摘要:
于2012~2013年5月、8月、10月份,对茅岭江入海口水质进行定点监测,通过分析该水域水体中总氮、总磷、无机氮、无机磷、化学需氧量、石油类等数据,研究该水域各水质指标的动态变化及趋势,并采用单因子评价法、氮磷比、富营养化指数法等方法对其结果进行水质分析和评价。结果表明:2012~2013年茅岭江入海口水质全年均有超标现象,其中总氮、总磷、石油类超标不严重,而无机氮和无机磷在2012年8月份和10月份超标最严重,超过了国家标准中的四类水质标准。2012~2013年茅岭江入海口水体氮磷比均处于不同程度的失衡状态,其中2012年各站位在5月份水体中磷是限制浮游藻类生长的主要因素,而2013年各站位水体中氮却成为了限制浮游藻类生长的主要因素。2012~2013年茅岭江入海口水体出现了不同程度的富营养化,其中2012年和2013年10月份富营养化程度最为严重,主要原因是水体COD含量严重超标,表明水体受到城镇生活污水及畜禽养殖业来源方面的有机物污染已经很严重。相关部门为此应制定好切实可行的方案,严格控制和治理茅岭江沿岸生活污水,生产废水和养殖废水的排放,降低各种人为因素对钦州茅岭江沿岸水质的影响与破坏。
Abstract:
In May, August and October from 2012 to 2013, the water quality of the Maolingjiang River inlet was monitored. The total nitrogen, total phosphorus, inorganic nitrogen, inorganic phosphorus, chemical oxygen demand (COD) and petroleum data were analyzed in order to research the dy-namic changes and trends of the water quality indicators. Meanwhile, the single-factor evaluation, nitrogen and phosphorus ratio, eutrophication index methods were used to analyze and evaluate the water quality. The results showed that the water quality of the Maolingjiang River inlet ex-ceeded the standard throughout the year from 2012 to 2013, and the total nitrogen, total phos-phorus and petroleum excessive situations were not serious, but the inorganic nitrogen and inor-ganic phosphorus in August and October of 2012 exceeded more than the national standard and reached in the four level water quality standards. The nitrogen and phosphorus ratios in the Maolingjiang River inlet from 2012 to 2013 were all in different degree of imbalance. Among them, phosphorus was the main limiting factor of phytoplankton growth in May in 2012, but the nitrogen had become the limiting factor of phytoplankton growth in 2013. There were different degrees of eutrophication phenomena in the Maolingjiang River inlet from 2012 to 2013. Among them, the eutrophication phenomenon was the most serious in October in 2012 and 2013. The main reason is that the COD content in water is seriously exceeding the standard, which indicates that the water body is affected by urban sewage and the livestock and poultry breeding industry sources of organic pollution have been very serious. Relevant departments should formulate a practical program for the strict control of the domestic sewage, production wastewater and aquaculture wastewater emissions along the Maolingjiang River and reduce the human factors on the Maolingjiang River so as to decrease the impact of water quality and destruction.
1. 引言
近年来随着北部湾的开发,钦州工业生产水平迅猛发展,环境受到的污染也越来越严重。茅岭江是钦州的主要河流之一,与钦江、大榄江共同构成了茅尾海的入湾水系 [1] 。茅岭江入海口是多种鱼、虾、贝类的繁殖、索饵场所,是生态环境极其脆弱的海域。茅尾海与茅岭江相接邻,是我国南部沿海重要的海湾,在环北部湾地区的经济发展和我国与东盟之间的贸易往来中发挥着重要作用 [2] 。茅尾海是中国最大的近江牡蛎天然苗种产地,茅岭江的污染势必会影响到茅尾海的近江牡蛎苗种健康。茅尾海内还有钦州湾最大片的红树林群落—茅尾海红树林保护区,保护区内有由桐花树,白骨壤、秋茄等树种组成的红树林,保护区还是雁、鸭、鹬等禽类迁徙的驿站和越冬地,重要性不言而喻。茅岭江水质污染会使该保护区的生态系统遭到破坏,使一些珍惜濒危物种灭亡 [3] 。因此,为保护入海口生态环境,渔业资源,进行茅岭江入海口生态环境的研究刻不容缓。另外,茅岭江一带水质状况调查研究较少,缺乏比较全面的调查研究。再者,近年来随着钦州湾经济区的快速发展,陆源污染物在不断增加,使得茅岭江水质污染加重。因此,进行茅岭江入海口水质研究对于评价茅岭江的环境质量、控制环境污染、保护生态环境和为相关部门治理污染提供建议等都具有重要意义。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 研究区域概况
茅岭江干流全长112 km,流域面积2959 km2。茅岭江河流水量极为丰沛,平均年径流量为25.9 × 108 m3。由于受降水变化的影响,河流流量的年内变化较大,在汛期(4~9月),径流量为19.99 × 108 m3,占年径流量的77.2%,最大月径流量一般出现于6~8月,约占全年的50%;枯季(10~翌年3月)径流量为5.9 × 108 m3,占年径流量的22.8%,最小月径流量出现于12~2月,仅占全年的9%。茅岭江年输沙量为55.3 × 104 t [4] [5] 。
茅岭江入海口即为茅尾海,是以钦江、茅岭江为主要入湾径流的河口海滨区,面积约135 km2 (见图1)。茅尾海位于钦州湾内湾,是一个典型的受径流影响的半封闭性海湾,位于钦州湾西海域最北部。海湾内宽口窄,呈椭圆形,东、西、北三面为陆地所包围,大部分为浅滩,平均水深小于2 m,属于南亚热带海洋性气候,年平均气温约22.1℃,年平均降雨量为2135 mm,潮汐为不规则全日潮,潮汐不等现象明显,平均潮差约2.5 m。该海域滩涂广布,沿海周围有大片红树林,现有广西茅尾海红树林自然保护区,总面积2784 m2。茅尾海中部建有国家海洋公园,属典型海洋生态系统,还是我国南方最大的近江牡蛎采苗基地,采苗区约2340 hm²,分布在茅尾海红树林外围滩涂、中北部和中南部海区,最高年产牡蛎苗种10亿串,为农业部水产健康养殖示范区,同时盛产鲈、鲻、鲷、黄鱼、青蟹等。此外,海湾内还生长有茂盛的菅草、水草和海榄树,盛产水鸭等野生水禽。一年四季,成千上万的野鸭、海鸥、沙螺鸠、蓑衣鹤在这里栖身出没。
研究水域为茅岭江入海口,设P1、P2、P3三个站位点,每个站位点分别于2012~2013年5月、8月、10月进行水质监测取样,共采样6次(见图2)。
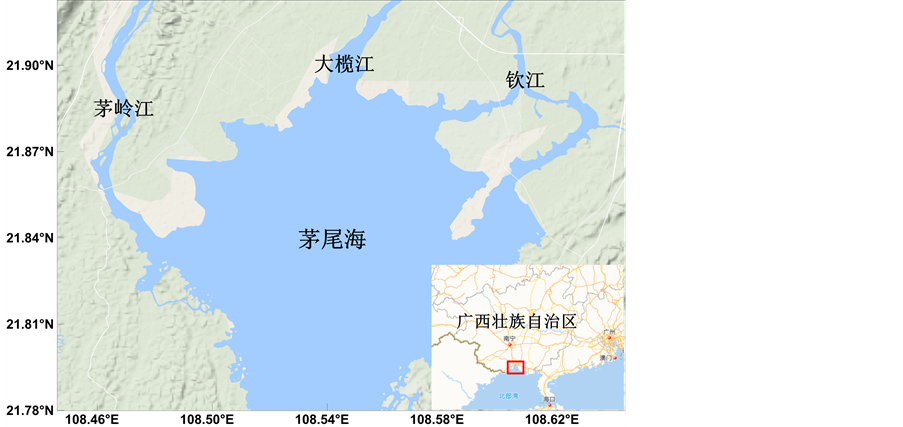
Figure 1. The geographical location of Maolingjiang River
图1. 茅岭江地理位置
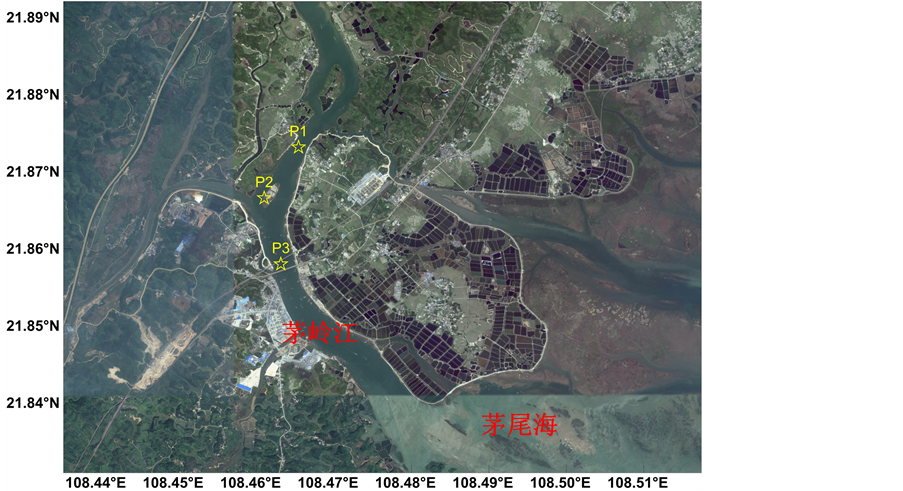
Figure 2. The monitoring stations of Maolingjiang River
图2. 茅岭江监测点站位
2.2. 样品采集与分析
在各监测点站位采集表层水样品(水面下0.5 m),监测项目包括总氮、总磷、无机氮、无机磷、化学需氧量、石油类,其中总氮分析方法为中华人民共和国国家标准( GB 11894-89) 中“水质总氮的测定:碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法” [6] ;总磷分析方法为中华人民共和国国家标准( GB 11893-89) 中“水质总磷的测定:钼酸铵分光光度法” [7] ;其它各监测项目的样品采集、处理和分析方法均按照国家标准《海洋监测规范,第4部分:海水分析GB17378.4-2007》进行 [8] 。采样和分析过程均采取运输空白样、现场平行样、密码样和加标样等进行质量控制。
2.3. 数据分析方法
本次水质评价采用单因子评价法,即根据《海水水质标准 GB3097-1997》 [9] 和《地表水环境质量标准GB3838-2002》 [10] 选取相应类别标准,将实测值与国家标准值进行比较,进行茅岭江水质的评价。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1. 总氮(TN)
总氮(TN)是海水中所含NH4-N、NO3-N、NO2-N 和有机氮(ON)之和总称 [11] [12] [13] 。2012~2013年茅岭江的总氮值在0.634~2.31 mg/L之间,波动较大(图3)。其中,2012年每个站点都是5月份总氮含量最高,10月份次之,8月份最低。2013年每个站点的总氮含量都为8月份最高,5月份次之,10月份最低。2012年5月份,除了1号站点的总氮含量为1.47 mg/L,达到第四类水质标准,其余的2个站点都超出了2 mg/L,即超出了第五类水质标准。2012年8月份与2013年10月份各站点总氮含量均小于1 mg/L,达到第三类水质标准。2012年10月份总氮含量各站点均小于2.0 mg/L,达到第四类水质标准。2013年5月份各站点总氮含量均小于1.5 mg/L,达到第四类水质标准。2013年8月份各站位总氮含量均小于2.0 mg/L,达到第五类水质标准。

Figure 3. The Variation of total nitrogen in water of Maolingjiang River from 2012 to 2013
图3. 茅岭江2012~2013年水体中总氮变化情况
3.2. 总磷(TP)
2012~2013年茅岭江的总磷值在0.0626~0.415 mg/L之间,波动较大(图4)。其中,2012年5月份总磷含量都小于0.1 mg/L,达到第二类水质标准。2012年8月份,1号站位与2号站位的总磷含量都小于0.4 mg/L,达到第五类水质标准,3号站点总磷含量小于0.2 mg/L,达到第三类水质标准。2012年10月份各站位总磷含量均小于0.4 mg/L,达到第五类水质标准。2013年5月份1号站位总磷含量小于0.1 mg/L,达到第二类水质标准,2号站位与3号站位总磷含量小于0.2 mg/L,达到第三类水质标准。2013年8月份,1号站点与3号站点总磷含量小于0.3 mg/L,达到第四类水质标准,2号站点总磷含量小于0.2 mg/L,达到第三类水质标准。2013年10月份1号站点与3号站点总磷含量均小于0.4 mg/L,达到第五类水质标准,2号站点总磷含量超出了0.4 mg/L,超出了第五类水质标准。
3.3. 无机氮(DIN)
海水无机氮包括氨氮、硝氮、亚硝氮,是海洋植物生长所必须的营养元素,但当其含量过高时,与水中其它营养盐类共同作用便可能引起水体富营养化 [14] [15] [16] (图5)。2012~2013年的无机氮值在0.06~0.66 mg/L之间,波动较大。以不同站位相同时间比较,不同区域的水中无机氮含量变化很小,因此水中无机氮分布较为均匀。以相同站位不同时期比较,2012年的无机氮含量远高于2013年,且2012年5月、8月、10月无机氮的含量不断增高。这主要是因为8月份为丰水期,由于降雨、城区生活污水及生产废水排放量增加等因素,大量陆地上的生活污染物进入茅岭江,由此造成了8 月份水质略劣于5月份的现象;而10月份无机氮含量最高,则是因为2012年的丰水期延长了,造成10月份无机氮含量比8月份还要高的现象。2013年茅岭江水中的无机氮含量比2012年低很多的原因是2013年的丰水期水量较小,因此从陆地带入江中的污染物少了很多。
3.4. 无机磷(DIP)
2012~2013年5月份、8月份和10月无机磷范围在0.0016~0.11 mg/L之间,波动较大,每年10月份无机磷含量相对较高,5月份含量相对较低,8月份则在中间(图6)。这主要是由于茅岭江沿岸较多水产养殖户,每年的8月至10月是水产养殖病害的高发期,须在水中投入较多的药物,用以防止和治疗病害。
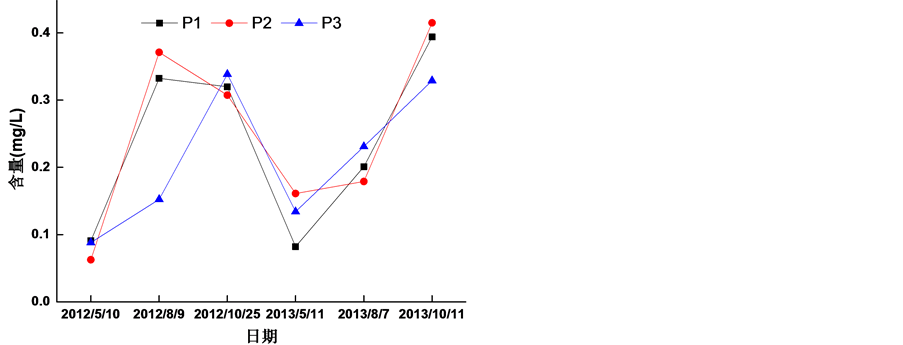
Figure 4. The Variation of total phosphorus in water of Maolingjiang River from 2012 to 2013
图4. 茅岭江2012~2013年水体中总磷变化情况

Figure 5. The Variation of inorganic nitrogen in water of Maolingjiang River from 2012 to 2013
图5. 茅岭江2012~2013年水体中无机氮变化情况
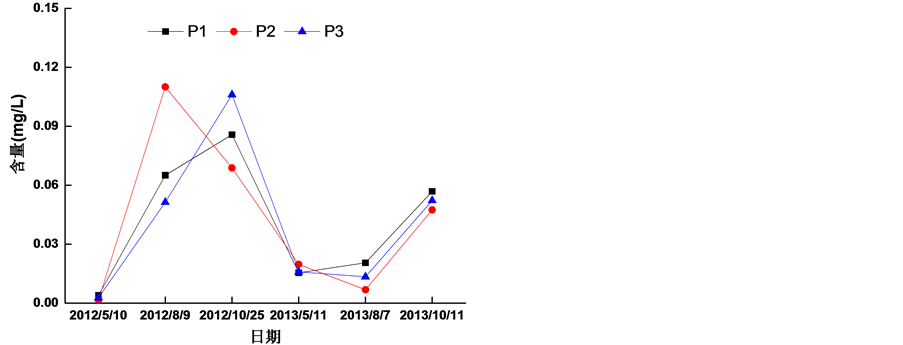
Figure 6. The Variation of inorganic phosphorus in water of Maolingjiang River from 2012 to 2013
图6. 茅岭江2012~2013年水体中无机磷变化情况
2012与2013年同月份相比较,2012年5月份无机磷略低于2013年5月份,2012年8月份和10月份无机磷含量远高于2013年8月份和10月份无机磷含量。
3.5. 氮磷比(N/P)
浮游藻类的生长离不开氮、磷等营养元素,但是浮游藻类对水体中氮、磷的需求又具有一定的比例,N/P直接影响藻类生长、细胞组成及其对营养的摄取能力。一般水体中正常的N/P 约为16:1,浮游藻类从水体中摄取的N/P也约为16:1,该比值偏离过高和过低都可能引起浮游藻类受到某一相对低量元素的限制。浮游藻类营养盐吸收动力学研究得出,当N/P > 16时,表明水体缺磷,磷是控制生物量的限制因素;而当N/P < 16时,表明氮相对不足,氮是限制因素 [17] [18] [19] [20] 。表1所示,2012年各站位在5月份的N/P大于16,其中P2站位高达111.25,而各站位在8月和10月的N/P小于16,最低为P2站位的4.58,根据N/P平衡理论可知,2012年各站位在5月份水体中磷是限值浮游藻类生长的主要因素,结合图6可以发现,2012年5月份茅岭江的DIP含量处于较低水平,平均值仅为0.0027 mg/L。2013年各站位的N/P除在8月份的P2站位大于16外(为23.53),其余站位在调查期内皆小于16,最小值为10月份的P1站位,仅为1.8,同样根据N/P平衡理论可知,2013年各站位水体中氮是限值浮游藻类生长的主要因素,结合图5可知,2013年茅茅岭江的DIN含量确实是处于一个较低的水平,要远远的低于2012年同期DIN含量,平均值仅为0.12 mg/L。
3.6. 富营养化指数(E)
水体中氮、磷的含量,对水质富营养化起着决定性作用,富营养化是环境恶化的衡量指标之一。实际中常用富营养化指数对水质富营养化程度进行评价。富营养化指数(E)以水体中DIN、DIP含量为基本环境要素,以COD含量升高表征水体富营养化间接环境生态效应 [21] 。E值越大,表示水体富营养化程度越严重,E ≥ 1认为水体处于富营养化状态。富营养化评价采用下式进行计算:

式中:E——富营养化指数,无量纲
DIP—— -P浓度,mg/L
-P浓度,mg/L
DIN——溶解无机氮浓度,mg/L
COD——化学需氧量浓度,mg/L
茅岭江不同站位不同时期的E值如表2所示。结果显示,所有站位的E值都大于1,表明水体都达到了富营养化。2012年和2013年10月份的E值要远远的高于其它月份的E值,而结合前文对茅岭江的DIP、DIN、COD的数据分析发现,茅岭江的DIP、DIN含量值处于正常的水平范围内,而COD值要远远的高于正常范围值,正是由于极高的COD值拉高了E值,这也说明COD是影响茅岭江水质状况的主要因素。COD值常作为衡量水中有机物含量多少的一个指标,COD值越大,说明水体受到的有机物污染越严重。陈群英等(2016)通过调查与收集2012年茅岭江流域内各类污染源排污及污染物处理处置情况的数据,依据排污系数法和入河系数法核算污染物排放量及入河量得出,2012 年茅岭江流域污染物排放量为34,654吨,各类污染物中,化学需氧量排放量最大(占总量77.9%),其次是总氮(占总量14.3%)。本文研究结果与陈群英等(2016)研究结果相近,这近一步证实了茅岭江受到的有机物污染是非常的严重了。陈群英等(2016)指出畜禽养殖业是流域内排放污染物量最多的污染源,年排污染物量15,548吨(占总量的44.9%),农村生活源排放污染物量位居第二,年排放污染物量11,390吨(占总量32.9%)。并且指出主要是由于茅岭江流域内没有完善的生活污水处理厂,城镇和农村生活污水不经处理,直接或间接排入茅岭江

Table 1. The N/P ratio in Maolingjiang River monitoring site in different periods
表1. 茅岭江监测站点不同时期N/P

Table 2. The eutrophication index in Maolingjiang River monitoring site in different periods
表2. 茅岭江监测站点不同时期富营养化指数(E)值
或排入支流汇入茅岭江;农村垃圾无序堆放,经过雨水冲刷流入茅岭江支流及干流;流域内以散养的畜禽养殖为主,畜禽粪便大都无序排放,动物粪便经降水淋洗或排灌等形式注入茅岭江,造成茅岭江水质污染 [22] 。
3.7. 化学需氧量(COD)
2012~2013年5月、8月和10月化学需氧量范围在9.6~113 mg/L之间,说明茅岭江入海口水域受到的污染已经很严重了(图7)。可能原因是钦州海水养殖主要集中在茅岭江和钦江入口的茅尾海,养殖形式是开放、半开放性养殖,养殖污水几乎未经任何物理、化学、生物处理就直接排入大海。海水养殖区的养殖污水有机物沉降量比非养殖区大的多,养殖区的底泥中碳、氮、磷的含量比周围水体沉积物要高,耗氧量也要高。从同一站点不同时期的数据折线图可以看出每年10月份水体中化学需氧量最大,5月份次之,8月份相对最小。可能原因是10月份水产养殖户在这段时期对养殖区的饵料投放较为密集,致使水体中有机物无机物含量增加。
3.8. 石油类
2012~2013年茅岭江出海口水中的石油类在0.0109~0.1593 mg/L之间。3个站点的石油类污染物都在四类水(即≤0.5 mg/L)以下(图8)。其中1号站点与2号站点的石油类污染物随时间的变化趋势较为相同,都是每年8月份石油类污染物含量较高,5月份次之,10月份最低,是因为5至8月份都为丰水期,上涨的江水把茅岭江沿岸的生活污水带进了江水中,因此造成了5月份和8月份较高的原因。而3号站点的变化趋势则是每年的5月份与10月份较高,8月份较低。
4. 结论
1) 2012~2013年茅岭江入海口水质全年均有超标现象,其中总氮、总磷、石油类超标不严重,多数时期处于一类与三类水质标准之间;而无机氮和无机磷在2012年8月份和10月份超标最严重,超过了国家标准中的四类水质标准,2013年此两项水质指标恢复正常。
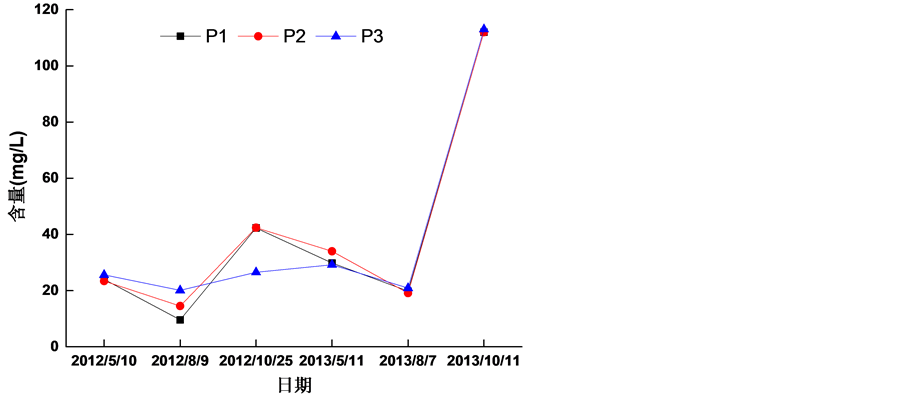
Figure 7. The Variation of chemical oxygen demand in water of Maolingjiang River from 2012 to 2013
图7. 茅岭江2012~2013年水体中化学需氧量变化情况
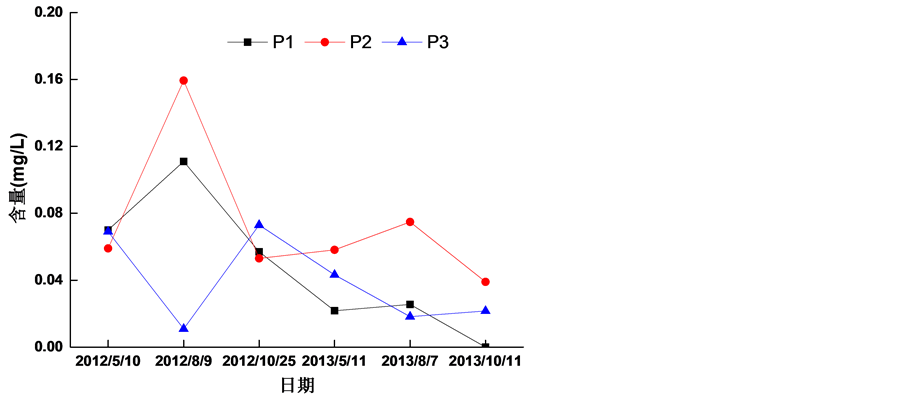
Figure 8. The Variation of chemical oxygen demand in water of Maolingjiang River from 2012 to 2013
图8. 茅岭江2012~2013年水体中石油类变化情况
2) 2012~2013年茅岭江入海口水体氮磷比均处于不同程度的失衡状态,其中2012年各站位在5月份水体中磷是限制浮游藻类生长的主要因素,而2013年各站位水体中氮却成为了限制浮游藻类生长的主要因素。
3) 2012~2013年茅岭江入海口水体出现了不同程度的富营养化,其中2012年和2013年10月份富营养化程度最为严重,主要原因是水体COD含量严重超标,表明水体受到城镇生活污水及畜禽养殖业来源方面的有机物污染已经很严重。
基金项目
广西自然科学基金青年基金项目(2016GXNSFRA380108);广西高校科学技术研究项目(KY2015YB315);钦州学院校级重点项目(2014XJKY-01A);广西北部湾海洋生物多样性养护重点实验室探索项目(2015ZB08);广西北部湾海岸科学与工程实验室自主项目(2016ZYB12);钦州学院大学生创新创业训练计划项目(201511607183)。