1. 引言
土地利用/土地覆被变化是当前全球变化研究的核心命题之一 [1] [2] 。土地作为陆地生物活动的地理载体和气候形成的重要下垫面基础,土地利用方式与覆被植物的变化深刻影响到了区域生态系统结构和气候环境的演变过程。作为人类与地球环境开展物质流、能量流、信息流交互作用的重要表现之一,土地利用/土地覆被变化贯穿于人类社会和自然环境演变的每一个发展阶段 [1] [3] 。当前研究已经表明,土地利用/土地覆被变化已逐渐成为诱发全球和区域变化的主要驱动力,深刻影响了陆地生态系统的地理分布格局及其生产力 [3] [4] 。因此,适时开展土地利用/土地覆被变化研究,探索全球以及区域尺度土地利用/土地覆被变化的时空演变规律,分析其发生发展的动力机制,可以更有效地为全球和区域生态环境保护提供理论支撑和决策参考,服务于区域的可持续发展 [5] 。
黄土高原地区作为华夏文明的发源地,其土地开发与利用历史达几千年之久。长期以来,“重开发,轻保护”的土地利用方式,造成黄土高原地区地表覆被率日趋低下。加之气候干旱、土质疏松、降水集中且多暴雨等自然条件的影响,在长期流水侵蚀下,黄土高原地区地面被分割得非常破碎,形成沟壑交错其间的塬、墚、峁等地貌类型,成为土地利用/覆被变化改变区域地形地貌的典型案例区。此外,在全球与区域气候变化的大背景下,土地利用/覆被变化将在大程度上改变了黄土高原地区地表反照率、水分以及养分循环,深刻影响了这一地区的土壤、水文等生态环境,危及到了区域的粮食安全、生态安全 [6] 。因此,黄土高原区区生态系统具备了脆弱生态系统的一切性质。结构简单、生态系统服务价值低下、生态功能脆弱的系统特征,使得黄土高原对自然或人为的干扰活动极为敏感。土地利用/覆被的变化在一定程度上影响到黄土高原地区的生态系统稳定性,牵动着该区域经济发展、社会稳定、生态和谐的敏感神经 [7] 。
20世纪90年代以来,伴随大规模的退耕还林还草、生态绿化等工程的实施,黄土高原地区的土地利用/覆被变化的强度和活跃度不断增强,地表覆被情况得到大幅改善,土地利用结构类型发生巨大变化 [8] 。因此,亟需开展黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化研究,探究这一变化究竟给黄土高原的生态环境、社会经济发展带来了怎样的改变,分析这一变化的时空规律,剖析其动力机制,从而为保护黄土高原地区生态环境持续健康发展,合理规划区域土地利用,实现经济、社会可持续发展,提供科学理论指导与参考。
2. 黄土高原土地利用/覆被现状
黄土高原为我国四大高原之一,西起乌鞘岭,东至太行山,南靠秦岭,北连内蒙古高原(大致以长城为界),跨青海、甘肃、宁夏、内蒙古、陕西、山西、河南七省(图1),全区总面积63.5万平方千米。四周群山环绕,北有阴山,南望秦岭,东面吕梁,西眺六盘,海拔800~3000米,地势由西北向东南倾斜,山地、丘陵、平原与宽阔谷地并存。高原大部分为厚层黄土覆盖,是地球上分布最集中且面积最大的黄土区。经流水长期强烈侵蚀,逐渐形成千沟万壑、支离破碎的特殊自然景观。
作为中华民族农业文化的发祥地之一,长期以来,耕地一直是黄土高原地区的主要土地利用类型。然而,伴随水土流失带来的土壤肥力下降以及生态环境的恶化,弃耕抛荒、退耕还林已成为最为活跃的土地利用变化活动。目前,黄土高原区土地利用结构中耕地虽然仍占有较大比重,但林草地的比例已显著大幅增加。为了进一步绿化黄土高原,我国先后启动实施了三北工程、天保工程、退耕还林工程等一系列生态“治黄”工程。2010年,国家制定颁发《黄土高原地区综合治理规划大纲(2010~2030年)》,开启了黄土高原生态建设的新篇章。

Figure 1. Geographic position and land use/cover change in the Loess Plateau in 2010
图1. 黄土高原地理位置与土地利用/覆被变化现状(2010年)
3. 黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化研究现状
近几十年来,黄土高原地区开展的大规模绿化建设工程,已经显著改变了这一区域的土地利用/覆被结构。对其展开相应的研究有助于了解黄土高原地区生态工程建设的效果,以及生态工程建设对区域社会经济发展的影响。对此,国内外各高校与科研机构持续开展了黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化系列研究。
基于web of science文献数据库与中国知网文献数据库,分别以“Land use of Loess Plateau”“黄土高原土地利用”为搜索词,全文查询得知,国内外文献库中关于黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化研究的文章呈逐年攀升趋势(图2,图3)。2000~2015年间,国内关于黄土高原土地利用的研究论文发表数量增加了16倍多,国际上更是增加了将近20倍。
就国际上开展黄土高原土地利用/覆被变化研究的地区分布而言,中国和美国仍是研究的热点区域,研究发表数量遥遥领先于其他地区(图4)。此外,日本、澳大利亚、加拿大、巴西、英国、瑞典等国家也对黄土高原地区的土地利用/覆被变化研究保持了较高的关注度(图4)。
4. 土地利用/覆被分类体系
土地利用/覆被分类体系是开展土地利用/覆被变化研究的基础工作之一。通过土地利用/土地覆被分类,不仅可以了解各种土地利用/土地覆被类型的基本属性,而且可以认识土地利用/土地覆被的区域结构与分布特点,为进一步分析土地利用/土地覆被变化的地域差异性奠定基础。土地利用/覆被类型划分应遵循相似的社会、环境条件以及产生相似LUCC模式的相似人类驱动力 [9] 。
20世纪70年代之前,土地利用/覆被分类以土地利用分类为主,该分类体系重点突出土地用途差异,其用途侧重于土地资源利用现状调查和土地利用信息制图,服务于区域土地利用规划、管理以及国土资源开发等社会需求 [10] 。20世纪70年代之后,伴随着遥感科学的发展,计算机技术的进步,土地利用/覆被分类逐渐向以土地覆被为主的分类体系迅速发展,注重突出土地类型的差异,主要用于土地覆被变化研究 [10] 。
具体的分类体系研究方面,国际上,国际地圈–生物圈计划(IGBP)对应着定量化的地表覆被信息的物理指标,从反映土地覆被中地表的生理参数特征角度出发,构建了全球土地覆被分类系统(表1)。但是,该分类体系过于注重定量化的地表物理参数,缺乏对土地利用信息的表达,灵活性和兼容性较差。因此,各国针对不同的研究区和研究需求,各自设定了符合区域地表覆被实际的分类体系,如1985年为加强对各成员国环境和自然资源的管理,欧共体启动了环境信息协作计划,其中的土地覆被项目将土地覆被类别划分为人工表面、农业用地、林地和半自然用地、湿地、水体5个一级类,下分15个二级类和44个三级类 [11] 。1976年美国国家地质调查局发展了一套适用于遥感数据的土地覆被分类系统 [12] 。该分类系统由4个层次构成:一级分类和二级分类适用于全国或全州范围,其中一级类是根据当时的卫星遥感影像可以直接目视判读的地物,包括城镇或建成区、农业用地、草地、林地、水体、湿地、荒地、苔原、冰川或永久积雪9类;二级类是根据比例尺小于1:8万的航空像片可以判读的地物,分为37个类别。三级、四级分类适用于州内的、区域性的、县域的研究,其中三级类适用于比例尺大于1:8万小于1:2万的航空遥感,四级类适用于比例尺大于1:2万的航空遥感。
国内的土地利用/覆被变化研究中,土地利用/覆被类型划分多采用中科院的土地资源分类系统 [13] ,该系统将土地利用与覆被分为耕地、林地、水域、草地、城乡工矿居民用地、未利用地6个Ⅰ级类,25个Ⅱ级类以及针叶林地、阔叶林地、针阔混交林地3个Ⅲ级类(表2)。而国家土地调查过程中,面向国家土地精细管理和土地用途管制的政策需求,统一采用国土资源部的国家级土地利用与覆被分类系统(将土地利用与覆被分为耕地、林地、水域、草地、建设用地、未利用地、湿地7个Ⅰ级类,26个Ⅱ级类以及
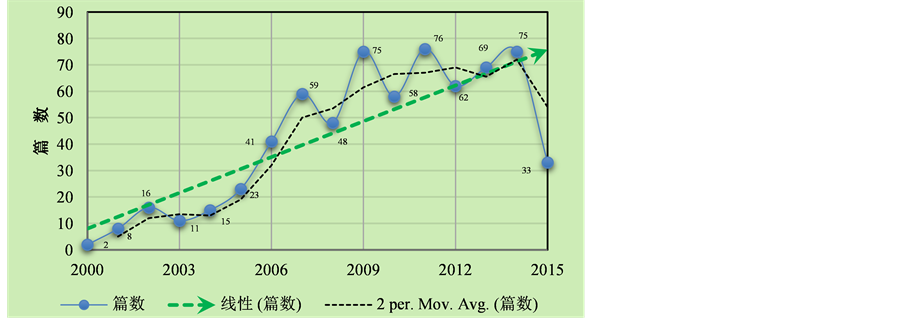
Figure 2. Changes in the number of domestic research published about Land use of Loess Plateau (2000-2015), CNKI
图2. CNKI全文搜索“黄土高原土地利用”得到的国内研究发表数量变化趋势(2000~2015年)
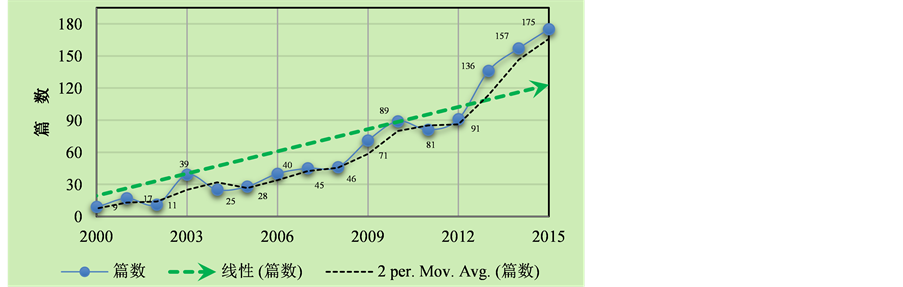
Figure 3. Changes in the number of International research published about Land use of Loess Plateau (2000-2015), Web of Science
图3. Web of Science全文搜索“Land use of Loess Plateau”得到的国际研究发表数量变化趋势(2000~2015年)
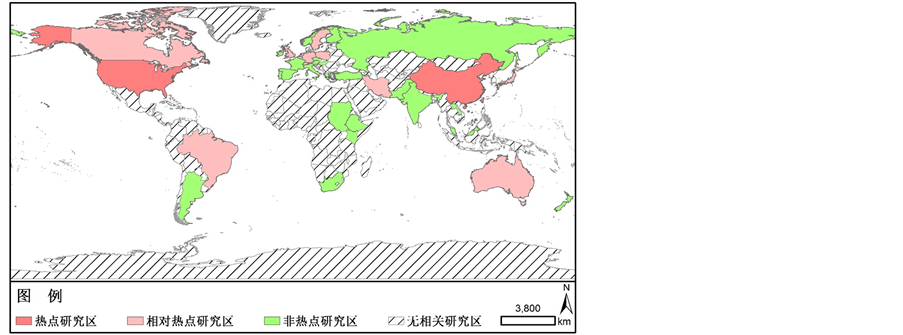 注:热点研究区,研究发表论文100篇以上;相对热点,研究发表论文10~100;非热点研究区,研究发表论文0~10;无相关研究区,研究发表论文为0
注:热点研究区,研究发表论文100篇以上;相对热点,研究发表论文10~100;非热点研究区,研究发表论文0~10;无相关研究区,研究发表论文为0
Figure 4. Distribution of land use/cover change research hotspots in the Loess Plateau (2010-2015)
图4. 黄土高原土地利用变化研究热点地区分布图(2000~2015年)

Table 1. Classification system of global land use/cover change in IGBP [1]
表1. IGBP全球土地利用覆被分类体系 [1]


Table 2. Classification system of land resources in Chinese Academy of Sciences [13]
表2. 中国科学研究院土地资源分类系统 [13]
针叶林、阔叶林、混生林3个Ⅲ级类)。但是这两种分类系统都存在一定的局限性,如土地分类系统过分依赖特定的遥感数据源,造成系统的通用性不强、难以适应不同目的的相关研究等。所以,已开展的黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化研究种,大部分研究者在采用这两类分类系统的同时,多结合研究区域的土地变化状况、景观变化等实际情况构建了符合当地土地利用与覆被现状的分类体系。但是,由于黄土高原土地利用/覆被变化研究多集中于小流域尺度。因此,分类体系多仅适用于特定的小流域,缺少可以反映整个黄土高原地区土地利用与覆被特色的分类体系,这一定程度上也阻碍了黄土高原区域尺度土地利用/覆被变化研究的开展。
5. 土地利用/覆被分类技术
土地利用/覆被变化研究必须具备一定精度的土地利用分类数据,这是研究土地覆被变化的数据基础条件 [13] 。土地利用/覆被分类制图精度既影响土地利用变化信息的表达,也决定分析结果的精度和应用参考功能。
由于资源卫星影像具有成本低、覆盖范围广、监测时间频度高等优点,而且获取相对容易且操作简单,可实现多时空尺度地表覆被信息的连续监测 [14] [15] 。因此,当前世界范围内土地利用/覆被变化研究的信息和数据来源大都源于对各类遥感卫星数据、遥感影像的解译。在现代条件下,遥感解译需要利用各种光学和数字图像处理设备,事先对原始的遥感图像进行加工处理,以便把所需要的信息从中提取出来。在具备有关专业(如地质、地理、水文、农林、气象等)的知识并熟悉遥感图像的特点、地物波谱和地面实况的基础上,研究者可根据各种应用的需要,观察和判断遥感图像的光学、纹理、形状特征等遥感解译标志,以监督或非监督、人机交互操作等技术手段,实现遥感影像地表覆盖信息判读 [15] 。
当前应用较多的土地利用/覆被分类方法仍是一些算法成熟、操作简单的传统分类方法,如目视解译、监督分类和非监督分类。相对于传统分类法,近年来出现的新分类方法,如时间序列分析法 [16] 、多特征融合法 [17] 以及基于频谱特征 [18] 的分类法等,具有能够更准确地提取出目标地物的优点。因此,在实际应用中传统分类方法通常结合新方法。但是,在对遥感图像解译的过程中,受到研究者本身图像判读能力、地学知识掌握程度、图像本身存在的误差,以及云雨等气象条件带来的遥感影像质量差异,导致单纯的使用遥感数据并不能准确提取区域土地利用/覆被变化信息。所以,如果土地利用/覆被分类与制图单纯依赖于遥感信息技术,忽视实地调研验证、野外信息观测等传统信息获取方式,将会使得研究结果与实际出现较大的偏差。黄土高原地区千沟万壑、支离破碎的地貌形态,农牧林交错的地表覆被现状等都进一步加大了遥感解译的难度。如果单纯的依靠目视遥感判读手段,无法分解混合像元和复杂地貌带来的错误分类。对此,已有的黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化研究多采用将遥感数据与野外调查数据、统计资料等多数据源复合分析,在图像的处理过程中更加注重了野外调查与室内解译的结合。根据已有各类研究结果表明,多源数据融合解译可以实现区域土地利用/覆被变化信息的快速准确提取 [17] 。
6. 黄土高原土地利用/覆被变化格局–过程–驱动研究
格局、过程与驱动力的比较是揭示区域尺度土地利用/覆盖时空变化规律的有效方法 [18] 。其中,格局意指地理单元(土地利用/覆被类型)的空间结构与分布特征,包括土地利用/覆被的数目、空间分布与配置。过程是各土地利用/覆被类型之间物质、能量、信息的流动和迁移转化的总称,强调事件或现象的发生、发展的动态特征 [19] [20] 。格局与过程相互作用而存在。格局是过程的空间载体,格局变化影响过程进度,过程改变格局特征 [19] 。当前关于黄土高原土地利用/覆被变化的格局与过程研究多侧重于小流域和小尺度范围的研究 [21] [22] 。
其中,黄土高原土地利用/覆被变化的格局研究方面,重点侧重于景观格局与土地利用动态变化分析 [21] [23] 。过程研究方面,集中在黄土高原土地利用/覆被格局变化对土壤环境的生态过程影响,包括土壤侵蚀过程 [24] 、水土流失过程 [25] 以及土壤养分的空间分异规律 [26] 等。格局与过程耦合已经成为黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化格局过程研究的主流方向。傅伯杰等 [27] 以陕西省延安市羊圈小流域(延河流域二级子流域)为研究区,基于生态水文过程的监测和分析,开展了基于直接观测的格局–过程耦合研究,分析了不同土地利用类型的水土保持效应、土地利用类型及环境因子耦合下的水土流失过程以及不同生态系统组合的水土保持功能研究。以国际上通常采用的分布式SWAT模型,开展了土地利用格局与流域生态水文过程模拟研究。这一系列研究,为黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化格局与过程耦合分析提供了研究范式。野外长期观测和综合调查,以及在此基础上的格局–过程耦合模型模拟预测已成为黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化格局与过程耦合的主要方法。
此外,伴随土地利用/覆被变化研究的深入开展,探索影响土地格局与过程变化的驱动机制已经成为研究的核心和主题之一 [13] [28] [29] 。土地利用/覆被变化驱动力研究的目的在于从影响土地的各因素出发,构建经验模型,解释二者之间的相关关系,为远期的土地利用变化模拟预测提供理论基础。引起黄土高原土地利用变化的驱动力既有自然系统力,也有社会经济系统力 [30] 。在不同时空尺度上,自然与社会的驱动作用地位不尽相同。已有研究成果表明 [31] ,短时间尺度上(百年以下),自然因素的影响主要体现为累积效应,社会经济因素对LUCC过程的影响相对活跃;长时间尺度上(百年以上),自然系统为土地利用变化的主导驱动因素。此外,受地形、降水等基础自然地理背景的影响以及经济发展进程、人口空间密度等人文地理背景的内外驱动,黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化的驱动机制存在显著的空间分异特征 [28] 。陇东至晋西,陕北到关中等地的土地变化驱动机制均有明显的空间差异特征。因此,土地利用/覆盖变化驱动机制研究必须在耦合格局与过程的基础上,开展地理综合分析研究。当前,国际上关于黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化驱动机制的分析方法以地理综合模型法为主 [30] 。这些模型方法多为基于经验的统计模型和基于过程的动态模型 [32] 。其中,基于经验的统计模型通过构建土地变化与各自然、社会、经济因子之间的数学相关关系模型,可以快速简化问题,准确抓住复杂系统中的主要矛盾,但是由于个别因变量难以量化,如土地利用政策,从而使得建立的关系并不是确定的因果关系。不同于经验统计模型,基于过程的动态模型,如clue-s模型,在耦合土地利用/覆被变化格局与过程的基础上,能够实现驱动因子对土地利用变化过程的深度刻画。从而在土地利用变化过程模拟预测的基础上,分析其驱动机制。然而,由于模型的构建准则过于复杂,往往仅适用于小尺度的模拟分析,难以实现尺度上推。因此,建立综合性模型无论在当前还是以后都将是黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化驱动力研究的一个必然趋势 [28] 。
7. 讨论和结论
1) 黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化研究首先应构建适应地区特色的分类体系。黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化研究应在综合国家与中科院分类系统的同时,以区域土地变化状况、景观变化等实际情况的基础上,结合已有的各小流域尺度土地利用/覆被分类研究成果,构建符合黄土高原地区土地利用与覆被现状的分类体系,服务于黄土高原区域尺度土地利用/覆被变化研究。
2) 土地利用/覆被遥感解译必须注重计算机技术与传统地理野外观测的结合。土地利用/覆被遥感解译是开展后续的格局、过程变化分析以及驱动机制研究的最根本数据基础,只有达到一定制作精度的土地利用/覆被数据,土地利用/覆被变化相关研究成果才具有科学指导和理论参考意义。针对黄土高原地区地貌复杂、遥感影像混合像元丰富等地理环境差异和遥感影像特征,土地利用/覆被遥感解译必须建立在充足野外观测信息的基础之上,监督与非监督结合,人机交互。
3) 黄土高原土地利用/覆被变化格局–过程–驱动研究方面,格局与过程的耦合研究、驱动机制分析已成为土地利用/覆被变化研究的主流和核心命题。其中,格局与过程的耦合研究方面,野外长期观测和综合调查,以及在此基础上的格局–过程耦合模型模拟预测已成为黄土高原地区土地利用/覆被变化格局与过程耦合的主要方法。驱动机制分析方面,研究方法以构建基于经验的统计模型和基于过程的动态模型为主。然而,受限于不同尺度研究区的地理环境差异,当前的模型仍缺乏普适性。因此,建立综合性模型,实现多尺度土地利用与覆被变化驱动机制的科学解释已成为当前研究的迫切需求。
NOTES
*第一作者。