1. 引言
人脸跟踪对计算机视觉、模式识别等领域的发展具有重大的促进作用,近年来,人脸跟踪技术在电视电话会议、远程教学、监控等场合都需要对人脸目标进行实时跟踪。目前已经提出了MeanShift算法 [1] ,Camshift算法,粒子滤波 [2] 等经典算法,怎样在目标与背景颜色相似,光照变化,遮挡等条件下快速准确跟踪人脸依旧是需要解决的难题。
SOAMST算法基于Mean Shift算法,能够解决跟踪过程中不能估计目标的尺寸和方向变化问题。同时此算法利用颜色直方图特征建立模型,人脸颜色区别于其他背景颜色存在一定范围区域内,因此适用于对人脸进行跟踪,但在复杂环境下仍然存在跟踪失败问题。
本文针对背景与目标颜色相似与视频光照变化问题,提出在SOAMST算法中将二阶直方图代替颜色直方图,同时结合MBLBP特征建立目标模型,在跟踪过程中自适应调节两种特征值的权重比例。以提高跟踪的准确性。
2. SOAMST原理
SOAMST算法是Ning等 [3] [4] 在Mean Shift算法基础上提出的,针对目标尺度和方向变化问题,该算法结合权重的零阶矩和Bhattacharyya系数来估计目标尺度,并对权重图像的二阶矩进行奇异分解,最终得到跟踪目标的位置和具体大小。
2.1. 目标面积估计
通常在目标跟踪过程中连续帧之间目标的尺寸变化是连续光滑的过程,可令当前一帧候选目标的尺寸比上一帧稍微大一点;考虑到目标尺寸变化一般是连续光滑的,所以当前帧目标区域不管是变大或者变小都会在大的跟踪结果候选区域内。
如图1所示,以三种灰度组成矩形代表目标(a),在一个大于目标尺寸的候选目标区域(b)内分别存在
着小于(图c)、等于(d图)和大于(图e)真实目标尺寸的目标,并根据Mean Shift算法计算出这三个候选目标中三种灰度颜色的权重。
候选区域的像素权重代表着成为目标的可能性,因此,使用所有像素权重之和代表权重的零阶矩,来估计候选目标的真实面积,定义如下:
 (1)
(1)
式中 表示候选目标点的个数,
表示候选目标点的个数,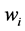 为每个点的权重。
为每个点的权重。
在最后的跟踪结果中,目标由两部分组成,真实目标和被错误判断为目标区域的背景部分。候选区域一般都大于真实目标尺寸,所以在候选模型中计算出来属于目标部分的概率密度将小于真实目标模型中的概率密度,因此由权重图像计算出的零阶矩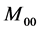 的面积也将大于真实目标面积,因此需要提高目标权重减少背景部分,以提高
的面积也将大于真实目标面积,因此需要提高目标权重减少背景部分,以提高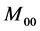 估计目标面积的可靠性。此外,
估计目标面积的可靠性。此外,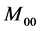 估计目标面积与真实面积差距越小,则候选模型和目标模型之间的相似度即Bhattacharyya系数越大,因此估计目标面积和具有反比例关系。估计目标实际面积可通过定义下式得到
估计目标面积与真实面积差距越小,则候选模型和目标模型之间的相似度即Bhattacharyya系数越大,因此估计目标面积和具有反比例关系。估计目标实际面积可通过定义下式得到
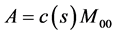 (2)
(2)
式中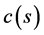 (
(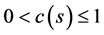 )是关于Bhattacharyya系数s的单调递增函数。当相似度很高时
)是关于Bhattacharyya系数s的单调递增函数。当相似度很高时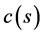 接近1,此时,权重的零阶矩便能准确的估计实际目标面积。
接近1,此时,权重的零阶矩便能准确的估计实际目标面积。
2.2. 目标尺寸和方向估计
估计出目标区域后,由矩特征通过对权值图像进行分析可以得到目标的尺寸和方向,基于权值图像可以得到下列矩特征:
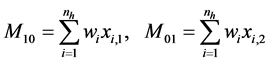 (3)
(3)
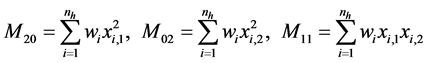 (4)
(4)
式中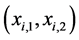 是候选区域中点的坐标。
是候选区域中点的坐标。
由式(3)、(4)可以得到实际上是一阶矩和零阶矩的比值。
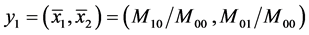 (5)
(5)
式中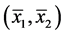 表示候选目标区域的质心。
表示候选目标区域的质心。
由于要求出目标的尺寸和方向,所以需要将二阶矩转换为二阶中心距。
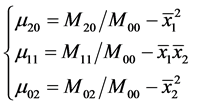 (6)
(6)
式(6)写成协方差矩阵的形式,便于对该矩阵进行奇异分解从而估计目标的尺寸和方向。
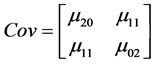 (7)
(7)
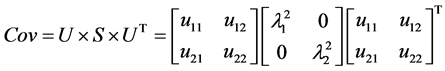 (8)
(8)
式中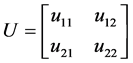 ,
,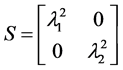 ,
,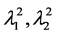 是
是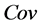 的特征值。矩阵U的第一列和第二列分别表示目标的
的特征值。矩阵U的第一列和第二列分别表示目标的
坐标轴方向。假设目标区域用椭圆表示,长半轴和短半轴的长度分别用a,b表示,那么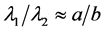 ,根据已经估计的面积A,得到如下公式:
,根据已经估计的面积A,得到如下公式:
 (9)
(9)
所以
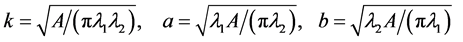 (10)
(10)
将真实目标区域的长半轴和短半轴替换到原来的协方差分解后的奇异矩阵中,便得到真实目标宽度、高度和方向向量的协方差矩阵,如下式。
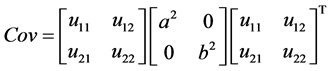 (11)
(11)
3. 对SOAMST算法的改进
SOAMST跟踪算法在开始前首先需要对跟踪目标进行建模。针对跟踪过程中由于颜色模型在背景和人脸颜色相似和视频光照变化时无法准确计算权值图像,导致目标跟踪不准确问题。本文提出使用二阶直方图和MBLBP特征两种模型对人脸目标进行建模。MBLBP特征是对目标纹理的描述,特征值的计算不受光照和颜色的影响。二阶直方图在包含颜色信息的前提下包含了像素的均值和协方差,抗干扰性更强,受光照影响低。所以二阶直方图和MBLBP特征结合能够解决该问题。
3.1. 二阶直方图
设二阶直方图 [5] [6] 分布即目标模型为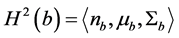 ,
,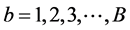 ,其中,
,其中, 为每个区间的概率,
为每个区间的概率,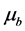 是均值向量,
是均值向量,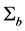 为协方差矩阵。B为直方图横坐标空间,在灰度图像中B = 256。当忽略
为协方差矩阵。B为直方图横坐标空间,在灰度图像中B = 256。当忽略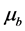 和
和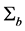 时,
时,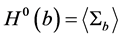 就是零阶直方图,即颜色直方图,两个直方图采用的是加权相似度。
就是零阶直方图,即颜色直方图,两个直方图采用的是加权相似度。
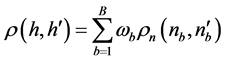 (12)
(12)
图2形象地说明了颜色直方图和二阶直方图两者的相似和区别之处。
Figure 2. The color histogram and second-order spatial histogram
图2. 颜色直方图和二阶空间直方图
针对权值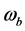 ,假设图像成正态分布,用高斯函数来描述权值
,假设图像成正态分布,用高斯函数来描述权值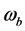 。
。
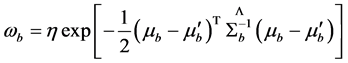 (13)
(13)
式中,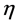 为高斯常数,而
为高斯常数,而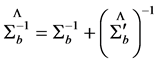 ;
;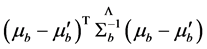 就是到的Mahalannobis距离平均值。仍然用Bhattacharyya相似度描述两颜色直方图的相似度。得到如下式子:
就是到的Mahalannobis距离平均值。仍然用Bhattacharyya相似度描述两颜色直方图的相似度。得到如下式子:
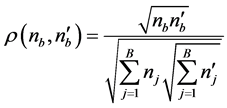 (14)
(14)
因此,目标和候选目标模型之间的二阶空间直方图相似度可以进一步表示为
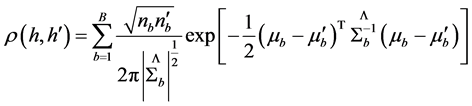 (15)
(15)
至此,由基于二阶直方图的均值漂移向量可以得到目标的跟踪点:
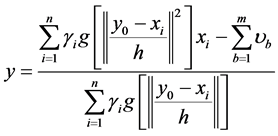 (16)
(16)
式中,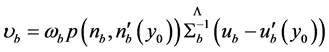 。
。
3.2. MBLBP特征
纹理特征是图像中由于灰度和颜色的不同而表现出的一种特征,与其他特征相比,不仅包含了灰度信息的空间特性,其特征值的计算不受光照和颜色的影响。
MBLBP特征值是在LBP [7] [8] 的基础上通过中心区域矩形内像素的平均值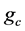 和该矩形区域的八邻域矩形
和该矩形区域的八邻域矩形 进行比较,如果八邻域矩形平均值大于中心区域像素点平均值标记为1,反之标记为0,将八个邻域标记按照从左上角顺时针方向进行组合得到MBLBP二进制编码值。计算公式如下:
进行比较,如果八邻域矩形平均值大于中心区域像素点平均值标记为1,反之标记为0,将八个邻域标记按照从左上角顺时针方向进行组合得到MBLBP二进制编码值。计算公式如下:
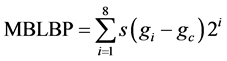 (17)
(17)
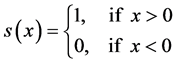 (18)
(18)
式(17)中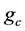 是中心矩形内像素点的平均值,
是中心矩形内像素点的平均值,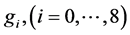 是中心矩形的八邻域方向每个矩形的均值。
是中心矩形的八邻域方向每个矩形的均值。
MBLBP图像纹理特征 [9] 的计算过程如下图3所示。
统计MBLBP特征直方图的方法和颜色直方图基本相同,最后进行归一化后便得到人脸的MBLBP特征直方图。
3.3. 基于颜色空间纹理融合特征的SOAMST算法
我们利用包含颜色和空间信息的二阶空间直方图与提取的MBLBP特征代替SOAMST原算法的颜色直方图 [10] 来建立目标模型,解决目标颜色与背景相似,光照,尺度变化等复杂环境问题。
在跟踪过程中,多特征融合时如果采用固定的权值计算,当空间颜色纹理各特征发生明显变化时,特征融合进行建模得到的目标模型是不准确的。为此,我们分别计算各特征的概率密度函数得到各特征直方图所占权重 [11] 。如下式定义:
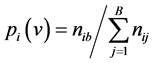 (19)
(19)
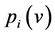 表示某一特征的归一化直方图,根据特征概率密度函数建立概率分布图,在各特征直方图的概率分布图中,分别计算目标与背景的Bhattacharyya系数,设为
表示某一特征的归一化直方图,根据特征概率密度函数建立概率分布图,在各特征直方图的概率分布图中,分别计算目标与背景的Bhattacharyya系数,设为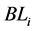 。
。
最后,计算各特征对应权重为:
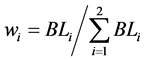 (20)
(20)
4. 实验结果分析
使用多组视频对本文改进算法进行试验。试验中包括了目标与背景颜色相似,光照变化,遮挡,以及人脸尺度和方向变化复杂情况,跟踪效果如下图4~6所示。
对比图4~6实验结果可以发现当目标颜色和背景颜色基本相似时,图像的概率密度梯度基本不再变化,基于颜色模型的原SOAMST算法也就不再收敛,认为当前位置就是最佳目标位置,但是实际情况是,背景颜色和目标颜色相似的原因。
同时在光照变化情况下,颜色模型的SOAMST算法在跟踪过程中开始阶段能够准确跟踪,但是当光线逐渐变化时,人脸跟踪不再准确。因为光线变化后人脸颜色信息发生变化,颜色模型不能够得到准确的相似信息,所以跟踪效果不好。
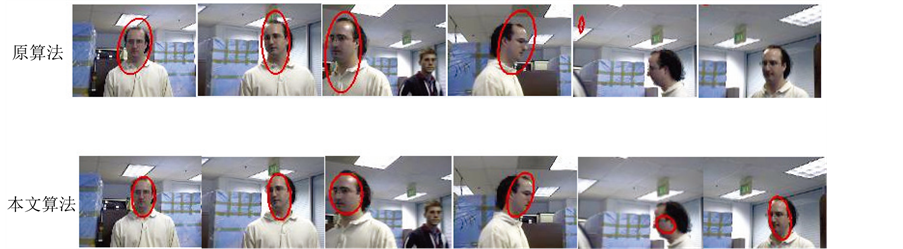
Figure 4. The comparison of the algorithm (one)
图4. 算法比较(1)

Figure 5. The comparison of the algorithm (two)
图5. 算法比较(2)

Figure 6. The comparison of the algorithm (three)
图6. 算法比较(3)
而本文算法将颜色空间信息即二阶空间直方图和纹理信息即MBLBP特征结合起来对目标进行建模。当颜色信息相似度低时,也就是颜色信息不再可靠时,空间信息和MBLBP纹理特征会对颜色信息起到补偿作用。所以本文算法在复杂条件下比原算法具有更好的跟踪效果。
5. 总结
本文以SOAMST算法为基础,针对人脸跟踪过程中背景和人脸肤色相似、光照变化问题;提出了将二阶空间直方图结合MBLBP特征直方图代替SOAMST的颜色直方图建立目标模型,同时在颜色信息基础上增加空间和人脸纹理特征信息 [12] ,使得当人脸和背景颜色相似和光照变化等复杂条件下也有很好的区分度。实验结果显示本文算法相比原算法有更好的跟踪效果,更好的鲁棒性和准确性。