1. 引言
肩胛舌骨肌综合征(omohyoid muscles syndrome)是1969年由Caswell和Zachary等首先报道的,特征性改变是当患者吞咽时具有X形侧方突出性颈部肿块 [1] [2] 。另外,绝大多数病人发病隐匿,且无外伤病史。国内由叶必远(1978年)首先报道,因其发病原因不明,且临床较少见,故易被误诊或漏诊 [2] [3] [4] [5] 。我科曾收治肩胛舌骨肌综合征3例,现报告如下。
2. 病例报告
病例1:患者、男性、22岁。吞咽时右颈前部隆起8 d,来我院就诊。检查:颈部无肿块,仅吞咽时右颈前部隆起约2 cm × 3 cm大小“包块”,吞咽动作完毕后,“包块”消失,颈部B超无肿块发现,诊断为“右肩胛舌骨肌综合征”收入住院。局麻 + 颈丛麻醉下以患侧肩肿舌骨肌隆起最高点作横形切口,长约5 cm,分离皮下组织,将胸锁乳突肌拉向外侧,暴露出突起的肩胛舌骨肌,同时分离该肌与周围筋膜的粘膜,分别挟持该肌膨隆的上下端中间切断,断端缝扎,嘱患作吞咽无隆起,术后4 d创口I期愈合,痊愈出院。
病例2:女、39岁。13年前患者吞咽时发现左颈部出现一肿块,吞咽动作结束肿块即消失。近半年来自觉肿块增大,伴有吞咽不适,曾到多家医院就诊,均不能确诊。否认外伤史及异物吞咽史。体检:吞咽时左侧胸锁乳突肌下段出现一肿块(图1),约5 cm × 3 cm × 2 cm,质中等,无压痛,边界不清,吞咽动作结束肿块即消失。颈部B超及纤维喉镜检查均未发现异常。临床诊断为肩胛舌骨肌综合征(左侧)。在局麻下行左侧肩胛舌骨肌切断术。于左侧锁骨上做低位横切口,长约4 cm,从胸锁乳突肌后缘入路,找到呈带状的肩胛舌骨肌,分离出肩胛舌骨肌下腹和中间腱部。嘱患者做吞咽动作,见该肌绷紧,将其前面的胸锁乳突肌顶起,形成肿块。探查周围无肿物后,切除中间腱部及部分下腹肌组织,长4 cm,结扎断端,再嘱患者做吞咽动作,肿块消失。术后病理组织学检查为横纹肌组织,肌纤维萎缩、变性,间质见少数脂肪浸润及纤维增生(图2)。术后5 d出院。
病例3:男、67岁。2年前患者吞咽时发现双侧颈前下方出现肿块,吞咽动作后肿块消失,无其他不适,未引起注意。近3个月来感吞咽时有阻挡感,曾在外院就诊,临床诊断为甲状腺肿,但甲状腺扫描、颈部B超及CT检查均未发现异常。体检:吞咽时双右胸锁乳突肌中、下段显著隆起,可触及肿块,约6 cm × 4 cm × 2 cm,质中等,边界不清,无压痛;吞咽动作结束,肿块随之消失,颈部恢复如常。
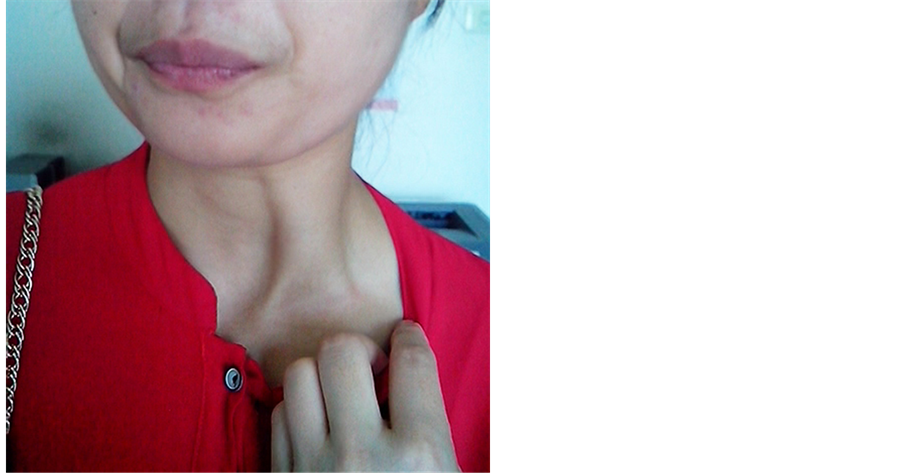
Figure 1. Macroscopically, a protruding anterolateral neck mass in the region of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle while swallow, and disappear after swallow
图1. 吞咽时左侧胸锁乳突肌下段出现一肿块,吞咽动作结束肿块即消失

Figure 2. The postoperative histopathological examination revealed that was striated muscle with atrophy and degeneration, and a few fatty infiltration and fibrous hyperplasia were also found
图2. 术后病理组织学检查为横纹肌组织,肌纤维萎缩、变性,间质见少数脂肪浸润及纤维增生
临床诊断为肩胛舌骨肌综合征(双侧)。在全麻下行双侧肩胛舌骨肌切断术。取颈前低位横切口,长约3.0 cm。从胸锁乳突肌后缘入路,显露双侧肩胛舌骨肌,嘱患者做吞咽动作,见肩胛舌骨肌向外顶起胸锁乳突肌,使该处隆起形成肿块,吞咽动作结束肿块消失。切除肩胛舌骨肌中间腱和部分下腹组织,长约5.0 cm,再观察患者,吞咽时肿块明显缩小。探查发现胸锁乳突肌锁骨头仍紧张,遂切断该肌外侧部分肌纤维,再嘱患者作吞咽动作,肿块消失,吞咽时阻挡感也随之消失。术后病检:镜下见纤维组织轻度增生,灶性出血,肌纤维萎缩,轻度变性。病理诊断镜下见横纹肌部分萎缩、纤维化,呈透明变性(慢性间质性肌炎)。术后6 d出院、无复发。
3. 讨论
肩胛骨舌肌综合征临床少见,1969年由Caswell和Zachary等首先报道 [1] [2] ,国内由叶必远(1978)首先报道,截止2011年全国仅报道123例 [3] [4] [6] [7] 。正常吞咽时,随着舌骨上下移动,肩胛舌骨肌随之伸缩;一旦此肌弹性减退,在吞咽时舌骨上移时而该肌不能相应伸长,向外顶起位于其浅面的胸锁乳突肌,使该处隆起形成肿块,吞咽动作结束后,舌骨下降后该肌回位,隆起的胸锁乳突肌亦随之恢复到原位,肿块消失。
本病病因不明,目前认为,本病系因先天局部筋膜发育薄弱、劳损或撕裂导致中间腱鞘松弛所致,其主要病理改变是肩胛舌骨肌横纹肌细胞变性、肌纤维萎缩、弹性减退。肩胛舌骨肌综合征的病因目前尚无定论,插胃管、激烈呕吐及咳嗽可能是其诱因。目前认为有以下几种病因:① 先天性中间腱膜发育不良使肩胛骨舌骨肌失去约束,长期处于低张力状态,逐渐发生肌肉萎缩,久之肌肉变性,以致弹性丧失;② 局部粘连:肩胛舌骨肌与周围的粘连,可使其收缩受限,吞咽动作时舌骨上升,肩胛舌骨肌因周围粘连而受到牵引力增大,久之使肌萎缩 [2] [3] [4] [5] 。
主要临床特征是吞咽时颈部出现包块,同时伴有吞咽不适、或吞咽困难。吞咽动作完成后,颈部包块随之消失,局部触诊及颈部B超、CT检查及食管造影等检查均无阳性发现。只要掌握本病的这些临床特征,诊断并不困难,但应与颈部囊状水瘤、颈侧鳃裂囊肿、颈内静脉扩张症、颈淋巴结肿大、甲状腺肿及胸骨舌骨肌综合征(Sternohyoid muscle syndrome)等疾病相鉴别,以免误诊 [3] - [6] [8] [9] 。
本病治疗主要是手术切除与胸锁乳突肌相交叉部分的肩胛舌骨肌,且在手术台上即见效果。入路、后缘入路、胸骨头和锁骨头之间入路三种。大多数患者只需切断肩胛舌骨肌中间腱和下腹即可治愈,但少数患者需要分离切断与周围肌肉筋膜间的粘连,才能取得满意的效果 [3] [4] [5] [8] [9] 。近年来,也有作者报道采用微创方法成功实施腔镜下肩胛舌骨肌离断术 [7] 。
*通讯作者。