1. 引言
随着近年来地铁在国内大中型城市的高速发展,地铁引起的振动问题也受到越来越广泛的关注。特别是沿线的高层建筑、古代建筑以及一些对振动要求较高的实验室仪器室等对振动敏感的区域。现在世界上以及有很多国家出现由于列车的振动和噪声引起的建筑物的破坏、沿线居民对振动噪声影响的投诉 [1] 。钢弹簧浮置板轨道作为一种地铁减振轨道可以较好的抑制环境振动,但其造价昂贵,因此多作为特殊地段的减振措施。目前,国内外已经有20多个城市地铁使用了钢弹簧浮置板轨道,其在抑制环境振动方面取得了较好的效果 [2] - [5] 。2000年,新加坡学者F. Cui等 [2] [6] 利用简谐载荷研究了浮置板轨道和普通整体轨道对大地的减振效果,并未考虑轮轨力的真实作用。2006年,G. Lombaert等 [2] [7] 建立了三维数值模型对浮置板轨道诱发的大地自由场的振动效果进行了预测。台湾学者Chen-Ming Kuo利用车轮和轨道耦合系统方程,研究了浮置板的振动性能 [8] ,使用的是动力学方程求解并没有考虑振动在大地等的传播特性。2007年,上海交通大学吴天行研究了轨道减震器与浮置板轨道组合的隔振性能,对浮置板的柔度计算以及隔振性能进行了详细的研究 [9] 。
本文建立了完整的地铁减振模型,模型中考虑了轨道结构、隧道以及大地,并通过粘弹性人工边界条件模拟大地无限大的效果。同时模型考虑了更为真实的轮轨粗糙度激励作为输入条件,对比分析了钢弹簧浮置板轨道结构和传统地铁无砟轨道结构的振动特性以及钢弹簧浮置板的减振效果。
2. 模型介绍
2.1. 有限元模型
图1给出了地铁钢弹簧浮置板三维实体有限元模型。由图1可见,模型中考虑了钢轨、轨道板、弹簧、地基、隧道和大地等,模型为对称建模。大地四周采用粘弹性人工边界条件。
2.2. 粘弹性人工边界
为了使有限长度的有限元模型产生的剪切波和压缩波能传出去,模型中使用了粘弹性人工边界 [10] [11] 。人工边界条件通过弹簧阻尼单元来模拟,相关计算公式如下 [11] :

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 1. The finite element model of steel spring floating slab
图1. 钢弹簧浮置板有限元模型
 (1)
(1)
式中:Kn为法向刚度;Ct为法向阻尼;Kt为切向刚度;Ct为切向阻尼;G为剪切模量;ρ为密度;△l为最小单元尺寸;R为激励点到界面距离。
2.3. 接触刚度
为了模拟车轮在平直轨道上的轮轨接触关系,仅考虑钢轨的垂向接触刚度 [12] [13] ,公式如下:
 (2)
(2)
式中:RR为轨顶面曲率半径;Rw为名义滚动圆处车轮半径;P0为轮重;ξ为与接触半径相关的无量纲常数;E为车轮和钢轨的弹性模量;μ为车轮和钢轨的泊松比。
2.4. 接触滤波
接触滤波是车轮粗糙度中波长小于或者等于轮轨接触斑长、短半轴的波长,其激发轮轨系统振动作用被减弱的现象 [14] [15] 。圆形接触滤波估计公式如下 [14] [15] :
 (3)
(3)
式中:k为粗糙度波数;b为接触椭圆长半轴与短半轴的算数平方根值;J1(x)为第一类一阶贝塞尔函数;α为轮轨表面粗糙度相关系数。
2.5. 轮轨相互作用力
轮轨间相互作用力与车轮导纳、钢轨导纳、接触刚度以及车轮钢轨联合粗糙度等有关,具体公式如下 [14] - [16] :
 (4)
(4)
式中,r是轮轨表面联合粗糙度,aC为轮轨接触导纳,ar为钢轨导纳,aw为车轮导纳。其中,aC = 1/kH,kH为轮轨接触刚度。
2.6. 计算参数及取点
本文中取钢弹簧支撑部件刚度为5.76 kN/mm [1] [2] ,阻尼为13.2 (kN·s)/m [1] [2] ;扣件刚度20 kN/mm,阻尼1.0 (kN·s)/m,其他计算参数如表1所示。
本文在计算轮轨力时,使用的的轮重为4.5吨,车轮名义滚动圆半径为0.42 m,列车运行速度为60 km/h;传统地铁无砟轨道和浮置板轨道使用相同的轨道粗糙度谱。
图2给出了轨头、轨道板、底座板、隧道以及大地的振动取点图。
3. 轮轨力作用下的浮置板轨道减振特性分析
图3给出了浮置板轨道与传统地铁无砟轨道的轨头激励点处振动加速度。
由图3中可见,在相同轮轨粗糙度谱下,浮置板轨道与传统地铁无砟轨道的轨头激励点处的振动加速度基本一致,表明浮置板轨道并不能降低钢轨的振动。
根据城市区域环境振动标准GB_10071-88,使用振动加速度级作为评价地铁轨道振动特性的重要指标,具体公式如下:
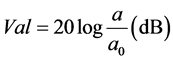 (5)
(5)
式中:a——表示观察点振动加速度;
a0——表示基准加速度。
当基准加速度a0 = 1.0时,可以得到浮置板轨道和传统地铁无砟轨道轨头激励点处的振动加速度级均为46.6 dB,在钢轨处两者的加速度级基本一致。
根据GB_10071-88,为了表征轨道的减振特性,使用钢轨的振动加速度级减去隧道、大地观察点的振动加速度级,得到其减振级如表2所示:
根据北京地方标准DB11/T838—2011,标准测量点即隧道壁S0点处,浮置板轨道减振级相对于传统无砟轨道降低了18 dB。依据标准中评判减振措施等级的指标范围,浮置板轨道在隧道壁减振级处在[15,20) dB之间,属于高级减振措施。
由表2中还可以得出:
1) 从钢轨到隧道壁(S0)振动衰减量最大,传统轨道为49.5 dB,浮置板轨道为67.8 dB。从隧道到大地传统无砟轨道减少10~20 dB,而浮置板轨道从隧道到大地减少20~30 dB;
2) 当地面沿着水平方向达到GD1点后,水平距离对浮置板和传统地铁无砟轨道减振水平的影响不再显著;
3) 在隧道壁处,浮置板轨道比传统无砟轨道减振效果好18 dB;在地表面,浮置板轨道比传统轨道减振效果好16 dB以上。
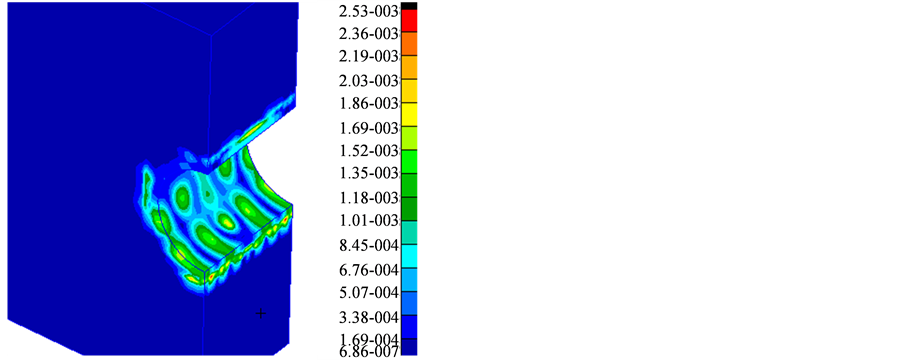
为了深入分析浮置板轨道的隔振原理,图4给出了浮置板轨道和传统无砟轨道底座板的振动加速度频谱。图5给出了在340 Hz时,浮置板与传统地铁砟轨道的隧道壁加速度云图。图6给出了在340 Hz时,浮置板与传统地铁砟轨道的地表加速度云图。
由图4可见,浮置板轨道与传统地铁无砟轨道相比,在大部分频率区域,浮置板的隔振效果好。根

Table 1. The material parameters of steel spring floating slab
表1. 钢弹簧浮置板材料参数

Table 2. Tunnel, ground observation point of vibration reduction (unit: dB)
表2. 隧道、大地观察点减振级(单位:dB)

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 2. The point drawing of vibration
图2. 振动取点图
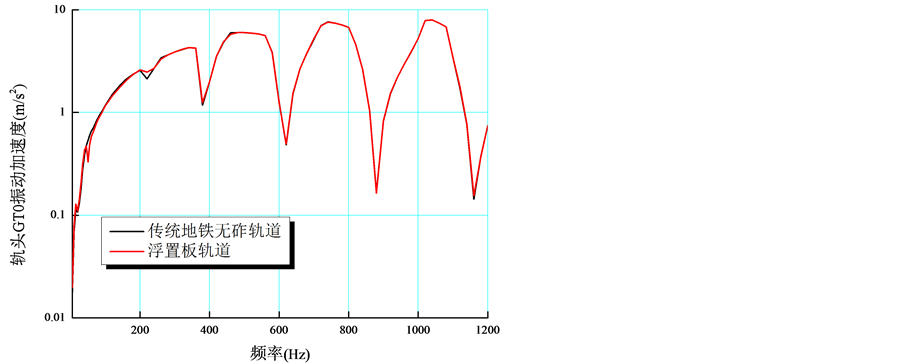
Figure 3. The rail head vibration of floating slab track with traditional ballastless track
图3. 浮置板轨道与传统无砟轨道轨头振动

Figure 4. A comparison of the vibration acceleration of floating slab track and traditional ballastless track in the base plate
图4. 浮置板轨道与传统无砟轨道底座板振动加速度
 (a) floating slab track (b) traditional ballastless track
(a) floating slab track (b) traditional ballastless track
Figure 5. Vibration acceleration map of tunnel on 340 Hz
图5. 在340 Hz附近的隧道壁振动加速度云图
 (a) floating slab track
(a) floating slab track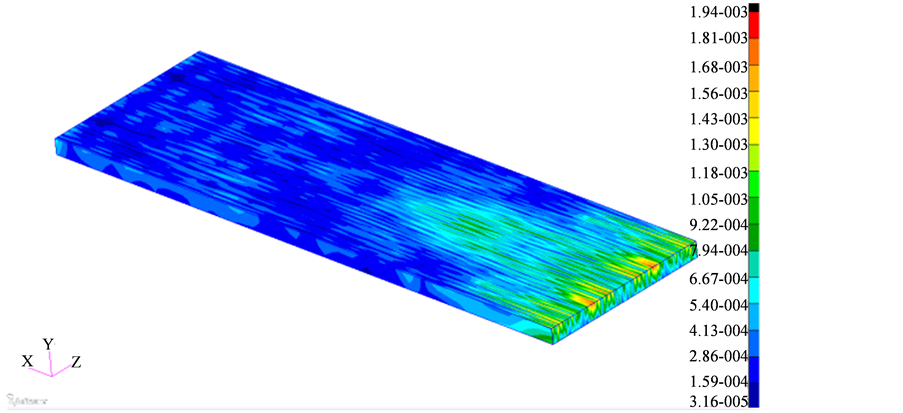 (b) traditional ballastless track
(b) traditional ballastless track
Figure 6. Vibration acceleration map of ground on 340 Hz
图6. 在340 Hz附近的地表振动加速度云图
据标准GBT13441.1-2007,主要关注的频率在400 Hz以下(高频经过大地后会大幅衰减),从图中可以看出在20~400 Hz范围内浮置板隔振效果最高可达99% (340 Hz附近)。由图5可见,在340 Hz时,传统地铁无砟轨道的振动加速要比浮置板轨道的振动加速度大一个数量级,可以看出嵌入式轨道的减振效果非常明显;由图6可见,在340 Hz时,传统地铁无砟轨道的振动加速要比浮置板轨道的振动加速度大两个数量级,浮置板轨道对地表环境振动具有很好的抑制效果。由图4可见,在20 Hz以下浮置板轨道的隔振效果并不明显,这与浮置板轨道的固有频率以及其隔振原理有关 [1] [2] ,本文浮置板的固有频率为19.6 Hz。
由此可见,浮置板轨道对周围环境振动具有很好的抑制效果,然而,该轨道对轨道板自身及以上部分的振动并没有抑制效果,甚至会放大轨道板的振动,如图7所示,振动的放大,有可能带来轨道伤损、列车运行舒适性差等问题。
由图7中可见,浮置板轨道的轨道板振动高于传统地铁无砟轨道的轨道板振动,这跟浮置板轨道的支撑刚度有关,支撑刚度大有利于振动的传递减小自身振动,支撑刚度小有利于减小振动的传递但自身振动就会增加。从能量角度讲,浮置板轨道结构有效的实现了轨道板到隧道、大地的隔振,但导致轨道板自身振动的加强,也有一些文献为了解决轨道板自身振动强的问题而使用减振器等 [9] 。
图8分别给出了传统无砟轨道与浮置板轨道的振动传递特性。
由图8(a)可以得出:
1) 从轨道板到底座板的振动加速度曲线基本重合,可以看出对于传统无砟轨道,轨道板到底座板的减振效果有限,仅由砂浆层或自密实混凝土等填充层提供减振;
2) 从底座板到隧道的振动加速度曲线可以看出在低频(400 Hz以下)振动加速度有所减少,但是高频(400 Hz以上)振动加速度几乎没有减少;
3) 从隧道到大地,低频振动加速度较大,占主导地位,大地对高频振动加速度衰减非常显著。
由图8(b)可以得出:
1) 轨道板到底座板的振动加速度均有较大衰减,可以看出钢弹簧浮置板轨道结构有利于减少轨道板到底座板的振动传递;

Figure 7. A comparison of the vibration acceleration of floating slab track and traditional ballastless track on the track slab
图7. 浮置板轨道与传统无砟轨道板振动
 (a) traditional ballastless track
(a) traditional ballastless track (b) floating slab track
(b) floating slab track
Figure 8. The vibration transfer characteristics of floating slab track and traditional ballastless track
图8. 浮置板轨道与传统无砟轨道振动传递特性
2) 从底座板到隧道、隧道到大地的振动传递规律与普通地铁轨道相近。
通过对比图8(a)和图8(b)可见,两者最大的差异在于轨道板到底座板的振动传递,浮置板轨道有良好的隔振效果使轨道板到底座板的振动衰减显著,而传统地铁无砟轨道在轨道板到底座板之间振动衰减效果并不明显。
4. 结论
本文建立了包含轨道结构、隧道、大地等的传统地铁无砟轨道和钢弹簧浮置板轨道有限元模型,并考虑了粘弹性人工边界条件以模拟大地无限大的特性,在频域轮轨粗糙度激励作用下,分析了浮置板轨道的减振特性,可以得到如下结论:
1) 浮置板轨道对钢轨振动几乎没有影响;
2) 浮置板轨道可以有效的降低底座板、隧道、大地的振动;主要通过抑制轨道板到底座板之间振动的传递实现减振,特别是高于其固有频率范围的振动传递;
3) 浮置板轨道在减振的同时也使轨道板振动加强,可能引发轨道自身伤损问题以及列车运行舒适度下降等问题,可以通过在轨道板上进一步采取其他减振措施来衰减其振动。
基金项目
本文的研究得到教育部博士点基金(20130184110005)和牵引动力国家重点实验室自主课题(2015TPL_T01)的资助。
*通讯作者。