获取的地表信息比较多样化。本文结合归一化植被指数对地表温度进行空间降尺度操作,得到降尺度后的地表温度更加接近于真实地表温度,说明降尺度后地表温度值更加精确。详细参数见表3。
3.3. 城市热景观格局变化
2001~2013年自贡城市地表覆盖发生了较大变化,为了定量分析城市热环境格局的变化情况,本文采用了景观指数来表征城市热环境景观的变化。因为城市热岛效应是普遍存在的,但是对城市环境构成影响的是高等级的热岛景观斑块 [10] - [12] 。因此本文从景观水平上选取如下指标:
1) 表征破碎度特征:斑块数(NP)、斑块密度(PD)。NP是指景观中斑块总个数;PD为斑块数和斑块总面积的比值,值越大说明面积内的斑块数量越多,斑块被分割得越严重。
2) 表征多样性特征:多样性(SHDI)、均匀度(SHEI)。SHDI越接近于0说明整个景观由一个斑块组成,SHDI越大说明斑块类型增加;SHEI越接近于0说明景观由一种斑块组成,无多样性,SHEI接近1说明各板块类型均匀分布,存在最大的多样性。

Table 2. The table of surface temperature inversion
表2. 地表温度反演表

Table 3. The table of contrast downscaling land surface temperature before and after
表3. 降尺度前后地表温度对比表
3) 表征聚集度特征:景观聚集度指数(CONTAG)。CONTAG是指景观中不同类型斑块的聚集程度,值越大说明景观是由少数聚集的大斑块组成,值越小则是说明景观由众多分散的小斑块组成。
从图5中可以看出,2001年到2013年,各等级的热岛景观斑块数(NP)和斑块密度(PD)除在2007年处出现下降拐点外,其余年份均呈现上升趋势,说明强热岛和较强热岛等级的斑块在迅速增长,2007年由于图像获取的时间刚好处于城市郊区农作物收割阶段导致大片的裸地出现,斑块效应不明显;且从图中可以看出降尺度前各等级的斑块数(NP)、斑块密度(PD)普遍高于降尺度后,说明降尺度后各等级的热岛范围有所减小。2001年到2013年,各等级的景观多样性指数(SHDI)、景观均匀度指数(SHEI)曲线和斑块数级斑块密度曲线趋势相同,都在2007年处出现下降拐点,其余年份也呈现上升趋势,说明随着年份的增加,景观斑块类型也在增长,而且斑块分布越来越不均匀;从图中也可以看出,降尺度前的景观多样性指数和景观均匀度指数高于降尺度后,说明降尺度后景观多样性降低,均匀度有所提升。2001年到2013年景观聚集度指数(CONTAG)与上面图形的趋势刚好相反,说明在2007年优势斑块形成了很好的连续性,之后斑块的连续性遭到一定程度的破坏;从图中也可以看出,降尺度后景观聚集度指数普遍高于降尺度前,说明降尺度后各热岛等级斑块之间的连接更加密切。
4. 结束语
1) 不同等级的热岛景观类型分布不均衡。在研究的时段中低等级的热岛景观类型占据主要的比例,较强热岛和强热岛景观类型所占的比例较小,均匀度指数呈现上升趋势说明热岛景观类型面积之间的差距在逐渐缩小,整体上逐渐趋于均匀化;
2) 各等级的景观之间聚集程度下降,说明整个景观趋于破碎化。高等级热岛景观斑块数量呈现增长趋势,斑块之间的连通性下降,聚集度指数出现了上升后下降的趋势,热岛景观斑块总数和斑块密度均呈现增长趋势,说明景观趋于破碎化;
3) 由于本文中对图像像元进行了降尺度操作,因此降尺度前后各景观指数也有所差异。其中景观斑
块个数、景观密度在降尺度前普遍高于降尺度后,说明降尺度前景观破碎化程度更高;景观多样性指数和均匀度指数也是在降尺度前普遍高于降尺度后,说明各斑块类型在景观中呈现更加均匀化分布并有更大的多样性;景观聚集度指数却普遍呈现降尺度后高于降尺度前的现象,说明降尺度前景观的破碎化程度更高一些。
基金项目
本文为2014年四川省院士(专家)工作站基金项目(编号:2014YSGZZ02),2014年四川自贡市科技局项目(2014DZ02)阶段成果,感谢这两个项目对本文的大力支持。