1. 引言
卫星遥感降水在21世纪有着广阔的应用前景,其高时间分辨率和更大的空间覆盖范围对比传统地面观测有着极大的优势,能在一定程度上弥补其它来源降水数据的缺陷,为水文气象实际应用及相关研究提供有力的数据支持 [1] [2] [3] 。相比较众多的卫星降水产品,美国和日本联合执行的热带降雨观测计划产品(Tropical Rainfall Measurement mission, TRMM)取得了突破性成功,产生自TRMM以来“最好”的卫星降水产品,开创了全球降水监测的新时代 [4] 。TRMM 卫星于1997年11月28日发射升空,2015年4月由于燃料耗尽停止运行,卫星运行以来积累了海量覆盖陆地和海洋的高时空分辨率降水数据。作为TRMM卫星后续计划的GPM (Global Precipitation Measurement)卫星已于2014年2月发射,GPM不但将延续TRMM的星基降水传统,还将更大程度提高其时空分辨率、观测精度和准确性,进一步提升卫星降水在水文气象等领域的应用能力 [5] 。目前由于GPM卫星降水的时间序列较短(2014年2月至今),TRMM卫星降水仍具有不可替代的研究意义和应用价值。此前,国内很多学者已经研究了TRMM卫星降水数据在不同流域内的精度与误差特征,如杨秀芹 [6] 、胡庆芳 [7] 、李剑锋 [8] 、费明哲 [9] 分别研究了TRMM卫星降水在淮河流域、赣江流域、老哈河流域和鄱阳湖流域的精度与误差特征,发现TRMM卫星降水在我国不同流域具有一定的精度。关于TRMM卫星降水的水文模拟预报效用,我国学者也在国内部分流域进行了实例研究,如杨传国 [10] 、Yong [11] 、江善虎 [12] 、唐国强 [13] 、王佳伶 [14] 分别利用TRMM卫星降水在淮河流域、老哈河流域、洣水流域、赣江流域和湘江流域进行了径流模拟,发现TRMM卫星降水具有一定的水文模拟效用,但在不同流域的模拟精度存在一定差异。
本文以淮河息县水文站以上集水流域为研究区,基于地面雨量站点观测数据评估不同时间尺度最新一代TRMM卫星降水(3B42V7和3B42RT)的精度;并采用栅格新安江模型进行径流过程模拟,探讨TRMM卫星降水在现代水文模拟预报中的应用能力。
2. 研究区域与数据
2.1. 研究区域
选择淮河上游息县水文站以上集水流域作为研究区,流域范围为东经113˚15'~114˚46',北纬31˚31'~32˚43',流域面积为10,190 km2 (图1)。流域地处我国中纬度湿润气候与半干旱气候过渡带,多年平均降水量为800~1400 mm,多年平均径流深为371 mm,多年平均水面蒸发量为800~1000 mm。流域内土地利用方式以旱地、林地和水田为主。
2.2. 研究数据
收集息县流域22个雨量站和1个流量站(息县站)2000年3月~2013年12月的逐日降水和流量观测数据。采用临近三站点反距离加权(Inverse Distance Weighted, IDW)将点雨量插值到流域面分布。流域潜在蒸散发采用世界粮农组织(Food and Agriculture Organization, FAO)1998年修订的Penman-Monteith模型 [15] 计算,模型所需要的日平均气温、日最高气温、日最低气温、日照时数等气象观测资料来源于流域内信阳气象站。流域地形资料采用美国地质调查局(United States Geological Survey, USGS)的全球30″数字高程模型数据(Digital Elevation Model, DEM)。应用ArcGIS提取构建分布式水文模型所需的基本空间信息,包括流域边界、栅格水流流向、各栅格至流域出口断面的河长等。
采用的卫星降水数据为TRMM多卫星降水分析产品最新一代降水产品TRMM 3B42RT和TRMM 3B42V7,它是TRMM 3B42V6数据的升级版本 [16] 。TRMM 3B42RT为准实时卫星降水数据,在降水发生后的6~9 h可获取;TRMM 3B42V7为经过地面站点月尺度偏差校正的研究型数据,在降水发生后一个月的第10~15 d可获取。数据可由美国NASA(National Aeronautics and Space Administration)的Goddard数据分发中心免费下载。数据空间分辨率均为0.25˚,时间步长为3 h,将卫星数据在日、月尺度上进行累积,分别得到日降水和月降水。
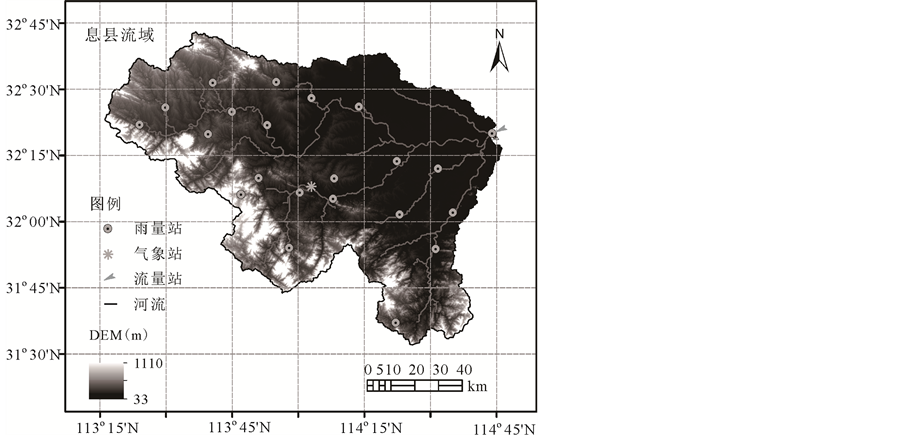
Figure 1. Location of Xixian Basin and Distribution of stations
图1. 息县流域位置及站点分布图
3. 模型与方法
3.1. 水文模型
采用栅格新安江模型进行流域径流过程模拟,模型基于蓄满产流计算每个栅格单元的总产流量;采用具有底孔和侧孔的溢流型水库将总径流划分为地表径流、壤中流和地下径流;采用线性水库进行各种径流成分的坡地汇流演算;采用马斯京根分段连续演算进行河道汇流演算 [12] [17] 。模型共有16个参数,根据流域观测径流资料进行率定,率定的目标准则是使根据参数值计算的出口断面流量与实测流量拟合最优,研究采用单纯多边形进化算法(SCE-UA)对模型参数进行优选 [18] 。
3.2. 模拟情景
选用2000年3月-2006年12月为模型率定期,2007年1月-2013年12月为模型验证期。为了探讨卫星降水在无/缺资料流域的径流模拟效用,论文采用两种情境(I,II)分别进行在有地面降水站点资料和无地面降水站点资料或地面降雨站点资料不足情况的径流模拟 [13] 。情景I利用地面雨量站点观测降水来率定模型参数,然后固定率定好的模型参数来进行TRMM卫星降水的水文过程模拟效用评估。情景II选用3B42RT和3B42V7卫星降水分别重新率定模型参数,然后使用卫星降水率定的模型参数进行水文过程模拟,评价TRMM卫星降水数据模拟径流的精度。
3.3. 评估指标
采用偏差(BIAS)、绝对偏差(Absolute Bias, ABIAS)和相关系数(Correlation Coefficient, CC)反映TRMM 卫星数据的精度,其中BIAS反映卫星数据对基准数据的偏差情况,ABIAS反映卫星数据对基准数据的绝对偏差情况,CC反映卫星数据与基准数据的相关性 [12] 。采用探测率(Probability of detection, PD)、击中率(Frequency of hit, FH)和Heidke技巧评分指数(Heidke's skill score, SH)反映TRMM 卫星数据判断降雨事件是否发生的准确性。PD越高,卫星数据对日降水事件的漏报程度越小;FH越高,空报程度越小;SH则综合表达了卫星数据对降水事件是否发生的估计能力 [7] 。采用Nash-Sutcliffe效率系数(NSCE)、BIAS、CC和均方根误差(Root mean square error, RMSE)来评价模型模拟径流的精度,其中NSCE系数表征模拟径流和观测径流的吻合程度,RMSE表征模拟径流和观测径流的误差大小 [12] 。
4. 结果分析
4.1. TRMM卫星降水的精度评估
表1为TRMM降水数据的精度统计指标,图2展示了日尺度上地面站点数据与卫星数据的散点相关情况。如表1所示,在日尺度上,3B42RT的BIAS值达到了25.25%,3B42V7的BIAS值为14.88%,说明在系统偏差方面,TRMM卫星降水数据都具有一定的误差,同时高估了息县流域降水量,其中准实时卫星降水数据3B42RT的误差尤为明显。在绝对偏差意义上,3B42RT的ABIAS值为70.57%,3B42V7的ABIAS值为67.6%,两者都具有较大的绝对偏差。相关性方面,3B42RT的CC值为0.76,3B42V7的CC值为0.78,二者都表现出与地面站点数据较好的相关性。在降雨事件探测率上,3B42V7与3B42RT有相同的FH值0.81,而3B42V7的PD和SH分别为0.62与0.48,略高于3B42RT的0.55和0.38;总体上二者对于降雨发生事件都能有较好的反映。
在月尺度方面,卫星数据在绝对值偏差和相关性方面都有明显的改善。绝对偏差方面,3B42RT与3B42V7的ABIAS值分别降低了28.23%与43.43%;相关性方面,3B42RT与3B42V7的CC值分别达到了0.90与0.97,图3直观的表示了月尺度上卫星降水与地面站点数据的高度相关性。总体来说,TRMM卫星数据在月尺度上有着较高的准确性,经过偏差校正的研究型数据3B42V7明显优于准实时数据3B42RT。比较日尺度和月尺度的

Table 1. Statistical measures of TRMM precipitation estimates at daily and monthly time scales
表1. TRMM卫星降水数据日尺度和月尺度精度统计指标

Figure 2. Scatterplots of daily precipitation comparison between satellite estimates and rain gauge observations
图2. TRMM卫星降水与地面观测数据日尺度散点图
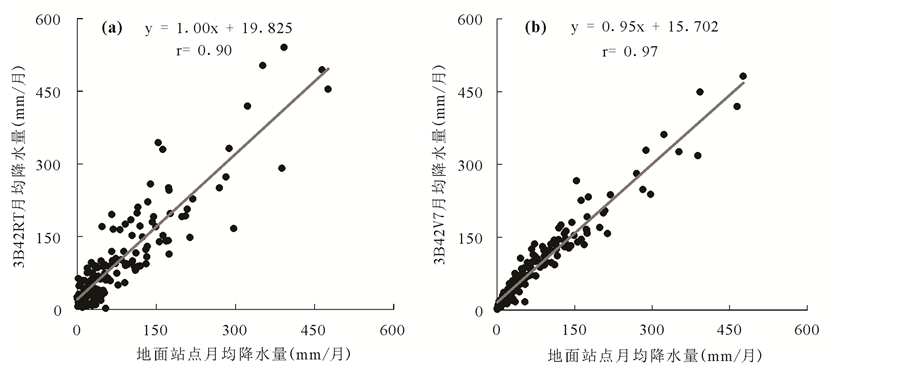
Figure 3. Scatterplots of monthly precipitation comparison between satellite estimates and rain gauge observations
图3. TRMM卫星降水与地面观测数据月尺度散点图
BIAS与ABIAS可以发现,TRMM算法中全球地面资料月尺度偏差校正能有效地保证TRMM日降水的BIAS接近于0,但其没有削减日降水的ABIAS数值。
4.2. TRMM卫星降水的水文模拟效用评估
表2给出了不同情景下(I,II)TRMM卫星降水数据在率定期和验证期模拟径流的精度评估指标。分析3B42RT

Table 2. Comparison of daily observed and simulated streamflow under different calibration scenarios
表2. 不同率定情景下日观测与模拟径流的比较
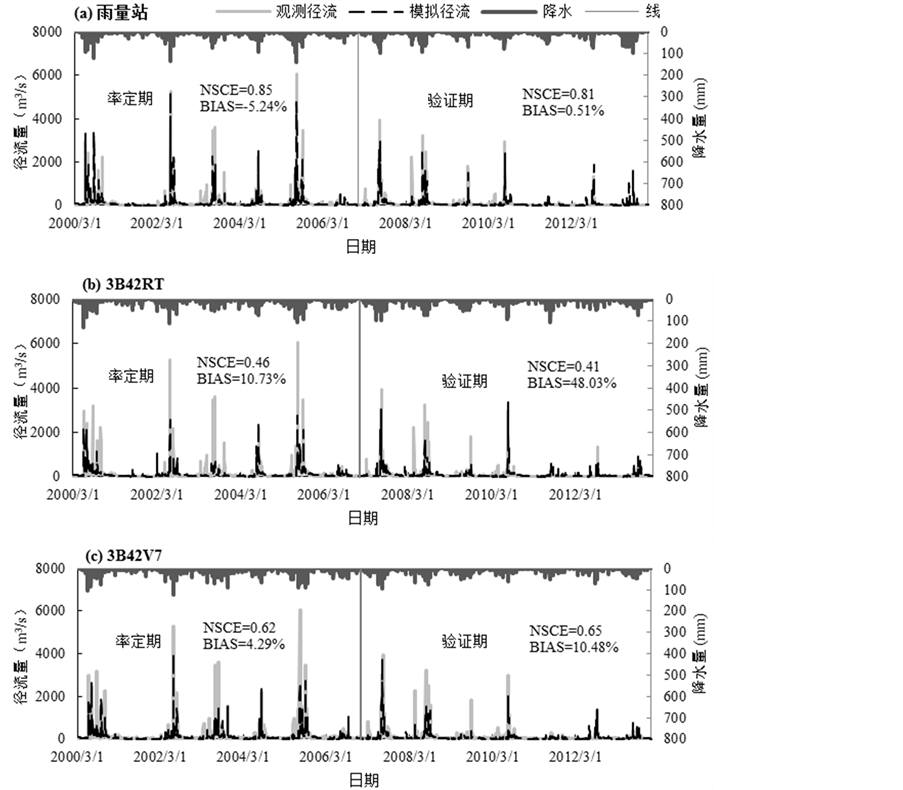
Figure 4. The Xinanjiang simulated daily streamflow based on TRMM data at case I
图4. 情景I下基于地面观测降水和TRMM卫星降水的新安江模型径流模拟结果
卫星数据在情景I、II下的径流模拟结果,发现在情景I,验证期的相关系数虽然高于率定期,由0.71提高到了0.77,但是验证期的偏差却明显增大,BIAS值由10.73%增加到了48.03%。这说明,在情景I的情况下,3B42RT卫星降水模拟径流虽然有着较好的相关性和峰值再现时间,但是在验证期其偏差BIAS过于偏大,影响了径流模拟的准确性,这可能受3B42RT降雨误差和模型参数影响造成。在情景II中,模型的参数经过重新率定,不论是率定期还是验证期,3B42RT卫星降水模拟径流的各方面指标(NSCE,BIAS,CC,RMSE)较情景I都有所提高,尤其在验证期NSCE、BIAS和RMSE值得到显著改善,其中NSCE增加到0.58,BIAS下降到19.52%,RMSE下降到177.85 m3/s。这说明对于偏差较大的3B42RT卫星数据,经过情景II下模型参数的重新率定,能够一定程度提高模拟径流的精度。分析3B42V7卫星数据在情景I,II下模拟结果发现:相对于3B42RT模拟数据,3B42V7在不同情景下模拟径流的精度有明显提高,NSCE达到0.62以上,BIAS在±10.48%之间,CC提高到0.79以上,RMSE也有明显的减小,说明3B42V7较3B42RT具有更好的水文模拟效用。在不同模拟情景方面,情景I与II下3B42V7模拟径流的精度相差不大,但整体上情景II的模拟结果略优于情景I。图4为情景I下基于地面雨量站点和TRMM卫星降水数据的新安江模型径流模拟结果,自上而下分别是地面雨量站模拟径流,3B42RT数据模拟径流和3B42V7数据模拟径流。可以发现,TRMM卫星降水(特别是3B42V7数据)模拟结果与实际径流量在时间序列上有着很好的吻合,能较好再现峰值的出现时间,具有一定水文模拟应用能力。
总体来说,运用TRMM卫星降水数据替代地面站点观测数据模拟径流具有一定的可行性,其中3B42V7模拟结果有着更高的精确性和更好的适用性。而GPM作为TRMM的后续计划,将提供时空分辨率更高、观测精度更为准确的卫星降水产品,在现代水文模拟预报领域将起到更加重要的作用 [5] 。
5. 结论
本文评估了最新的TRMM卫星降水(3B42RT, 3B42V7)在淮河息县流域的精度及水文模拟效用,发现日尺度上TRMM卫星降水与地面站点数据具有较好的相关性,但存在一定的系统偏差,3B42RT与3B42V7分别高估流域降水量25.25%和14.88%,ABIAS分别达到70.57%和67.61%;TRMM卫星降水能较好探测降水事件的发生情况,探测率在0.55以上,探测降水事件发生的可信度达到0.81。月尺度上,TRMM卫星降水精度有较大提高,ABIAS大幅度下降,CC值有较大提高,3B42V7的CC为0.97。径流模拟方面,3B42RT在情景II下模拟结果较好,但仍不及3B42V7模拟结果;3B42V7在情景I,II下都有较好的径流模拟表现,NSCE达到0.62以上,BIAS在 ± 10.48%之间,CC达到0.79以上,表明TRMM卫星降水具有替代地面站点数据模拟径流的可行性,随着更高时空分辨率、更高精度的GPM卫星降水的出现,多卫星降水在现代水文模拟预报领域将具有更广阔的应用前景。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(41501017);大学生创新训练计划项目(2015102941012)。