1. 引言
在世界范围内,大约有1/3油气资源储存于碳酸盐岩储层中,特别是中东、北美、俄罗斯的许多大型或特大型油气田均与碳酸盐岩密切相关 [1] [2] 。据统计,中东地区石油产量约占全世界产量的2/3,其中80%的含油层产于碳酸盐岩 [1] ,白垩系Mishrif组碳酸盐岩储层是波斯湾盆地乃至中东地区最主要的储集单元 [3] [4] 。米桑油田群作为伊拉克一个重要的油田,位于伊拉克东南部米桑省,毗邻伊朗边界,南距巴士拉约175公里,西北距巴格达约350公里,该地区构造上位于扎格罗斯山脉隆起带和N-S向的阿拉伯构造带东部边缘的过渡带上 [5] [6] 。该油田群包含(AG, BU, FQ)三个油田,其中古近系渐新统Asmari组(AG和FQ)和白垩系Mishrif组(FQ和BU)是研究区的主要产层。区域沉积表明,Mishrif组沉积期,阿拉伯地区发生区域构造活动,形成地貌高地和低地,大部分高地成为有机体建造(厚蛤礁)发育部位,其中研究区主要发育缓坡碳酸盐岩台地相 [4] [7] 。前人研究表明,白垩系Mishrif组储层具有连片性好、有效厚度大、物性好等特征 [7] [8] [9] [10] 。
国内外学者针对研究区周边Mishrif组碳酸盐岩储层做过大量的研究 [7] - [15] ,但就研究区而言受控于资料有限,针对性的研究甚微,且有限的研究也主要集中在沉积作用以及成岩作用类型方面 [7] [16] 。目前,Mishrif油藏在开发过程中存在部分井产能低、局部含水及“甜点带”认识不清等问题,这些成为制约油气田“增储上产”的关键因素。鉴于此,本文在已有10口取心井实测物性资料的基础上,借助研究区4口新取芯井分析化验资料,通过岩心观察、铸体薄片、扫描电镜以及阴极发光等资料,详细分析了储层孔隙在整个成岩过程中的演化规律,认清了储层形成过程及影响因素,为优质储层平面分布的预测以及新井井位部署提供了依据。
2. 储层岩石类型及成岩作用特征
2.1. 岩石类型
根据4取心井岩心及66件样品的铸体薄片统计分析表明,Mishrif组储层段以颗粒灰岩为主,次为泥晶灰岩。颗粒灰岩类包括亮晶颗粒灰岩、微亮晶颗粒灰岩和泥晶颗粒灰岩,其骨屑颗粒包括海藻、有孔虫、腹足类、瓣鳃类、腕足类、厚壳蛤类、骨针等,非骨屑颗粒包括球粒、砂屑及少量砾屑(图1)。镜下观察到的灰泥大多数是微泥晶,但在孔隙度高的灰岩中灰泥容易发生新生变形而变为微亮晶,形成微亮晶灰岩,发育较多的晶间孔和晶间溶孔。垂向上泥晶灰岩主要发育在滩体的下部及泻湖环境中,颗粒细小,岩石较致密;颗粒灰岩主要发育在滩体的上部,是研究区最主要的储层岩石类型,显示了储层发育与滩相沉积密切相关。
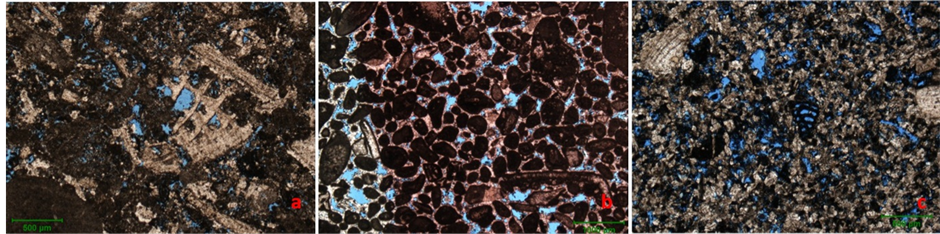 (a) 3882.5 m,B-51井,亮晶内碎屑生物灰岩,溶孔发育,以粒间溶蚀为主,少量粒内溶孔(偶见铸模孔),见有孔虫;(b) 3907.0 m,B-52井,亮晶生屑灰岩,以粒间溶孔为主,砂屑发育;(c) 3886.0 m,B-52井,微亮晶颗粒灰岩,粒间溶孔发育,生物碎屑呈残余状,见有孔虫、双壳及棘皮类生物碎屑
(a) 3882.5 m,B-51井,亮晶内碎屑生物灰岩,溶孔发育,以粒间溶蚀为主,少量粒内溶孔(偶见铸模孔),见有孔虫;(b) 3907.0 m,B-52井,亮晶生屑灰岩,以粒间溶孔为主,砂屑发育;(c) 3886.0 m,B-52井,微亮晶颗粒灰岩,粒间溶孔发育,生物碎屑呈残余状,见有孔虫、双壳及棘皮类生物碎屑
Figure 1. Photomicrographs showing lithologies of Mishrif Formation
图1. Mishrif组岩石学镜下特征
2.2. 物性特征
通过对14口取心井1915个实测物性样品物性统计发现,研究区孔隙度主要分布在5%~25%的范围之内,占到了总样品个数的85%;渗透率主要分布在1~10 mD之间,占总样品个数的53.7%,次为10~100 mD,占总样品个数的27.2%,储层主要以中孔低渗储层为主,纵向上局部发育中孔高渗储层,体现了储层具有较强的非均质性。研究区储层孔隙度与渗透率之间相关性差(图2),整体上没有明显的相关性,主要是由于滩相储层不同孔隙类型的叠加作用所影响。
2.3. 成岩作用类型及成岩序列
研究区Mishrif组碳酸盐岩油藏中深113℃,处于中成岩阶段。因此,研究区Mishrif组碳酸盐岩储层可划分为三个成岩阶段,并与之相对应的环境分别为:① 准同生成岩阶段-海底环境与大气淡水(潜流带、渗流带)环境;② 早成岩阶段-浅埋藏成岩环境;③ 中成岩阶段-中埋藏及深埋藏成岩环境。研究区Mishrif组碳酸盐岩储层埋深4000 m,成岩时间较长,成岩作用复杂,成岩作用类型多样 [16] ,主要成岩作用、产物及成岩环境见表1。
成岩序列具体表现为:海底环境的泥晶化作用,一世代纤状、马牙状胶结,准同生白云岩化,大气淡水选择性溶蚀作用,大气淡水和浅埋藏期的二世代粒状胶结,埋藏期的压溶,早期胶结物充填作用,构造挤压作用、重结晶作用,中成岩早期埋藏溶蚀及局部充填,微破裂作用,中成岩晚期-晚成岩早期开始进油演化为沥青。
整体而言,准同生期形成的溶蚀孔隙对储层形成具有重要意义,为优质储层形成奠定了基础;早成岩阶段发生的压实、胶结充填作用对储层先存孔隙破坏力度大,在该阶段同样会形成抗压实骨架,对后期储层孔隙形成具重要意义;埋藏期的溶蚀作用及构造作用对储层的贡献相对较小。
3. 储层孔隙演化
3.1. 准同生成岩阶段
研究区储层在准同生成岩阶段主要经历了正常浅海海底环境、大气淡水(潜流带、渗流带)环境。在海
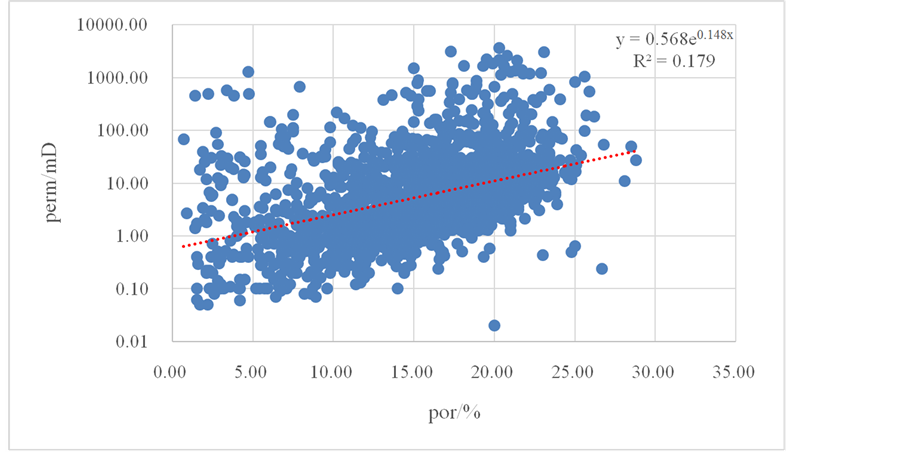
Figure 2. Relationship between porosity and permeability of the Mishrif Formation reservoir rock
图2. Mishrif组储层孔隙度渗透率交会图

Table 1. Diagenesis and diagenetic environment of Mishrif Formation in Missan Oilfields
表1. 米桑油田群Mishrif组成岩作用及成岩环境
底成岩环境,以发生颗粒硬化、泥晶化、海底胶结作用。泥晶化作用主要表现为在生物碎屑颗粒的外缘不同程度的被暗色泥晶所取代(图3(a)),虽然对孔隙度的增加影响不大,但增加了颗粒的抗压强度。准同生成岩阶段的胶结作用呈纤状垂直颗粒或粒缘呈等厚环边栉壳状生长,厚约0.01~0.05 mm。该期胶结物主要表现为充填粒间孔,镜下观察统计第一期胶结物使孔隙度降低了8%左右(图3(b)、图3(c))。
前人针对白垩系Mishrif组沉积时期的古气候的研究显示,该时期气候整体上表现为温暖潮湿 [7] 。在颗粒灰岩中发育的原生粒间孔内,可见到第一期纤状方解石胶结物遭到溶蚀而变得残缺不全,这是因为这类碳酸盐岩沉积物在经历了海底成岩环境的胶结作用后,受海平面频繁升降的影响,生屑滩暴露在大气淡水环境中,受到大气淡水溶蚀形成粒间溶孔、粒内溶孔、铸膜孔以及溶洞等(图4)。薄片观察表明,
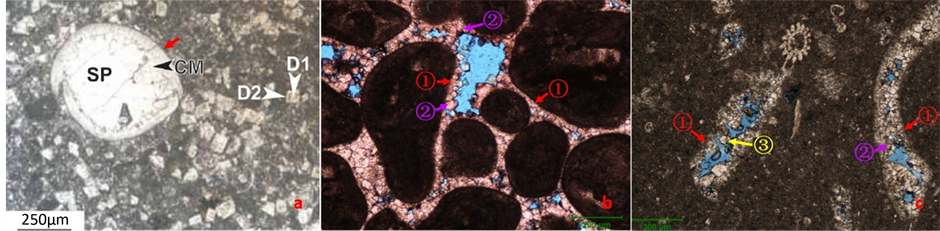 (a) B-1井,3887.0 m,生屑泥晶灰岩,颗粒外缘发育泥晶环;(b) B-52井,3907 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,见多期胶结物;(c) F-28井,4113 m,微晶生屑灰岩,见多期胶结物
(a) B-1井,3887.0 m,生屑泥晶灰岩,颗粒外缘发育泥晶环;(b) B-52井,3907 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,见多期胶结物;(c) F-28井,4113 m,微晶生屑灰岩,见多期胶结物
Figure 3. Photomicrographs showing lithologies of Mishrif Formation
图3. Mishrif组岩石学镜下特征
 (a) B-22井,3915 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,铸体;(b) B-1井,3927 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,铸体;(c) B-22井,3918 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,岩心
(a) B-22井,3915 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,铸体;(b) B-1井,3927 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,铸体;(c) B-22井,3918 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,岩心
Figure 4. Photomicrographs showing lithologies of Mishrif Formation
图4. Mishrif组岩石学镜下特征
这期溶蚀作用溶蚀强度大,大量溶孔被保存下来,成为Mishrif组储层中主要的孔隙类型,改期溶蚀作用使岩石孔隙增加15%左右,但大部分次生溶孔与剩余粒间孔一起保存下来进入中成岩阶段。
总之,在准同生成岩阶段,海底胶结作用以破坏孔隙为主,泥晶化作用能增大岩石的抗压强度,对沉积物沉积孔隙起到一定的保护作用,溶蚀作用形成的大量孔隙对储层形成具重要意义,同时也为后期流体运移和进一步溶蚀作用的进行提供条件,为优质储层形成奠定基础。
3.2. 早成岩阶段
在经历了准同生成岩阶段以后岩石己经固结,便进入早成岩阶段的浅埋藏成岩环境 [17] [18] [19] 。在浅埋藏环境中粒间(溶)孔内沉淀粒状方解石和白云石,粒间(溶)孔内沉淀的粒状方解石能增大岩石的抗压实能力,早成岩阶段的压实作用导致部分粒间孔的丧失,以及生物碎屑(厚壳蛤碎屑)折断。镜下观察统计受压实作用影响的颗粒仅占4%,更多的颗粒未受压实作用的影响。当埋藏深度达到一定程度时,开始形成压溶缝合线,产生大量溶解态的碳酸钙,这部分碳酸钙在早期溶孔、溶洞中缓慢结晶形成粗晶方解石。阴极发光特征显示出弱发光性或不发光,表明粗晶方解石为还原环境下的产物(图5)。
第二期胶结物主要形成在浅埋藏环境,呈粒状充填于第一期胶结后的残余原生粒间孔中(图2(b)、图2(c)),含量可达10%以上。受第二期胶结作用的影响,孔隙可降低70%~90%,剩余孔隙为第三期胶结作用创造了条件。
综上所述,在早成岩阶段发生的压实作用对储层先存孔隙的影响不大,而胶结充填作用对储层先存孔隙破坏力度大。
3.3. 中成岩阶段
中成岩阶段,随着有机质的成熟逐渐进入生油高峰期,在该环境中,温度、压力、构造活动、烃类
生成等是成岩作用发生的主导因素,温度、压力是使岩石重结晶作用进一步加强的主要应力,在压实压溶作用下形成压溶缝合线等,构造活动会形成微裂缝,烃类活动使有机质热降解过程中产生的有机酸与孔隙水混合后产生溶解并形成各类溶孔(洞)或缝等 [20] 。
随着埋藏深度的增大,地层温度压力增大,岩石发生重结晶作用,泥微晶重结晶为粉晶、细-粗晶,原来的晶间微孔合并增大,为酸性流体进入岩石发生溶蚀提供通道。Lambert (2006) [21] 对伊拉克地区白垩系Mishrif组中发生的重结晶作用做过详细研究,认为碳酸盐岩在重结晶与溶蚀作用的共同作用下可以形成优质储层。经详细研究,研究区碳酸盐岩沉积物,尤其在含生屑泥晶灰岩中晶间(溶)孔特别发育(图6(a)、图6(b)),这也是该类岩石能够成为储层的主要原因之一。
研究区碳酸盐岩中埋藏溶蚀作用发生,一个方面来自随着埋藏深度增大、温度和压力的变化,CO2等酸性气体在地层水中的溶解度增大,增强地层水的腐蚀性;另一方面,有机质成熟过程中会产生大量的除CO2外的各种气体,随着烃类一起运移到储集层中与有机酸混合到孔隙水中与碳酸盐岩发生化学反应,对先存孔隙进行扩溶或增加新的溶蚀孔隙 [22] [23] 。该阶段的溶蚀作用主要对早期胶结作用所保留下来的粒间孔、白云化作用形成的晶间孔以及同生期未发生溶蚀的颗粒进行溶蚀改造,形成粒间溶孔、晶间溶孔以及粒内溶孔等重要的孔隙类型。镜下薄片观察,部分溶孔中见沥青充填,并有少量白云石、方解石及石英充填(图6(c)、图6(d))。
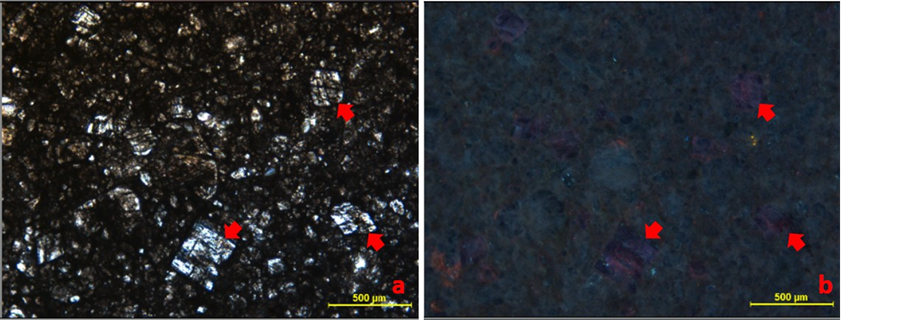 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 5. Cathodeluminescence characteristics of B-52 well of Mishrif Formation
图5. B-52井Mishrif组储层镜下及阴极发光特征(a为常规薄片,b为对应的阴极发光照片)
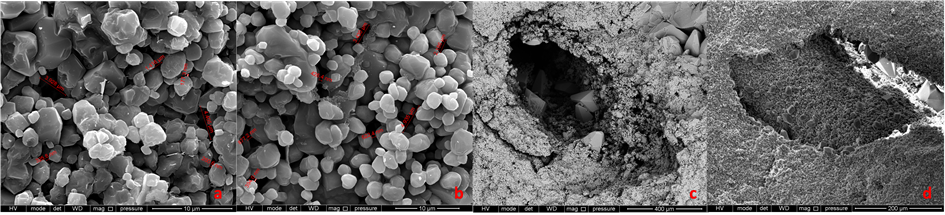 a 4055.59 m,晶间孔发育 b 4038.91 m,晶间孔发育c 4039.91 m,溶孔中充填方解石d 4087.7 m,溶孔中充填石英
a 4055.59 m,晶间孔发育 b 4038.91 m,晶间孔发育c 4039.91 m,溶孔中充填方解石d 4087.7 m,溶孔中充填石英
Figure 6. Scanning electron microscope characteristics of F-28 well of Mishrif Formation
图6. F-28井Mishrif组储层扫描电镜特征
总之,在中成岩阶段,控制储层孔隙演化的主要成岩作用有重结晶作用和埋藏溶蚀作用。其中重结晶作用虽然没有为储层增加新的孔隙,但为后期的溶蚀作用提供了良好的流体通道和大量水岩接触的溶蚀界面。受埋藏期溶蚀作用的影响,岩石孔隙度增加约2%~4%,这些孔隙中后期被少量的白云石、方解石以及石英等矿物充填,使孔隙减少1%~2%,总体上储层孔隙降低有限。经过整过成岩作用的改造,目前储层总有效孔隙度为15.34%,局部溶蚀作用发育处孔隙度可达25%以上。
4. 结论
(1) 米桑油田白垩系Mishrif组储层以颗粒灰岩为主,次为泥晶灰岩;储层以中孔低渗为主,局部发育中孔中渗储层,孔渗相关性差,体现出较强的非均质性;
(2) 研究区储层经历了准同生成岩、早成岩及中成岩三个阶段。其中准同生期在海底环境形成的胶结作用使孔隙度降低了8%左右,但生屑滩受海平面频繁振荡的影响,暴露在大气淡水环境中遭受大气淡水溶蚀,增加了次生溶孔约15%;
(3) 早成岩阶段发生的压实作用对储层先存孔隙的影响不大,而胶结充填作用对储层先存孔隙破坏力度大,可使孔隙降低70%~90%;中成岩阶段的重结晶作用没有增加储层孔隙,但为后期的溶蚀作用提供了良好的流体通道和大量水岩接触的溶蚀界面;
(4) 现今储层的有效储集空间主要是准同生成岩阶段大气淡水溶蚀作用形成的溶蚀孔、洞,中成岩阶段埋藏期溶蚀作用对岩石孔隙度的贡献能力有限。
基金项目
国家重大科技专项“亚太及南美地区复杂油田开发地质关键技术研究”(2011ZX05030-005)资助。