摘要:
室内定位技术解决了卫星信号到达地面时较弱,不能穿透建筑物的问题。传统的室内定位技术由于RSSI受限于多径效应和时间波动性,定位时有很大的不稳定性。针对WSN室内定位的关键性问题的研究,本文提出了一种基于RSSI的WSN的最速下降的定位算法。该方法通过三个接入点即参考节点来求出待测节点的坐标,结合了对数正态阴影衰落模型、三边定位算法以及最速下降法。本文先采用对数正态阴影衰落模型得出待测节点相对于各个参考节点的距离值;然后用三边定位算法求出定位节点的估计坐标;最后用最优化方法对估计的坐标值进行优化。仿真结果表明,相对于基于RSSI的传统定位方法,基于最速下降法的室内定位技术具有更高的定位精度。
Abstract:
Indoor positioning technology solves the problems that the satellite signal is weak when it reaches the ground and the signal cannot penetrate the structure. Due to the RSSI being limited by multipath effect and the volatility of time, the traditional indoor positioning technology is unstable when positioning. Aiming at the key issues of research in indoor positioning of WSN, a method based on RSSI positioning of the steepest descent algorithm WSN is proposed in the paper. The method uses three access points, namely the reference node, to find the coordinates of the nodes. In addition, the method combines log-normal shadow fading model, trilateral localization algorithm and steepest descent method. Firstly, using the log-normal shadow fading model the value of RSSI has been gotten from the node under test to the reference signal; besides, the trilateral localization algorithm is used to estimate the locating node coordinates; finally, the estimated coordinates are optimized by the optimization method. The simulation results show that, compared with the traditional positioning method based on RSSI, the indoor positioning technology based on the steepest descent method has better positioning accuracy.
1. 引言
随着物联网相关技术的兴起,基于无线传感网络(wireless sensing networks, WSN)和无线局域网(wireless local area networks, WLAN)等面向区域的定位技术越来越受到各行业研究者的关注。目前的室内定位技术有GPS [1] [2] ,红外线 [3] ,超声波 [4] ,蓝牙 [5] ,WiFi [6] 等,这些技术运用广泛。测距的方法有TDOA [7] [8] ,TOA [9] [10] ,AOA [11] ,RSSI [12] [13] 等测距方法。RSSI的测距定位技术因具有硬件要求低,功耗小,没有时间同步,易实现等优点,得到了广泛的应用。但是复杂的室内环境使得定位精度较低,无法满足正常的室内定位要求。另外,室内环境中人员走动带来的突发性的干扰更使得室内定位的效果很难达到理想的程度,于是寻找一个比较理想的室内环境定位系统已经成为室内定位研究的热点。以前的通过三边定位算法求出来的坐标值存在一定的缺陷,它所求出来的是一个区域内的一个估计点,因此提出来一种用最速下降法的最优化方法对区域内的坐标值进行最优估计,使得误差值降低。
面向区域的定位技术是一个前景广阔的研究方向,而室内定位技术是其中的典型代表。文献 [6] 中H等人选择室内参考节点区域,并利用多构造分类器来测量参考节点的无线信号强度。M等人在文献 [7] 提出了一种射频方法的一部分,用高压变压器的局部放电检测和定位。文献 [8] 中韩霜等人计算出了时间补偿参数,然后计算移动节点与信标节点之间的距离,最后采用极大似然估计算法实现目标的定位。文献 [9] 中Z等人使用距离偏差模型来推导出一系列估计量作为第一步,然后使用三边测量发现目标的估计位置。文献 [10] 栾凤刚等人利用非视距(None Line of Sight, NLOS)状态鉴别的方法对室内信道环境的NLOS进行鉴别,并对各传感器分配权重,最后通过经典到达时间(Time of Arrival, TOA)算法,得到未知节点的位置。在众多定位测距技术中,基于RSSI的测距定位技术通过发射点和接收点之间的信号强度值来估计两点之间的传播损耗,再根据经验模型和相关理论知识将发射节点和接收节点之间的传输损耗转换为两点之间的距离,最后根据相应的算法推算出未知节点的位置。相对于其他技术来说,定位精度比较高。
2. 主要算法
室内定位算法中主要运用到的模型是对数正态阴影衰落模型,主要算法是三边定位算法和最速下降法。
2.1. 对数正态阴影衰落模型
利用传统的经验模型对数正态阴影衰落模型 [14] [15] 求得理论距离值 ,公式为:
,公式为:
 (1)
(1)
简化成:
 (2)
(2)
其中A为距离为1的时候接收信号强度值,n为衰减因子。
2.2. 三边定位算法
三边定位算法是分别以已知位置的三个接入点(Access Point,简称AP)为圆心,以各个到待测标签的距离最近参考标签的距离为半径做圆。所得的三个圆的交点为D。三边定位算法 [16] [17] 示意图,如图1所示。
设位置节点 ,已知A,B,C三点坐标分别为
,已知A,B,C三点坐标分别为 ,它们到D点的距离分别为
,它们到D点的距离分别为 。依据距离值以及室内布置的参考节点,采用三边定位算法求出目标的估计位置。列三组方程式:
。依据距离值以及室内布置的参考节点,采用三边定位算法求出目标的估计位置。列三组方程式:
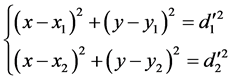 (3)
(3)
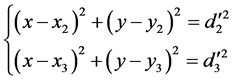 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)

Figure 1. Sketch map of trilateral localization algorithm
图1. 三边定位算法示意图
分别求出三组解,每一组方程组的解舍去离剩下的第三个点距离最远的解,三组解分别设为
 ,用三边定位算法估计出D点的坐标
,用三边定位算法估计出D点的坐标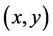 ,即,
,即,
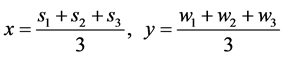 (6)
(6)
2.3. 最速下降法
对所求出的坐标值进行最优估计,采用最优化中的无约束优化条件中的最速下降法进行求解,首先建立目标方程,对于正定二次函数:
 (7)
(7)
精确一维搜索问题
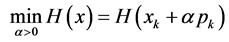 (8)
(8)
其中
 (9)
(9)
其中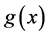 为一阶偏导,
为一阶偏导, 为二阶偏导,
为二阶偏导, 为求解
为求解 的最优解时,在某一点
的最优解时,在某一点 处,沿着负梯度方向
处,沿着负梯度方向 求得使目标函数
求得使目标函数 下降最快的方向,依次迭代下去,求得最优解。
下降最快的方向,依次迭代下去,求得最优解。
3. 实验与结果分析
本实验是在15*15 m的室内环境中进行的,在设置障碍物以及人员走动的情况下,经过多次移动参考点的位置,记录其移动距离以及移动后的实验数据,首先对采集到的RSSI值用均值滤波的方法进行去噪分析,再采用经验模型中的对数正态阴影衰落模型确定出距离值,然后用三边定位算法和最速下降法分别实现目标节点的定位。仿真图最后采用基于matlab的仿真平台,利用RSSI信息来定位待测点的信息。实验中统计的数据如表1所示。
仿真所示横坐标是参考节点在距离盲节点越来越远时,每多移动0.1 m的距离,纵坐标是所测得的误差。如图2所示,是当A = −42,n = 2.5,(A是距离为1时信号强度值时,n为衰减因子),三边定位算法和最速下降法的误差比较图。如图3所示,是当A = −42,n = 2时,两种算法的误差比较图。
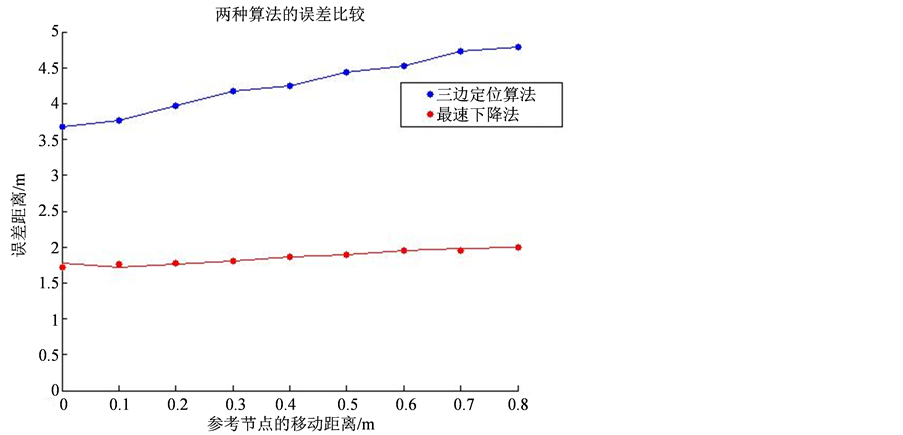
Figure 2. A = −42, n = 2.5 error comparison
图2. A = −42,n = 2.5时误差比较

Figure 3. A = −42, n = 2 error comparison
图3. A = −42,n = 2时误差比较图
从图3中可以看出,当衰减因子为2.5时,使用三边定位法测得的结果的误差距离始终比使用最速下降法测得的结果的误差大。当衰减因子为2时,参考节点移动距离越小,精度越高,其中用最速下降法测得的精度最高,最低误差值为0,随着参考点移动距离的增大,最速下降法测得的误差距离也迅速增大,但是仍然比使用三边定位算法精确。通过对比图2和图3可以看出衰减因子不同,误差变化也比较大。
4. 结论
本文利用对数正态阴影衰落模型求得距离,结合了三边定位算法和最速下降法提高定位的准确性。和前人所用的直接用三边定位算法求出来的坐标估计值相比,利用最速下降法求出来的坐标值更精确,误差范围也相对于之前的减小了一点。通过蒙特卡洛实验,从实验结果可以看出使用最速下降法比使用三边定位算法的误差距离更小,精度更高,并且误差值也相对比较稳定。由此可以得出结论,使用最速下降法可提高室内定位精度的有效性和可行性,可基本满足实际定位需求。由于本算法不需要增添额外的硬件开销,所以具有较广的实际应用范围和较高的应用价值。
*通讯作者。