1. 问题的提出
全国现有大型灌区430多处,重点中型灌区1500多处,其中部分灌区自“十五”期间开始进行信息化建设试点,目前多数试点灌区已经初步搭建起水情雨情自动采集、通信和计算机网络等灌区信息化系统的基础框架,但对水位、流量等监测数据的应用和挖掘明显滞后,更未见到关于灌区渠系水情错误数据判别等方面的研究成果。导致上述情况发生的主要原因是:灌区渠系水流是一个复杂系统,对于异常水情数据,常常难以区别是由于灌溉用水存在的明显不确定性造成的,还是监测系统出现故障采集到了错误数据。本文针对上述存在的问题,引入信息融合理论和相关技术,着眼于挖掘灌区水情监测数据隐含信息,将目前灌区的水情监测系统提供的实时数据,与基于领域知识开发的灌区渠系水情态势估计及态势预测系统相结合,通过信息融合技术实现灌区渠系水情错误数据判别。
灌区水情监测系统发生故障可能源于水位、闸位、流量等传感器故障,也可能源于传输、存储等环节,但无论何种原因,最终都反映在监控系统接收的水位、闸位、流量等监测数据上。灌区渠系水情态势估计及态势预测系统,不仅能跟踪实际灌区系统运行,而且生成的具有全局性的状态信息和预测信息,还具有广泛的应用前景。当灌区发现个别监测数据异常并不能简单剔除。故障诊断 [1] [2] [3] 通常针对具体设备或生产线进行,可以诊断到设备级,也可以诊断到部件(功能板卡)级,甚至到零件(元器件)级。受信息获取层次的限制,本文并不针对故障发生部位、性质等的具体判别,而是希望基于实时检测数据,并通过灌区态势估计及预测系统及时发现灌区水情监测系统运行异常情况,避免使用存在错误的数据,避免对灌区渠系水情态势做出误判。
基于解析模型 [4] [5] 的故障诊断方法的指导思想是用解析冗余取代硬件冗余,进而通过构造观测器估计系统输出,再与系统输出的实际测量值作比较得到残差信号。当系统没有故障时,残差为零或近似为零;当系统中出现故障时,残差显著偏离零点。本文拟借鉴这一思路,通过将不同信息组合的态势预测结果作为不同证据,并基于证据理论构建监测数据错误判别模型。
2. 基于态势预测的灌区渠系水情监测数据错误判别方法
灌区工程设施和运行调度通常实行分级、分片管理,灌区信息化建设依据灌区管理体制进行总体设计,因此灌区水情实时监测系统实际上已经将灌区渠系分割为若干相对封闭的区域,但这些区域又不是孤立的,区域之间存在一定程度的相互影响。如相邻闸门的过闸流量信息对推测该区间用水流量具有较强的约束作用,但过闸流量不仅与本侧水位有关,同时也受另一侧水位的影响,即受相邻区域的影响。这些特点说明,实现灌区渠系水情信息融合时按照大系统处理方法划分计算区间,并区分计算区间的内部关系以及计算区间之间的相互关系有利于复杂问题的求解。显然计算区间需要灌区水情实时监测系统为其提供必要的边界条件,故受到一定限制,故提出如下计算区间划分方法:
1) 分析灌区渠系水情监测系统的测站分布,标注其中可以直接或间接提供流量监测数据的测站。实际上除少数专门的流量测站外,利用工程条件较好、经过率定的闸门等建筑物也可以根据上下游水位和闸门开度计算其过闸流量。
2) 合理确定计算区间范围,使各计算区间的边界具有流量监测数据,且应充分利用灌区水情实时监测系统提供的过闸流量、断面流量信息,划分为数量相对较多的计算区间。各计算区间如果包括水位测站则可显著提高渠槽蓄水和渠段渗漏量的计算精度,进而提高干扰用水的估计精度。
灌溉用水通常可以分解为计划用水和不确定用水(指明显超出计划用水随机性和量测精度的用水偏差)。不确定用水通常包括:① 在计划用水期间额外增加或减少流量;② 提前或推迟关闭用水;③ 提前或推迟开启用水;④ 未列入用水计划但开启用水等情况,所以当发现有数据异常时,要甄别出是发生了不确定用水流量,还是出现了监测数据错误。
假定存在不确定用水流量和水情监测数据发生错误是彼此完全独立的事件,可能其中任何一个事件单独发生,但也有可能同时发生,故判别监测数据错误的问题较为复杂。将该问题分为两个子问题考虑,一是首先判断发生了不确定用水流量还是监测数据异常;二是如果发现监测数据异常,则进一步判断哪个数据发生错误。
1) 不确定用水流量的合理性判断
考虑到无论哪个监测数据发生错误,最终都会归结到不确定用水流量上,而不确定用水实际上受工程、管理等方面的限制,不可能是任意大小,也不可能任意分布,故可对提取的不确定用水流量的合理性进行限制。即当qdi > qdimax或qdi < −qdimax时,判定提取的不确定用水流量不可用,系有关监测数据发生错误所致。其中qdi为第i个计算区间的不确定用水流量,qdimax和qdimin分别为该计算区间的不确定用水流量合理性判别阈值的上下限。qdimax一般可取各用水设计流量之和的20%~30%,qdimin可取各用水设计流量之和的30%~50%。
2) 监测数据错误判别的提法
尽管水情监测数据量较大,但在特定的“考察时段”内发生新的监测数据错误的概率仍属小概率事件,同时发生一个以上数据错误的概率更小。另外,尽管不确定用水流量在灌区时有发生,但在特定的“考察时段”内发生新的不确定用水流量也属于小概率事件。因此,在已经确定发生新的监测数据错误的情况下,同时又发生新的不确定用水流量的概率更小,故在判断哪个监测数据发生错误时可以排除监测数据错误和不确定用水流量同时新发生的情况。由此本文将实际问题转化为如下较为简单的问题:将上一个监测时刻到当前监测时刻的时段作为故障考察时段,考虑到这个时段不长(一般为10分钟),假定在考察时段内不确定用水流量不发生变化,且渠系水情监测数据仅可能新发生一处错误,在此条件下判断哪个监测数据错误发生。显然在上述假定条件下的问题较原问题的不确定性显著减少。
实际上,监测数据错误判别的假定条件可以适当放宽,如将“考察时段内不确定流量不发生变化”放宽为“考察时段内不确定流量可以发生变化,但不得与监测数据错误发生在同一个或相邻子区间”;将“渠系水情监测数据仅可能发生一处错误”放宽为“渠系水情监测数据在相邻子区间范围内仅可能发生一处错误”等。假定条件的上述放宽一般不会改变对错误数据的判断,但将增加判断过程的复杂性。
即使在上述假定下,水源等边界条件仍可能发生变化,正常用水仍可能按计划开启、关闭,节制闸也可以在给定运行方式下调节开度甚至开启或关闭。因此,错误数据判别仍难以单纯依靠实时监测数据进行,需要综合考虑多种信息。证据理论是综合多种信息进行不确定推理的有效方法,其基本策略是将证据集合划分为2个或多个互不相关的部分(证据),利用它们分别对识别框架进行独立判断,然后再进行组合。应用证据理论的关键是设法获取相互独立的多个证据,除采用常用的外推法外,本文还尝试使用不同数据进行态势预测,并由预测信息获取证据的方法。这些方法可提供的证据如下:
1) 根据前一时刻状态估计结果,且在不使用当前时刻监测数据(即仍使用前一时刻的监测数据)的情况下,预测当前时刻的系统状态,并与某个基准进行比较,以其差别大小为依据进行基本概率赋值。该类证据的优点是可以考察全部监测数据,缺点是易受闸门调节的影响。
2) 根据前一时刻状态估计结果,但在使用当前时刻闸门开度监测数据(即部分监测数据)的情况下,预测当前时刻的系统状态,并与某个基准进行比较,以其差别大小为依据进行基本概率赋值。该类证据的优点是不受闸门是否调节的影响,缺点是无法考察全部监测数据。
3) 根据以往监测数据的时间序列,预测当前时刻的数值,并与某个基准进行比较,以其差别大小为依据进行基本概率赋值。该类证据的优点是可以考察全部监测数据,缺点是易受用水和边界条件改变以及闸门调节等多种因素影响,特别是当系统状态变化趋势发生改变时易给出错误结果。
尽管上述三类证据均与实时监测数据有关,但提取证据的方法并不相同,即并不单纯依赖于实时监测数据或依赖于态势预测数据,故证据本身仍具有一定的独立性。
假定在考察时段内每个传感器提供且仅提供一个监测数据,则判别范围内的监测数据构成故障识别框架,命题表示其中某一个数据发生错误(即对应的传感器发生故障),定义 为A的基本概率赋值,则基本概率赋值函数
为A的基本概率赋值,则基本概率赋值函数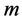 满足当A属于U框架上的事件时,所有
满足当A属于U框架上的事件时,所有 之和为1,即所有数据发生错误的基本概率赋值之和为1。
之和为1,即所有数据发生错误的基本概率赋值之和为1。 表示对命题的精确信任程度,即对的直接支持。若
表示对命题的精确信任程度,即对的直接支持。若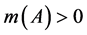 ,则是
,则是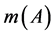 的一个焦元。由于假定考察时段内渠系水情监测系统仅可能发生一处故障,即仅可能有一个监测数据发生错误,任意2个或2个以上监测数据同时发生错误的基本概率赋值等于零,因此基本概率赋值函数
的一个焦元。由于假定考察时段内渠系水情监测系统仅可能发生一处故障,即仅可能有一个监测数据发生错误,任意2个或2个以上监测数据同时发生错误的基本概率赋值等于零,因此基本概率赋值函数 的全部焦元只可能是单独监测数据发生错误,而不含有这些监测数据同时发生错误的任何组合。
的全部焦元只可能是单独监测数据发生错误,而不含有这些监测数据同时发生错误的任何组合。
识别框架上的信任函数 ,也称为信任区间的下限函数。由于这里事件A并没有包含的子集,故有:
,也称为信任区间的下限函数。由于这里事件A并没有包含的子集,故有:
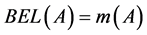 (1)
(1)
即对事件的总信任也就是它的基本概率赋值。
似真函数PL定义为:
 (2)
(2)
即在本文所作假定下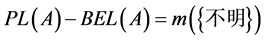 ,表示某个数据发生错误的不确定性或证据的不确定性。
,表示某个数据发生错误的不确定性或证据的不确定性。
相对获取的3类证据,设EL1,BEL2,BEL3是同一识别框架上的3个信任函数,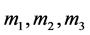 是其分别对应的基本概率赋值函数,并由获取的证据分别赋值。按照Dempster组合规则有:
是其分别对应的基本概率赋值函数,并由获取的证据分别赋值。按照Dempster组合规则有:
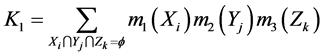 (3)
(3)
则
 (4)
(4)
式中:K1反映证据冲突的程度。若K1<或>1,则 确定一个对命题A的联合基本概率赋值;若K1 = 1,则认为m1,m2,m3矛盾。
确定一个对命题A的联合基本概率赋值;若K1 = 1,则认为m1,m2,m3矛盾。
由于本文假定在考察时段内渠系水情监测数据仅可能新发生一处错误,故各命题之间没有交集,证据冲突问题有可能比较突出,需设法解决。Smets [6] 认为引起出冲突的原因在于识别框架不够完备,Yager [7] 则认为证据冲突是由不可靠信息源引起的,围绕对证据冲突原因的不同认识,研究者提出了各种改进的证据合成方法和证据预处理方法。本文提出的三类证据均源于解析方法,存在一定的不确定性,同时识别框架也存在各命题之间完全没有交集的不足,综合考虑认为采用折扣系数法较为适合,即将基本概率赋值函数m满足当A属于U框架上的事件时,所有 之和为1改为满足:
之和为1改为满足:
 (5)
(5)
式中: 为信任程度的折扣系数,
为信任程度的折扣系数, ,
,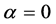 表示完全怀疑该证据,
表示完全怀疑该证据, 表示完全信任该证据。在本文中,
表示完全信任该证据。在本文中,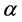 取值过小则难以判别哪个监测数据有误,
取值过小则难以判别哪个监测数据有误, 取值过大又难以有效减少证据冲突,一般可在0.6~0.9的范围内取值,其中可靠性高的数据源取较大值,可靠性低的数据源取较小值。折扣系数法一般将折扣下来的信任(基本概率)分配给识别框架的全域,考虑到本文通过干扰流量合理性判断已经确认在判别范围内存在错误数据,故可将折扣下来的信任(基本概率)分配给命题‘不确定’,表示支持在判别范围内监测数据有误但又不能确定哪个监测数据有误。
取值过大又难以有效减少证据冲突,一般可在0.6~0.9的范围内取值,其中可靠性高的数据源取较大值,可靠性低的数据源取较小值。折扣系数法一般将折扣下来的信任(基本概率)分配给识别框架的全域,考虑到本文通过干扰流量合理性判断已经确认在判别范围内存在错误数据,故可将折扣下来的信任(基本概率)分配给命题‘不确定’,表示支持在判别范围内监测数据有误但又不能确定哪个监测数据有误。
至此,如何进行基本概率赋值尚待解决。本文构建的三类证据与当前时刻监测数据无关或不完全相关,故可以各证据数据源相对于当前时刻对应监测数据偏差的绝对值作为基本概率赋值的依据。即满足:
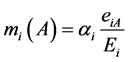 (6)
(6)
 (7)
(7)
式中: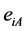 表示对于命题
表示对于命题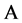 ,证据
,证据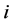 的数据源相对当前时刻对应监测数据偏差;
的数据源相对当前时刻对应监测数据偏差; 表示对于全部命题,证据
表示对于全部命题,证据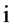 的数据源相对当前时刻对应监测数据偏差绝对值之和;
的数据源相对当前时刻对应监测数据偏差绝对值之和;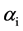 为证据
为证据 的信任程度折扣系数。
的信任程度折扣系数。
根据证据理论组合证据后,可以根据联合基本概率赋值 的分布情况进行决策,判定哪个数据存在错误。一般可以采用以下方法:
的分布情况进行决策,判定哪个数据存在错误。一般可以采用以下方法:
1) 根据联合基本概率赋值 ,用式(1)计算组合证据的信任函数
,用式(1)计算组合证据的信任函数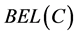 ,选择其中最大值对应的监测数据作为最可能发生错误的数据。显然这样的决策规则不包含不明确支持事件
,选择其中最大值对应的监测数据作为最可能发生错误的数据。显然这样的决策规则不包含不明确支持事件 的不确定性,是“相对保守”的判断。
的不确定性,是“相对保守”的判断。
2) 根据联合基本概率赋值 ,用式(2)计算组合证据的似真函数
,用式(2)计算组合证据的似真函数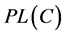 ,选择其中最大值对应的监测数据作为最可能发生错误的数据。显然这样的决策规则包含了不明确支持事件
,选择其中最大值对应的监测数据作为最可能发生错误的数据。显然这样的决策规则包含了不明确支持事件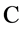 的全部不确定性,是“相对激进”的判断。
的全部不确定性,是“相对激进”的判断。
3) 介于上述方法之间的方法,如最大Pignistic概率方法等。
无论采用哪种方法,决策时还需要预先确定一个判别阈值以进行比较,这个判别阈值与组合证据时解决冲突的方法有关,需要根据经验确定。判别出的错误数据可以暂时不用,只要渠系水情监测信息整体上仍有一定冗余,则灌区渠系水情态势评估仍可正常进行,但必要时需重新划分计算区间,故计算区间划分工作应由信息融合系统动态完成。
3. 模拟试验
考虑到在比较基准选择上,水位监测数据发生错误的情况与闸位监测数据发生错误时有所不同,故2种传感器的错误判别需分别进行,且由于灌区渠系水情监测系统运行中前者比较常见,故模拟试验针对水位监测数据发生错误的情况进行。另外,为避免模拟试验内容过于庞杂,模拟试验范围限定于干渠的部分相邻渠段。显然模拟试验方法可以推广到闸门开度,也可以推广到灌区的全部渠系。
模拟试验对象是我国华北地区一个大型灌区的北干渠范围。灌区由一座大型水库供水,设北、南2条干渠,分别沿山前冲积扇两侧的台地布设。作为模拟试验对象的北干渠设计流量12 m3/s,长度约32 km,设计灌溉面积约6.67 hm2;支渠和由干渠直接取水的主要斗渠共有19条,其他斗渠均简化作为干渠或支渠上的用水处理,即模拟试验对象包括干、支二级渠道。模拟试验的渠系网格如图1所示,渠道分段长度取500 m,干渠划分为63段,支、斗渠划分为92段,合计155个计算渠段,覆盖全部灌溉面积。渠系建筑物包括引水闸1座、节制闸13座,退水闸2座等。
图2所示为距离渠首7.6 Km的“新干斗节制闸”的运行过程线,其中实线为闸门开度过程线,虚线为过闸流量过程线,点线为闸门上游渠段水深过程线,点划线为闸门下游渠段水深过程线。在第1天至第2天期间,灌区运行为初始阶段,各闸门处于逐渐开启和频繁调节状态,且往往下游部分节制闸尚未开启或开度很小,导致水位变化较大,错误判别的不确定性也较大,因此验证本文错误数据判别方法的针对性更强些。表1所示为第1天12时至16时新干斗节制闸运行数据,即正常情况下该期间新干斗节制闸开度由0.399 m增加到0.481 m,其上游水深由1.157 m变化为1.342 m,下游水位由0.925 m变化为1.087 m。
模拟试验设定的情景为:第1天14时,该节制闸上游水位传感器发生故障,致使报出的水位数值比实际数值大0.2 m。表2为第1天14时新干斗节制闸(闸门编号5)及其上下游各2个相邻节制闸的运行数据,其中新干斗节制闸上游水深监测数据属错误数据,比较可见该数据与表1的对应数据明显不匹配。在试验情景下,通过水情监测数据发生器模拟实际系统运行,并给出包括错误数据在内的全部监测数据。表2中也给出了新干斗节制闸(编号5)及其上下游各2个相邻节制闸(编号分别为3、4以及6、7)在第1天14时的运行仿真数据。
数据错误判别证据理论模型对识别框架 上的
上的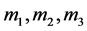 3个基本概率赋值,结果如表3所示。
3个基本概率赋值,结果如表3所示。
根据式(3)计算,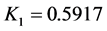 ,它反映证据冲突的程度。由于
,它反映证据冲突的程度。由于 远小于1,故可根据式(4)计算监测数据错误各命题的联合基本概率函数
远小于1,故可根据式(4)计算监测数据错误各命题的联合基本概率函数 ,结果示于表4。
,结果示于表4。
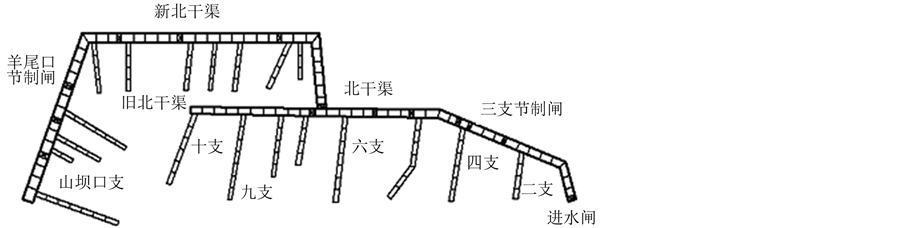
Figure 1. Grid of experiment irrigation area canal for water information state
图1. 灌区渠系水情状态估计模拟试验渠系网格图

Figure 2. The running hydrograph of new bucket control gate in the normal circumstances
图2. 正常情况下新干斗节制闸运行过程线

Table 1. Running data of first day 12:00 to 16:00 of the new bucket control gate
表1. 正常情况下新干斗节制闸第1天12时至16时运行数据

Table 2. Monitoring data of new bucket control gate in the test circumstances and simulation running data
表2. 试验情景下新干斗等节制闸运行监测数据和仿真数据

Table 3. Basic probabilities of failure of each sensor in the current test circumstances
表3. 试验情景下各传感器发生故障的基本概率

Table 4. Joint probabilities of failure of each sensor without monitoring data on the current test circumstances
表4. 试验情景下各传感器故障的联合基本概率赋值
由以上模拟可以知道:新干斗节制闸(编号5)上游水位数据发生错误命题的置信度BEL (即联合基本概率赋值)等于0.7564,似然度PL等于0.8005 (即0.7564 + 0.0441),比融合前的置信度(即基本概率赋值)和似然度均有明显提高,且与其他其他命题(如编号7节制闸上游水位数据发生错误命题)的差距更为明显,因此更容易判定新干斗节制闸上游水位数据发生了错误。
4. 结论
一般而言,只要监测时间间隔不大,且这一期间灌区水情无大幅度急剧变化,本文建立的监测数据错误判别方法应该是有效的。另外,在不确定推理中还可以针对“监测数据固定不变”(如传感器严重损坏所致)、“缺报数据”等具体问题,引入新的证据,进一步提高错误判别的针对性和准确性。