1. 引言
在中国南方红壤地区,尤其是花岗岩区,因其风化壳结构松散及降水量丰富等自然特征,土壤的抗侵蚀能力低,易受流水侵蚀,特别在坡地缺乏植被覆盖时,土壤侵蚀极为严重,生态系统出现退化,水土流失是我国最严重的生态环境问题 [1] 。一些国内外学者 [2] [3] 曾构建模型对相关区域的水土流失及水土保持做了研究,但对于水土流失可视化模拟实现较少报道,在我国目前还处于探究阶段,大部分可视化项目是基于动画制作,缺少用户实时交互式操作。Unity3D在21世纪初曾作为Web端与虚拟现实开发的引擎,近年来,Unity3D可支持Windows、IOS、Android等多系统,并成为应用广的开发引擎。有人 [4] - [11] 利用Unity3D在相关领域做了模拟研究,但在水土流失情景模拟应用方面较少报道。本文以福建西部上杭县为研究区,解决了尝试基于Unity3D的RUSLE [12] [13] 水土流失模型情景模拟。
2. 研究区简况
上杭县位于福建省西南部,龙岩市西部,汀江中游,地处北纬24˚46'~25˚28'至东经116˚16'~116˚57'之间,东接龙岩新罗区,西连武平,北倚长汀,东北毗连城,东南邻永定,西南与广东省梅州市蕉岭县接壤。全县东西宽69 km,南北长78 km,全县总面积约2879 km2 [14] ,主要为红壤区,是福建三条重要江流汀江、闽江、九龙江的主要流经之地。夏季受南海暖湿气流北上影响,暴雨、台风频发,长期以来人为过度开发,生态环境脆弱,是土壤侵蚀较为严重的区域之一,研究区位置如图1。
3. 研究方法
本文基于GIS软件开发中常用的Unity3D模块中的粒子系统和光影系统,使用WorldComposer插件与TerrainComposer插件,以研究区上杭县为例导入模拟地形,解决了实际地形在Unity3D中可视化表达的技术难点,系统尝试实现三维可视化系统情景模拟以及探讨模拟中可能出现的问题及解决方案。
3.1. Unity3D主要系统说明
3.1.1. 粒子系统主要参数及其意义
Unity3D中粒子系统模型常用于打雷、下雨、爆炸、蒸汽、燃烧等各类特效的制作,模型主要参数见表1。其原理在于赋予粒子一些属性(如表1)后不断重复绘画给予人视觉上的特效。一个完整的粒子由四部分构成,即粒子发射器、粒子播放器、粒子渲染器、粒子碰撞器。粒子发射器赋予粒子发射时具有的物理属性,播放器决定了粒子发射后的属性如运动阻尼,粒子渲染器决定了粒子的外貌形态,如图2。
表1. 粒子系统

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 2. The rainfall simulated by continuous emission of particles (a) and the rendered particle (b)
图2. 连续发射粒子模拟的雨滴图(a)和渲染后的粒子图(b)
3.1.2. 光影系统主要参数及其意义
通过Unity3D中的光影系统定义各类参数意义(如表2),并可用于气候、地形等要素的模拟。
3.2. Unity3D模拟情景的技术关键
利用Unity3D模拟情景可视化系统常出现的问题有地形与贴图如何有效对应,水土流失因子的模拟以及漫游等。本文考虑解决方案如下。
1) 地形与贴图的问题及解决
在Unity3D构建模拟地形时,需求的数据有当地的数字高程模型(Digital Elevation Model),简称DEM;当地地表遥感数据,可转换为贴图与DEM结合导入系统。而分辨率作为DEM的重要指标之一,贴图与DEM分辨率要相互对应。且Unity3D并不支持DEM直接导入作为其支持的HeightMap数据,需要将DEM数据重新解析为引擎可以直接识别的格式,将DEM转换为Tiff格式并导入DEM2Raw中,转化为Unity3D所支持的Raw格式,导入为HeightMap识别。
2) 水土流失因子模拟问题及解决
研究区是闽西水土流失较明显区域,本文选用RUSLE模型 [3] [15] 作为估算研究区年均土壤流失量的方法。需要考虑降雨(月降雨量)、土壤类型、地形(坡长坡度)、植被覆盖和管理和水土保持措施5大主要因子。降雨因子在Unity3D中以粒子方式呈现,土壤类型以地形抓力(Drag)方式呈现,地形因素由DEM导入,植被覆盖由遥感图像导入,水土保持措施由建立阻挡物进行碰撞的方式呈现。系统设计及实现见本文第4部分。
表2. 光影系统
3) 漫游问题及解决
在系统中建立第一人称摄像机作为化身人类,以空中视角观看模拟水土流失过程。为避免用户漫游时难以判断所处位置,系统中加入了用户定位小地图功能,可以帮助用户实时获取摄像机所在位置。
4. 系统设计及实现
4.1. 系统设计流程
系统设计包括需求分析、可行性分析、系统开发环境、系统功能设计以及水土流失RUSLE应用模型,技术路线流程见图3,系统结构功能见图4。关于需求分析、可行性分析、系统开发环境本文在上述已提及,下面简要说明对水土流失模型的因子选择。
4.2. 水土流失模型的因子选取
本文选用RUSLE通用水土流失模型(A) [12] [13] ,并根据研究区的特点,选取影响因子。各因子的计算简要说明如下:
1) 降雨侵蚀力因子R
R作为降雨侵蚀力因子,反映了降雨引起土壤侵蚀的潜在能力,是确定降雨量与土壤流失量之间的相互关系,本文研究对象为中国闽西地区,则参考上杭县城总体规划 [14] ,并根据周伏建等提出的适用于福建地区的简便算法 [16] ,选取中国气象站2015年上杭县降水由公式(1)计算其降水侵蚀力因子。
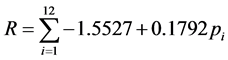 (1)
(1)
式pi中为月降雨量,本文选取中国气象站2015年上杭县降水计算其降水侵蚀力因子。
2) 土壤可侵蚀性因子K
由Sharply和Williams把土壤可侵蚀性因子K的计算方法 [17] 根据公式(2)计算,根据《遥感图像植被判读与土壤判读》重分类闽西地区土壤类型图,由参考文献 [18] [19] 得出各类土壤K值,取其表层K值赋值予上杭县土壤类型图,得到K值因子图层。
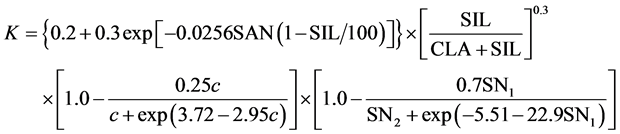 (2)
(2)
式中,SAN为砂粒含量(%),SIL为粉砂含量(%),CLA为粘粒含量(%),c为有机碳含量(%),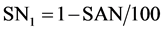 。
。
3) 坡度坡长因子LS
AML (ARC Macro Language,ARC宏命令语言)是ARC下的语言开发环境,用户可以利用Arc/Info命令语言进行在原有基础上的二次开发。本文以美国学者Hickey基于AML语言编译的LS坡度坡长因子提取语句,通过闽西地区DEM数据,在Arc/Info Workstation中得出闽西地区LS因子图层,并以闽西地区上杭县县界文件对得出的LS因子图层进行裁切。
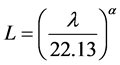 (3)
(3)
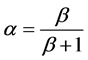 (4)
(4)
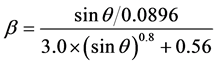 (5)
(5)
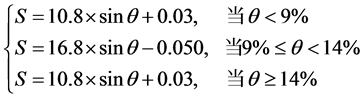 (6)
(6)
以上各式中,λ为水平坡长,α为坡长指数,θ为坡度。
4) 植被覆盖与管理因子C
植被覆盖与管理因子C为在土壤、坡度和降雨条件相同时,某一特定作物或植被情况下的土壤流失量与耕种过后连续休闲土地的土壤流失量的比值,本文采用现有文献中对植被覆盖与管理因子C的求解公式 [20] - [22] ,根据植被覆盖与管理因子和植被覆盖度之间的相互关系对C值进行求解。
① 求解植被覆盖度C [21]
本文通过ENVI分析闽西地区Landsat8 TM影像,根据公式(4) [22] 计算出统计NDVI最大值与最小值,最大值为0.530564,最小值为−0.296243,求出植被覆盖度C (如表3)。
② 解算植被覆盖与管理因子C [23]
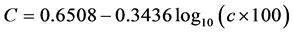 (7)
(7)
由公式(2)在ArcGIS中得出C因子的栅格图像。
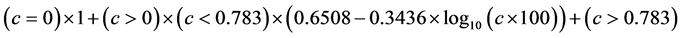 (8)
(8)
5) 水土保持措施因子P
水土保持措施因子P是指特定水土保持措施下的土壤流失量与相应未实施该措施的顺坡种植时的土壤流失量之比值 [23] 。本文通过2015年闽西Landsat8遥感影像对其进行土地利用类型监督分类,并参考现有研究 [24] 确定了不同土地利用类型的水土保持措施,总结其P值后对分类后土地利用类型图赋值,得到闽西上杭县地区P值分布栅格图像。
4.3. 土壤侵蚀程度模型构建
将以上水土流失因子栅格图像导入ArcGIS,利用栅格计算器将各个因子进行连乘,并由RUSLE模型的英制单位转为公制单位,按照《土壤侵蚀分类分级标准》 [25] 将闽西上杭县地区的水土流失情况分为6个等级,得出水土流失系列专题图,即LS因子、C因子与上杭县土壤侵蚀分布情况(如图5)。

Table 3. Normalized Differential Vegetation Index (NDVI)
表3. 归一化植被指数


 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 5. The factor LS (a) and C (b) and the soil erosion distribution of Shanghang (c)
图5. 上杭县LS因子、C因子与土壤侵蚀分布情况图示
4.4. 系统实现关键技术说明
1) 研究区模拟地形的构建
通过申请微软地图BingKey获得微软地图在Unity3D中的接口,选定坐标为的闽西地区,在Unity3D中调用WorldComposer可在微软地图的卫星图像中导出最高为19级分辨率为0.3米的遥感影像数据,高程数据为级别14级分辨率为10米数据,但在微软地图中中国闽西地区卫星遥感图像只能达到70m的分辨率。WorldComposer只有输出不带高程的卫星图像,但结合TerrainComposer可以添加高程,增加地形起伏度,添加噪声提高地形细节,在卫星图像和纹理的基础上,加上云、山体阴影等。
2) 水土流失模型的应用
根据上述RUSLE模型计算,选取上杭县旧县镇为水土流失严重区域,系统选取该地区作为主要模拟区域。
3) 空间坐标系的转换
系统将闽西地区由地理空间坐标系的绝对坐标转化为Unity3D虚拟环境的相对坐标,需要重新定义其XYZ三个方向的相对坐标值(图6(a))、旋转程度(图6(b))、缩放程度(图6(c))。本系统定义参数如表4。
5. 应用系统
本系统将地理信息数据与游戏开发相结合,解决了将实际地形导入Unity3D技术难点,使地理数据能在游戏引擎中二次开发,同时添加了复杂的天气系统,可对目标区域进行一天24小时任意时段的气候模拟,并附带多形式的地图信息,模拟效果与实际较吻合。系统实现的关键技术包括:1) 模拟地形的构建;2) 水土流失模型的应用;3) 空间坐标系转换。可视化模拟系统的实现包括1) 模拟地形漫游;2) 鹰眼效应显示;3) 水土流失模型的模拟。
5.1. 可视化应用系统实现
1) 模拟地形漫游展示
通过设定第一人称控制器各类参数(如表5),将主摄像机与控制器相绑定,在控制器移动时同时移动其摄像机。用户可实时控制控制器,从各个方向、不同距离观看水土流失过程,如图7。
表4. 地形变换式

Table 5. The first person controller
表5. 第一人称控制器参数
 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 6. The terrain position and rotation and scale
图6. 地形相对坐标值(a)、旋转程度(b)和缩放程度(c)
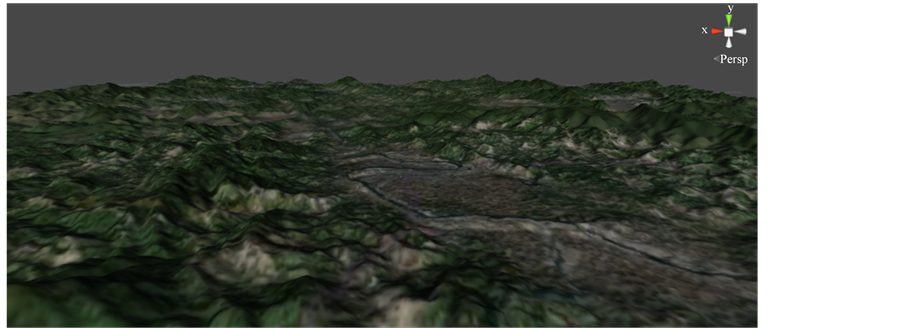
Figure 7. The virtual terrain wandering of Shanghang county
图7. 上杭县城地形漫游
2) 地图形式的鹰眼效应
系统包含三维与二维形式的地图信息,二维形式的地图以小地图的形式展现给用户。
小地图原理即在第一人称控制器中添加作为标记的子物体,以另一个摄像机作为高空摄像机作为总览,即可对第一人称控制器进行定位,并设置小地图初始缩放倍率与单次缩放值(见表6),完成小地图的制作(图8(a))。用户可以通过调用小地图,并通过放大或缩小小地图分辨率实时获取第一人称控制器所处的位置,弥补三维地图地理位置信息的显示的不足之处(图8(b))。
5.2. 水土流失应用模型及可视化
5.2.1. 降水侵蚀力因子
本文通过Unisky插件、Rainscapes插件制作闽西上杭县天气特效,通过语句调用其API,设置降雨量(等级)修正降雨强度、设置降雨覆盖等级定义积雨云覆盖面积、设置雨滴速度定义降落速度、设置大气散射半径修改天空的颜色、设置云到大气的距离修改用户的视距,设置太阳的亮度及其浓度、闪电与雷声发生频率、降雨发生的时间、降雨中心坐标,为提高近距离视觉效果,系统中加入了粒子系统辅助模拟降雨的过程,粒子具有初始发射速度与衰减时间,可用于控制雨量的大小,如图9。
实现图9的脚本关键语句如下:
void Awake() {
uniSky = GameObject.Find(UniSkyAPI).GetComponent(UniSkyAPUniSI) as kyAPI;//调用API
uniSky.SetStormLevel(float stormLevel,floatsfxLevel); //降雨等级
uniSky.LerpCloudCover(float cloudCover, float milliseconds);//循环降雨覆盖等级
uniSky.SetDropletLevel(float dropletLevel);//雨滴降落速度
uniSky.SetScatteringRadius(float scatteringRadius);//大气散射半径
uniSky.SetViewDistance(float viewDistance);//云层到大气的距离
uniSky.SetSunIntensity(float intensity);//太阳浓度
uniSky.SetLightningFrequency(float frequency);雷声频率
uniSky.LerpTime(float time, float milliseconds);//时间及流速
uniSky.SetStormCenter(Vector3 stormCenter);//降雨中心坐标
}
5.2.2. 土壤可蚀性因子
设置地形阻力模拟土壤可侵性(如表7),表现土壤对降水侵蚀的抑制作用(见图10)。
5.2.3. 坡度坡长因子
LS是地形地貌特征对土壤侵蚀影响的程度。DEM可转换为Unity3D可识别的HeightMap,将遥感影像作为贴图并修改HeightMap属性即可得到真实地形数据。最高处为梅花峰为1778 m,因此系统最高处不必高于最高峰过多,可提高加载速度。见表8和图11。
5.2.4. 措施因子
粒子可添加碰撞特性,将雨点与植被进行碰撞(如表9)。此处定义了粒子的碰撞抑制,使雨点碰撞后一定时间内消失;粒子反弹,实现雨点与植被碰撞后以一定角度反弹;粒子生命周期损耗,一定碰撞次数后生成新的粒子;粒子碰撞范围,使粒子与所有具有碰撞特性的物体碰撞。
综上,可实现措施因子的模拟——雨滴碰到植被能够受其影响,在树下时落下的雨点更少。模拟效果如图12。

Table 6. The parameters of mini map
表6. 小地图参数
表7. 地形详细参数
表8. 地形参数
表9. 粒子碰撞参数
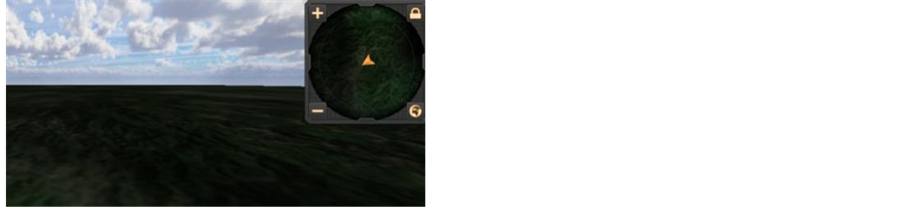
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 8. The mini map (a) and map zooming (b)
图8. 小地图(a)和小地图缩放(b)


 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 9. The nocturnal precipitation (a) and morning precipitation and the evening precipitation
图9. 模拟夜间降水(a)、晨间降水(b)以及傍晚降水

Figure 10. The erosion resistance of the soil
图10. 土壤对降雨的抗侵蚀性
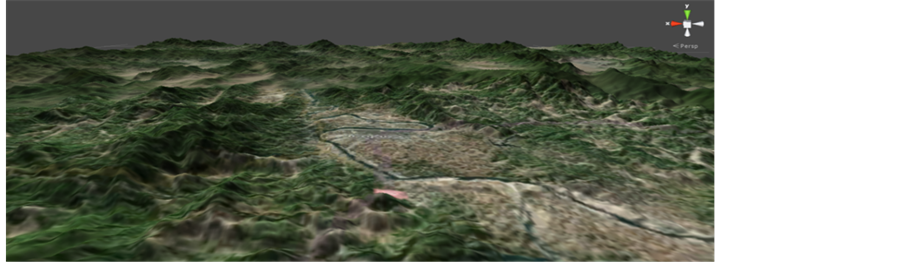
Figure 11. Simulation terrain at the Shanghang county
图11. 上杭县地形模拟

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 12. Collision between particle and trees (a) and less particle falls under the tree (b)
图12. 粒子与树碰撞(a)和树下落下的粒子较少(b)
6. 结论
本文以研究区典型水土流失区域为例,实现基于Unity3D的RUSLE水土流失情景模拟系统。以Unity3D开发的水土流失可视化系统,在实现其“可视”的同时,增加了用户一定的“可控”性。但在具体应用时,对于计算机性能要求较高,尤其是平面缩略地图的载入需要16 G以上的内存,所以优化缩略图的贴图分辨率,降低内存占用率,保证低配置环境运行,则在今后要进一步研究。总之本文在虚拟可视化技术方面做了有益探讨,研究结果对上杭县水土保持研究有一定的实用价值,对我国南方红壤侵蚀区保护也有一定的参考意义。
基金项目
福建省自然科学基金(2014J01149),福建省公益类重点项目基金(2013R02)。
*通讯作者。