1. 引言
我国水电资源主要集中在西南地区,随着近年来澜沧江、金沙江等特大流域水电站群的竣工投产,水电在整个西南地区电力系统的比重迅速攀升,给水火电优化调度带来了新的挑战。水火电长期优化调度能够为电网中、短期调度提供必要的参考,并在较长时间尺度上协调电网发电资源,对于减少富水电地区水电弃水、降低电网发输电成本、提高电网整体发电效益具有十分重要的意义。
水火电联合优化调度一直是电力调度领域研究的热点问题,经过几十年的研究,已经在我国得到了广泛的应用。单从梯级水电站优化调度的角度出发,以发电量最大、水库蓄能最大、弃水最小、保证出力最大等目标,建立了大量的单目标优化模型,提高了水电站调度效率 [1] - [3] ;从电网水火电协调优化调度的角度出发,国内外学者围绕着火电出力最小、火电煤耗最小、发电成本最低、水耗最低等单目标优化展开了大量研究,提高了水火电力系统的经济性 [4] - [7] 。在水火联合优化调度多目标模型研究中,文献 [8] 提出了提高水电上网电量且保证火电输出功率的多目标、多约束的动态短期调度模型,文献 [9] 提出了水电水耗价格系数、火电煤耗价格系数和环保价格系数的概念,并将多目标问题转化为单目标问题,文献 [10] 从购电成本和煤耗的角度,建立了基于内点法的水火协调模型。然而上述研究均未涉及到,使用优化方法解决多目标水电发电量、水电弃水、电网网损、火电煤耗的问题。
本文将电网最优潮流和水电站群优化调度相结合,考虑电网调度的经济性和节能性,采用水电发电量最大、水电弃水最小、火电煤耗最小以及全网网损最低为目标,建立了水火电长期联合优化调度多目标模型,引入水力约束、水火电出力约束及潮流节点电压上下限约束等,并将每月典型日出力分配嵌入长期调度,以此进行潮流计算、网损统计及电网安全校核,最后应用遗传算法对模型进行求解。以IEEE-30节点为实例的研究表明:本文提出的调度模型能够在发电量、弃水、网损和火电煤耗等目标中得到合理的方案,降低系统总损耗,保证调度方案经济节能的目标。
2. 数学模型
2.1. 目标函数
对于水火电力系统长期优化调度,不仅需要考虑电网安全,而且需要尽量减少水电弃水,并降低煤耗和网损,以提高电网发输电的可行性和经济型。因此,建立水电发电量最大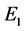 、水电弃水最小
、水电弃水最小 、火电煤耗最少
、火电煤耗最少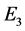 和网损最低
和网损最低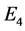 的多目标调度模型。具体是:
的多目标调度模型。具体是:
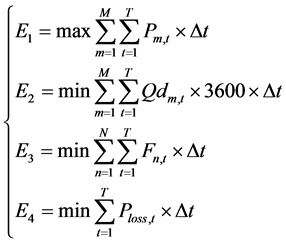 (1)
(1)
式中:m、M分别为水电站编号和水电站总数,n、N分别为火电站编号和火电站总数,t、T分别为长期调度时段编号和时段总数,本文以月作为长期调度时段,T = 12,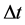 是第t个调度时段总小时数;
是第t个调度时段总小时数; (kW)、
(kW)、 (m3/s)分别为水电站m在t时段的平均出力和弃水流量;
(m3/s)分别为水电站m在t时段的平均出力和弃水流量;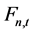 (t/h)为火电站n在t时段的平均煤耗;
(t/h)为火电站n在t时段的平均煤耗; (kW)为t时段的平均网损,
(kW)为t时段的平均网损,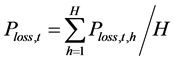 ,
,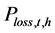 (kW)为根据典型日负荷进行水、火电负荷分配后通过潮流计算得到的全网第t个长期调度时段在第h个典型日时段的网损。
(kW)为根据典型日负荷进行水、火电负荷分配后通过潮流计算得到的全网第t个长期调度时段在第h个典型日时段的网损。
2.2. 约束条件
2.2.1. 电网约束
1) 功率平衡约束
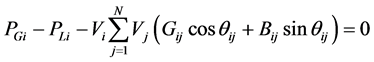 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
式中: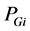 、
、 为典型日情况下各时段潮流计算中节点i的出力有功功率、无功功率,
为典型日情况下各时段潮流计算中节点i的出力有功功率、无功功率,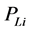 、
、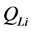 是节点i的负荷有功功率、无功功率,N是节点总数,
是节点i的负荷有功功率、无功功率,N是节点总数, 、
、 、
、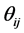 分别是节点i、j的电压幅值和相角差,
分别是节点i、j的电压幅值和相角差, 、
、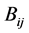 是节点导纳矩阵第i行、第j列的实部和虚部。
是节点导纳矩阵第i行、第j列的实部和虚部。
2) 节点电压上下限约束
 (4)
(4)
式中: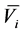 、
、 是节点i电压
是节点i电压 的上下限。
的上下限。
2.2.2. 电源约束
1) 水电站水量平衡方程
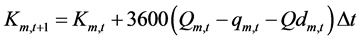 (5)
(5)
式中: (m3)和
(m3)和 (m3)为水电站m在t时段末和t+1时段末的蓄水量,
(m3)为水电站m在t时段末和t+1时段末的蓄水量,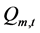 (m3/s)、
(m3/s)、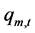 (m3/s)和
(m3/s)和 (m3/s)分别是水电站m在t时段的入库流量、发电流量和弃水流量。
(m3/s)分别是水电站m在t时段的入库流量、发电流量和弃水流量。
2) 水电站发电流量约束
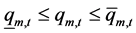 (6)
(6)
式中: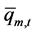 、
、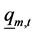 是水电站m第t个长期调度时段发电流量
是水电站m第t个长期调度时段发电流量 的上下限。
的上下限。
3) 水电站出库流量约束
 (7)
(7)
式中: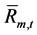 、
、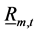 是水电站m第t个长期调度时段出库流量
是水电站m第t个长期调度时段出库流量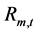 (m3/s)的上下限,
(m3/s)的上下限,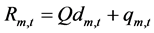 。
。
4) 水电站水位约束
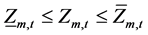 (8)
(8)
式中: 、
、 是水电站m第t个长期调度时段末水位
是水电站m第t个长期调度时段末水位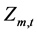 的上下限。
的上下限。
5) 水电站出力约束
 (9)
(9)
式中: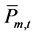 、
、 是水电站m第t个长期调度时段平均出力
是水电站m第t个长期调度时段平均出力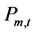 (kW)的上下限。
(kW)的上下限。
6) 水电站已知起始水位和调度末水位
 ;
;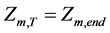 (10)
(10)
式中: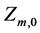 、
、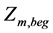 、
、 、
、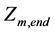 分别是水电站m调度期的初水位、末水位和给定的初始水位、期望末水位。
分别是水电站m调度期的初水位、末水位和给定的初始水位、期望末水位。
7) 火电站出力约束
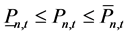 (11)
(11)
式中: 、
、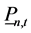 是火电站n在t时段平均出力
是火电站n在t时段平均出力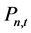 (kW)的上下限。
(kW)的上下限。
3. 求解方法
3.1. 典型日水火电出力分配
由于水火电长期优化调度难以精确考虑短期调度的影响 [11] ,本文选用每个长期调度时段中接近月平均负荷的某一天日负荷过程作为该长期调度时段的典型日负荷。为了让火电出力平稳,本文以水电站长期调度时段的平均出力作为典型日的水电站给定的平均出力,采用逐次切负荷方法进行水电负荷分配 [12] ,让水电尽量承担电网负荷峰值,剩余的负荷由火电承担,火电总出力按等微增率原则分配。水电逐次切负荷的方法是将各水电站按照负荷率由小到大排序,然后按照此顺序进行切负荷,单个水电站出力分配的计算过程是:1) 轮到某电站参与平衡时,计算系统剩余负荷过程和剩余负荷最大值,该电站的工作位置是剩余负荷最大值减去该电站的最高出力限制;2) 如果该电站日电量大于给定工作位置的电量,则抬高工作位置,反之则降低工作位置,工作位置以上的负荷由该电站承担;3) 不断重复第2)步,直至电站分配到的平均出力与给定的平均出力相等或电站的工作位置达到最低。
3.2. 火电机组最优分配处理
3.2.1. 火电机组煤耗特性
火电机组出力与煤耗呈现二次函数关系,单个火电机组煤耗量是:
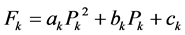 (12)
(12)
式中: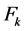 是火电机组k的煤耗,单位是t/h,
是火电机组k的煤耗,单位是t/h, 是火电机组k的出力(MW),
是火电机组k的出力(MW),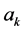 、
、 、
、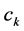 是火电机组k的煤耗特性系数,煤耗特性系数由机组实验数据拟合所得。
是火电机组k的煤耗特性系数,煤耗特性系数由机组实验数据拟合所得。
3.2.2. 等微增率机组出力分配
在给定火电机组总出力的情况下,为了火电机组总煤耗最小,通常采用基于数学极值理论的等微增率法处理火电机组出力最优分配问题 [13] 。设有K台火电机组,由式(12)可知机组的二次函数煤耗特性,火电机组总煤耗F最小目标函数是:
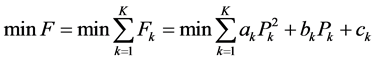 (13)
(13)
火电机组的总出力给定,对机组的煤耗特性函数求偏导,按照等微增率准则,微增率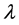 相等,可得线性方程组:
相等,可得线性方程组:
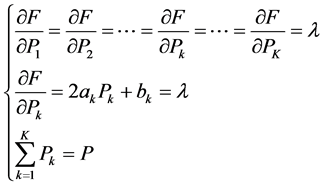 (14)
(14)
求解公式(14),可得机组k的出力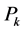 是:
是:
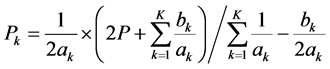 (15)
(15)
3.3. 多目标函数预处理
对于多目标函数问题,有效的求解方法之一是将多目标问题单目标化。本文引入线性加权和的方法,权重是各个目标重要程度的体现,权重越高说明目标越重要,权重的选择将直接影响到优化结果。引入权重因子后,目标函数变为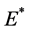 :
:
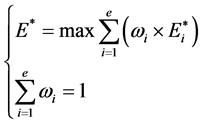 (16)
(16)
其中,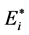 是第i个归一化子目标函数,e是子目标总数,本文e = 4,
是第i个归一化子目标函数,e是子目标总数,本文e = 4,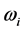 是权重系数,
是权重系数,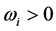 。
。
由于各个子目标量纲不同,无法直接计算,将它们采用归一化处理,子目标弃水最小、煤耗最小和网损最小归一化的目标函数是:
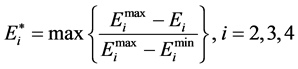 (17)
(17)
水电发电量最大归一化的目标函数是:
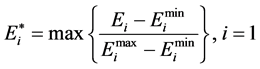 (18)
(18)
其中, 和
和 分别是子目标函数
分别是子目标函数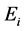 的极大值和极小值。
的极大值和极小值。
3.4. 模型求解
本文的水火电长期联合优化调度多目标模型,涉及到水电站群调度、水火协调以及电网潮流计算,求解相当复杂。遗传算法有寻优能力强、收敛速度快的优点。因此,本文将梯级水电站的水位组合作为染色体,采用十进制编码遗传算法进行求解。
具体计算步骤如下:
1) 初始化种群,对参与计算的各水电站的水位运行序列进行编码,设种群数为100,随机初始化种群,并设置当前进化代数g = 0;
2) 设置长期调度时段t = 0,总时段长度为T;
3) 根据典型日负荷分配方法,计算典型日水电站的出力分配,根据电力平衡计算火电总出力,采用等微增率法计算火电站出力分配;
4) 采用牛顿拉夫逊法进行潮流计算,并计算出典型日各时段的全网网损,设t = t + 1,若t < T,返回到第3)步,否则到第5)步;
5) 计算个体适应度,对违反约束条件的个体给予惩罚。如果满足终止条件,则计算结束,保存最优个体作为求解结果,否则到第6)步;
6) 选择运算是轮盘赌选择,个体的选择概率与其适应度大小成正比;
7) 采用算术交叉的方法进行交叉运算;
8) 变异运算,生成下一代种群。g = g + 1,返回第2)步。
4. 算例
如图1所示,本文在IEEE-30节点系统的基础上,系统基准容量取100 MVA。节点1是平衡节点,选用可调节的火电站;节点2、5、7、11是梯级水电站A、B、C、D,节点1、13处是火电站。电站A是多年调节电站,电站C是不完全年调节电站,B和D是季调节电站。A水库总库容145.57亿m3,正常蓄水位1240 m,死水位1166 m,B水库总库容9.2亿m3,正常蓄水位994 m,死水位988 m,C水库总库容9.42亿m3,正常蓄水位899 m,死水位882 m,D水库总库容11.4亿m3,正常蓄水位602 m,死水位591 m,入库流量数据采用频率为25%的丰水年的径流数据。本文长期调度时段是12个时段,时段长度是一个月,典型日负荷选取24个时段,时段长度为一小时。遗传算法种群数100个,交叉概率是0.8,变异概率是0.02,算法用Java实现。
计算结果如表1所示,方案一是水电常规调度结果,从表中数据可知,该方案水电发电量较低,系统煤耗和网损较大,水电弃水较多。方案二是单目标水电发电量最大模型的计算结果,在系统负荷给定的情况下,是火电发电量最小的方案,但是存在大量弃水,与梯级水电站实际调度不符。方案三是本文调度方案,梯级水电站年发电量532.01亿kWh,火电年发电量514.14亿kWh,弃水是83.56亿m3,总煤耗1524.45万t,总网损21.05亿kWh,由于采用频率为25%的径流数据,来水较多,梯级水电站会有一定的合理弃水。从表中可知,相比于方案一,本文方案的水电发电量大幅提高,弃水、煤耗、网损等指标均大幅减小,相比于方案二,本文方案的水电发电量降低1.2%,但是弃水减小了18.79%,因此本文所提方案更具可行性;另外,本文所提方案得到的系统网损也比另外两种方案的网损要少,有效减少了清洁能源的浪费,达到了电力系统经济性的目标。
图2和图3是本文调度模型与水电发电量最大模型的梯级水电、火电的出力对比,相对于水电发电量最大模型,本文模型得到的水电在枯期稍稍加大出力,有助于枯水期电网调峰,汛期电量变化较小,弃水量大幅减小。图4是本文方案的水火电出力分配,水电在枯期总出力较少,完成抬高水位蓄能,在汛期水电的出力增大;火电出力稳定,在枯期承担主要出力,在汛期火电上网电量减小,充分实现了两种电源的互补,并有利于实现电网节能减排,更加符合实际调度。
表2是本文调度方案梯级水电站的流量表,本文的入库流量数据采用频率为25%的丰水年的径流数据,从结果可以看出,7~9月,汛期来水量很大,水电发电流量达到最大,总弃水量是83.56亿m3。弃水是实际水电调度中十分重要的一个考核指标,从表1可知,本文所提模型能够大幅减小弃水,与实际调度更加吻合。
表1. 方案对比

Table 2. The flow of cascade hydropower stations in this paper
表2. 本文调度方案梯级水电站流量表

Figure 1. IEEE-30 bus system diagram
图1. IEEE-30节点系统图
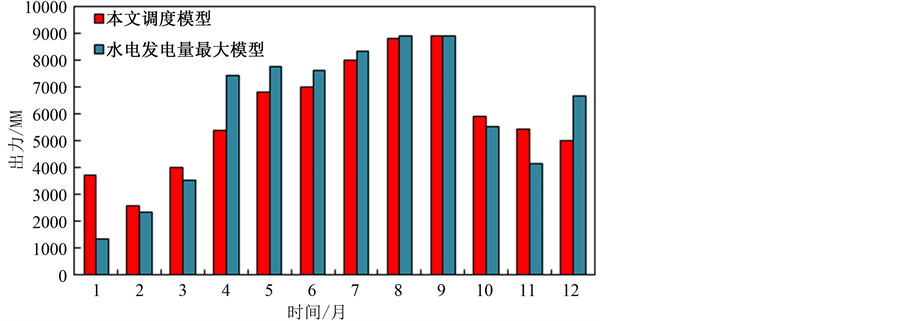
Figure 2. Output comparison of hydro power stations
图2. 梯级水电站出力对比
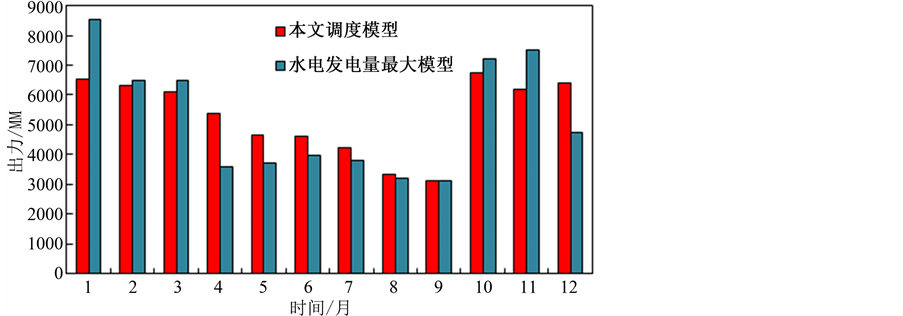
Figure 3. Output comparison of thermal power stations
图3. 火电出力对比

Figure 4. Hydropower and thermal power allocation
图4. 本文调度方案水火电出力分配
5. 结语
本文将电网最优潮流与水火电站经济调度运行相结合,在保证了电网潮流收敛的前提下,考虑水电站的弃水最小、网损最小和火电节能等目标,实现了电网水火电长期发电计划节能、稳定。以IEEE-30为基础的梯级水电站群、火电站系统为实例的研究结果表明,本文所提模型能够显著减小梯级水电站的弃水,降低电网输电损耗,提高电力系统经济性,为电网长期发电计划制作提供有效的方案。
基金项目
中央高校基本科研业务费(DUT15RC(3)077)。