1. 引言
胶原蛋白约占总蛋白含量的30%,是生物体内含量最丰富的蛋白质 [1] 。胶原蛋白广泛存在于皮肤、骨骼、血管系统以及机内结缔组织中,起着支撑器官和保护机体的功能。目前,已经发现的胶原蛋白类型至少有28种,并且每一种胶原蛋白的氨基酸序列、结构和功能都各不相同 [2] 。由于其独特的生物学性质,胶原蛋白已经广泛应用于食品、药品、化妆品、照相、皮革以及生物材料等工业领域中 [3] 。
通常,生产胶原蛋白的原料是猪和牛的皮和骨。对于一些宗教如犹太教和伊斯兰教来说,猪源性的胶原蛋白很难被接受,而牛源性的胶原蛋白易受到疯牛病的污染 [4] 。鱼类废弃物如鱼鳞、鱼皮和鱼骨都是胶原蛋白极好的来源。尽管水产动物胶原蛋白的理化性质不同于哺乳动物来源的胶原蛋白,但是鱼类胶原蛋白不易受到疯牛病、口蹄疫以及宗教等原因的限制。随着水产品加工业的迅速发展,大量的废弃物被丢弃,这些废弃物占原料的50%~70% [5] 。因此,合理使用这些副产物不但能减轻环境污染,增加产品附加值,而且还能创造更多的工作和商业机会 [6] 。
罗非鱼是一种广泛存在于热带的鱼种。它是继鲤鱼之后第二大重要的养殖鱼类。据FAO(联合国粮食与农业组织)的统计数据,到2005年,中国的罗非鱼产量每年增长接近100万吨 [7] 。中国罗非鱼的产量占据了世界罗非鱼产量的50%。罗非鱼通常被加工成鲜鱼片和冻鱼片,而在加工过程中产生的废弃物包含了大约27.8%的胶原蛋白 [8] 。因此,从罗非鱼皮中提取胶原蛋白将具有很好的发展前景。响应面分析法能产生一组数学模型并优化各因素水平 [9] ,本研究通过响应面分析法来考察乳酸溶液pH、液固比和提取时间对罗非鱼皮酸溶性胶原蛋白提取率的影响以得到最优的提取条件,并研究在此条件下提取的罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白的理化特性。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 材料与设备
尼罗罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)鱼皮广东省明基水产品有限公司提供;其它化学试剂均为分析纯。
PHS-3C精密PH计 上海大谱仪器有限公司;CT15RT台式高速冷冻离心机上海天美生化仪器设备工程有限公司;722E紫外可见分光光度计上海光谱仪器有限公司;DYY-11型电泳仪(北京市六一仪器厂);JSM-6490LV扫描电子显微镜(JEOL日本株式会社)。
2.2. 实验方法
2.2.1. 胶原蛋白提取率的测定
脯氨酸和羟脯氨酸为胶原蛋白特有氨基酸 [10] 。通过测定羟脯氨酸的含量,然后乘以羟脯氨酸的换算系数即得到胶原蛋白的含量。取1 ml胶原蛋白粗提液至安瓿瓶中,加入6 mol/L盐酸1 ml,在130℃下水解3 h,每个试样重复测定3次,将水解液定容至100 ml。根据关静 [11] 等人的方法测定1 ml粗提液中羟脯氨酸含量(ω)/g。
胶原蛋白提取率(ε)按下式计算:
 (1)
(1)
式中:11.1为羟脯氨酸的换算系数。
2.2.2. 原料的预处理
剔除鱼皮上残余的鱼肉、脂肪及结缔组织,剪刀剪碎,用水洗净。4℃条件下,用0.1 mol/L NaOH溶液浸泡鱼皮12 h以去除杂蛋白和色素,反复清洗。然后,用8倍体积的环己烷浸泡12 h去除脂肪。
2.2.3. 胶原蛋白的提取
为防止鱼皮胶原蛋白变性,提取过程应严格控制温度在10℃以下。经预处理后的罗非鱼皮,用乳酸进行浸提,离心收集上层清液,将下层沉淀物再次进行提取,合并两次上层清液即为胶原蛋白粗提液。
2.2.4. 胶原蛋白提取工艺优化
以胶原蛋白的提取率为考察指标,通过单因素试验和Box-Behnken中心组合试验确定乳酸提取罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白的最佳工艺条件。
2.2.5. 单因素试验
单因素的基本条件定为提取剂pH 2.1、液固比为60:1 (mL/g)、提取时间为48 h。改变其中一个条件,固定其他条件,以分析各因素对胶原蛋白提取率的影响。各因素水平为pH 1.9、2.1、2.3、2.5、2.7;液固比(mL/g)40、50、60、70、80;提取时间(h)12、24、36、48、60。每个结果重复实验三次,取平均值。
2.2.6. 胶原蛋白最佳提取工艺条件的确定
在单因素实验基础上,根据Box-Behnken中心组合设计原理,以胶原蛋白提取率为响应值,设计三因素三水平的响应面分析实验,因素水平及编码值见表1,数据采用Design-expert V8.0.6.1软件进行分析。模型方程如下所示:

Table 1. Factors and their coded levels in Box-Behnken experimental design
表1. Box-Behnken设计实验因素水平及编码值
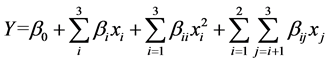 (2)
(2)
式中:Y为因变量(胶原蛋白提取率,%);β0为常数项,βi,βii,βij为回归系数;Xi,Xj为自变量水平。
2.2.7. 胶原蛋白的SDS-PAGE电泳
采用8%分离胶和5%浓缩胶,样品浓度为1 mg/mL,上样量为10 μL。采用直流恒流电源:电压为100 V,电流为50 mA进行电泳。
2.2.8. 胶原蛋白热变性温度(Td)的测定 [4] [12]
参考Zhang等的方法并作适当修改,用0.5 mol/L的醋酸溶液将冻干的胶原蛋白配制成0.5 mg/mL的溶液。用乌氏粘度计测定20℃~45℃范围内的胶原蛋白溶液的粘度,每个温度间隔为5℃,各温度保持20 min,以0.5 mol/L的醋酸溶液为对照,每个样品重复测试3次。
增比粘度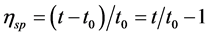
其中,t是胶原蛋白样品溶液流出的时间,t0是同温度下溶剂(醋酸)流出的时间。
以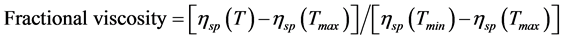 对温度作胶原蛋白热变性曲线,Fractional viscosity = 0.5时所对应的温度即为热变性温度(Td)。
对温度作胶原蛋白热变性曲线,Fractional viscosity = 0.5时所对应的温度即为热变性温度(Td)。
2.2.9. 胶原蛋白的扫描电镜观察
分别取冷冻干燥后的胶原蛋白置入液氮中冷冻定型,将定型后的样品切成薄片再真空喷金,然后用1000倍的放大率观察样品的表面形态。电压:20 kV。
2.2.10. 数据处理与统计分析
数据用均值±标准偏差(x ± s)表示。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 单因素实验结果及分析
3.1.1. 溶液pH值对胶原蛋白提取率的影响
溶液pH值对胶原蛋白提取率的影响见图1。由图1可知,胶原蛋白的提取率在pH 2.1时达到最大,在pH < 2.1时,胶原蛋白提取率随着乳酸溶液pH值的增大而提高。当pH > 2.1时,提取率开始下降,再继续增大溶液的pH值,胶原蛋白的提取率趋于平稳。因此,当乳酸溶液pH为2.1时,胶原蛋白提取效果最好。
3.1.2. 液固比对胶原蛋白提取率的影响
液固比对胶原蛋白提取率的影响见图2。从图中可以看出,在液固比小于60(mL/g)时,胶原蛋白的提取率随着液固比的增大而增大,当液固比高于60(mL/g)时,胶原蛋白提取率略微下降之后又趋于平稳,故选择液固比为60(mL/g)较为合适。
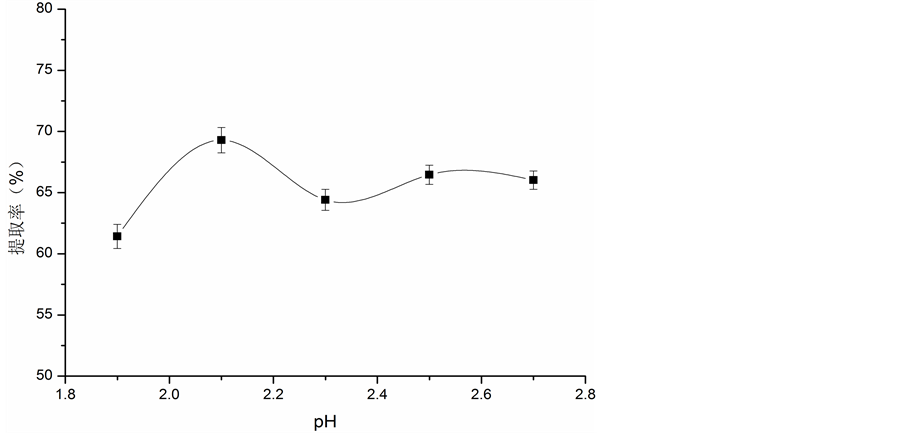
Figure 1. Effect of pH on extraction rate of collagen with lactic acid
图1. 不同pH值对胶原蛋白提取率的影响
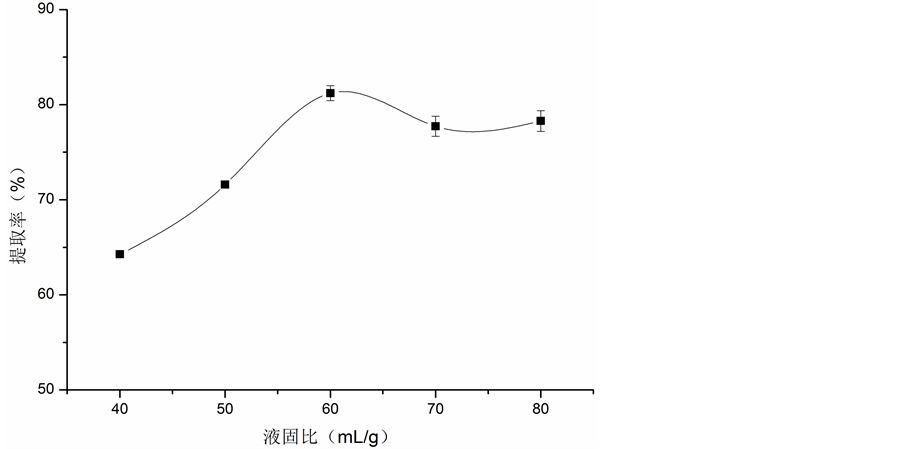
Figure 2. Effect of liquid-to-solid ratio on extraction rate of collagen with lactic acid
图2. 液固比对胶原蛋白提取率的影响
3.1.3. 提取时间对胶原蛋白提取率的影响
提取时间对胶原蛋白提取率的影响见图3。从图中可以看出,随着提取时间的延长,胶原蛋白提取率逐渐增加,36 h后胶原蛋白提取率虽仍有一定程度的提高,但上升幅度明显减缓。另外,在60 h后提取率有轻微的降低,这可能是因为有小部分胶原蛋白降解。因此从经济和实际生产上考虑,确定提取时间为36 h。
3.2. 胶原蛋白最佳提取工艺条件的确定
3.2.1. 回归模型的建立及方差分析
罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白提取工艺响应面优化的具体试验方案及试验结果见表2。
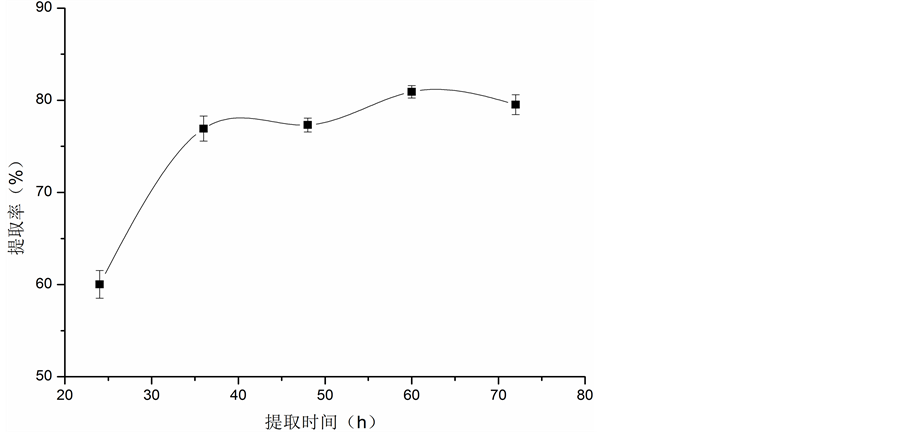
Figure 3. Effect of extraction time on extraction rate of collagen with lactic acid
图3. 不同提取时间对胶原蛋白提取率的影响

Table 2. Response surface experimental design and corresponding results
表2. 罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白提取工艺响应面试验方案及试验结果
将表2中响应值与各因素通过Design-expert V8.0.6.1 数据分析软件进行回归拟合后得到二次多项回归方程: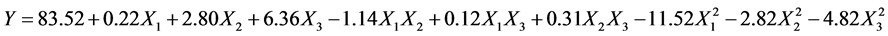 ,其中Y表示胶原蛋白提取率;X1、X2、X3分别为乳酸溶液pH值、液固比和提取时间的编码值。
,其中Y表示胶原蛋白提取率;X1、X2、X3分别为乳酸溶液pH值、液固比和提取时间的编码值。
由表3可知,模型得决定性系数R2 = 0.9765较大,回归方程拟合度很好;模型的变异系数CV = 2.65%,可看出实验稳定性较好;失拟P = 0.0399 < 0.05,证明模型失拟不显著;模型P < 0.0001,表明回归模型极其显著。综上所述,各因素与响应值之间的关系可通过回归方程得到较好地描述,因此可以利用该模型来确定胶原蛋白提取的最佳工艺条件。回归方程系数的显著性分析结果表明,模型的一次项回归系数X2和X3极显著;二次项回归系数X1 (乳酸溶液pH)和X3 (提取时间)极显著,X2的二次项回归系数较显著;其他项的影响不显著。由此可以看出各因素对于罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白提取率的影响并不是简单的线性关系。剔除回归方程中的不显著项,简化后的方程为:
Y=83.52 + 2.80X2 + 6.36X3 − 11.52X12 − 2.82X22 − 4.82X32
3.2.2. 胶原蛋白提取工艺的响应面分析及优化
图4为通过模型方程所做的三维响应面图,曲线越陡峭,表明该因素对胶原蛋白提取率的影响越大 [13] 。从图4可以看出,提取时间的延长,可以一定程度提高胶原蛋白的提取率;但随着液固比的增大或乳酸溶液pH值的升高,胶原蛋白提取率呈现先增大后减小,之后又趋于平稳的趋势。
3.2.3 胶原蛋白最佳提取工艺条件的确定及验证试验
利用Design-expert V8.0.6.1软件分析得到胶原蛋白的最佳提取条件为乳酸溶液pH 2.1、液固比65.4、提取时间44.16 h,此条件下胶原蛋白提取率的理论值为86.42%。为检验响应曲面法所得结果的可靠性,对乳酸提取罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白的优化条件进行验证。考虑到实际生产与操作因素,将上述优化提取条件修正为乳酸溶液pH 2.1、液固比65、提取时间44 h,此条件下胶原蛋白提取率为85.57%,实验值与理论

Table 3. Test for significance and analysis of variance (ANOVA) of regression coefficients
表3. 回归方程各项系数的显著性检验及方差分析
注:R2 = 0.9765,R2:预测模型的决定系数;*显著,P<0.05;**极显著,P<0.01。

Figure 4. Response surface plot and contour plots showing the effects of process conditions on extraction rate of collagen with lactic acid
图4. 两两因素交互作用对胶原蛋白提取率影响的响应面和等高线图
值的相对误差为0.99%,证明该模型得到的胶原蛋白提取工艺参数可行。
3.3. 胶原蛋白理化性质的测定
3.3.1. 胶原蛋白的SDS-PAGE电泳结果
胶原蛋白的SDS-PAGE电泳结果见图5。胶原蛋白呈三股螺旋结构,每个胶原分子以3条α肽链缠绕成三股螺旋,其中每股链自身是一种左手螺旋 [14] 。从图中可以看出,酸法提取的胶原蛋白在相对分子量125 kDa左右出现2条条带,且两条带宽度不同,说明罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白是由两条α1链和一条α2链组成,类似于哺乳动物的I型胶原蛋白 [15] ;在200 kDa附近出现β链,说明胶原蛋白分子中存在分子内和分子间的交联作用 [16] 。
3.3.2. 胶原蛋白的热变性温度(Td)测定
胶原蛋白的热稳定性是由其在溶液中分子的热变性温度(Td)所表达的,同时Td也表示了胶原蛋白三螺旋结构被破坏时的温度。图6为罗非鱼皮ASC的热变性曲线。由图可知,ASC的热变性温度为32.56℃。可以看到,在最初升温阶段,ASC的黏度有明显的降低,随着温度的升高,ASC的黏度迅速降低,蛋白质分子受热迅速解螺旋并发生断裂,之后又趋于平稳。
3.3.3. 胶原蛋白的微观结构
图7为罗非鱼皮ASC在放大1000倍下的扫描电镜图。从图中可以看出乳酸提取的鱼皮胶原蛋白在放大1000倍的情况下,呈现纤维结构且分布比较均匀。有研究表明胶原蛋白的微观结构(包括折叠和薄

Figure 5. SDS-PAGE electrophoresis pattern of collagen from Nile tilapia skin (M. marker; 1.ASC)
图5. 罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白的SDS-PAGE电泳谱图(M. marker; 1.ASC)
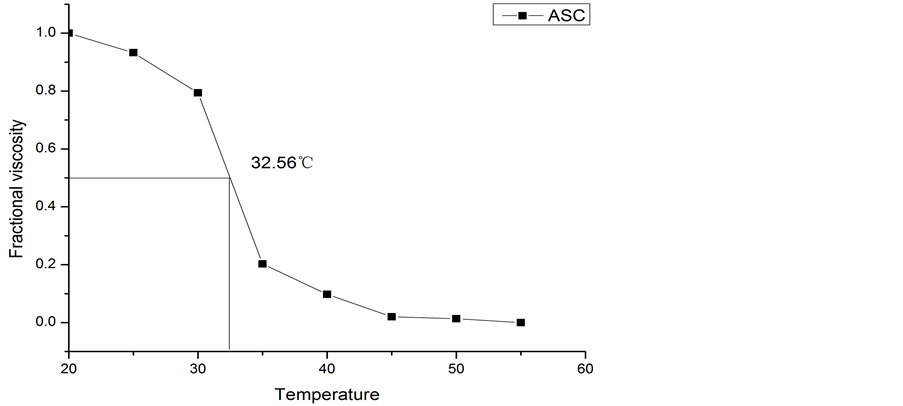
Figure 6. Thermal denaturation curve of collagen from Nile tilapia skin
图6. 罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白热变性曲线

Figure 7. SEM images of collagen from Nile tilapia skin
图7. 罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白的扫描电镜图
片大小、胶原网络连接性和表面积大小)是其作为生物医学材料的重要参数 [17] 。从乳酸提取的胶原蛋白的扫描电镜图来看,乳酸提取的胶原蛋白能较好的保持胶原纤维原有的纤维结构以及空间网状结构,比较适合作为生物医学材料的基料。
3. 结论
本文通过单因素试验,初步考察了乳酸溶液的pH值、液固比和提取时间对胶原蛋白提取率的影响。在单因素试验的基础上,利用Box-Behnken组合实验设计和响应面分析法对乳酸提取罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白的工艺条件进行优化,建立了胶原蛋白提取率与乳酸溶液pH值、液固比和提取时间之间的回归模型,对该模型进行显著性检验,最终确定了乳酸提取罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白的优化工艺参数为乳酸溶液pH2.1、液固比65 (mL/g)、提取时间44 h,此条件下胶原蛋白提取率为85.57%,并分析了最优条件下ASC的理化性质。SDS-PAGE电泳分析可知,三种胶原蛋白的亚基组成形式为(α1)2α2,且分子量为360 KDa左右;罗非鱼皮ASC热变性温度为32.56℃;罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白的扫描电镜图表明罗非鱼皮ASC为均匀的纤维状结构。本文的研究结果可为罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白的高效提取和进一步应用提供参考。