1. 引言
科学计算可视化(简称可视化,英文是Visualization in Scientific Computing,简称ViSC)的基本含义是运用计算机图形学或者一般图形学的原理和方法,将科学与工程计算等产生的大规模数据转换为图形、图像,以直观的形式表示出来。电力系统可视化技术是指将可视化技术应用到电力系统中来,一方面可以将电力系统设备的各种属性、系统运行状态以图形或图像的方式显示出来,使系统运行人员更方便、更明晰地了解当前系统的运行状态,以便其采取更有效、更有针对性的运行控制措施;另一方面可以将电力系统的计算分析功能与可视化技术结合起来,通过图形操作和图形参数设置,使得数据从输入到数据输出的整个过程都与图形图像紧密结合,让计算分析人员摆脱过去单调、枯燥的计算分析模式,能生动、直观的查看数据分析和计算结果 [1] [2] 。随着电力系统可视化研究的不断深入,人们对其认识程度不断加深。越来越多的电力系统可视化研究者发现在电力系统可视化设计中必须要全面考虑电力系统信息特征和调度人员的认知规律,将两者有效结合才能实现电力系统运行数据的形象展示、实现信息的高效表达。“感知化”设计方法由此酝酿诞生。
感知化技术实质上是一种深层次的信息加工技术,通过模仿人的感知与思维方式,用人工智能方法执行一些基本的识别与推理任务,使得人类能够具备对模糊、庞杂的特定信息集产生快速准确判断的能力,并直接在脑海中产生具体的认知图景 [3] - [11] 。感知化技术需要满足两个层面上的技术要求,一个是“可视化”,一个是“可知化”,两者缺一不可,前者是感知化技术的“前台”,后者则是感知化技术的“后台”。可视化更多的是一种信息的表达方式,赋予感知对象更加清晰、鲜明、可视的表达方式;可知化则更多的是一种信息组织方式,以符合人类认知习惯,提高感知效率为目的,对信息进行再组合、再组织与再处理。
2. 感知化设计理论与技术基础
2.1. 理论基础
“感知化”设计方法不仅需要考虑电力系统信息内在特征,同时需要深入研究调度人员的认知规律,调度人员对电网运行情况的感知、理解和预测是“感知化”设计方法的先决条件 [12] 。“感知化”设计方法以认知心理学、视觉心理学、思维科学、人工智能、信息组织学等为其理论基础。
认知心理学是用信息加工的观点和术语说明人的认知过程的学科。它主张研究认知活动本身的结构和过程,并把这些过程看作信息加工过程。它关注人类处理外界信息及以此决定所采取的适当行动这样一些内部过程,这些内部过程包括注意、感知觉、学习、记忆、语言、问题解决、推理和思维等。可视化设计服务于人类认知的全过程:人在接触到可视化界面时,首先通过注意、感知觉过程识别界面上的信息;然后通过学习、记忆、回忆过程提取并保存相关的信息;并基于以上信息来源完成思维、推理等高级认知过程。由此可见,认知心理学与可视化设计紧密联系;遵循人类认知过程、按认知心理学的理论科学设计的可视化系统将迅速抓住观察者的注意力,便于其把握、理解关键信息,给其留下深刻印象,并有效辅助其思考、判断。
视觉心理学是研究视觉信息加工过程中的心理和生理机制的心理学分支学科。它侧重于发掘认知过程的初级阶段——即信息的接收和识别中的规律。由于可视化方案直接作用于视知觉过程,因此该学科的相关理论将对可视化的设计大有裨益。
思维科学(noetic science)是研究人类思维过程、思维规律、思维机理的学科的总称。它的研究对象是思维、推理等高级认知过程。可视化方案的终极目标是更有效的辅助人的思维决策,因此人类的思维规律、思维机理可作为可视化设计的深层次、根本性指导原则。
人工智能(Artificial Intelligence, AI)是研究、开发用于模拟、延伸和扩展人的智能的理论、方法、技术及应用系统的一门技术科学。它企图了解智能的实质,处于思维科学的技术应用层次,是思维观的部分方法论的体现。人工智能开发中的一些原则和方法对可视化设计也有借鉴意义。
信息组织是指人们根据信息本身的特点,运用一定的科学规则和方法,对其进行选择分析、排列组合,使之有序化、系统化、规律化、高级化,增强信息对象的表现效能和运用效能,以促进用户对信息的有效获取和利用。可见,可视化的目标与信息组织的诉求不谋而合;可视化设计应借鉴该学科的方法,以实现系统、有序的信息组织。此外,信息组织学也与研究认知规律的学科紧密联系,它是基于认知观的方法论,是对认知规律的一次具体实践。科学的信息组织方法将提高认知过程的效果和效率。
2.2. 技术基础
在技术手段方面,“感知化”设计方法需要基于实际数据展示需要,融合多种先进的展示技术,主要包括科学计算可视化技术、图形处理技术、网络镜像技术、互动式显示技术等。同时依靠挖掘数据的内在联系,形成数据挖掘、钻取的组织方法等。
科学计算可视化技术是一种将符号或数据转换为直观的几何图形的计算方法。它能够高效、直观地表达电网中的大量数据,便于调度人员观察其模拟和计算过程,并了解当前系统中存在的问题及其严重程度,使调度人员对电网运行有整体的把握 [13] - [20] 。它能够解析输入到计算机中的图像数据,并从复杂的多维数据中生成图像。
图形处理技术 [9] 是高级的图表加工技术,利用该方法可以根据展示数据的需要,对图表进行合理的二次处理,使之适应于电力系统的数据展示需要。
互动显示技术是指在可视化设计中充分考虑使用者各种可能的需要,引导使用者习惯的方法。
3. 系统设计
3.1. 体系架构
基于感知化理论的城市电网运行综合评估体系充分利用先进的电力自动化技术、信息化技术、信息集成技术以及智能电网技术,以电网运行中的电网模型、设备参数、历史数据、发电计划等原始数据为起点,通过抽取、转换、载入等技术将分散的信息整合起来,形成台账数据、量测类数据、业务管理类数据,通过对基础数据的加工计算形成各专业指标数据,为分析评估的数据质量提升提供了坚实的基础 [21] 。系统具体的体系架构如图1所示。
3.2. 技术架构
系统主体应用功能建设采用基于J2EE和B/S模式的应用技术架构。
B/A/S模式的三层架构模式是一种严格的分层定义,它首先将整个软件系统的开发分成相对简单的几个小分块,然后在每一层中只实现系统相应层的功能设计,层间的交互由相邻层对应的功能模块进行调用,信息传递只由接口进行传送 [21] 。其具体的技术架构如图2所示。
3.3. 功能结构
基于感知化理论的城市电网运行综合评估体系包括6个模块:电网规模、安全运行、经济运行、优质运行、节能环保以及工作管理。这6个模块又分别包含了4个、9个、6个、6个、4个和3个功能。其具体功能如表1所示。
表1. 功能结构
4. 感知化功能设计思路、方法及实现
4.1. 设计思路
“感知化”设计区别于其他设计方法的显著特点在于感知化设计中需要结合调度人员的认知规律、深度融合其使用习惯。因此感知化设计需要深入了解人类的认知规律。
认知(Cognition)过程是个体认知活动的信息加工过程。认知心理学将认知过程看成一个由信息的获取、识别、编码(Encoding & Coding)、贮存、提取和使用等一系列连续的认知操作阶段组成的、按一定程序进行信息加工的系统。人脑接受外界输入的信息,经过头脑的加工处理,转换成内在的心理活动,再进而支配人的行为,这个过程就是信息加工的过程,也就是认知过程。
信息的获取就是接收直接作用于感官的刺激信息,感觉的作用就在于获取信息。
信息的识别是将感官获得的刺激信息片段综合加工,并形成事物的整体映像。
信息的编码是将一种形式的信息转换为另一种形式的信息,以利于信息的贮存和提取、使用。个体在知觉、表象、想象、记忆、思维等认知活动中都有相应的信息编码方式。
信息的贮存就是信息在大脑中的保持,在记忆活动中,信息的贮存有多种形式。
信息的提取就是依据一定的线索从记忆中寻找所需要的信息并将它取出来。
信息的使用就是利用所提取的信息对新信息进行认知加工,具体表现为信息重建、概念形成、判断和问题解决等。
人类的认知过程,实际上描述了人类通过心理活动获取知识、认识世界的全过程。科学的理解、剖析人类对事物的认识过程,是可视化设计的必要准备工作。基于以上分析,在感知化设计中需要注意以下几个方面:
(一) 遵循视觉规律,提高信息的接收与获取效率
感觉是我们认识世界的起点,是人们对客观事物的个别属性(比如物体的颜色、形状、明暗、声调、粗细、软硬等)进行直接反映的过程。感觉分为外部感觉(视、听、味、嗅、触觉)和内部感觉(平衡觉、运动觉、机体觉)。在各种感觉中,至少有80%以上的外界信息经视觉获得,视觉是人和动物最重要的感觉。通过视觉,人和动物得以了解外界物体的大小、明暗、颜色、动静,获得对机体生存具有重要意义的各种信息。
可视化的展示方案直接与人的视觉系统打交道,理解视觉规律将提高人对信息的接收与获取效率,对于开发新型、友好、科学的可视化系统有重要的指导意义。
(二) 遵循知觉规律,提高信息的综合与识别效率
知觉是紧随视觉的认知阶段。它是人脑对直接作用于感官的客观事物整体的综合反映,是较为复杂的心理现象,是大脑对感觉信息进行综合加工的结果。知觉以感觉为前提,但它不是感觉的简单的集合,而是在将感觉综合的基础上形成的整体映像,使人能看到一面红旗、听到一阵嘈杂的人声、摸到一件轻软的毛衣等。这时候我们所认识到的已经不再是事物的个别属性或特性,而是事物的联系与关系了。知觉非常复杂,涉及众多转换和解释感觉信息的过程。
(三)遵循记忆规律,提高信息的贮存与提取效率
可视化展示方案虽不直接参与人的学习、记忆环节,但遵循、符合人类记忆特点的方案能提高人们对信息的贮存与提取效率,不仅会给人留下深刻印象,而且对人思考、判断、决策等后续认知过程不无裨益。在可视化方案进入视野并引起注意后,人须提取记忆中的相关知识、概念对看到的式样进行识别,了解式样的含义;然后对式样编码,贮存到工作记忆或长时记忆系统中。当人们需要基于展示的信息分析决策时,又需要将头脑中贮存在长时记忆系统中的、长期积累的先验知识提取至工作记忆中,综合二者,加以运用。高效的可视化信息组织方法是以上信息加工过程的润滑剂。
4.2. 感知化功能设计方法
“感知化”设计所提出的新型的可视化方法与技术,不仅追求图像层的表达,而且追求在信息层、乃至思维层上与电网运行人员深度互动。
1) 在图像层上,要求替代原有的大量数字表述,转而以生动、直观的图形图像形式进行加工与表达,充分利用颜色、形状等图形图像要素传达既定的信息内涵,更为生动和深刻地揭示电网运行的综合水平和内在机理。
2) 在信息层上,要求对信息进行基于可视化的重新组合,形成更加有效的信息组织和表达形式,让电网运行和评估人员对于信息的获取更为便捷和准确。
3) 在思维层上,则要求研究科学的人机交互方案,建立更优的信息获取通道以及信息间的交叉与联想,加强计算机辅助调度员实施合理决策的功能。
4.3. 感知化功能应用示例
我们选取了4个示例来说明感知化理论在城市电网运行综合评估体系中的应用。其中:
图3显示了电网规模模块装机规模功能分析。
Ø 图中上半部分表格显示了各种发电类型及电压等级的机组数量及合计值,下半部分3个饼图则分别展示了机组按机组类型、按电压等级及按调度类型分类的分布情况。当我们点击表格中的数字时,可以弹出该数字所代表类型的机组的详细情况,如图4所示。
图5显示了安全运行模块变压器重载功能分析。
Ø 界面上半部分表格显示了全年各月变压器重载情况,下半部分,左侧2个柱图是对全年各月变压器重载时间和数量的统计,右边的热谱图则显示了某一个月(默认最后一个月5月份)的重载信息(X-轴是当月的天数,Y-轴是当月出现重载的变压器,在变压器出现重载的日期用红色颜色表示)。当我们点击表格上的某一统计日期时,下面的热谱图会随之刷新,并弹出详细的变压器重载情况。如点击统计日期 时,会弹出2016年5月的变压器重载情况,如图6所示。点击变压器重载明细表格中的某一电压等级时,将只显示该电压等级的变压器重载详情。点击表格右侧的
时,会弹出2016年5月的变压器重载情况,如图6所示。点击变压器重载明细表格中的某一电压等级时,将只显示该电压等级的变压器重载详情。点击表格右侧的 ,则会弹出潮流信息曲线,如图7所示。此外,热谱图上的红色区域也可点击,可以弹出设备在对应时间的详细重载情况,如图8所示。
,则会弹出潮流信息曲线,如图7所示。此外,热谱图上的红色区域也可点击,可以弹出设备在对应时间的详细重载情况,如图8所示。
图9显示了安全运行模块断面负载功能分析。
Ø 图中列出了所有断面最高负荷、限值及负载率。负载率用颜色填充加数字表达,负载率<80%用蓝色表现,80%≤负载率≤90%用黄色表现,负载率>90%用红色表现,直观表现了断面重载信息。
图10显示了经济运行模块地方电厂电量功能分析。
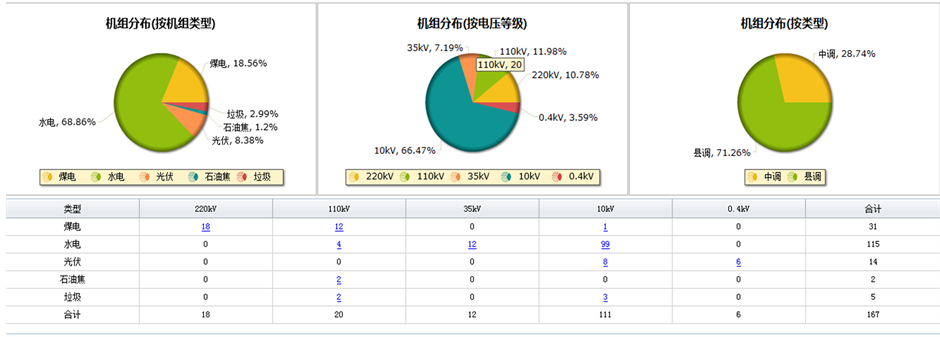
Figure 3. Power grid size-scale of power system installed
图3. 电网规模–装机规模

Figure 4. Detailed situation of the 110 kv coal unit
图4. 110 kv煤电机组的详细情况
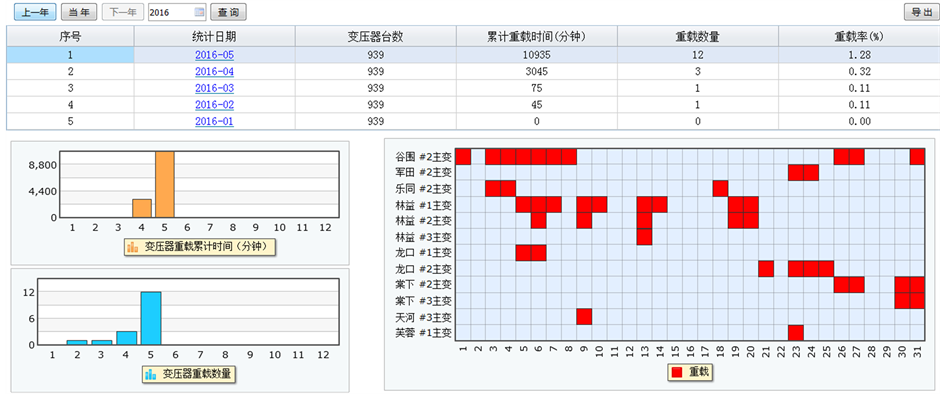
Figure 5. Safe operation-transformer overload
图5. 安全运行-变压器重载

Figure 6. Details of transformer overload
图6. 变压器重载明细

Figure 8. Detailed overload situation of failed device
图8. 故障设备的详细重载情况

Figure 9. Safe operation-section load
图9. 安全运行–断面负载
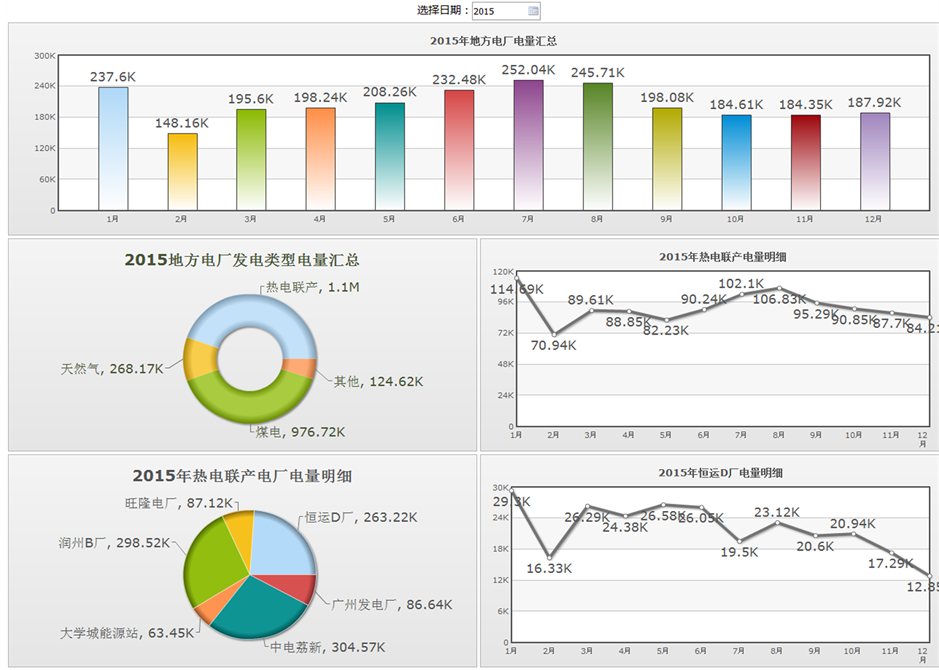
Figure 10. Economic operation-local power plant capacity
图10. 经济运行–地方电厂电量
Ø 上半部分柱图展示了各月的地方电厂发电量,下半部分,左侧饼图分别展示了当月/当年的各发电类型发电量的构成、当月/当年电厂的发电量构成,右侧曲线图则分别为发电类型全年发电量曲线、电厂全年发电量曲线。点击其中一个柱子,下面的饼图可以随之刷新。点击发电类型饼图时,发电类型全年发电量曲线和电厂发电量饼图也同时刷新。电厂发电量饼图根据所选的发电类型不同而显示不同的电厂,点击电厂发电量饼图的饼块,电厂全年发电量曲线会随之刷新。
5. 结论
与一般的城市电网运行评估体系相比,基于感知化理论的城市电网运行综合评估体系着重考虑了电力系统的信息特征和调度人员的认知规律。该评估体系在进行模块分组和功能设计时,充分结合了电力系统运行数据的特征以及调度人员评价电网运行结果的一般规律,使得系统界面清晰直观、一目了然,调度人员在使用该评估体系进行电网运行结果的评估时也能更加得心应手。基于感知化理论的城市电网运行综合评估体系将人的认知能力和系统的信息处理能力有机的结合在了一起,将人–机互动的设计思想与可视化界面进行了有机结合,利用人工智能技术从海量数据中挖掘出表征电网运行特性的关键数据,能够快速全面的揭示系统运行管理中的效益与不足。
基金项目
南方电网有限责任公司广州供电局科技项目《城市电网运行综合评估体系研究与系统开发》项目编号K-GZM2014-142。