1. 引言
新安江模型是洪水预报中常用的预报模型之一,其产流与分水源模块方法成熟,精度高 [1] 。新安江模型汇流模块因为流域的汇流存在较强非线性,且模块仍然是对流域的高度概化,尚难以直接建立模型的汇流参数与流域的自然地理特征参数间的物理关系,目前主要是通过建立两者之间的经验统计关系,以期待该关系在无资料地区的推广。经验单位线法属于黑箱模型,是在实际汇流计算中常用的简便易行且具有一定物理意义的方法 [2] 。使用经验单位线法进行汇流计算将简化汇流计算的步骤,降低预报模型使用难度,并达到较高精度,以满足基层水文预报工作者的工作需要。丰乐河流域地处江淮之间的中部,东临巢湖,西傍大别山,流经合肥市的肥西县、六安市的舒城县和金安区3个县区70余个乡镇,是巢湖的主要支流之一。其洪水预报的准确性将对流域内居民的人身财产安全和巢湖的防洪调度产生重要影响。该流域洪水预报所使用的经验单位线是上世纪90年代时推求的,由于20多年来流域水文条件的改变,该条单位线已难以满足预报精度要求。现收集到流域内1984年至2013年的时段(流域内7个雨量站测量的时段雨量步长均为6小时)降雨量、径流量和每日的蒸发量资料,用来推求新的经验单位线。共选取30场洪水,其中14场作为率定样本,16场作为检验样本。
目前单位线的研究集中于对纳西瞬时单位线 [3] 、地貌瞬时单位线 [4] 和分布式单位线 [5] 参数的推求 [6] [7] 、敏感性分析 [8] 和汇流路径计算 [9] 等方面,侧重于建立单位线的参数与流域的自然地理特征之间的关系,便于在无资料地区进行洪水汇流计算。在径流资料较丰富的流域,根据流域出口断面的流量过程和(通过产流模型)推求的净雨过程,直接推求时段单位线,是一种简便且具有一定物理意义的汇流计算方法。基于14场率定洪水资料,采用三水源新安江模型进行流域产流计算和水源划分,以计算的径流深和实测径流深的平均绝对误差最小化为目标,采用遗传算法确定模型的参数;并将地表径流和壤中流作为直接径流,采用经验单位线法将其汇流至流域出口,地下径流采用线性水库模拟,通过叠加直接径流的汇流过程和线性水库的出流,得流域出口断面的流量过程,构建丰乐河流域洪水预报模型,并对模型的模拟精度进行评定。
2. 预报模型组成
2.1. 流域平均雨量计算
基于DEM数据 [10] (来源于由美国太空总署(NASA)和国防部国家测绘局(NIMA)联合测量的SRTM90m分辨率的原始高程数据,下载地址:http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/SELECTION/inputCoord.asp),采用ArcGIS10.0软件水文模块 [11] 提取出所需流域面积边界图,并根据流域内雨量站点位置使用泰森多边形法分割区域,得计算流域面雨量时的各雨量站权重,流域平均雨量计算如下:
 (1)
(1)
式中:di为第i个雨量站权重;Pi为流域内第i个雨量站雨量,mm;n为流域雨量站个数。
2.2. 流域产流计算
使用三水源新安江模型 [12] 进行流域的产流与分水源计算,以新安江模型模拟计算的洪水径流深和实测径流深的平均绝对误差最小化为目标,采用遗传算法率定模型参数 [13] :
 (2)
(2)
式中:f为率定洪水径流深的平均绝对误差,mm;n为率定洪水场次;Rj为次洪实测径流深,mm; 为洪水计算径流深,mm。
为洪水计算径流深,mm。
2.3. 流域汇流计算
2.3.1. 基流分割
实测流量的基流分割直接影响到径流量与洪峰流量的计算精度。通常采用目估法、直线切割法和退水曲线法 [14] 等方法进行基流的分割。根据不同的概念,对于基流的组成有很多种解释。这里采用线性水库法对基流进行模拟:
 (3)
(3)
式中:Qg,t为t时刻基流,m3/s;CGd为地下水时段消退系数,与日消退系数CG之间有 ;Rg,t为t时刻前的时段地下产流,mm;U为转换系数,U = F/(3.6Δt)(F为流域面积,km2;Δt为单位线时段长,h);n为地面径流过程历时TQ;初始基流量Qg,1一般以长时间无降水后的实测初始流量表示。
;Rg,t为t时刻前的时段地下产流,mm;U为转换系数,U = F/(3.6Δt)(F为流域面积,km2;Δt为单位线时段长,h);n为地面径流过程历时TQ;初始基流量Qg,1一般以长时间无降水后的实测初始流量表示。
2.3.2. 经验单位线推求
模型使用经验单位线法计算直接径流至流域出口的流量过程,而推求流域经验单位线的常用方法有试错法与分析法 [15] ,试错法通过不断调整初始单位线纵坐标的值来提高流量过程的确定性系最后得到流域经验单位线,但单位线的纵坐标初始值较难确定。分析法虽可通过公式快速推求出单位线纵坐标,但纵坐标值往往会出现负值和锯齿状的情况,不能直接使用 [16] 。为更为有效地推求出流域经验单位线,可结合两种方法的优点,即采用分析法计算出单位线初值,再采用经验试错法调整纵坐标提高确定性系数,最终得到流域经验单位线。
选取率定期内一场降雨时段少(如2或3个时段)、降雨量大并且降雨空间分布均匀的洪水,利用以下公式推算此场洪水的单位线纵坐标:
 (4)
(4)
式中:qt为时段单位线纵坐标,m3/s;Qt为实测流量,m3/s;Rt为实测径流深,mm。
利用式(4)求出的单位线纵坐标作为流域经验单位线的初值。经验单位线时段长Tu为地面径流过程历时TQ与净雨历时TR的差值加上一个时段。随后通过不断修改单位线纵坐标值,使率定样本的平均确定性系数尽可能提高,平均确定性系数为:
 (5)
(5)
式中: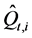 为第i场洪水在t时刻的计算流量,m3/s;Qt,i为第i场洪水在t时刻的实测流量,m3/s;
为第i场洪水在t时刻的计算流量,m3/s;Qt,i为第i场洪水在t时刻的实测流量,m3/s; 为第i场洪水实测流量均值,m3/s;TQ,i为第i场洪水地面径流过程历时,Δt;n为率定洪水场次数。
为第i场洪水实测流量均值,m3/s;TQ,i为第i场洪水地面径流过程历时,Δt;n为率定洪水场次数。
因采用的时段单位线的净雨深为10 mm,所求单位线纵坐标值须利用下式修正:
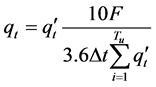 (6)
(6)
式中: 为修正前单位线纵坐标值,m3/s。Tu为经验单位线的总时长,Δt。
为修正前单位线纵坐标值,m3/s。Tu为经验单位线的总时长,Δt。
3. 应用实例
3.1. 流域概况
丰乐河古称桃溪,清代称后河,又名界河,是巢湖较大的一条支流,也是舒城、肥西两县交界的河道。丰乐河流域跨六安、合肥两市,河道全长117.5 km,流域面积2124 km2,其中山区350 km2,占全流域面积16.48%;丘陵区面积为1430 km2,占全流域面积的67.32%;平原圩区面积为344 km2,占全流域面积的16.20%。河道在肥西县三河镇下游与杭埠河汇合后注入巢湖。本文所选取的桃溪水文站位于六安市舒城县桃溪镇,地处丰乐河中段,测站以上河道长度65 km,集水面积1510 km2,见图1。
3.2. 水文预报站介绍
流域内共设配套雨量站7个,分别是东河口、张母桥、张家店、双河镇、椿树岗、山南和桃溪,各雨量站权重如表1所示。
3.3. 计算结果及分析
根据丰乐河流域30年(1984年至2013年)的降雨量、流量和蒸发资料,选取30场洪水进行模拟计算。其中,14场作为率定样本用于新安江模型参数的率定与流域经验单位线的分析提取,率定出的参数如表2所示。

Figure 1. Location map of Taoxi Watershed and rainfall stations
图1. 桃溪站控制流域与各雨量站位置图

Table 1. Area weight of rainfall station
表1. 各雨量站权重

Table 2. The results of the parameters of the Xin’an river model
表2. 新安江模型参数率定结果表
在提取经验单位线时,因水文资料时段均为6 h,故推求的经验单位线时段长Δt取为6 h。率定样本中980915场洪水降雨时段数较少(仅为2个时段)、降雨量大(12 h降雨量达到90.1 mm) (见图2),故选取作为推求流域经验单位线的初值洪水场次。在利用公式(4)求解初始经验单位线纵坐标时,峰值出现在第5个时段,而从第6个时段起出现了振荡与负值(见表3),显然与实际不符。利用该流域上世纪90年代的经验单位线的退水段手动修正本次推算的单位线纵坐标值(在无可参考的单位线情况下可利用退水曲线法计算)。
修正振荡后的单位线纵坐标累加值为770,与标准值 相差不多,利用式(6)修正。通过振荡修正后的经验单位线对980915场洪水进行汇流计算,得其确定性系数为0.97。
相差不多,利用式(6)修正。通过振荡修正后的经验单位线对980915场洪水进行汇流计算,得其确定性系数为0.97。
采用修正后的单位线对所有率定洪水进行汇流计算,结果显示14场洪水的平均确定性系数为0.80,最高为0.95,最低为0.23。有4场次洪的确定性系数小于0.85,其模拟和实测的流量过程如图3所示。
图3中所有洪水的计算流量在涨水阶段均大于实测流量。4场降雨的降水量和平均降水强度均小于980915场洪水的90.1 mm和7.5 mm/h,分别为78.3 mm和3.3 mm/h (020623场)、79.8 mm和3.3 mm/h (070708场)、71.3 mm和2.4 mm/h (070827场)、87.4 mm和3.6 mm/h (100902场)。980915场降雨强度大,流域汇流速度大,据此推求的经验单位线在计算降雨量和降雨强度较小的洪水汇流时,会导致峰现时间提前,峰量增加,所以在利用此条经验单位线计算降水量和降雨强度相对较小的洪水时会出现涨水阶段计算流量偏大的情况。现提出两种解决方案:1) 使用1条单位线计算所有洪水,但为了提高预报精度,需对经验单位线的纵坐标做调整;2) 使用2条不同的经验单位线分别计算由不同降水量和降雨强度形成的大洪水和中小洪水。
方案(1):将式(6)修正后单位线涨水阶段的纵坐标值适当减少,并将减少的部分分摊到退水时段坐标值上,使模拟时率定样本平均确定性系数升高。利用调整后的单位线模拟11场率定次洪,得其平均确定性系数由0.80上升到0.91,最低的0.23也上升到了0.71,以此条单位线作为丰乐河流域汇流计算的经验单位线。
14场率定洪水的径流深平均相对误差为7%、平均洪峰误差为8%、峰现时间的误差为2.57 h,评定合格率分别为93%、93%和86%,平均确定系数为0.91;16场检验次洪的模拟径流深、洪峰与峰现时间的误差分别为8%、9%和3.38 h,合格率分别为88%、94%和88%,平均确定系数为0.89;总体平均确定性系数为0.90,为甲级预报方案。
不同单位线的比较,如表4所示。

Figure 2. Simulation and observed flood process of No. 980915
图2. 编号980915场洪水计算图

Table 3. Calculation results of initial of unit hydrograph
表3. 经验单位线初值计算表

Table 4. Comparison form of comparison for different unit hydrograph
表4. 不同单位线的比较表
注:表中修正后单位线即为式(6)计算的单位线;调整后单位线为最终确定的丰乐河流域经验单位线。
丰乐河流域洪水预报率定洪水精度评定表,如表5所示。
丰乐河流域洪水预报检验洪水精度评定表,如表6所示。

Table 5. Accuracy assessment test of calibrated floods of Fengle River basin
表5. 丰乐河流域洪水预报率定洪水精度评定表
注:峰现允许误差为Δt(6h)。

Table 6. Accuracy assessment test of validated floods of Fengle River basin
表6. 丰乐河流域洪水预报检验洪水精度评定表
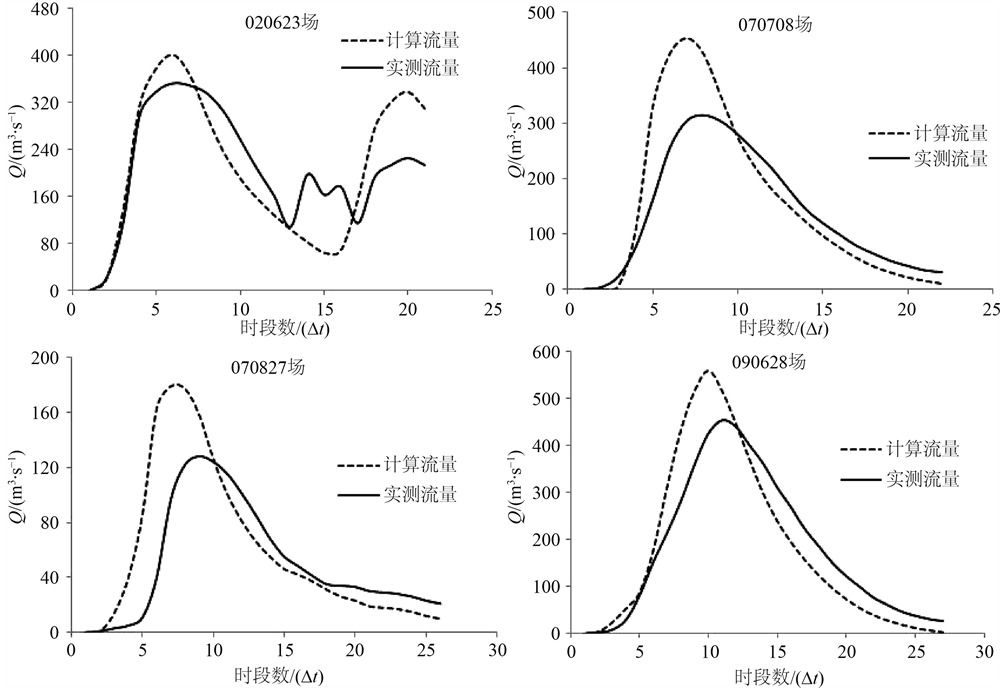
Figure 3. Simulation and observed process of floods with determination coefficient less than 0.85
图3. 确定性系数不到0.85的洪水场次模拟结果
方案(2):130525场洪水的降水量和平均降水强度分别为50.2 mm和2.1 mm/h,为洪水样本中的较小值,以该场降雨洪水作为中小洪水的代表,推求该场洪水的经验单位线;980915场洪水的降水量和平均降水强度分别为90.1 mm和7.5 mm/h,以该场降雨洪水作为大洪水的代表。推求的980915场和130525场洪水的经验单位线如图4所示,当降雨量和平均降雨强度较大时,流域汇流速度快,峰现时间提前,洪峰流量增加,经验单位线为高瘦状;而当降雨量和平均降雨强度较小时,流域汇流速度较小,峰现时间相对偏后,洪峰流量较小,经验单位线为矮胖状。
使用降水量和降水强度较大的980915场洪水推求的经验单位线对降水量和降水强度均较小的000905场洪水(降水量为40.9 mm、平均降水强度为1.4 mm/h)进行汇流计算,得其洪峰相对误差为10%,峰现误差为6.0h,确定性系数为0.89;而使用降水量和降水强度均较小的130525场洪水推求的经验单位线对该场洪水进行汇流计算,得其洪峰相对误差、峰现误差和确定性系数分别为1%、0.0 h和0.94。同理,使用降水量和降水强度较小的130525场洪水推求的经验单位线对降水量和降水强度均较大的980816场洪水(降水量为70.6 mm、平均降水强度为4.0 mm/h)进行汇流计算,得其洪峰相对误差7%,峰现误差为6.0 h,确定性系数为0.82;而使用降水量和降水强度均较大的980915场洪水推求的经验单位线对该场洪水进行汇流计算,得其洪峰相对误差、峰现误差和确定性系数分别为1%、0.0 h和0.95。可见,在使用经验单位线计算流域汇流时,可根据降雨量和降水强度的不同,采用相应于大洪水和中小洪水的的多条经验单位线分别进行汇流计算,以提高预报精度。

Figure 4. Comparison chart of unit hydrograph obtained based on two different rainfall intensity floods
图4. 两场不同降雨推求的洪水经验单位线对比图
4. 结论
采用三水源新安江模型计算了流域产流和分水源,以新安江模型计算的洪水径流深和实测径流深的平均绝对误差最小化为目标,采用遗传算法确定了该模型的参数;并将地表径流和壤中流作为直接径流,采用经验单位线法将其汇流计算至流域出口,地下径流采用线性水库模拟,通过叠加直接径流的汇流过程和线性水库的出流,得流域出口断面的流量过程,构建了丰乐河流域洪水预报模型,用于该流域的洪水模拟和预报,得以下结论:
1) 基于三水源新安江模型和经验单位线法分别进行洪水的产流和汇流计算,构建丰乐河流域洪水预报模型是可行的。14场率定洪水的径流深平均相对误差为7%、平均洪峰误差为8%、平均峰现误差为2.57 h,合格率分别为93%、93%和86%,平均确定性系数为0.91;16场检验洪水的径流深、洪峰和峰现的误差分别为8%、9%和3.38 h,合格率分别为88%、94%和88%,平均确定性系数为0.89。
2) 采用基于大洪水推求的单位线进行中小洪水汇流计算时的精度较低,反之亦然。在丰乐河流域应根据降水量的不同推求出相应于大、中小洪水的经验单位线,进而可依据形成次洪的降水量的大小,采用不同的经验单位线对洪水进行预报,以提高预报精度。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(51579060, 51509065)。