1. 引言
近些年以来,随着我国工业化进程的加快,经济持续高速增长,汽车数量突飞猛进,石油、化工、冶金等行业都得到了长足发展,但是环境问题却越来越严重,波及范围越来越广 [1] ,持续时间越来越长。京津冀地区由于聚集了大量的水泥、钢铁、炼油石化等高污染产业和遍布各地的无组织零散高危害产业,产生大量大气污染物 [2] ,是目前我国大气污染较严重的地区之一。尤其是像北京这样的超大型城市,因经济发展迅速,人口众多,而且周边多是一些如:石家庄、唐山、保定、廊坊、邢台、衡水、邯郸等工业型城市,这些城市在拉动经济增长的同时,不可避免的会向空气中排放一些大气污染物。由于大气污染物受到天气因素的影响,诸如:温度、湿度、空气气流流速等 [3] ,在这些因素的作用下大气污染物会发生扩散,所以北京周边工业城市,如石家庄等地区排放的大气污染物在一定程度上也会影响北京地区的空气质量。因为大气污染物具有区域扩散性 [4] ,因此从城市区域(指城市群,非单独城市)角度 [5] ,研究北京周边城市大气污染物对北京空气质量的影响,对于分析北京地区大气污染物的来源,控制周边城市大气污染物向北京扩散和进一步改善北京地区空气质量具有一定的意义,也有助于为北京及其周边地区大气污染的控制和治理提供科学依据。
2. 对北京市及石家庄市AQI的分析
由图1可以看出,北京地区在2013年11月1日至2014年5月1日和2014年10月1日至2015年2月1日这两个时间段中的AQI指数变化幅度较大。在这两个时间段中大气污染较为严重,其中严重污染(AQI > 300)天数为17天,占所有严重污染天数(18天)的94.4%;重度污染(300A ≥ QI ≥ 201)天数为35天,占所有重度污染天数(43天)的81.4%;空气质量优良(100 ≥ AQI ≥ 0)天数为87天,占所有优良天数(251天)的34.7%。在2014年5月1日至2014年10月1日这段时间中,AQI指数相对较低且变化较为平缓。在此时间段内空气质量总体较好,其中严重污染天数为0天;重度污染天数为5天,占所有重度污染天数的11.6%;空气质量优良天数为89天,占所有优良天数的35.6%。
从图2中的AQI地变化趋势可以得知,石家庄地区在2013年12月1日至2014年5月1日和2014年10月1日至2015年1月1日这两个时间段中的AQI指数变化幅度较大,而且在这两个时间段中空气质量都较差,严重污染天数为53天,占所有严重污染天数(61天)的86.9%;重度污染天数为56天,占
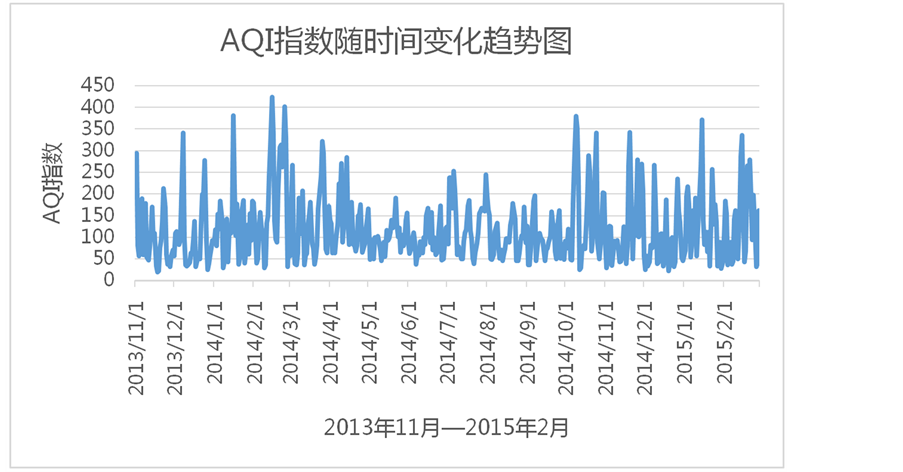
Figure 1. Analysis on air quality of Beijing from November 1, 2013 to February 28, 2015 (AQI: Air quality index)
图1. 北京市2013年11月1日至2015年2月28日的空气质量分析(AQI:空气质量指数)
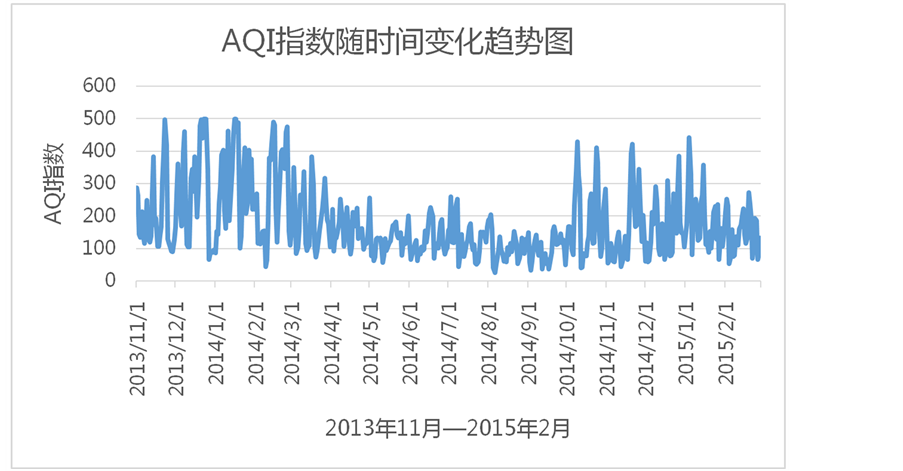
Figure 2. Analysis on air quality of Shijiazhuang from November 1, 2013 to February 28, 2015 (AQI: Air quality index)
图2. 石家庄市2013年11月1日至2015年2月28日的空气质量分析(AQI:空气质量指数)
所有重度污染天数(85天)的65.9%;优良天数为46天,占总优良天数(121天)的38%。在2014年5月1日至2014年10月1日这个时间段中AQI指数变化幅度较小,空气质量也相对较好,其中严重污染天数为0天;重度污染天数为9天,占所有重度污染天数的14.8%;优良天数为77天,占所有优良天数的63.6%。
对北京地区和石家庄地区的AQI指数进行线性拟合,拟合后的方程为:Y = 0.91613X + 66.01468 (令北京市AQI指数为Y,石家庄AQI指数为X)相关系数R(Y − X) = 0.42433;由线性拟合方程可知,两地的AQI指数存在着正相关关系,相关系数R(Y − X)为0.42433,所以两者之间存在着较强的相关性。
通过对两地的AQI数据进行分析,发现北京地区和石家庄地区的AQI变化趋势相似。AQI值出现较大波动的时间段近乎一致,而且同一范围空气质量指数所对应天数占总天数的比例也近似。对这些数据的分析表明,两地的空气质量不是相互独立的,即:北京地区和石家庄地区的空气质量在一定程度上会相互作用,相互影响,而且由于石家庄地区的AQI值远大于同时期北京地区的AQI值,所以石家庄地区大气污染物对北京地区的影响要大于北京地区大气污染物对石家庄地区空气质量的影响。
3. 北京和石家庄不同月份大气污染物的月平均值
3.1. 北京与石家庄污染物月均浓度随时间变化
为了分析各类大气污染物的变化规律,在图3~图7 (S:石家庄市、B:北京市)中分别给出2013年
11月~2015年2月北京地区和石家庄地区各类大气污染物(PM2.5, PM10, CO, NO2, SO2)浓度的月平均值随时间变化图像。通过图像容易发现,在这些大气污染物中PM2.5浓度的月平均值逐月变化一般表现为,在冬季(12、1、2月)达到一年中的峰值,夏季(6、7、8月)达到一年中的最低值;除此特征以外,也有月平均浓度在夏季突然增大的情况,如2014年7月北京市的PM2.5浓度为89 µg/m3,与同一季节中的其他月份相比偏高,比6月份增长64.8%,比7月份增长43.5%。PM10浓度的月平均值变化与PM2.5基本相似,但是与同一时期其他污染物(PM2.5、CO、NO2、SO2)的浓度相比,PM10在同时期的浓度值却远远高于其他污染物,例如:石家庄地区PM10月均浓度最大值为401 µg/m3,而PM2.5、CO、NO2、SO2的月均浓度最大值分别为237 µg/m3、3.49 µg/m3、90 µg/m3、173 µg/m3,北京地区PM10月均浓度最大值为155 µg/m3,而PM2.5、CO、NO2、SO2的月均浓度最大值分别为148 µg/m3、2.16 µg/m3、68 µg/m3、56 µg/m3。这种现象说明,像PM2.5、CO、NO2、SO2这样的大气污染物对PM10的形成有着重要促进作用,这些大气污染物是PM10形成的重要前提物质。北京地区和石家庄地区的PM10月平均浓度在2013年11月至2015年2月这16个月中都维持在较高水平,说明PM10一旦形成极难分解和扩散,会长期存在于形成地区,造成严重危害。CO和SO2的月平均浓度也是在冬季达到一年中的最大值,在夏季达到一年中的最小值。NO2的月平均浓度虽然大体上
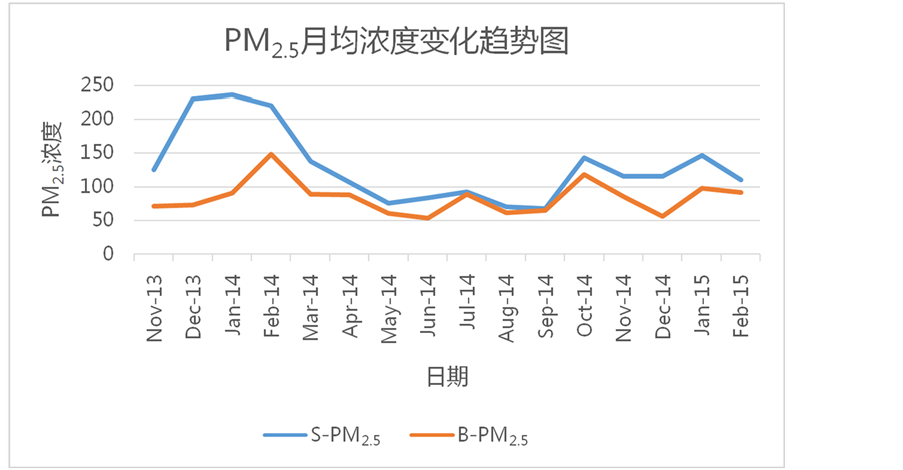
Figure 3. The change trend chart of PM2.5 monthly average concentration
图3. PM2.5月均浓度变化趋势图
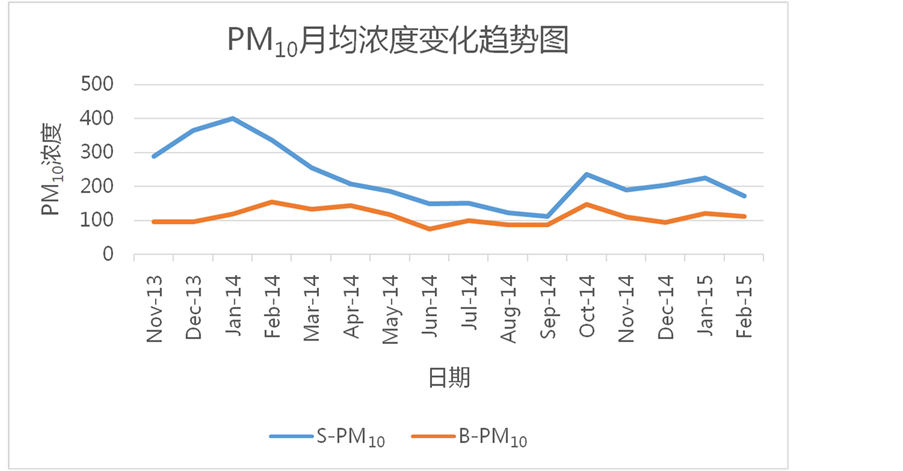
Figure 4. The change trend chart of PM10 monthly average concentration
图4. PM10月均浓度变化趋势
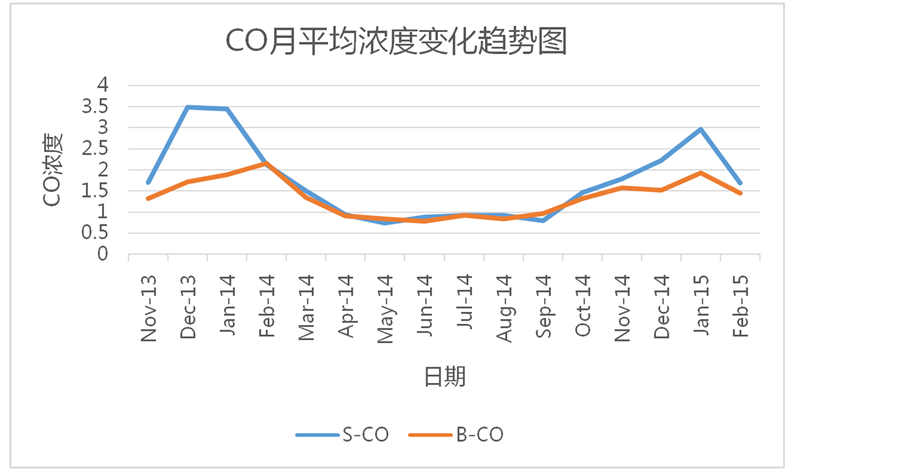
Figure 5. The change trend chart of CO monthly average concentration
图5. CO月均浓度变化趋势图
和其他污染物的变化趋势类似,但是其波动性较大,如北京市NO2月均浓度在2014年12月为53 µg/m3,而在2014年11月和2015年1月却分别达到了64 µg/m3和66 µg/m3,同比增长了20.8%和24.5%。
通过对2013年11月~2015年2月两地PM2.5、PM10、CO、NO2、SO2月平均浓度随时间变化图像的观察可以发现,各类污染物在冬春季污染最为严重,秋季次之,而夏季相对较轻,污染物浓度变化呈现出明显的“V”型规律 [6] 。冬季污染高峰期过后,往往伴随着春季污染的次高,呈现出明显的过程性。北京地区和石家地区各类污染物的月平均浓度几乎都在相同的季节达到最大值和最小值,但是北京地区各类污染物月平均浓度达到最大值和最小值的时间较石家庄地区晚1~2个月。在比较污染物变化趋势后
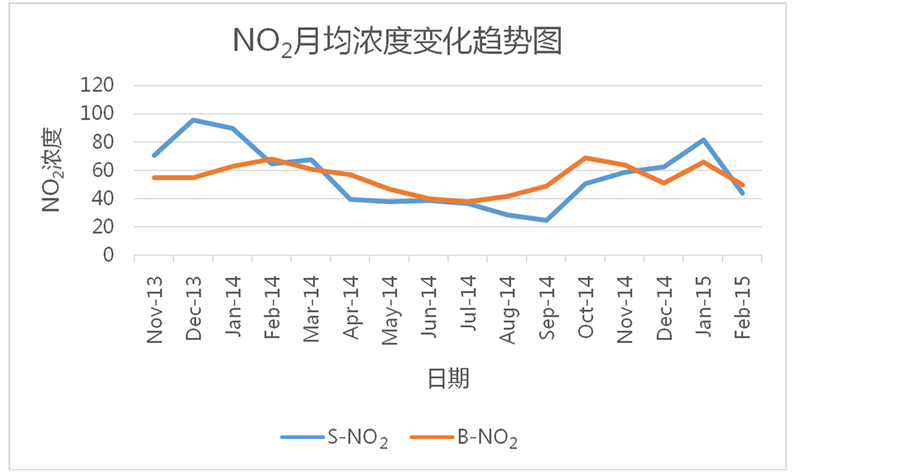
Figure 6. The change trend chart of NO2 monthly average concentration
图6. NO2月均浓度变化趋势图
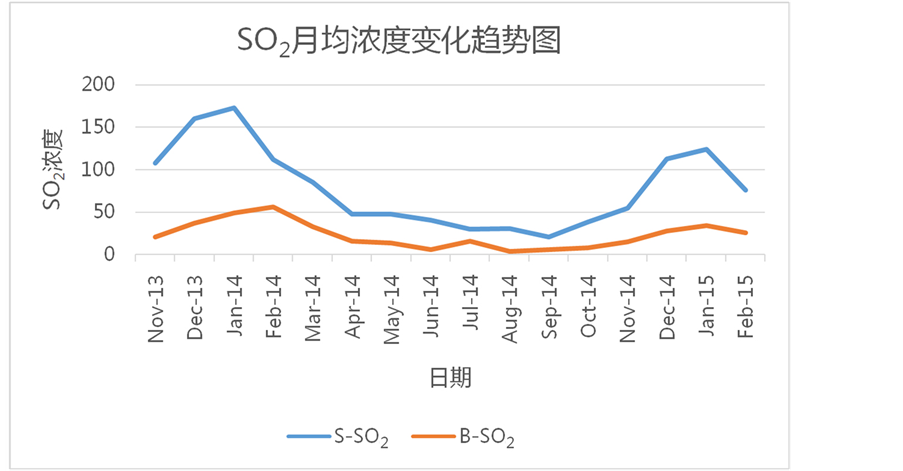
Figure 7. The change trend chart of SO2 monthly average concentration
图7. SO2月均浓度变化趋势图
会发现,石家庄地区污染物月平均浓度的波动较北京地区更为平缓,且各类污染物浓度都较同时期的北京地区偏高。这些现象表明,石家庄地区的大气污染物在扩散到北京地区的过程中会有一定程度的减弱,而且北京地区的各类污染物不仅仅受到本地区污染物排放和石家庄地区各类污染物扩散的影响,同时也可能会受到其他周边城市(如:唐山、廊坊、邢台、衡水、邯郸)大气污染物扩散的影响。
3.2. 北京与石家庄大气污染物的相关性分析
对北京地区和石家庄地区的各类大气污染物进行相关性分析发现,两地相同污染物之间的相关性有较大差别。首先,依次对北京和石家庄地区的PM2.5、PM10、CO、NO2、SO2月平均浓度进行线性拟合(石家庄各类污染物浓度为Y,北京相应各类污染物浓度为X),PM2.5拟合后的方程为Y = 1.26653X + 24.27638,相关系数R = 0.26338;PM10拟合的方程为Y = 1.52935X + 54.21856,相关系数R = 0.1171;CO拟合的方程为Y = 1.79905X − 0.70211,相关系数R = 0.71724;NO2拟合的方程为Y = 1.3357X − 16.96282,相关系数R = 0.33947;SO2拟合方程为Y = 2.6232X + 18.85709,相关系数R = 0.70991。把拟合后的方程和相关系数进一步比较可以得到,北京地区的大气污染物月平均浓度值与石家庄地区相应大气污染物月平均浓度值都呈现出显著正相关关系,但是也容易看出两地的CO之间和SO2之间的拟合度更高,相关性更强,PM2.5之间和NO2之间相关性次之,PM10之间的相关性最弱。
这一分析结果在图3~图5中也有所体现。北京市PM2.5在2014年2月达到最大值148 µg/m3,比同时期石家庄地区的PM2.5月平均浓度值221 µg/m3低49%;在2014年6月达到最小值54 µg/m3,比同时期石家庄地区的月平均浓度值84 µg/m3低56%;石家庄地区PM2.5的月平均浓度值在2014年1月达到最大值238 µg/m3,而北京市同时期浓度值为91 µg/m3,与石家庄地区相比低162%,在2014年9月PM2.5月平均浓度达到最小值为68 µg/m3,比同时期北京市的65 µg/m3高4.6%。通过数据分析发现,两地区PM2.5月均浓度变化趋势大体相似,但是北京地区PM2.5月平均浓度最大值和最小值出现的时间与石家庄地区有1~2个月的时间延迟。
北京地区PM10月平均浓度与石家庄地区PM10的相关性最差。从图中可以看到,两地的PM10月平均浓度变化与PM2.5十分相似。两地PM2.5和PM10月均浓度值出现最大值和最小值的时间都有一定的时间间隔,同时也发现两地PM10之间的月均浓度值相关性较差,而且浓度值相比于其他污染物偏高,这种现象也说明PM10不易于扩散,即:PM10会长期出现在形成地域,而不容易随着气象条件的变化扩散到其他地方,所以石家庄地区的PM10对北京地区的影响并不十分显著。
北京与石家庄地区CO之间、SO2之间的月平均浓度相关性较好。这是因为两地的CO和SO2月平均浓度的最大值和最小值几乎出现在同一时间段,而且同一时间段的月平均浓度值之间相差较小。如:北京地区CO月平均浓度值在2014年2月达到最大值2.16 µg/m3,同时期石家庄地区为2.12 µg/m3,相比于北京地区低1.9%;北京地区CO月平均浓度值在2014年6月达到最低值0.79 µg/m3,同期石家庄地区为0.88 µg/m3,比北京地区要高10.2%。石家庄地区CO月平均浓度值在2013年12月达到最大值3.49µg/m3,同期北京地区为1.73 µg/m3,相比于石家庄地区要低101%;石家庄地区CO月平均浓度值在2014年5月达到最小值0.74 µg/m3,同期北京地区为0.84 µg/m3,相比于石家庄地区高11.9%。北京地区SO2月平均浓度值在2014年2月达到最大值为56 µg/m3,石家庄地区同期浓度值为173 µg/m3,比北京地区高出209%;北京地区SO2月平均浓度值在2014年9月达到最小值为6 µg/m3,同期石家庄市浓度值为22 µg/m3,比北京市高267%;石家庄地区S02月平均浓度值在2014年1月达到最大值为173 µg/m3,比同时期的北京地区高253%,在2014年9月达到最小值22 µg/m3比同期的北京地区高267%。尽管两地的CO、SO2月平均浓度之间有较好的相关性,但是各自月平均浓度达到最大值和最小值的时间仍有一定的间隔,并不能完全同期达到最大值和最小值。
4. 结论
通过数据的分析可知,石家庄地区CO、SO2对北京地区的空气质量影响较为严重,PM2.5、NO2影响次之,PM10影响最小。两地区的各类污染物月均浓度达到最大值和最小值的时间有一定的间隔,这是因为受到气象条件、地理位置的影响使石家庄地区产生的大气污染物在向北京地区扩散时会延缓并减弱,因此虽然石家庄地区污染物浓度对同时期北京地区空气质量影响不大,但是却会严重影响到以后的1~2个月时间内北京地区各类污染物的浓度变化。所以当周边城市发生大规模空气污染时北京地区的相关部门一定要采取各项有效措施,如人工降雨等,尽可能减弱周边地区大气污染带来的滞后影响,最大限度的减轻北京地区空气污染程度。
但是这些措施并不能根治北京地区大气污染问题,因为京津冀地区区域产业结构失衡,电力、钢铁、建筑材料和交通运输需求旺盛,造成燃煤和燃油污染物的排放大大超过了区域大气负荷,加之北京北部山区和南部平原构成的“马蹄形”山谷使得北京南面的城市 [7] ,诸如:石家庄、天津等,产生的大气污染物借助一定的气象条件输送到北京地区并聚集而产生严重污染。因此要想彻底有效的改善北京地区空气质量就不能仅仅采取一些暂时性的措施,更要推动当地产业转型升级,企业技术改造,能源结构调整,建立区域协作机制统筹区域环境治理 [8] 。在将北京地区的诸如:钢铁、水泥等高能耗、高排放企业迁至周边地区,完善城市公共交通体系的同时,更需要采取专门针对周边环境的联动治理措施,如:控制周边地区工业燃煤及加强高排放车辆的管理和淘汰 [9] ,以消减周边源排放,这些措施的采取都可以有效改善北京地区大气污染状况。