1. 引言
混凝土中钢筋的腐蚀破坏已被确认为钢筋混凝土耐久性降低的首要因素。氯盐侵蚀引起的钢筋耐久性问题在我国十分的普遍 [1] 。北方寒冷地区混凝土结构受到氯离子和冻融循环等因素的影响;南方混凝土结构区受到氯离子、温度、湿度等因素的作用,特别是南海和东海南部地区混凝土结构,常年处于高温、高湿、高盐度的腐蚀环境下,对结构的耐久性造成了十分不利的影响。
2. 模型建立
Fick第二定律将混凝土表面氯离子浓度、扩散系数与扩散时间联系起来,得到其传质过程中的数学模型 [2] :
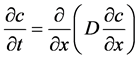 (1)
(1)
式中,t为氯盐侵蚀时间,x为距混凝土表面的距离,D为氯离子扩散系数;c是距混凝土表面x处的氯离子浓度。
研究表明:混凝土中氯离子的扩散系数是一个与时间有关的变量,并且随着时间的增加而减小,将氯离子的扩散系数随时间增加而降低的现象用幂函数表示 [3] :
 (2)
(2)
式中,D0(t0)为t0时刻混凝土中氯离子的扩散系数,t0为参考时间,a为经验系数。
基于文献 [4] 研究成果,氯离子扩散系数与混凝土相对湿度的关系:
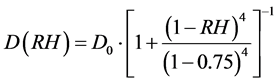 (3)
(3)
式中,D(RH)为相对湿度下的扩散系数,D0为饱和状态下的扩散系数,RH混凝土相对湿度。
试验研究和工程调查表明,环境温度对混凝土中氯离子的输运有着直接的影响。温度修正系数k,如表1所示 [5] 。
表1中的温度是工程所处环境的平均温度。应用插值法求得表1中未给出的温度修正系数。当温度小于5℃时刻按5℃计,当温度大于35℃式以35℃计。由表1可知,文献 [5] 指出当工程所处环境温度大于20℃时,温度对氯离子的输运起到了促进作用;当工程所处环境温度小于20℃时,温度对氯离子的输运起到了削弱作用。
假设对于某项工程而言,所处ti时间段内的平均温度为Ki(i取1~8)。
其中,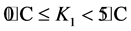 ;
; ;
;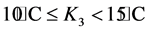 ;
;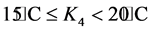 ;
;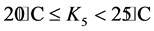 ;
;

Table 1. Temperature correction coefficients
表1. 温度修正系数
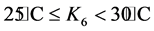 ;
;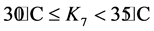 ;
;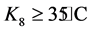 。
。
则温度因素对氯离子扩散的影响系数f3:
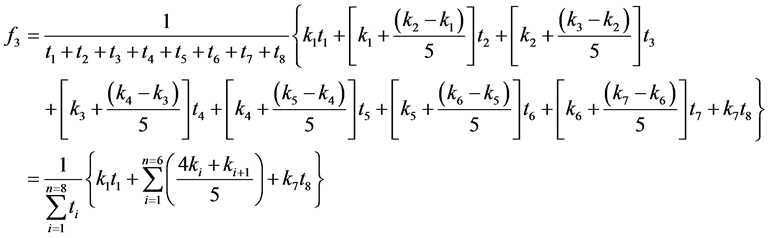 (4)
(4)
式中,k1 = 0.5;k2 = 0.6;k3 = 0.8;k4 = 1.0;k5 = 1.2;k6 = 1.6;k7 = 2.0。
综合以上因素,可得湿热环境下混凝土内氯离子侵蚀模型:
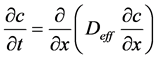 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
式中,f1为时变因素对氯离子扩散的影响系数,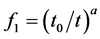 ;f2为环境湿度对氯离子扩散的影响系数,
;f2为环境湿度对氯离子扩散的影响系数,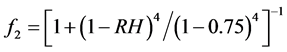 ;f3为温度因素对氯离子扩散的影响系数。
;f3为温度因素对氯离子扩散的影响系数。
3. 混凝土结构耐久性寿命评估
混凝土结构在服役的过程中,存在3个关键的特征时间段 [6] :混凝土结构建成到混凝土内钢筋开始锈蚀的时间段(去钝化)T1;钢筋钝化膜破坏至钢筋锈胀引起混凝土保护层开裂的时间段T2;混凝土保护层开裂至裂缝宽度发展到1 mm所需的时间段T3。
文献表明 [7] ,钢筋的锈蚀速度与锈蚀电流有密切的关系。同时,文献 [8] 中指出当混凝土中氯离子浓度小于0.4%时(混凝土中的临界氯离子浓度一般都小于0.4%),其腐蚀电流变化较小,因此可以近似考虑T2和T3时间段钢筋的锈蚀均以均匀速度进行的。
T2时间段以后,由于保护层开裂,会导致氧气和水分进入混凝土的速率明显加大,因此T3时间段钢筋的锈蚀速度应大于T2时间段钢筋的锈蚀速度。混凝土结构使用寿命全过程如图1所示。
由图1所示,混凝土结构耐久性寿命T为:
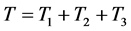 (7)
(7)
式中:T1为钢筋表面去钝化所需时间;T2钢筋开始锈蚀至保护层开裂所需时间;T3保护层开裂至裂缝宽度发展到1 mm所需时间。
3.1. 钢筋表面去钝化所需时间T1
钢筋表面去钝化所需时间T1取决于氯离子在混凝土中输运,这个过程可以用菲克第二定律描述:
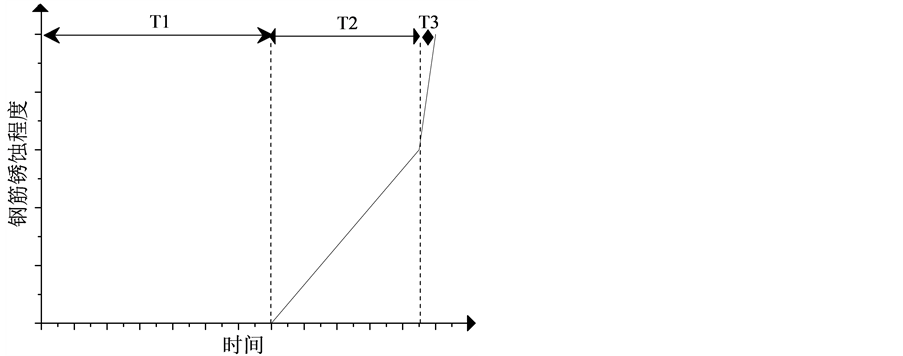
Figure 1. The whole life process of concrete structure
图1. 混凝土结构的全寿命过程
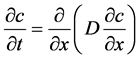 (8)
(8)
式中,c为经时间t后距表面x处氯离子的浓度;D为氯离子扩散系数;x为距混凝土表面的深度;t为扩散时间。
一维状态下,其解析解为:
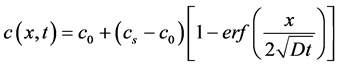 (9)
(9)
式中,c0为混凝土内部初始浓度,cs为混凝土表面氯离子浓度,erf(x)为误差函数。
假设钢筋混凝土结构的保护层厚度为C,氯离子的临界浓度为cr,可以推导出T1:
 (10)
(10)
由于f1、f2、f3均与x无关,将式(2)、(3)、(4),代入式(8):
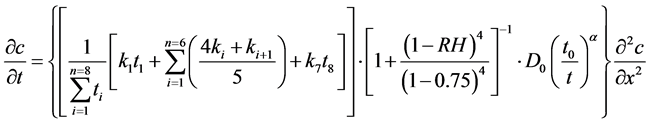 (11)
(11)
令:
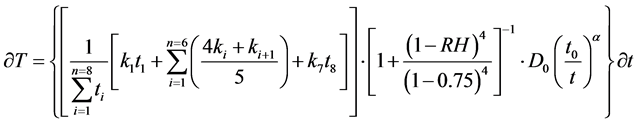 (12)
(12)
则式(11)可以写为:
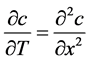 (13)
(13)
参考(10)式,其一维状态下的解析解为:
 (14)
(14)
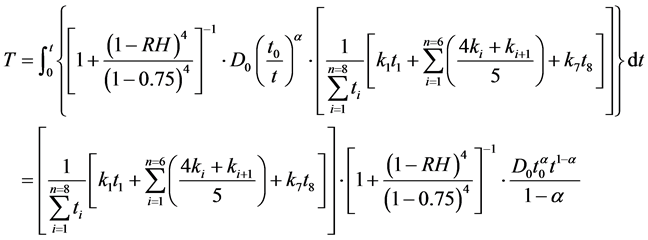 (15)
(15)
则温度和荷载耦合作用下,钢筋表面去钝化时间T1为:
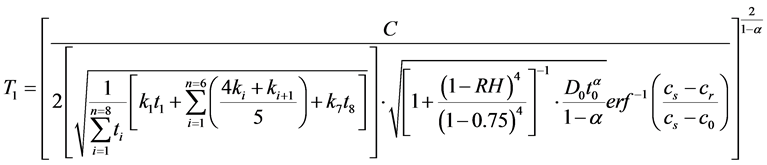 (16)
(16)
由图1可知,计算钢筋开始锈蚀至保护层开裂时间T2以及保护层开裂至裂缝宽度发展到1 mm所需时间T3,最直接的方式是通过计算钢筋锈蚀程度发展所需时间确定的。本文计算中采用钢筋的锈蚀深度这一变量来说明钢筋的破坏程度,从而确定钢筋混凝土使用寿命全过程的T2和T3。
3.2. 钢筋开始锈蚀至保护层开裂时间T2
由文献 [9] 可知,保护层开裂前钢筋的锈蚀速度:
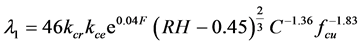 (17)
(17)
式中,l1为保护层开裂前钢筋的锈蚀速度,kcr为钢筋位置的修正系数,kce小环境条件修正系数,F环境温度,RH环境湿度,C混凝土保护层厚度,fcu混凝土立方体抗压强度。
Rodriguz [10] 通过电化学锈蚀试验和长期暴露试验研究了混凝土保护层开裂时钢筋的锈蚀深度,给出了计算公式:
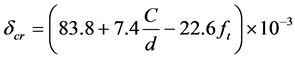 (18)
(18)
式中,dcr混凝土保护层开裂时钢筋的锈蚀深度;d为钢筋的直径;ft为混凝土的抗拉强度。
则钢筋开始锈蚀至保护层开裂时间T2
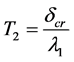 (19)
(19)
3.3. 混凝土保护层开裂至裂缝宽度发展到1 mm所需的时间段T3
混凝土内部出现裂缝是由于钢筋锈蚀膨胀产生的膨胀压力大于混凝土的抗拉强度所引起的。内部裂缝出现后,会进一步扩张到混凝土表面,从而导致保护层开裂。因此钢筋的锈蚀程度与裂缝宽度存在一定的关系,Reodriguez [10] 通过试验给出了裂缝宽度与钢筋锈蚀深度的关系为:
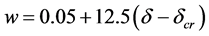 (20)
(20)
即
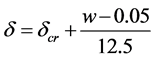 (21)
(21)
式中,w为保护层裂缝宽度,d为钢筋锈蚀深度。
混凝土保护层开裂至裂缝宽度发展到1 mm时间段内,钢筋的锈蚀速度 [6] 为:
 (22)
(22)
式中,l2为保护层开裂至裂缝宽度发展到1 mm时间段内钢筋的锈蚀速度,icor平均锈蚀电流。
由文献 [7] 可知:
 (23)
(23)
式中,w/c为水灰比。
因此,混凝土保护层开裂至裂缝宽度发展到1 mm所需时间T3为:
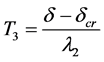 (24)
(24)
4. 工程实例
南海与东海过渡海域的某跨海大桥,跨海大桥工程路线全长26.676 km,其中跨海桥梁部分约12.455 km,工程结构材料主要采用钢筋混凝土,其设计使用年限为100年。
主要工程特点如下:
1) 耐高温腐蚀:跨海大桥建设地属亚热带海洋性季风气候,气温高,离子的活动能力较强,腐蚀介质渗透速率快。
2) 抗氯盐侵蚀:
跨海大桥所处的海域,海水中氯离子含量23.6 g/L。大桥箱梁处于大气区,会受到盐雾和除冰盐的作用。大桥的承台处于浪溅区,会经常受到海水中氯盐的侵蚀。
3) 强度要求
结构体系中主要的受力构件为箱梁和承台。箱梁是由C50的混凝土配制而成。主要用于承受弯曲应力。大桥承台主要承受压应力作用。
跨海大桥所处区域的月份平均温度如图2所示。
计算参数如表2所示。
计算的过程中分别采用氯离子与氢氧根浓度的比值Cl/OH和总氯离子占水泥或混凝土重量百分比这两种形式作为临界氯离子浓度。
以氯离子与氢氧根浓度的比值Cl/OH 作为临界氯离子浓度的寿命预测结果
工程中,通常采用下列式子作为判断钢筋脱钝的临界条件 [11] :
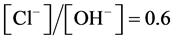 (25)
(25)
式中,混凝土中氢氧根的浓度主要取决于氧化钾、氧化钠的含量,可由下式进行计算:
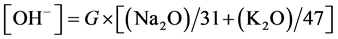 (26)
(26)
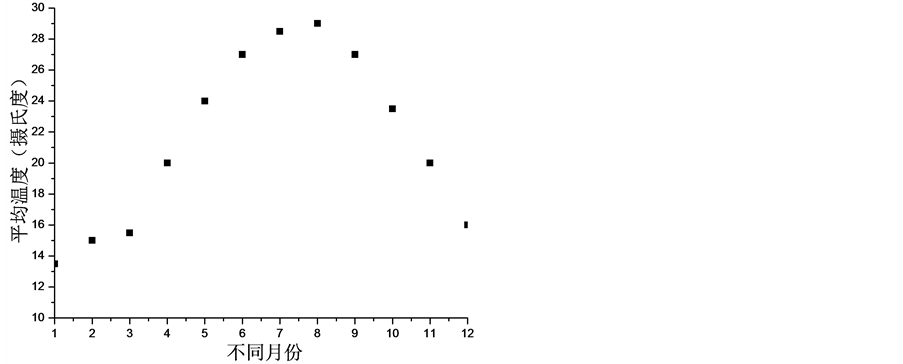
Figure 2. The average temperature of months in a year
图2. 全年月份平均温度
表2. 计算参数
式中G为每立方米混凝土中的胶凝材料用量。
具体预测结果如表3所示。
以总氯离子占水泥或混凝土重量百分比作为临界氯离子浓度的寿命预测结果
根据文献 [12] ,采用cr = 0.154%作为临界氯离子浓度,构件耐久性寿命预测结果如表4所示。
从表3和表4可以看出:
1) 以氯离子和氢氧根离子的比值作为临界氯离子浓度进行寿命预测,跨海大桥承台和主梁寿命预测值分别为139.62年和101.96年;以总氯离子占混凝土或水泥重量百分比作为临界氯离子浓度进行寿命预测,跨海大桥承台和主梁寿命预测值分别为152.92年和125.80年,均满足大桥设计基准期100年的耐久性要求。

Table 3. The durability life prediction results 1 of components
表3. 构件耐久性寿命预测结果1

Table 4. The durability life prediction results 2 of components
表4. 构件耐久性寿命预测结果2
2) 钢筋表面去钝化所需时间T1和钢筋开始锈蚀至保护层开裂所需时间T2对混凝土结构耐久性寿命T的预测起控制作用。这是因为保护层一旦开裂,会导致氧气和水分进入混凝土的速率明显加大,为钢筋的锈蚀提供了有利的条件,使钢筋的锈蚀速度迅速增加,从而导致结构的寿命大大降低。
3) 临界氯离子浓度对结构的寿命预测有着重要的影响。这主要是因为,临界氯离子浓度的选取,直接影响钢筋表面去钝化所需时间T1的计算结果。
4) 从本算例的计算结果可以看出,以氯离子和氢氧根离子的比值作为临界氯离子浓度,比用总氯离子占混凝土或水泥重量百分比作为临界氯离子浓度进行结构的寿命预测,有着更好的安全储备。这是因为以氯离子和氢氧根离子的比值作为临界氯离子浓度进行寿命预测,考虑了混凝土内部PH值的变化对钢筋锈蚀的影响。随着内部钢筋的锈蚀,混凝土内部的PH值是不断降低的,氢氧根对氯离子的抑制作用也不断的减弱,从而在一定程度上也加速了钢筋的锈蚀。
5. 结论
本文首先建立了湿热耦合环境下氯离子的输运模型;以临界氯离子浓度和钢筋锈蚀宽度作为寿命评估指标;最后以某工程实例进行预测说明,得到了如下结论:
1) 钢筋表面去钝化所需时间T1和钢筋开始锈蚀至保护层开裂所需时间T2对混凝土结构耐久性寿命T的预测起控制作用。
2) 临界氯离子浓度对结构的寿命预测有着重要的影响。并且参考本算例的计算结果,以氯离子和氢氧根离子的比值作为临界氯离子浓度,比用总氯离子占混凝土或水泥重量百分比作为临界氯离子浓度进行结构的寿命预测,有着更好的安全储备。
3) 本文建立的湿热耦合环境下氯离子的输运模型可以为相关环境下的混凝土结构耐久性寿命预测提供有益的参考。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金资助项目(50908059);黑龙江省自然科学基金资助项目(E201415);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(HEUCF160207)。