1. 引言
感潮河段的洪水过程由于既受上游河道径流和下游潮汐的双重作用,此外,河口地区的复杂地理特性,因而使感潮河段的水文情势尤为复杂,感潮河段的设计洪水位计算成为研究的热点和难点 [1] 。目前,国内感潮河段设计洪水位计算常用的方法有水动力学法、水文统计法及水文信息法等 [2] [3] [4] [5] 。水动力学法基于完全圣维南方程组,建立考虑潮水顶托影响的感潮河段设计洪水位计算,目前已得到广泛应用。水文统计法根据水文要素自身随时间演变规律或建立统计回归分析的感潮河段设计洪水位计算。水文信息法将感潮河段视为一个水文系统,以上游流量、下游潮位和区间入流为输入计算感潮河段设计洪水位。上述感潮河段设计洪水位计算方法虽精度较高,但对资料要求较高,如河道断面和糙率资料等,导致感潮河段设计洪水位计算精度很大程度上依赖于水文资料及模型的求解。
随着“一带一路”战略的实行,越来越多的电力设计单位到世界各地去承揽工程,国外电厂工程经常位于感潮河段,同时受上游径流和下游潮汐的双重作用,但是国外感潮河段设计洪水位计算经常遇到缺少实测资料的情况,甚至无资料的情形,这种情形下,无法采用水动力学法、水文统计法及水文信息法进行设计洪水位计算,需要采用其它的方法。本文以某国外电厂工程为例,在短期实测潮位资料的基础上,通过潮位转引及数学模型计算,提出了一种实用的满足工程需要的无资料感潮河段洪水位计算,以供同类工程参考。
2. 实例研究
国外某电厂工程,西侧濒临阿拉伯海,南侧距河流入海口约2 km,河口上游约57 km为一水库,水库坝体结构为土石坝,设计总库容为8.09 × 108 m3。厂址、水库、海洋位置关系示意如图1所示。
由于厂址南侧距河流入海口仅约2 km,南侧河流属感潮河段,因此厂址百年一遇洪水位分析需要考虑阿拉伯海潮汐与河流径流相遇对厂址洪水的影响。
2.1. 潮位计算
于2015年4月8日~2015年6月3日于工程所在海域进行了潮位观测,距工程所在地约30 km处存在长
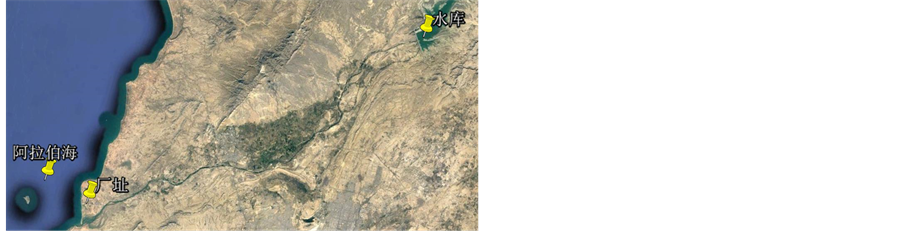
Figure 1. Sketch map of power plant, reservoir and the ocean
图1. 厂址、水库、阿拉伯海位置关系示意图
期潮位观测站,通过对比发现,工程所在海域潮时比长期观测站潮时滞后约4 h,把长期观测站潮时往后推4 h(比如将长期观测站5月1日8时的潮位数据作为5月1日4时的潮位数据)与工程海域的潮位数据进行准同步比较。通过准同步比较,长期观测站和工程海域潮位数据有着完全一致的规律。通常情况下长期观测站的高潮位略高于工程海域,低潮位置略低于工程海域,即长期观测站的潮差比工程海域略大。为了将长期观测站的潮位资料应用到工程所在地的潮位计算中,需要将长期观测站潮位站的资料转引至工程海域。转引的方法是将长期观测站的潮位过程数据乘以合适的系数或整体平移后使两者的一致性达到最好。通过对比分析发现,将长期潮位观测站数据通过下述关系转引后与现场实测潮位数据拟合最优,转引关系如式(1)。
 (1)
(1)
式中:h0为卡拉奇港潮位站实测潮位;h为转引后的潮位。
另外,长期潮位观测站与工程所在地同处阿拉伯海,受热带气旋影响相似。因此,可通过上述关系将长期潮位观测站的多年实测资料转引至工程海域。将长期潮位观测站逐年实测潮位资料转引至工程海域后,分别对逐年的极端高潮位采用PIII型频率曲线进行适线计算,得到不同频率设计高潮位。长期潮位观测站转引后与工程海域潮位数据对比曲线如图2所示,图中:红色为工程海域潮位数据蓝色为长期潮位观测数据。
2.2. 河流洪水计算
工程所在地位于河口附近,由于受地势及阿拉伯海海水顶托影响,导致上游来水不能得到很快下泄,易在工程位置产生洪水;此外,上游约57 km处为一水库,水库下泄洪峰流量叠加区间洪水流量将会对工程区域产生洪水影响。因此需要分析河流洪水叠加潮汐洪水对工程所在地的影响。洪水计算采用MIKE21水动力模型进行计算。
2.2.1. 模型介绍
模型的基本方程包括连续性方程和动量方程,控制方程有两种表达方式,分别是笛卡尔坐标系下的控制方程和球坐标系下的控制方程。其中笛卡尔坐标系下的控制方程形式如下。
连续性方程为:
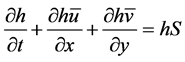 (2)
(2)
x向和y向运动方程为:
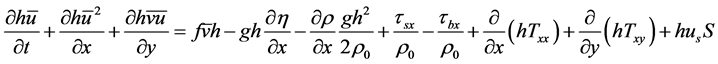 (3)
(3)
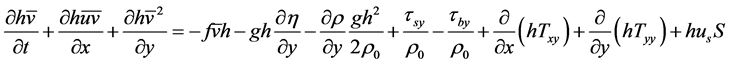 (4)
(4)
式中: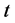 为时间;
为时间;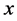 、
、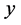 为笛卡尔坐标的两坐标轴;
为笛卡尔坐标的两坐标轴;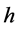 为总水深;
为总水深;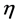 为水面高程;
为水面高程;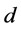 为水深;
为水深; 、
、 为对应于
为对应于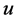 、
、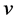 的速度分量;
的速度分量; 为科氏力;
为科氏力; 为重力加速度;
为重力加速度;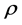 为密度;
为密度;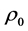 为密度;
为密度; 为涡粘系数;
为涡粘系数;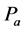 为大气压强;
为大气压强; 为源汇项的流量。
为源汇项的流量。
模型计算时,计算网格采用三角形非结构化网格。上游从水库开始作为上游边界,下游至河口的外侧海域。工程区域的地形采用现场实测高程,上游河道的地形从DEM提取进行插值得到。上游的边界为流量边界条件,下游边界为水位边界条件。
2.2.2. 边界条件
工程位置处的洪峰流量受水库最大下泄流量和区间流量的共同控制。水库溢洪道最大下泄流量为13,000 m3/s。不同重现期区间采用上下游的汇流面积比来推算。根据河流流域地形图,分别描绘出水库上、下游的汇流区面积,其上、下游汇流面积比约为23:1。在推算不同重现期洪水流量过程中,分两种情况进行考虑,当上游流量大于溢洪道最大设计流量时,采用溢洪道最大设计流量叠加下游汇流流量作为重现期洪水流量;当上游流量小于溢洪道最大设计流量时,采用上游流量叠加下游汇流流量作为重现期洪水流量。对应100年一遇的洪水流量为13,700 m3/s。
计算时下游边界条件为水位边界,采用一般大潮高潮位3.0 m作为下游水位边界(CD高程,一般大潮高潮位在3.0 m左右)。
由于河口存在着沿岸沙丘和河嘴,沿岸沙丘和河嘴对上游洪水存在着阻水,河口不同时期影像如图3所示,

Figure 2. Tidal comparison line of long-term tidal observation and the short- term tidal observation
图2. 长期潮位观测站转引后与工程海域短期潮位数据对比曲线

 (a) 2003.12.30 (b) 2016.3.29
(a) 2003.12.30 (b) 2016.3.29
Figure 3. Image of different time at the estuary
图3. 河口不同时期影像图
计算时假定发生洪水时沙丘被部分冲开,有效河口宽度为1000 m。
2.2.3. 计算结果
在工程区域提取不同计算点的水位高程结果,100年一遇洪水情形下洪水位高程为5.17 m,电厂附近已有一燃油电厂,2006年河流发生洪水曾导致该燃油电厂的排水明渠和电厂围墙附近的外围区域受淹,根据这次历史资料情况,燃油电厂采取了修建挡水墙措施,将该挡水墙高度与100年一遇洪水位进行比较,高度基本一致,因此可见,本次洪水计算的结果是基本合理的。将计算结果与实测的厂址高程数据相比较,判断厂址局部区域受河流100年一遇洪水影响,需要采取防洪措施。
3. 结论
感潮河段的洪水过程由于既受上游河道径流和下游潮汐的双重作用,使感潮河段的水文情势尤为复杂,感潮河段的设计洪水位计算成为研究的热点和难点。随着“一带一路”战略的实行,越来越多的电力设计单位到世界各地去承揽工程,国外电厂工程经常位于感潮河段,但是国外感潮河段设计洪水位计算经常遇到缺少实测资料的情况,甚至无资料的情形,这种情形下,无法采用水动力学法、水文统计法及水文信息法进行设计洪水位计算,需要采用其它的方法。
本文以某国外电厂工程为例,提出根据短期潮位对比观测,通过准同步比较,将长期潮位观测站逐年实测潮位资料转引至工程海域后,分别对逐年的极端高潮位采用PIII型频率曲线进行适线计算,得到不同频率设计高潮位,从而解决不同频率潮位计算问题;针对河流洪水计算,采用水库最大下泄流量加区间流量作为上游流量边界,采用一般大潮高潮位作为下游水位边界,同时对河口地形结合历年影像资料进行了适当假定,进行了河流洪水计算;上述所述方法对国外无资料感潮河段设计洪水位计算提供了重要参考。