1. 引言
传统的物理康复训练高度依赖于理疗师,理疗师必须手把手、面对面地指导患者进行康复训练,训练的效果直接取决于理疗师的技能水平和经验,而患者所需要付出的相应费用也非常高昂。同时,随着我国逐步迈入老龄化社会,脑卒中、脑外伤、脊椎损伤等疾病在人群中的发病率也会逐渐升高,未来传统康复训练对于理疗师的需求将更加迫切。由于传统康复方法存在诸多弊端,越来越多的研究机构开始研发康复机器人来辅助患者进行康复运动,并且已经取得了长足的进展。康复机器人的出现彻底释放了患者的就医压力,它的出现对于康复医学来说重大意义,其发展前景也十分可观。
康复过程实际上是一个动态的、不断变化的过程,康复训练的目的是使神经损伤的患者最大程度重获独立行走的能力,康复机器人通过提供助力并不断的纠正患者在运动过程中的异常行为姿态以达到预期的效果。因此,在康复过程中对患者运动姿态的跟踪就显得尤为重要。实时地、持续地对患者的运动姿态进行跟踪和记录,并对其科学地分析和评估,不但可以良好反馈患者当前的身体状况,实现康复效果的自动化诊断,还可以为患者康复计划的指定提供有效参考,同时也能为康复机器人的改进提供指导性意见。本文正是在此背景下,研究面向康复系统的人体步态检测与分析技术。
人体步态检测技术可以归类为三维运动捕捉技术,从捕获方式上讲可以分为非视觉和基于视觉的两类。与非视觉式的动作捕捉系统不同,基于视觉的动作捕捉系统采用光学元件来感知人体的动作,通常有带标记点式和无标记点式两种方式。VICON就是一套已被广泛应用的标记点式的动作捕捉系统,文献 [1] [2] 中分别使用它进行了人体步态识别与分析相关方面的研究工作。这种系统具有较高的精度,但它往往只能在专门的环境中使用,人体需要穿戴特设的装备,过程繁琐,费用高昂。而无标记点式系统则无需额外的标记点辅助即可实现人体动作跟踪,它成功地克服了标记点式系统所带来的一些问题。传统的无标记点式系统采用多台同步摄像机利用多目视觉技术进行动作跟踪与捕捉,如文献 [3] 中利用多视角录像机解决了两个彼此交互重叠的人体对象的骨骼跟踪重建问题,文献 [4] 中分别在虚拟环境和实验室环境下采用16/8台摄像机来跟踪人体的运动信息。可想而知,同时采用多台摄像机的动作捕捉系统的成本仍然很高,其对特殊环境的依赖性依然很强。在这种情况下,成本更低的基于深度摄像头的动作跟踪技术提供了一个新发展的方向。文献 [5] 中通过使用一个TOF(Time-of-Filght)摄像机便实现了实时人体姿态跟踪,它能在较高的帧率下提供场景中每个点的深度测量信息。Microsoft Kinect是微软于2009年发布的一款具有里程碑意义的体感传感器,它不仅能够提供RGB彩色图像数据和深度数据,同时还能实现人体骨骼追踪功能,使得人体运动跟踪变得更加容易和便捷。2014年微软发布了Kinect第二代产品,其在功能和精度上又有了进一步的提高。目前,在人体运动跟踪领域,越来越多的研究者开始选择采用成本低廉、使用轻便的Kinect设备,本文即采用Kinect二代来对患者在康复过程中的运动姿态进行跟踪和采集。
在人体的所有运动姿态中,步态是最常见的一种,它发生的频率最高,容易获取。对于步态的分析在康复医疗领域来说是一个重点内容并已得到了广泛的应用,通过对康复患者步行运动规律的研究,可以揭示患者的康复机能状态。步态分析已成为一种定量评价步行能力和科学研究的必要手段,可以帮助评估康复治疗的效果并指导康复方案的制定 [6] 。步态分析可以看作一种模式识别问题,将步态作为一个整体可以对其进行分类和识别。步态识别的研究最早可以追溯于上世纪七十年代,当时研究者采用MLDs (Moving Light Displays)进行目标跟踪,成功实现了人体运动识别 [7] 。之后的研究者们采用了多种方法进行步态的识别和分类研究,包括直接分类法 [8] [9] ,状态空间模型法 [10] [11] 和时间序列相似性法等,都取得了相当大的进展。在康复医学方面,步态识别和分类常被用于行为检测中的老年人健康问题的自动化监测方面,Bogdan等在中通过惯性传感器进行姿态捕捉,采用多种带有一定语义信息的步态特征并利用不同的机器学习方法对步态进行分类进而实现老年人健康问题的检测 [12] 。在文献 [13] [14] 中Bogdan等引入了动态时间规整法DTW,改进了步态特征的语义描述方式,并通过对比证明采用带有语义信息的步态特征在DTW方法中具有更好的步态分类效果。
本文即是受到Bogdan等的启发,采用类似的以关节运动参量为语义信息的步态特征以及动态时间规整DTW算法对步态进行分类识别,并且使用多种优化方法对传统DTW算法进行优化以解决奇异点以及计算效率问题。然而采用DTW算法将步态特征作为整体进行分类,只能在宏观上对步态进行分类,无法更加细化地从局部进行分析,对于康复过程的指导性并不是很强,这是康复训练中的步态分析同行为检测中的健康问题检测的应用场景及目的不同所致。针对于此,本文提出一种将步态特征按语义信息分割的步态分析方法,通过将步态特征按语义信息进行拆分,将拆分后的子特征分别进行匹配分析,这样就可以从局部入手,定位异常运动关节点,得到异常步态的异常来源,并且将局部的匹配结果进行加和,同样能够实现全局步态的分类。
2. 步态检测技术
2.1. Kinect体感传感器
Kinect是微软于2009年推出的一套3D体感传感器,可以同时采集视野中的RGB彩色图像和深度景深图像,并且具备人体骨骼跟踪功能,具有反应速度快,价格便宜等优点。Kinect v2是于2014年推出的第二代Kinect设备,它在图像分辨率,骨骼跟踪功能与精度、视野角度等方面相对前代都有了极大提高(图1)。
2.2. 步态数据的采集
本文所采用的是Kinect二代产品,它可以同时跟踪的人数达到6个人,而对于每一个人来说能跟踪人体25个关节的位置信息及旋转信息,各关节的分布如图2所示。
其中,位置信息即25个关节点在3D空间中相对于Kinect的坐标位置,以(x,y,z)进行表示。旋转信息即各个关节在3D空间中的绝对旋转方向,采用四元数进行表示。
在Kinect for Windows SDK 2.0开发工具包中提供了骨骼跟踪的API,在Visual Studio 2013中利用C++或C#语言可进行相关应用的开发工作。在SDK2.0中,读取骨骼跟踪数据需要用到IBodyFrameSource,IBodyFrameReader,IBodyFrame这三个类,获取数据流的步骤如图3所示。
2.3. 运动数据的预处理
由于环境变化等一些不确定性因素的影响,从Kinect所获取的原始骨骼数据难免会受到噪声的干扰,
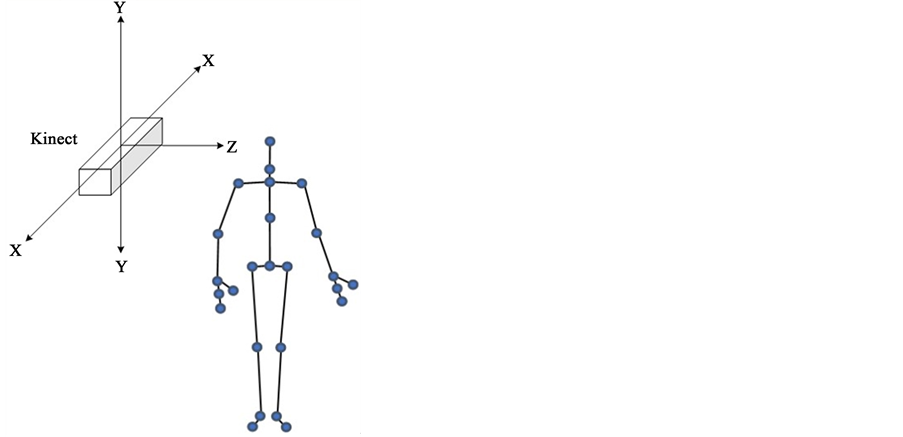
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of joint point distribution
图2. 关节点分布示意图

Figure 3. Steps of getting the data source
图3. 获取数据源步骤
比如在实际使用中发现相邻两帧的数据在同一关节位置上会出现较大距离的位置抖动,这会严重影响到后续的数据处理工作。因此在进一步工作之前必须对原始数据进行滤波和平滑工作。
Kinect中的骨骼数据以每秒30帧的速率提供,显然可以将其看作是一组带有一定周期的时间序列,对于时间序列的平滑可以通过对其趋势的合理预测来完成。时间序列预测有多种方法,如移动平均线法、时间线性回归法,指数平滑法等。其中,指数平滑法可以有效地利用全部的历史数据,操作简单,成本低,性能优良,适应性较强,能够适用于几乎所有的以时间序列为基础的各个领域中。因此本文采取Holt-Winter双指数平滑法 [15] ,其计算公式如下:
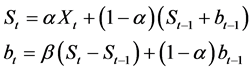 (1)
(1)
其中,α是数据平滑因子,0 <α< 1;β是趋势平滑因子,0 <β< 1;{Xt}是观察到的原始数据序列;{bt}是t时刻序列趋势的最佳估计。
如引言所述,三维人体运动捕捉可以采用多种方法,除了本课题中采用的Kinect深度传感器外,还可采用惯性传感器、电磁式传感器等等。基于不同方法的系统所得到的数据的量纲和数量级必然会有所不同,因此,为了方便今后将本文所采取方法的实验结果与其他系统进行比较,必须对得到的骨骼数据进行数据标准化处理。
数据的标准化处理主要包括数据同趋化处理和无量纲化处理两个方面,数据同趋化处理主要解决数据性质不同的问题,而数据无量纲化处理主要解决不同量纲数据之间的不可比较性问题 [16] 。目前对数据进行标准化的方法有很多,常见的方法有规范化法(Min-max normalization)、正规化法(Z-score normalization)、log函数转换法、atan函数转换法等等。正规化标准法又称标准差标准化,它是将变量中的观察值减去该变量的平均值,然后除以该变量的标准差,即
 (2)
(2)
其中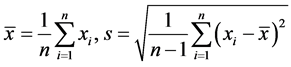 。
。
经过正规化标准法后,变量的所有观察值将会近乎均匀地分布在零点两侧,变量的平均值为0,标准差为1,符合标准的正态分布。正规化标准法是当前使用最多最广泛的数据标准化方法,本文中即采取这种方法对步态数据进行标准化。
3. 步态分析技术
3.1. 步态特征的选取
从步态检测系统得到的姿态原始数据是人体25个关节点在三维空间中的坐标位置(x, y, z)。为了能够恰当地反映患者的运动行为特征,患者的行为需要能够被简单且通用的特征描述子来表述,且带有语义信息的步态特征具有更好的分类成功率 [12] [13] 。选取不同的语义信息会对最后的分析结果产生不同的影响,通常步态分析中常用的基本参数包括步长、步幅、步频、步速、步行周期、步行时相以及重心移动,可以将这些基本参数当作语义特征,也可以将身体各部分关节的运动角度作为特征量。选取关节运动角度作为语义特征的好处是比较直观和便于理解,因为人体的运动可以看作各个关节运动的合成,所以本文中选择使用关节角度当作语义特征 [14] 。而在三维空间中,各关节的运动不仅有角度量,同时还有旋转量,因此各关节的旋转角度特征量并不一定是一维的。实际上,由于欧拉角在三维空间中表示旋转会出现万向节死锁的问题,我们通常采用四元数来表示三维空间中的旋转量。具体地,本文所选取的语义特征及其相应维数如下:
a) Qsl,Qsr:左、右肩相对躯干方向(2 × 4D);
b) Qhl,Qhr:左、右臀相对躯干方向(2 × 4D);
c) Qtu,Qtl:上身胸椎、腰椎方向(2 × 4D);
d) αel,αer,αkl,αkr:左、右肘和膝关节的角度(4 × 1D)。
其中,Qsl和Qsr是人体左右肩关节相对于上身的旋转方向,采用四元数表示旋转量,各4维一共为8维;Qhl和Qhr为左右髋关节相对于下肢的旋转方向,同样各4维一共为8维;Qtu和Qtl分别为胸椎和腰椎的旋转方向,各4维一共为8维;αel,αer,αkl,αkr分别为左、右肘关节和膝关节处的运动角度,角度量为1维量,所以共4维。因此,按以上特征选取方法,从每一帧骨骼数据中得到的步态特征描述子有28维,如图4所示。
3.2. 动态时间规整DTW
时间序列是一种常见的数据表示形式,在一些应用场景中常见的任务就是比较两个时间序列的相似性。在一些情况下,利用最简单的距离计算法,如欧式距离就可以满足要求。然而,通常会出现的一种情况是两个时间序列虽然具有相同的变化趋势,但其在X轴上并不是一一对齐的,在这种情况下就无法利用传统的欧几里得距离衡量序列间的相似性(距离)。如图5示例了一个简单的例子,如果使用在a图中所示的欧式距离直接进行距离匹配计算,显然不能得到正确的匹配结果。为了解决这个问题,能够正确地得到两个时间序列之间的相似性,我们必须要将其中至少一个序列的时间轴即X轴进行适当程度的扭曲(warping)。动态时间规整(Dynamic Time Warping, DTW)就是实现这种时间轴扭曲的有效方法,b图展示了采用DTW的理想匹配。
动态时间规整法DTW是一种衡量两个时间序列之间的相似度的经典方法,其最早于上世纪60年代被日本学者提出 [17] ,并于之后成功应用于语音识别领域中。与语音信号序列十分相似,步态序列序列也是一组与时间相关的序列,动态时间规整算法同样适用于步态识别和分析。
3.2.1. DTW原理
动态时间规整DTW是一个典型的优化问题,它利用满足一定条件的时间规整函数来描述测试序列和参考序列之间的时间对应关系,通过求解两个序列匹配时的最小累计距离来获得最佳匹配 [18] 。
假设有两个长度分别为n和m的时间序列X和Y,
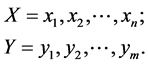 (3)
(3)
其中一个序列为参考模板,另一个序列为测试模板,序列中的每个点的值为当前时刻下的特征值。构造一个n × m的代价矩阵,矩阵中的每一个元素(i, j)表示xi和yj两个点之间的距离d,也就是序列X上每一个点和序列Y上每一个点之间的相似度,距离d越小则代表两个点之间越相似。距离d的计算一般采用欧式距离,即:
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 5. Comparison of different matching methods; (a) Euclidean distance matching; (b) Ideal matching
图5. 不同匹配方式对比;(a) 欧式距离匹配;(b) 理想匹配
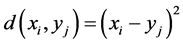 (4)
(4)
矩阵上的每一个点表示点xi和点yj之间对齐。如果在代价矩阵上定义一条路径,用W来表示,路径上的所有点都存在于代价矩阵中,其第k个元素定义为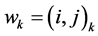 ,也就是说:
,也就是说:
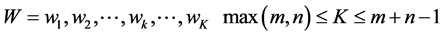 (5)
(5)
这样,该路径就定义了序列X到序列Y的一种映射,如图6所示。我们称这样的路径为规整路径。
在所有可能的路径中,我们所需要的是规整代价最小的路径,即
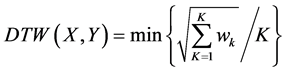 (6)
(6)
根据连续性和单调性约束可知,规整路径上每个点向下匹配的方向只有三个,因此累积距离D(i,j)可以按式(7)计算,
 (7)
(7)
最佳路径上的累加距离就是序列X和序列Y之间的匹配距离(即相似性)。
3.2.2. DTW优化
尽管DTW算法已经成功应用到了很多领域,但它依然存在一些问题,如在某些情况下会出现不自然的规整,通常称这种不理想的情况为奇异点,同时最佳路径的搜索范围不受限导致的计算效率低下。此外,以上所述的DTW算法均针对一维的实现序列,而本文所选取的步态序列有28维。针对于此,本文采取了一下四种方法对DTW算法进行优化和改进。
1) 加窗 [19]
较理想的规整路径大体上都是沿着代价矩阵主对角线的方向分布的,因此,我们可以从全局考虑,通过在代价矩阵上设置一个移动窗口来限制规整路径的分布范围。通常使用的全局约束有两种,分别是Sakoe-Chiba窗和Itakura窗,如图7(a)和图7(b)所示。
2) 坡度加权
为了在一定程度上引导规整路径的走向,也可以对三个不同的方向增加不同的系数进而对规整路径
的坡度进行加权 [20] [21] ,公式如下
 (7)
(7)
其中系数a为正实数,可以通过改变a的值来约束规整路径的走向,a越大路径越偏向代价矩阵的主对角线方向,这样就能在一定程度上避免奇异点的产生。
3) 带有微分的DDTW
在传统的动态时间规整算法DTW中,代价矩阵中的每一个元素(i, j)表示的是xi和yj两个点之间的欧式距离d,而在带有积分的动态时间规整算法DDTW中,代价矩阵中的元素d不再是两点之间的欧式距离,而是两点上的微分估计值的平方差 [22] ,即
 (8)
(8)
这种估计方式就是简单地以点yi及其左侧相邻点yi − 1的连线的斜率以及yi左侧相邻点yi-1和右侧相邻点yi + 1的连线的斜率的平均值作为点yi处微分的估计值。这样在匹配时不仅仅考虑每个点的Y轴坐标值,而是将其“形状”作为更高阶的比较特征量进行考虑,可以有效较少误匹配的发生几率。
4) 多维动态时间规整MDTW
在有些情况下,时间序列并不是简单的一维而是多维的,在多维动态时间规整算法中,代价矩阵上的每一个元素是相应点上每一维的距离差的和 [23] ,即
 (9)
(9)
相应地,累加路径W上的累加距离则为
 (10)
(10)
可以看出多维动态时间规整MDTW其实就是DTW在多维上的一个拓展。但在大多数情况下,多维动态时间规整法的性能更好,使用范围更广。
 (a) Sakoe-Chiba (b) Itakura
(a) Sakoe-Chiba (b) Itakura
Figure 7. The search scope of the constrained planning path
图7. 全局约束限制规划路径的搜索范围
3.3. 基于特征语义信息分割的步态分析方法
根据3.1节中所描述的特征选取方式,将从测试样本中得到的28维全局特征通过DTW算法与训练集中的样本进行相似度计算,然后利用最近邻算法便可以得到测试样本的最佳分类。这种方法只是将步态预先分为特定的几类,最终分类的结果只能是正常或异常,如果是异常则也只能给出异常步态属于哪一类,而且当异常步态不属于任何一个预先选取的特定步态时,就无法得到分类结果。而从步态分析的目的来说,显然是分析结果越具体、越详细越好。我们期望得到的结果不仅仅包含步态的全局特性,而应该同时能够从局部入手,得出的步态分析结果能够定位身体的哪一个部位出现了问题,由此才能够更加有效地为患者的康复过程提供指导。
传统的分类方法是将每一帧的步态数据根据选定的语义信息提取出全局特征然后送入分类器进行分类。为了能够从局部入手,洞悉步态异常的来源,可以将每一时刻的步态特征按语义信息进行拆分,将这些拆分后的子特征分别用DTW算法进行匹配分类,通过对各个子特征的匹配结果进行判别分析,就可以判断身体的各个局部是否出现异常。在对特征进行拆分后,由于只关心身体各部位的异常情况,只需要将采集到的步态与正常步态的样本进行对比即可。具体地,根据本文所采取的特征,其中包含的语义信息为关节的运动角度和旋转方向,因此可以将选定的各关节根据运动角度量和旋转方向量分割出来,成为10个独立的子特征,如图8所示。
对于每一个子特征来说,都可以根据其维数选择单维或者多维的DDTW算法与样本中相对应的子特征进行相似度计算,记计算结果为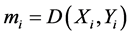 ,其中i的取值为1到10,分别代表了左右肩关节、左右髋关节、腰椎、胸椎、左右肘关节和左右膝关节共10个子特征。根据每个局部子特征的匹配相似度即可判断相应的关节在运动过程中是否出现异常,而通过所得到的关节局部信息就可以将步态进行反向归类,实现一个从局部到全局的过程。同时,对每个子特征的相似度进行相加,同样可以得到一个全局的相似度匹配结果,进而对步态进行全局分类。相加过程由式(11)定义,
,其中i的取值为1到10,分别代表了左右肩关节、左右髋关节、腰椎、胸椎、左右肘关节和左右膝关节共10个子特征。根据每个局部子特征的匹配相似度即可判断相应的关节在运动过程中是否出现异常,而通过所得到的关节局部信息就可以将步态进行反向归类,实现一个从局部到全局的过程。同时,对每个子特征的相似度进行相加,同样可以得到一个全局的相似度匹配结果,进而对步态进行全局分类。相加过程由式(11)定义,
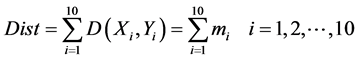 (11)
(11)
4. 实验结果分析
实验中主要考察的步态有四类,分别为正常步态,膝盖受损步态,腰部受损步态和脚部受损步态。
对于每一类步态的标准样本的采集,实验中通过正常人模拟的方式进行。因为样本的采集量需要有一定的规模,量级至少要在百人以上,而在研究初期对于小规模研究团队是不可能有资源联系到如此庞大的患者群体来做样本数据采集。因此本文参考文献 [12] - [14] 中的方法使用正常人模拟特定的步态来获取数据集。
在四种步态中,膝盖受损步态的特点是腿部无法打弯,受损的腿只能通过提胯的方式迈步;腰部受损步态的特点是腰部无法挺直,行走过程中上半身始终前倾;脚部受损步态的特点是受损脚着地时身体晃动,膝关节打弯不完全。对于每一类步态都分别采集20次,然后利用DTW算法相互匹配取得最佳路径所反向对应的序列作为样本集中的标准样本。建立样本集之后,随机复现四种步态中的任意一种,然后考察步态分析系统得出的分析结果与事实是否相符。实验过程中采用的是经过优化的基于Slope Constraints的坡度加权多维微分DTW算法。表1中所示为每种步态的分类成功率,实验中每种步态均复现20次。
从表1中可看出,正常步态和膝盖受损步态的识别率较高,腰部受损步态的识别率略低,而脚部受损步态的识别率最低。这可能是因为不同受损关节与其他关联关节的耦合程度不同所导致的。在膝盖受损步态中,膝关节的病态表现仅仅是不能弯曲,在这种情况下人体不自觉的提胯迈步,而其他关节的运动状况几乎不受影响,接近于正常步态,所以其匹配分类成功率也与正常步态相当;在腰部受损步态中,人体始终弯腰前行,身体前倾导致重心不稳,人体为保持平衡会而出现随机性的异常关节运动行为,进而影响匹配分类的成功率;而在脚部受损的步态中,受损脚着地时身体的晃动会明显干扰人的行走状态,其牵连的关节遍及全身,随机性更大,因此它的匹配分类成功率就更低。
从整体来看,实验中对步态进行全局分类的分类成功率相对较低,这是可能是实验过程中标准样本和测试样本的采集不一致所致。实验中样本的采集是通过健康人模拟的方式进行的,在模拟的过程中需要准确表现每种步态的病理特点,但每次步态的复现都会有所差异,不能完全模拟出步态的特点,这就使得步态样本在分类匹配时出现偏差进而导致分类成功率偏低。随着今后实验研究的逐步深入,如果能减少样本间的特性偏差,步态的分类成功率会有所提高。
以上进行的是步态的全局分类,下面进行步态的局部异常点检测实验。表2所示为每一种步态在复现5次的情况下每个子特征被检测为异常点的次数。
从表2中的数据可以看出,在膝盖受损步态中(以右膝关节受损为例),右膝关节和右髋关节均被检测为异常点,同时左膝关节和左髋关节也有一定概率被认定为异常点,这与事实基本符合,因为人体的运

Table 1. Global gait classification results
表1. 全局步态分类结果

Table 2. Detection result of abnormal points
表2. 异常点检测结果
动是各个关节的级联运动,任何一个关节受损都会影响到与其相关联的其他关节。在腰部受损步态中,腰椎和胸椎均被认定为异常点,而髋关节和膝关节也因为连带效应有一定可能被认定为异常点,但总体来说异常点的范围有限且基本符合腰部受损步态的特点。在脚部受损步态中(以右脚受损为例),异常点的检测出现漂移,多个关节均被检测为异常点,可见脚部作为人体步行的支点和作用点在受损时影响广泛,这也是对其分类成功率较低的原因。
从上述实验可以看出将全局特征经过拆分后确实能够得到局部的信息,但局部信息的获取受步态特点(即患者自身运动情况)的影响较大,而将局部信息进行拼合,仍能得到步态的全局分类结果。
5. 结语
本文采用Kinect二代设备实现康复过程中患者运动步态的跟踪与采集,以关节运动角度为步态特征,并通过DTW算法实现步态分析。同时完成了步态分析的两个层面,即步态的全局分类和步态局部异常点的检测。通过经过优化的基于Slope Constraints的坡度加权多维微分DTW算法实现步态的全局分类;而针对步态的局部异常点检测,本文提出了一种基于特征语义信息分割的步态分析方法,通过对步态全局特征按语义信息进行分割,实现了步态中的局部异常点的检测,解决了步态的局部分析问题。
通过实验可以看出,将全局特征经过拆分后确实能够得到局部的信息,但这种局部信息的正确性受步态类型(即患者自身运动情况)的影响较大,主要体现在试验准确度受到取样不同的限制。为更好解决个别特殊局部状态取样影响全局的情况,将拆分的局部匹配结果进行合并,则能够更好的实现步态的全局分类。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(61573047, 61573048)。