1. 引言
山洪泥石流灾害是黄土高原最严重、最频繁的地质灾害之一,它爆发突然,来势凶猛而迅速,破坏力强。通过对陕北黄土高原山洪泥石流特征和机理的研究,结合现场调查、模拟实验及数值模拟分析等手段,探索黄土高原山洪泥石流的特征、发生及运动机理,通过相应的水文模拟和临界降雨量的阈值确定,以期对陕北黄土高原山洪泥石流气象预警区划方法进行探索,为今后有效减少山洪泥石流灾害损失提供可靠的科学依据。
黄土高原的地貌,可粗略地划分为塬面和沟道两大部分。塬面地形平缓,多以种植农作物为主,已基本不发生土壤侵蚀,其径流主要通过道路、胡同汇集进入沟道。沟道部分地形复杂,利用方式多样,是山洪泥石流的多发区域 [1] [2] 。沟道由于其所处地质地貌基础和环境气候状况的不同而各具发育特点,每一条沟道都有其产生、发展和变化的规律。同时产生的两条沟道,会因侵蚀强度的不同而处于不同的发育阶段,处于同一发育阶段的沟道也会因地质地貌基础的不同而具有不同的沟道形态。这些都使该区域山洪泥石流灾害的发育具有一定的复杂性。
由于地质灾害现象本身的危险性和复杂性,所以地质灾害预报模型不仅要合理可靠,还需简单明了、易于实现,并且应以实际应用效果为准则。尽管国内外的学者在地质灾害预报方法上已经做了大量的研究工作 [3] [4] ,从指标判据法、概率统计法到人工智能方法等各有所长,但现有的气象预警理论方法尚不成熟,大多数的地质灾害预报模型都是针对某一特定的沟道或单个灾害的 [5] - [9] ,不具有普遍适用性。
本研究以地处黄土高原南部渭北黄土残塬区的陕西黄陵县为典型代表,在广泛收集前人资料的基础上,通过详细的野外地质灾害调查,确定了黄陵县现有灾害隐患点,并统计分析其时空分布规律。在对该区地质灾害发育规律进行分析的基础上,结合降雨资料,做出黄土残塬区地质灾害气象预警区划,并在陕西省黄陵县进行了初步检验。
2. 山洪泥石流发育的规律及气象预警区划方法
2.1. 山洪泥石流发育的规律
山洪泥石流多分布于中低山区,沟谷发育,流水侵蚀作用、季节冻融作用较为普遍;降水较丰富,多暴雨区和多雨区;第四季松散堆积物较发育;山洪泥石流也多发生于人类工程活动强烈的地方,容易受开矿、修路等人类活动对地质环境的影响,大量的人类工程降低了水土的抗冲蚀能力,易形成松散堆积物。山洪泥石流的暴发主要受连续降雨、暴雨的激发,发生的时间规律通常与集中降雨时间规律相一致,具有明显的季节性,一般发生在多雨的夏秋季节;山洪泥石流灾害受暴雨、洪水、地震的影响,且与它们的活动周期相一致。当暴雨、洪水两者的活动周期相叠加时,常形成山洪泥石流活动的一个高潮。
2.2. 山洪泥石流成灾机理
山洪泥石流的形成有三个基本条件:地形地貌条件、松散物质来源条件和水源条件。首先,在地形上沟谷深度较大,流域形状便于水流汇集。上游汇集区的地形多为三面环山,一面出口为瓢状或漏斗状;中游流通区的地形多为狭窄陡深的峡谷,谷床纵坡较大;下游堆积区的地形多为开阔平坦的山前平原或河谷阶地。其次,还需要有足够的松散物质来源,因此山洪泥石流常发生于新构造活动强烈、地震烈度较高的地方。地表岩石破碎,发育崩塌等不良地质灾害;岩层结构松软,易发生风化、节理;人类工程活动导致水土流失严重,都为山洪泥石流提供了物质来源。暴雨、冰雪融化等的突发或连续性冲刷,是山洪泥石流灾害的激发条件,同时也是泥沙石块的动力来源。具备这三个条件,达到一定程度时就能启动山洪泥石流。
2.3. 山洪泥石流时空分布与降雨的关系
山洪泥石流的发生是许多因素的组合,但降雨是诱发山洪泥石流的最主要、最直接的因素。据突发性山洪泥石流的分类统计,发现持续降雨诱发者占其总发生量的65%,其中的局地暴雨诱发约占总发生量的66% [10] 。可见2/3的突发性山洪泥石流是由于大气降雨直接诱发的或与气象因素相关的,这也说明降雨是山洪泥石流的主要诱发原因。
基于国内外研究成果,由降雨引发的山洪泥石流大概可以分为以下3种类型 [11] :
(1) 当日大降雨型:前期累计雨量不大,持续时间也不长,只要当时有足够大的强降雨,山洪泥石流就可能发生。大量的研究表明,当日大降雨与山洪泥石流的关系最为密切。(2) 持续降雨型:前期降雨持续时间长,已经使下垫面饱和,山洪泥石流易发地带变得很脆弱。对于这种类型,持续降雨天数是很重要的因子。(3) 前期降雨型:灾害发生前的降雨不一定持续,但前期的累计雨量大,也会使下垫面饱和,山洪泥石流易发地带变得很脆弱,即使当日雨量不一定很大,同样会激发滑坡、崩塌和泥石流等地质灾害。对于这种类型,有效(实效)降雨量是重要因子。
我国的山洪泥石流具有很大的空间差异性。泥石流灾害发生强烈的地区都是暴雨频发、降雨丰沛的地区。一般来说暴雨的覆盖范围差别较大,从几百平方公里以上到几平方公里之间都有覆盖,泥石流、滑坡的发生具有更强的局地性,一般都是小范围的局部灾害,水平尺度一般不超过千米。因此,在用降雨量做山洪泥石流预报时,要充分考虑降雨范围与山洪泥石流范围之间的尺度差异,精细的山洪泥石流预报必须建立在丰富及时的地学因子实时观测资料和精细的降雨预报的基础上。
2.4. 山洪泥石流灾害气象预报模型
山洪泥石流灾害预报通常是将山洪泥石流灾害预报简化为降雨量与山洪泥石流灾害发生(如阈值雨量)的简单判别关系,从而便于运作和实施预报分析。我们假定在同一个预警区内,发生山洪泥石流灾害的其它潜在条件都相似,降雨量成为唯一的决定因素。这样就可以根据各区内的降雨量与山洪泥石流灾害发生之间的统计关系建立分区预报方程。为了解决预警区山洪泥石流灾害的预报问题,我们挑选出预警区内附近有雨量测量站的地质灾害发生地,并对相应的降雨资料进行整理,图1是黄陵县境内六个气象站点(阿党、店头、隆坊、太贤、田庄、腰坪) 2008至2009年度的月平均降雨量,可以看出黄陵县6~9月份降雨量达到年内的最大值,因此,6~9月份是地质灾害预报的重点时段。然后通过统计历史记录中地质灾害过程与前期降雨的关系,建立气象预报模型。
模型采用有效降雨量、当日降雨量2个指标。用有效降雨量综合表示前期降雨特征 [12] 。有效降雨量计算式为:
 (1)
(1)
式中: ——有效雨量;
——有效雨量; ——预报当日雨量;
——预报当日雨量;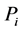 ——从灾害发生当日的前
——从灾害发生当日的前 算起的第
算起的第 (灾害发生当日
(灾害发生当日 ,灾害发生前1 d,
,灾害发生前1 d, ,前2 d,
,前2 d,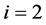 )的雨量;
)的雨量; ——前
——前 日的影响系数。通过优化方法求得
日的影响系数。通过优化方法求得 值为0.75。
值为0.75。
2.5. 临界降雨量确定
预报临界降雨量的确定需要对大量的样本进行统计分析,样本需要满足两个条件:(1) 样本数量能满足要求;(2) 各样本灾害发生时与其对应的降雨资料需要有详细的记录。本项目与陕西省气象局进行合作研究,以陕北黄土高原有详细记录的28个雨量站(见表1)及山洪泥石流等灾害的详细资料为样本进行分析研究,结合流域水文模型对流域水文过程进行模拟 [13] ,建立降雨和径流之间的数值模型,在此基础上,利用3S技术,对山洪泥石流致灾效应进行评估,进而确定预警降雨临界值。
研究结果表明:
(1) 在1984~2009年中,陕北黄土高原共出现P1h ≥ 10 mm的强降水2638时次,P1h≥20mm强降水574时次,年平均P1h ≥ 10 mm的强降水有106时次,P1h ≥ 20 mm强降水有23时次。
(2) P1h ≥ 10 mm发生时次最多的年份是1994年,为173时次;最少的是1980年,仅有36时次。P1h ≥ 20 mm强降水发生次数最多的年份是1994年,为56时次;最少的是1982年,仅有3时次。可见陕北强降水出现时次的年际差异较大,最多年份与最少年份相差十几倍之多。
(3) P1h ≥ 10 mm强降水旬分布具有多峰值的特点。7月中旬、7月下旬和8月上旬为第一高峰值,在数值比较接近也是全年的最大峰值;8月下旬为全年的次峰值,6月上旬为全年的第三峰值。P1h ≥ 20 mm单峰特征较明显,8月上旬为其高峰值,8月上旬之前,强降水频次缓升后,强降水的频次突然降低、减少。
(4) 淋雨(连绵雨)主要出现在9月,10月份也有淋雨和大雨发生。
(5) 黄陵县大雨日年频次为4次左右。
对比分析本区降水特征和地质灾害发生的关系,可以确定地质灾害气象预警的临界降雨量。预警的临界降雨量特征值分别是:
(1) 日降雨量 ≥ 50 mm (P24h ≥ 50 mm);
(2) 6小时降雨量 ≥ 25 mm (P6h ≥ 25 mm);

Figure 1. Distribution of monthly average rainfall during the year
图1. 月平均降雨量年内分布

Table 1. Information about the observation stations in north Shaanxi Province in the Loess Plateau
表1. 陕北黄土高原区测站
(3) 1小时降雨量 ≥ 20 mm或3小时降雨量 ≥ 25 mm并且日降雨量 ≥ 30 mm (P1h ≥ 20 mm或P3h ≥ 25 mm且P24h ≥ 30 mm);
符合以上条件之一就应该进行山洪泥石流灾害预警。
2.6. 气象预警的流程
山洪泥石流气象预警业务工作在每年的汛期4~9月每日进行。预警的基本流程为:实时资料处理、预警模型计算、图形结果显示、产品制作发布。图2是主体数据处理和预警计算过程示意图。
每日下午由气象台负责提供最新5 d累积降雨量实况数据、24 h降雨量预报数据,并制作成降雨量等值线图。环境监测部门从气象台专用服务器上读取雨量数据及图形资料,并在预警地理信息系统中与地质灾害易发分区图进行叠加分析,根据气象预警指标和判别标准,自动进行地质灾害预警等级计算,并生成山洪泥石流气象预警等级分布图(填色等值线图)。当出现较大范围三级以上山洪泥石流气象预警情况,一般由国土和气象两部门专家会商确定。
3. 研究区域及数据
本项研究以地处黄土高原南部渭北黄土残塬区的陕西黄陵县为典型代表。黄陵县地处西北内陆,E109˚27'58''~E108˚29'31'',N35˚17'49''~N35˚51'56'',属中温带大陆性季风气候区,四季分明,干旱少雨,雨量分布不均。根据黄陵县气象站多年观测资料,境内气温自西向东逐渐增高,多年平均气温9.4℃,极端气温最高36.5℃,最低−21.4℃。黄陵县多年平均降水量588.1 mm,受地形地貌、森林植被的影响,区内降水量地域分布差异较大,自西向东逐渐递减。黄陵县降水量年际变化明显,旱涝灾害时有发生,降水量年内分配也极不均匀,夏季降水集中,占全年降水量的51%,秋季占25%,春季占18%,冬季仅占6%。每年自四月份开始,降水量迅速增加,7、8、9三个月相对多雨,12月至下一年1、2月份降水量则显著偏少,降水形式多为暴雨和连阴雨。这是区内滑坡、崩塌、泥石流及地面塌陷、地裂缝等地质灾害形成的主要诱发因素之一,因此,区内绝大多数地质灾害多集中在夏秋两季发生 [14] 。
本文使用的基础资料由中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心提供,这部分资料分为基本历史资料、分县调查历史资料及SPOT-5卫星遥感资料。地质灾害资料主要根据遥感解译结果实地调查获得。其他地质资料取自黄陵县地质环境站。

Figure 2. Schematic diagram of early warning calculation
图2. 预警计算过程示意图
4. 结果与分析
4.1. 地质灾害气象预警级别
中国地质灾害气象预报预警分为5个等级 [15] 。参考陕西省地质灾害气象预报预警分级划分,结合调查区实际情况,将预警级别也划分为五级:
I级,预警是低级预警,地质灾害发生可能性很小,不发布预报;
II级,预警是低级预警,地质灾害发生可能性较小,为地质灾害注意级;
III级,预警是低级预警,地质灾害发生可能性较大,为地质灾害发布预报级;
IV级,预警是中级预警,地质灾害发生可能性大,为地质灾害发布预警级;
V级,预警是高级预警,地质灾害发生可能性很大,为地质灾害发布警报级。
发布地质灾害预警按以下原则考虑:
1~2级不发布预报;3级发布预报,用黄色表示;4级发布预警,用橙色表示;5级发布警报,用红色表示;假设降雨类型为当日大降雨型(前期累计雨量不大,持续时间也不长),公式(1)可以有以下三种情况:
(1) ;
;
(2)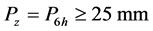 ;
;
(3)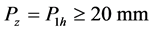 或
或 且
且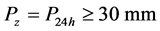 。
。
结合地质灾害易发程度分区图,初步确定各地质灾害易发区各级预警等级判别标准(见表2):
4.2. 山洪泥石流灾害气象预警区划
(一) 日降雨量 ≥ 50 mm预警区划
本降雨量级别在预警气象中相对降雨强度为最小(图3)。
1) I级预警区的范围最大,限于西部沮河流域,主要为西部双龙镇和腰坪乡的大部分区域,以及东部的一些塬面区域(图中白色)。总面积1536.00 km2,占调查区总面积的67.1%。这些地区位居沮河干、支流,河谷深切;以及较长支流的上游,沟谷强烈下切地带,植被茂盛,人类工程活动不强烈,为调查区的地质灾害极不发育区。
2) II级预警区的范围达到较大,主要分布在调查区东部沮河、淤泥河及葫芦河流域(图中浅灰色),面积535.86 km2,占调查区总面积的23.40%。
这一区域大多为次级支沟黄土残塬地区,主要沟谷多处于中游,人类工程活动较强烈,地质灾害发育强度稍低。
3) III级预警区的范围较小,分布于调查区东部沮河及寇家河流域(图中深灰色),面积218.45 km2,占调查区总面积的9.5%。这里沟谷密布,人类工程活动强烈,为地质灾害发育区。

Table 2. Geo-hazards early warning indicators and early warning grade criterion
表2. 地质灾害各易发区气象预警指标及预警等级判别标准
注:表中的符号“I”、“II”、“III”、“IV”、“V”即为上述的五个地质灾害气象预警等级。

Figure 3. The map of daily rainfall ≥ 50 mm
图3. 日降雨量 ≥ 50 mm预警区划图
(二) 6小时降雨量 ≥ 25 mm预警区划
本降雨量级别在预警气象中相对降雨强度为中等(图4)。
1) I级预警区的范围较前有所减少。除东部淤泥河流域少量塬面区域外,占据西部沮河流域大部分地区(图中白色)。总面积1512.22 km2,占调查区总面积的66.0%。植被茂盛,为调查区地质灾害极不发育区。
2) II级预警区的范围较前有所减少。主要分布在调查区东部淤泥河流域(图中浅灰色)。总面积437.57 km2,占调查区总面积的19.11%。这一区域大多为淤泥河、葫芦河次级支沟黄土残塬地区,人类工程活动较强烈,地质灾害发育强度稍低。
3) III级预警区的范围较前有所增加,分布于调查区东部沮河流域(图中深灰色),面积340.52 km2,占调查区总面积的14.9%。这里沟谷密布,人类工程活动强烈,为地质灾害极发育区。
(三) 1小时降雨量 ≥ 20 mm预警区划
本降雨量级别还包括3小时降雨量 ≥ 25 mm并且日降雨量 ≥ 30 mm,在预警气象中相对降雨强度为最大(图5)。
1) I级预警区的范围缩减至最小。只为东部一些塬面区域(图中白色)。总面积41.38 km2,占调查区总面积的1.81%。为调查区地质灾害极不发育区。
2) II级预警区的范围扩展至最大。从调查区东部沮河流域全部退出,分布在西部沮河流域主干流(图中浅灰色),分布面积1369.68 km2,占调查区总面积的59.8%。这一区域为沮川河主干流上中游,沟谷切割较强烈,地质灾害发育程度较其他地区稍强。

Figure 4. The map of 6 hours precipitation ≥ 25 mm
图4. 6小时降雨量 ≥ 25 mm预警区划图
3) III级预警区的范围扩展至最大,全部分布于调查区东部(图中深灰色),面积868.23 km2,占调查区总面积的37.9%。这里沟谷密布,人类工程活动强烈,为地质灾害发育区。
5. 结论与讨论
1) 本文在完成地质灾害易发程度区划的基础上,对降雨量与山洪泥石流灾害的关系进行了统计分析,发展了基于3S基础上的地质灾害气象预警模型,通过实例验证,表明该方法合理可行、简便实用。
2) 通过对降雨量资料进行统计分析,确定地质灾害的临界雨量或触发雨量,然后根据降雨量及阈值计算灾害发生可能性的预报,并准确确定灾害等级,以便采取相应的积极有效的措施。
3) 在广泛收集前人资料的基础上,基于黄土高原28个气象站1984~2009这25年的降雨数据的基础上,通过详细的野外地质灾害调查,确定了黄陵县现有地质灾害隐患点,并统计分析其时空分布规律。在对该区地质灾害发育规律进行分析的基础上,结合降雨资料,做出山洪泥石流气象预警区划,区划结果具有典型的代表性。
4) 基于实地调查与详细分析,提炼出的一套较为准确的黄土高原山洪泥石流气象预警区划方案,经过了实际应用的检验,突破了以往研究的局部性和单一性,具有广泛的应用与推广价值。
准确的气象预报将直接影响灾害预警的准确性,关系到人民的生命财产安全。本文的灾害实例验证是以当日实况雨量代替了预报雨量,与实际预警中使用预报雨量预警准确率存在一定的差异。山洪泥石流灾害易发程度区划的精确程度将直接影响预警的效果,并且随着环境的变化,易发程度也在发生变化,

Figure 5. The map of 1 hour precipitation ≥ 20 mm
图5. 1小时降雨量 ≥ 20 mm预警区划图
所以每隔一段时间争取对易发区进行更新。地质灾害气象预警指标及其参数应根据实际情况适时调整,以提高预警的效果。
基金项目
长安大学2016年国家级大学生创新创业训练计划(201610710077);陕西省社会发展科技攻关项目(2016SF-411);中国地质调查局地质灾害详细调查项目资助(1212010640403)。