1. 引言
溃疡性结肠炎(Ulcerative Colitis, UC)于1859年由Wilks首先描述为不同于细菌性痢疾的独立的结肠炎性疾病 [1] 。它是一种以大肠黏膜及黏膜下层的炎症为主要病变特征的难治性疾病,病理改变为溃疡形成,隐窝脓肿,小血管炎症,杯状细胞减少以及各种类型的炎症细胞浸润等非特异性表现,临床表现主要为腹泻、腹痛、黏液血便等 [2] 。目前治疗措施主要是使用皮质激素类药物、非甾体抗炎药或免疫抑制剂针对炎症反应对症进行治疗,虽有一定的疗效,但长期应用有毒副作用 [3] 。因此,寻找疗效良好,安全,价格便宜且副作用小的药物是目前治疗UC的重点。
温栀子,俗名黄枝,是种植在江浙的主要栀子,栀子中含有大量的环烯醚萜甙类化合物,种类有9~11种 [4] 。栀子苷是栀子环烯醚萜甙中的主要成分,具有显著的抗炎、解热、镇痛作用 [5] 。但温栀子是否具有UC的治疗作用,尚未见报道。本研究拟通过不同剂量温栀子治疗溃疡性结肠炎大鼠模型,初步探讨温栀子对UC的治疗效果,以及合适的治疗剂量,为寻求简单易行、经济实惠、能有效治疗溃疡性结肠炎的新药物、新剂型及治疗溃疡性结肠炎的临床应用提供帮助。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 材料
2.1.1. 实验动物
雄性SD大鼠48只,体重240.44 ± 16.92 g,由温州医科大学动物实验中心提供。
2.1.2. 主要实验药品及试剂
栀子苷:纯度:HPLC ≥ 98%,西安森卓生物科技有限公司;2,4-二硝基氯苯(DNCB):化学纯,长沙晶康新材料科技有限公司;大鼠肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α) ELISA试剂盒,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;大鼠白介素1 (IL-1)ELISA试剂盒,上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
2.1.3. 主要实验仪器
扫描电子显微镜(HITACH, S-3000N);透射电子显微镜(HITACH, H-7500);光学显微镜(LEICA, CME);高效液相色谱仪(Agllent-1260型);酶标仪(Varioskan Flash, Thermo Fisher)。
2.2. 实验方法
2.2.1. 温栀子的采集与栀子苷的提取
购买种植基地已干制的温栀子果实。采用乙醇提取法提取温栀子的有效成分—栀子苷,由高效液相色谱仪对比分析,由于条件有限,选择购买栀子苷成品用于灌肠。
2.2.2. 实验动物分组及处理
选取遗传背景明确,健康状况好的雄性七周龄SD大鼠48只,适应性饲养五天后,采用DNCB/乙酸复合法 [6] 建立SD大鼠溃疡性结肠炎模型。确定35只造模成功,用随机分组法将模型组SD大鼠分为低、中、高剂量温栀子组、SASP阳性对照组和生理盐水对照组,分别用以66.67 mg/kg、100.00 mg/kg、133.33 mg/kg浓度的栀子苷、750 mg/kg的SASP (一般成人SASP的日用量为50 mg/kg,因实验设计需要,我们给SD大鼠的用药为成人的15倍量,按本次实验大鼠的平均体重240 g计算其SASP的日用量为180 mg,(50 × 240 × 1000 − 1) × 15。根据中医药典,SASP相应的15倍量于人的栀子苷有效用量为16 mg,故每只大鼠的SASP的日用量为180 mg,栀子苷的日用量为16 mg)和生理盐水进行灌肠治疗14天。
2.2.3 解剖取材
SD大鼠经腹腔麻醉后,取出距肛门8 cm的结肠肠段,保存备用。观察大体形态结构。参考张涛等 [7] 文献的评分标准(表1)对结肠大体形态进行评分。
2.2.4 组织石蜡切片制备
经常规病理石蜡切片,HE染色,光镜下观察,参考杜群等 [8] 文献的评分标准(表2)对结肠组织的损伤进行评分。
2.2.5 扫描电镜样品制备
取待用结肠组织戊二醛固定,乙醇溶液梯度脱水,临界点干燥,用离子溅射仪镀膜。
2.2.6 统计分析
采用SPSS19.0软件进行统计学分析,计量资料采用均数 ± 标准差(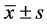 )表示,各组之间比较用方差分析,P < 0.05认为差异有统计学意义。
)表示,各组之间比较用方差分析,P < 0.05认为差异有统计学意义。

Table 1. The rats’ colon gross morphology score standard
表1. 大鼠结肠大体形态评分标准

Table 2. The rats’ colon histopathology score standard
表2. 大鼠结肠病理组织学评分标准
3. 实验结果
3.1. 黏膜大体形态评分分析
大体形态评分情况见表3。空白对照组大鼠结肠未见溃疡,结肠皱襞整齐;生理盐水对照组大鼠结肠可见明显的水肿,部分可见明显的溃疡;低剂量栀子组大鼠结肠溃疡水肿面积明显减少,水肿症状明显改善。中剂量温栀子组大鼠结肠溃疡较少,充血、水肿减少。高剂量温栀子组结肠水肿、充血情况不明显。SASP阳性对照组大鼠情况与高剂量温栀子组相似。
3.2. 病理切片结果分析
镜下肠道HE染色结果显示:空白对照组大鼠结肠的黏膜层、黏膜下层和肌层及浆膜层均完整,结肠各层结构清晰(如图1(a));生理盐水对照组大鼠肠道黏膜上皮受损,黏膜及黏膜下层可见,腺体变形,排列紊乱,大量炎性细胞浸润,血管充血(如图1(b));SASP阳性对照组、低、中、高剂量温栀子组大鼠肠道黏膜均得到改善,其中以SASP阳性对照组和高剂量温栀子组呈接近正常的组织像(如图1)。评分情况见表3。
3.3. 扫描电镜超微结构观察
扫描电镜观察结果显示:空白对照组可见许多结肠腺窝开口于黏膜表面(如图2(a)),表面衬贴具有微绒毛的单层柱状上皮和大量杯状细胞及吸收细胞(如图2(g))。生理盐水对照组结肠表面出现肿胀,肠腺开口周围隆起且形状不规则,腺管表面的界沟不明显(如图2(b)),黏膜中杯状细胞基本脱落且微绒毛稀疏,排列不整齐(如图2(h))。SASP阳性对照组结肠表面平滑,肠腺开口清晰(如图2(c)),表面有不同分泌周期的杯状细胞且微绒毛排列整齐致密(如图2(i))。低剂量温栀子组结肠表面较为平滑,肠腺开口略有变大(如图2(d)),表面有较多杯状细胞脱落且微绒毛排练较为稀疏(如图2(j))。中剂量温栀子组结肠表面平滑,肠腺开口清晰(如图2(e)),结肠表面微绒毛排列较为整齐且只有部分杯状细胞脱落(如图1(k))。高剂量温栀子组结肠表面较为平滑,肠腺清晰(如图2(f)),表面有不同分泌周期的杯状细胞且微绒毛排列整齐致密(如图2(l))。
4. 讨论
UC是临床上常见的一种反复发作、经久难愈的疾病,且与结肠癌关系密切。现代中医学将溃疡性结肠炎归为“泄泻”、“休息痢”、“肠癖”、“滞下”、“肠风”、“下血”、“脏毒”等范畴,对其病因、病机及分型有多种论述 [9] ,但其确切病因和发病机制迄今未明,多数学者认为,可能是遗传、环境和免疫等多因素共同作用的结果 [10] 。UC的发病机制可能是结肠黏膜局部免疫紊乱,同时伴有全身免疫功能失调 [11] 。本实验研究看到,温栀子治疗后,大鼠结肠溃疡坏死面积明显减少,充血、水肿明显
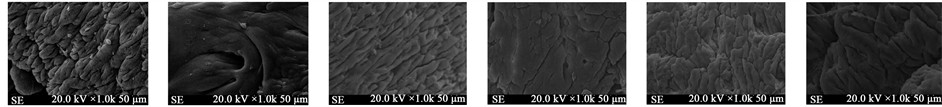 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f)
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f)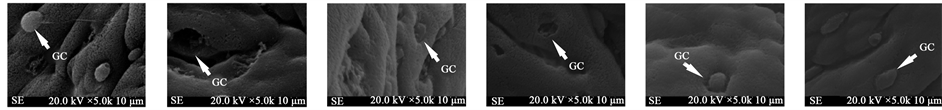 (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) (l)
(g) (h) (i) (j) (k) (l)
Figure 2. Group SD rats’ colonic surface and villous and goblet cell ((a)-(f) ×1000, (g)-(l) ×5000) (GC: goblet cell). (a) (g) Normol, (b) (h) NS, (c) (i) SASP positive control, (d) (j) low of dose Wen gardenia, (e) (k) Medium dose Wen gardenia, (f) (l) high dose Wen gardenia
图2. 各组SD大鼠结肠表面绒毛及杯状细胞((a)-(f) ×1000, (g)-(l) ×5000) (GC:杯状细胞)。(a) (g) 空白对照组,(b) (h) 生理盐水对照组,(c) (i) SASP阳性对照组,(d) (j) 低剂量温栀子组,(e) (k) 中剂量温栀子组,(f) (l) 高剂量温栀子组

Table 3. Every group of SD rats’ general form and pathology score average ()
表3. 各组SD大鼠大体形态病理学评分平均值( )
)
注:与空白对照组比较,*P < 0.05,与生理盐水组较,△P < 0.05,△△P < 0.01
改善,结肠粘膜上皮表面微绒毛基本完整,腺上皮间连接紧密,腺杯状细胞修复,分泌增强。温栀子含有大量的环烯醚萜甙类化合物,栀子苷酸可显著加快肉芽肿形成和胶原蛋白合成,促进创面快速良好的愈合 [12] ,表明温栀子可以修复受损结肠上皮细胞,促进细胞功能恢复。研究证实杯状细胞参与了肠粘膜损伤表面细胞重建的过程,并起着关键作用 [13] ,实验结果表明温栀子可能通过加快杯状细胞的转化、增殖,颗粒分泌增加,分泌的粘液有很强的细胞保护作用,可明显减轻多种因子介导肠粘膜损害进而加快肠道粘膜重建和溃疡修复过程。
实验表明温栀子具有一定的止泻、抗炎、减轻肠黏膜损伤和修复受损细胞的作用,其作用机理可能与其清热利湿、泻火解毒、活血化瘀、去腐生新的功效有关 [9] ,对溃疡性结肠炎具有治疗作用,但不同剂量温栀子组大鼠愈合情况存在差异,其中以高剂量温栀子治疗组(32 mg/kg)效果较佳,与SASP阳性对照组疗效相当。综上,温栀子对大鼠溃疡性结肠炎具有明显地治疗作用,因此温栀子在治疗溃疡性结肠炎中显现出了潜力,或许是治疗溃疡性结肠炎新的靶点。
基金项目
浙江省大学生科技创新活动计划(新苗人才计划)大学生科技创新项目资助(编号:2015r413055)。
致谢
这项研究由浙江省大学生科技创新活动计划(新苗人才计划)大学生科技创新项目资助(编号:2015r413055),特别感谢温州医科大学电镜室方周溪老师的支持。
NOTES
*通讯作者。