1. 引言
镁具有很高的储氢量(7.6 wt%)及循环性,资源丰富且价格低廉,对环境无污染,是一种很有潜力的储氢材料 [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] ,但由于氢在MgH2中扩散较慢,在普通Mg的表面吸氢形成MgH2层后氢很难通过MgH2层继续与Mg反应,即使在673 K,5 MPa氢气气氛下也不能很快吸氢,这些性能严重制约其在储氢领域中的广泛应用。
Zalaski等 [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] 研究发现,在相同温度和不活化的条件下,晶粒尺寸大于1 μm的Mg几乎不吸氢,当晶粒尺寸细化到50 nm时Mg的吸氢速率明显加快,吸氢容量也显著增加;晶粒越细,吸/放氢性能的改善效果越显著,当尺寸小于0.9 nm时,MgH2就可以在473 K的温度下放氢,此法无疑是改善镁基合金放氢特性的一种较好途径。G.Friedlmeier等 [11] 利用熔融快淬法制备了纳米结构的贮氢合金Mg0.87Ni0.13 (≤150 nm),其贮氢量高达6 wt%,同样,T.Spassov等 [12] [13] 和K.Tanaka等 [14] 也利用熔融快淬技术合成了纳米Mg-Ni-RE (RE = La, Ce and Y)贮氢材料(20~30 nm),且认为纳米贮氢材料具有优异的储氢性能,其原因为:1) 氢原子在大量的纳米晶界上或晶界上扩散容易;2) 纳米晶极高的比表面积,使氢原子容易渗透到贮氢材料内部;3) 纳米贮氢材料(20~30 nm)避免了氢原子透过氢化物层进行长距离扩散,而氢原子在氢化物层中的扩散是控制动力学性能的最主要因素。
本文通过在等离子体蒸发Mg的过程中引入乙炔气体,制备了平均尺寸约为40 nm的Mg的超小纳米颗粒,研究了Mg纳米颗粒尺寸随乙炔浓度的变化关系,探讨了纳米Mg颗粒尺寸对Mg吸放氢热力学和动力学的影响。
2. 实验过程
2.1. 纳米Mg颗粒的制备
纳米Mg颗粒是通过乙炔气氛的等离子体电弧蒸发镁块制备而成,仪器的原理示意图如图1所示。仪器由电弧反应腔、水冷铜底座、钨电极、热交换系统、粒子收集器、真空泵、气体循环泵和直流电源系统组成。用X射线衍射仪进行试样的相结构分析;用透射电镜(TEM)观察试样的微观形貌。

Figure 1. Schematic diagram of acetylene plasma arc apparatus
图1. 乙炔等离子体电弧设备原理示意图
2.2. 实验系统
图2给出了纳米Mg颗粒的贮氢性能测试系统。由氢气源、贮气罐、标准计量罐、反应器、真空泵、压力传感器、真空表、压力表、阀门及不锈钢管道等组成。用标准计量罐计量气体和标定管道及其它容器体积;用压力传感器指示吸/放氢过程的压力变化;数据采集系统对实验数据进行实时采集与记录。实验中准确称取纳米Mg颗粒约3.0 g装入反应器中,用2XZ-4B真空泵冷抽至4 Pa后,加热至
450 ℃
继续抽空至4 Pa,然后进行其贮氢性能测试。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1. 纳米Mg颗粒的微观表征
图3显示不同乙炔浓度下制备的纳米Mg颗粒的XRD谱图,从样品的XRD谱图上在θ = 42.8˚没有出现MgO的衍射峰,推断样品被氧化的程度极小。乙炔浓度为0%时,合成的样品为纯纳米Mg颗粒。随着引入乙炔气体及乙炔浓度的升高,Mg的XRD峰有所展宽,表明样品的晶粒尺寸有所减小。当乙炔浓度较高时,样品在θ = 26.2˚出现了不尖锐的衍射峰,推测其为某种特殊结构的C的衍射峰,该衍射峰强度随乙炔浓度的升高而升高。
图4显示不同乙炔浓度下制备的纳米Mg颗粒的TEM照片。从TEM照片中可以清晰的看出,当等离子体中没有引入乙炔时,得到的纳米Mg颗粒的尺寸在500 nm左右;当等离子体中引入乙炔时,得到的纳米Mg颗粒尺寸明显减小,且随着乙炔浓度的增大,Mg颗粒有进一步减小的趋势。图4(f)是对乙炔浓度为21.7%制备的Mg样品的TEM照片并进行统计得出的颗粒尺寸,约为40 nm,同理,当乙炔浓度分别为28%,21.7%,14.3%,5.3%和0%制备的纳米Mg颗粒平均尺寸分别约为40 nm,40 nm,100 nm,160 nm和500 nm。
3.2. 纳米Mg颗粒的C含量分布及BET分析
图5、图6分别显示了不同乙炔浓度下制备的纳米Mg颗粒的尺寸、C含量及BET分析结果。当乙炔浓度增大时,样品中的C含量随乙炔浓度呈线性升高趋势,而当乙炔浓度增大达到一定值时,纳米Mg颗粒的尺寸几乎不再减小,当乙炔浓度为21.7%时,样品中的C含量为24.8%,平均颗粒尺寸约为40 nm,其比表面积为27.1 m2∙g−1。同样,样品的比表面积随随乙炔浓度呈上升趋势,暗示其纳米Mg颗粒的尺寸逐渐降低。
3.3. 纳米Mg颗粒的吸放氢动力学行为研究
图7显示了乙炔浓度分别为28%,21.7%,14.3%,5.3%和0%制备的样品在473 K及4 MPa氢气压

Figure 2. Schematic of hydrogen storage property test system. 1—Hydrogen; 2—Buffer; 3—Pressure sensor; 4—vacuum gauge; 5—sampling; 6—reactor; 7—electric cooker; 8—Standard Vessel; 9—uranium bed; 10—Vacuum pump; k1~k10—valve
图2. 贮氢性能测试系统。1——氢气;2——缓冲器;3——压力传感器;4——真空规;5——取样;6——反应器;7——加热炉;8——标准罐;9——铀床;10——真空泵;k1~k10——阀门

Figure 3. XRD patterns of Mg nanoparticles synthesized at different acetylene concentration. (a) 28%, (b) 21.7%, (c) 14.3%, (d) 5.3%, (e) 0%
图3. 不同乙炔浓度下Mg纳米颗粒的XRD谱图。(a) 28%,(b) 21.7%,(c) 14.3%,(d) 5.3%,(e) 0%
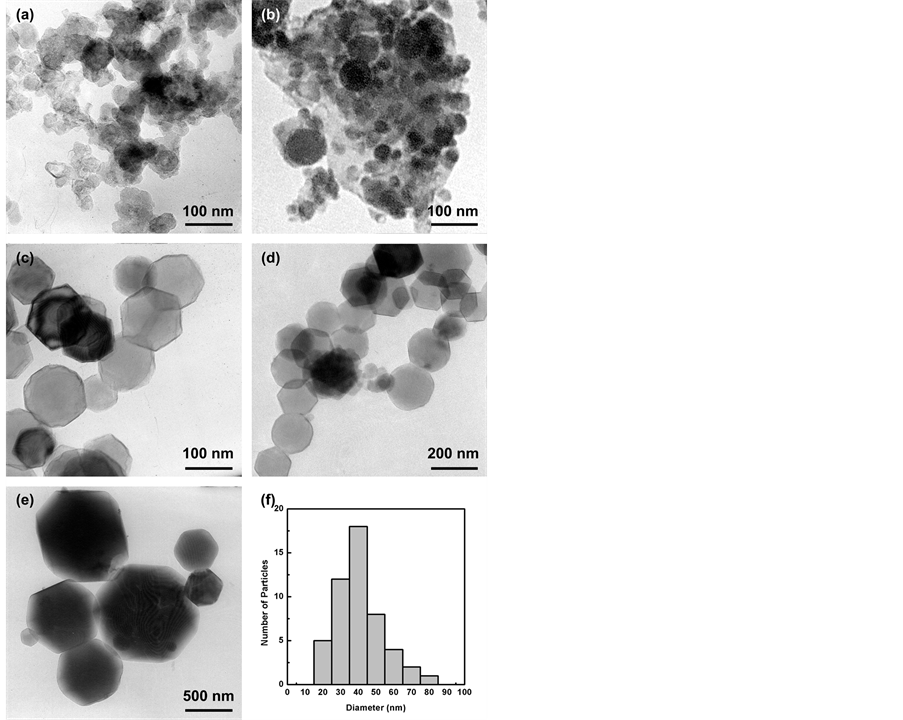
Figure 4. TEM image of Mg nanoparticles synthesized at different acetylene concentration. (a) 28%, (b) 21.7%, (c) 14.3%, (d) 5.3%, (e) 0%, (f) 21.7%
图4. 不同乙炔浓度下Mg纳米颗粒的TEM及尺寸分布。(a) 28%,(b) 21.7%,(c) 14.3%,(d) 5.3%,(e) 0%,(f) 21.7%
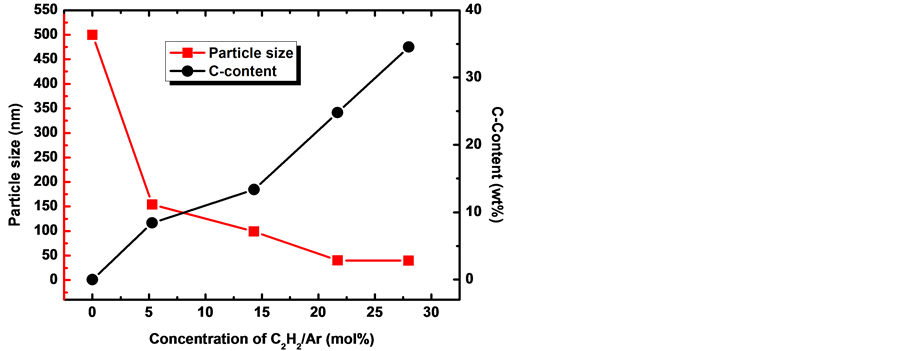
Figure 5. Carbon content and particle size of Mg nanoparticles synthesized at different acetylene
图5. 不同乙炔浓度下制备的Mg纳米颗粒的尺寸和样品中C的含量
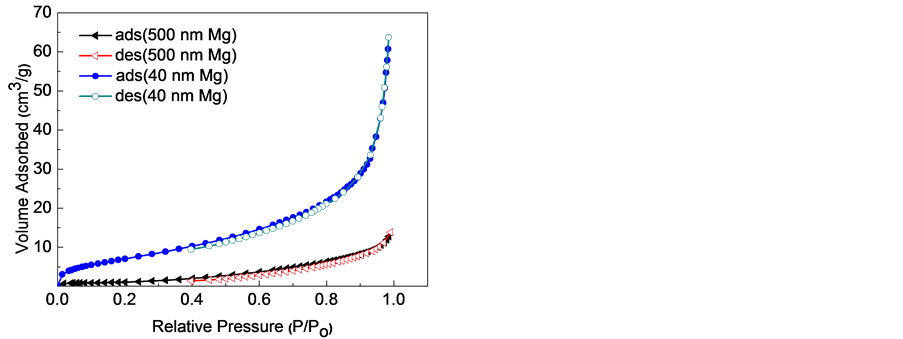
Figure 6. BET curve of Mg nanoparticles
图6. Mg纳米颗粒的BET曲线

Figure 7. Hydrogen absorption curve of Mg nanoparticles synthesized at different acetylene concentration in 4 MPa hydrogen gas at 473 K
图7. 不同乙炔浓度下制备的Mg纳米颗粒在200℃下的吸氢动力学曲线
力下的吸氢曲线。结果显示,乙炔浓度分别为28%,21.7%制备的样品吸氢速度很快,10分钟内吸氢量可达3 wt%,1小时内吸氢量可达6.5 wt%。乙炔浓度分别为14.3%,5.3%制备的样品吸氢较慢,1小时吸氢量分别为2.7 wt%和2.2 wt%。而乙炔浓度为0%制备的样品几乎不吸氢,1小时吸氢量不足1 wt%。由于纳米Mg颗粒的大小与乙炔浓度有近似反比的关系,故实验证明了在纳米尺度上,Mg的吸氢速度随颗粒尺寸减小而增大。此外,由于普通的Mg在673 K,5 MPa氢气气氛下也不能很快的吸氢,而通过乙炔等离子体得到的Mg纳米颗粒可以在473 K及4 MPa氢气气氛吸氢,显然Mg的纳米化可以极大的提高其吸氢性质。
图8分别给出了氢气压力为4 MPa、温度为440 K、500 K、560 K和620 K时,纳米Mg颗粒的吸氢量与时间的关系。可以看到,样品在620 K时吸氢量超过5 wt%仅需要不到1分钟。在560 K时,10分钟内也可吸氢超过5 wt%,接近吸氢完全饱和。样品在500 K时仍保持了较快的吸氢速度,30 min吸氢可以接近饱和状态。在相对较低的440 K温度下,样品仍能缓慢的吸氢,两小时吸氢量达3.5 wt%。
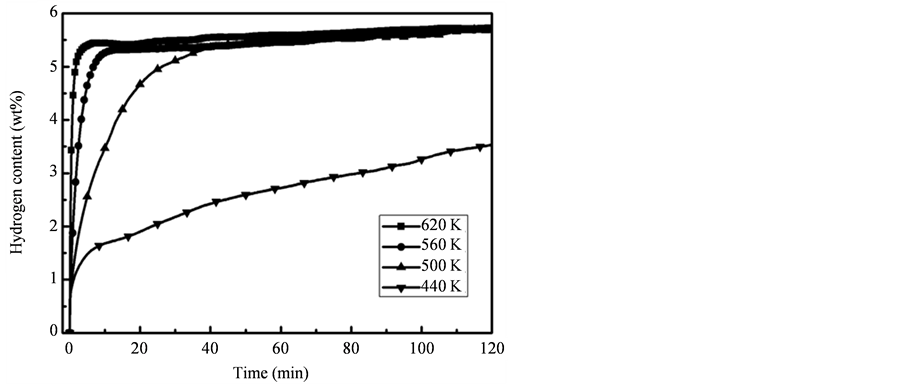
Figure 8. Time dependence of hydrogen absorption content in 4 MPa hydrogen gas at different temperature
图8. 不同温度下乙炔摩尔浓度为21.7%制备的Mg纳米颗粒在4 MPa下的吸氢曲线
图9给出了530 K、560 K、590 K、620 K和650 K的温度下,乙炔摩尔浓度为21.7%制备的Mg纳米颗粒的氢化物在~100 Pa H2下的放氢曲线。通常MgH2在573 K以下不放氢,但通过氢化的超小Mg纳米颗粒制备的MgH2却可以在530 K缓慢放氢,当温度升高到560 K时放氢速率加快,2小时放氢量超过4 wt%,当温度升高到650 K时,10分钟放氢量可超过5 wt%。通过Arrhenius公式(lnk = −E0/RT + lnA)计算得到该MgH2纳米颗粒的放氢活化能为114 kJ∙mol−1 H2。
3.4. 纳米Mg颗粒吸放氢热力学性能研究
图10分别给出了573 K,598 K,623 K测量了40 nm左右纳米Mg颗粒的吸放氢PCT曲线。结果显示,纳米Mg颗粒的吸放氢曲线均只存在一个坪台,该坪台对应着Mg相MgH2相的转变过程,也说明反应过程中样品中的C不参与Mg吸放氢的反应过程。由于样品中含有一定量的C,因此最大吸氢量没有达到Mg的理论吸氢量(7.6 wt%)。如果排除C的影响,则样品的吸氢量已经接近于理论上Mg的饱和吸氢量,这也同样说明样品中几乎没有MgO的存在,说明Mg纳米颗粒表面的无定形结构的C,可以减少Mg的氧化。
图11为该样品的吸放氢过程的lnP对1/T的函数曲线,利用van’t Hoff公式ln(P) = DH/T + DS分别获得材料吸/氢过程的van’t Hoff方程,分别式(1)和式(2),计算得到该样品的吸放氢反应焓ΔH = −65.5 kJ∙mol−1 (H2),反应熵ΔS = −122.7 J∙K−1∙mol−1 (H2)。
吸氢过程:
 (1)
(1)
放氢过程:
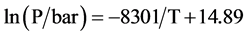 (2)
(2)
3.5. 纳米Mg颗粒循环吸放氢性能
图12显示了乙炔等离子体法制备的纳米Mg颗粒的循环吸放氢动力学曲线。测试过程为:将样品在真空下加热升温至623 K,在该温度下4 MPa下吸氢30 min,然后在0.1 MPa下放氢30 min,重复循环

Figure 9. Hydrogen desorption curve of Mg nanoparticles synthesized by 21.7% acetylene concentration in 100 Pa hydrogen gas at different temperature
图9. 不同温度下乙炔摩尔浓度为21.7%制备的Mg纳米颗粒的氢化物在~100 Pa H2下的放氢曲线
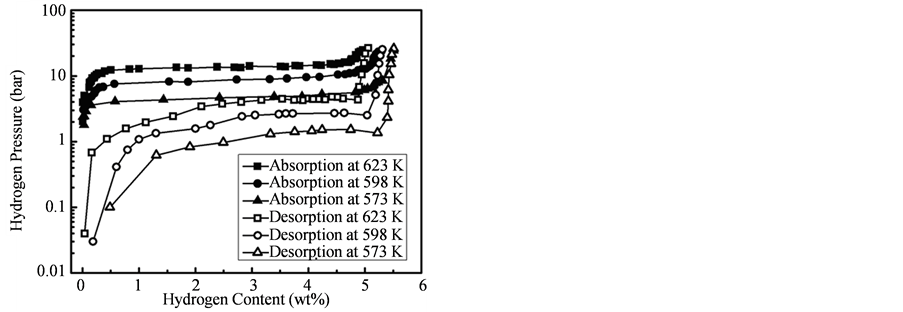
Figure 10. Hydrogen absorption and desorption PCT curve of 40 nm Mg nanoparticles at different temperature
图10. 乙炔摩尔浓度为21.7%制备的Mg纳米颗粒的吸放氢PCT曲线
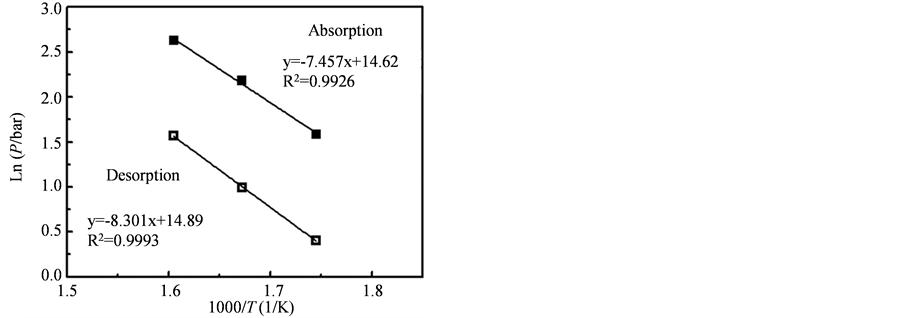
Figure 11. The relationship between lnP and 1/T of hydrogen absorption and desorption process
图11. 乙炔摩尔浓度为21.7%制备的Mg纳米颗粒的温度与1/T关系

Figure 12. Hydrogen absorption and desorption circulation kinetics curve at 623 K of 40 nm Mg nanoparticles
图12. 623 K下40 nm Mg纳米颗粒循环动力学曲线
至30次。可以看出,样品在第二个循环过程吸放氢量即可接近Mg的理论贮氢密度(样品中含有C,理论吸氢量为(1 − 24.78%) × 7.6% = 5.7%),而30个循环过程以后,样品的吸放氢量没有衰减,显示了该纳米颗粒具有很好的吸放氢循环性质。
4. 结论
通过上述实验,得出以下结论:
1) 通过在等离子体蒸发金属Mg的过程中引入乙炔气体,可制备出具有不同颗粒大小的Mg纳米颗粒。随着乙炔浓度的提高,制备出的Mg纳米颗粒的尺寸有减小的趋势,但乙炔浓度超过21.7%摩尔浓度时,制备出的Mg纳米颗粒的尺寸不再减小。
2) 制备的40 nm左右的Mg纳米颗粒在473 K,4 MPa氢气压力下1小时可吸氢接近饱和。其吸/放氢活化能分别为61.6 kJ∙mol−1 (H2)和114 kJ∙mol−1 (H2),其吸/放氢性能较块体Mg得到了较大的改善。
3) Mg纳米颗粒具有稳定的循环性能,在623 K,4 MPa H2条件下30次循环容量没有衰减。
致谢
在项目实施过程中,北京大学化学与分子工程学院的
李星国
教授、
陈军
博士参与了纳米Mg基合金的制备;郎丁木、王勤国等进行大量的样品微观结构表征;
敬文勇
、
何明民
、
常元庆
、
宋智蓉
、
魏英
等进行了大量的氢化与去氢化实验,在此一并感谢!