1. 引言
湿地是地球上水陆相互作用形成的独特生态系统,是自然界最富生物多样性的生态景观和人类最重要的生存环境之一,是陆地与水域之间的过渡地带,具有维持生态平衡、保持生物多样性以及涵养水源、蓄洪防旱、降解污染、补充地下水、控制土壤侵蚀等重要作用 [1] [2] [3] [4] 。近些年来由于自然因素和人为干扰,湿地遭到一定程度的破坏,主要表现为自然湿地类型和面积不断减小,湿地组织结构破坏,生态功能减弱等 [3] [5] 。其中,湿地面积减少是湿地生态系统退化最直观的表现,也是湿地退化的重要标准之一。遥感与GIS技术的结合为湿地资源的调查提供了极大便利,成为探讨景观格局演变、揭示其空间变化规律和建立其变化驱动力模型有力的分析手段 [6] 。
本文的研究对象辽宁省辽河流域处于中国东北地区的西南部,拥有的湿地资源,湿地总面积12196.15 km2,占全省国土面积的8.24 %,湿地类型包括滨海湿地、河流湿地、湖泊湿地、沼泽湿地、人工湿地5大类。这些湿地具有重要的生态服务功能,维持着区域间生态环境的平衡,并且在整个东北地区的经济发展中占有非常重要的位置。目前对辽河流域湿地的研究主要集中在滨海湿地,张华 [7] 等基于遥感、GIS技术和野外调查,对辽宁省滨海湿地进行三级系统分类统计,并对各个分级进行了景观格局分析。蒋卫国 [6] 等对辽河三角洲进行湿地资源的时空变化特征及驱动力分析,表明人工湿地不断增加,自然湿地不断减少,主要驱动力为人口增加,经济和工农业的发展。黄桂林 [8] 分析了辽河三角洲河口湿地近30年来的景观演变规律,得出自然湿地逐渐转化为人工湿地,城市建设用地大量增加,景观多样性减少,农业开发直接导致自然湿地、半自然湿地转换成人工湿地,而油田开采、道路及城市化建设除了占用湿地之外,更直接导致湿地的格局和破碎度的改变。
近些年来对湿地的研究倾向于滨海湿地,对河流湿地,人工湿地等的研究则较少,这不利于辽宁省制定不同类型的湿地修复方案,为了解决这一问题,本文根据湿地不同特点选出三个辽河流域典型湿地。通过对典型湿地进行2000年,2010年,2015年7~8月,共24期TM遥感数据分析,得出景观格局类型面积及分析其变化特征,并从自然因素和人为干扰两个方面分析典型湿地的主要退化因素。
2. 辽河流域典型湿地的确定
2.1. 辽河流域概况
辽河流域位于东经116˚54'至125˚32',北纬40˚30'至45˚17'之间,是我国七大江河流域之一,发源于河北省承德地区七老图山脉的光头山(海拔1490 m),流经河北、内蒙古、吉林和辽宁4个省区,主要包含“西辽河–东辽河–辽河”(简称辽河水系)和“浑河–太子河–大辽河”(简称浑太水系)等两大独立水系,干流全长2201 km,总流域面积21.96万km2,属树状水系,东西宽南北窄,东部、西部和西南部三面群山环绕,以构造剥蚀地貌为主,山地占48.2%,丘陵占21.5%,平原占24.3%,沙丘占6% [9] 。
辽河流域地处中温带大陆性季风气候区,雨热同季,日照多,冬季严寒漫长,春秋季短多风沙,夏季炎热多雨,东湿西干,平原风大。多年平均降水量为300~1000 mm,降水时空分布极不均匀,由东向西递减,多集中在6~9月,占全年降水量的70%~85%,易以暴雨的形式出现。水资源总量为221.9亿m3,其中地表水资源量137.2亿m3,可利用水资源总量115.04亿m3。浑太水系上游水资源相对较丰富,西辽河水资源严重短缺。
辽河流域是我国重要的钢铁、石油、化工、机械、建材基地,粮食生产基地和畜牧业基地。这些工业、农业、牧业及因此而进行的一系列人类活动都对辽河流域湿地产生极大负面影响。工业工厂一般都分布于大多数的地级市和乡镇中,其中绝大部分工厂的污水均直接排入相应的市、镇地下水系统中,甚至有部分大型工厂直接将污水排入地表水;农业又普遍使用含N、P的化肥。从而导致辽河流域的水质污染严重,仅有少部分区域呈III、IV类水标准,大部分流域呈现地表水V类标准情况,甚至有劣V类的水质地区,水质污染严重 [10] 。
2.2. 典型湿地确定
地的地理环境、水文条件以及水源补给状况等对湿地生态环境起着重要作用。在基本掌握辽河流域湿地概况的基础上,考虑湿地类型、湿地生态环境状况以及对辽河流域生态的影响程度等因素,选取辽河流域范围内具有代表性的三个湿地。
盘锦湿地属于滨海复合湿地。湿地类型主要有沼泽湿地、浅海水域、沿海滩涂以及河流等多种类型的自然湿地,和水稻和水库等人工湿地类型 [11] [12] 。湿地面积比较大,湿地内动植物种类繁多,景观结构复杂多样,具有很高的生态功能和经济效益,是国内外瞩目的湿地。对辽宁省乃至整个东北地区的生态环境和社会经济发展都起着非常重要的作用。
蒲河湿地属于污染型的湿地 [13] [14] 。其位于蒲河流域,补充水源匮乏,且由于城乡废水的大量排放,水质严重污染,景观类型不完整。明晰蒲河湿地景观类型变化特征并分析退化的主要原因,对辽河流域同类型湿地的生态修复具有指导意义。
铁岭莲花湖湿地属于自然和人工复合湿地,现有的湿地类型包括淡水沼泽和人工湿地两类,其中淡水沼泽包括泛洪平原、湖泊和草木沼泽;人工湿地主要包括池塘、水田和水库 [15] 。莲花湖湿地的代表性区域为莲花湖湿地公园,其是以人工库塘、稻田、河流及浅水型的小型湖泊群为主的复合型湿地 [16] ,具有明显的湿地性质,特殊的土壤结构和生物区系,景观特征显著,而且生态系统的结构基本保持着难得的完整性。因此对莲花湖湿
地的研究,有利于辽宁省对人工湿地恢复方案的制定。
3. 典型湿地退化原因分析
3.1. 盘锦湿地退化影响因素
3.1.1. 盘锦湿地概况及景观类型变化分析
盘锦湿地地处40˚39'~41˚27'N,121˚25'~122˚31'E,濒临渤海湾,属于暖温带大陆性半湿润季风气候,年平均气温9.1℃,无霜期171 d,年日照时数为2568.47小时,降水量逐年递减,近60年来年平均降水量为211 mm,降水最大月份7月,年平均相对湿度为65.78%,年平均风速3.2 m/s,属半湿润、半干旱地区。盘锦湿地地貌类型主要是冲积平原和潮滩,地势低洼平坦、北高南低,坡度在2˚以内,平均海拔4 m。该地区由于大辽河、双台子河、大凌河等河流和渤海的交互作用下形成了总面积为3.0 × 105 km2的湿地生态系统,是辽河三角洲的主体部分。其湿地类型主要包括芦苇沼泽、管理苇田、香蒲苇田、滩涂、湿草甸、水稻田和虾蟹田 [17] 。
盘锦湿地景观格局类型面积如表1所示,总面积3096.46 km2,其中湿地所占面积最大,占总面积的45%~52%,其次是耕地,占总面积的33%~40%,然后是建筑用地、林地、草地和其他土地类型,分别占总面积7%~12%、1%~1.5%、0.2%~8%和0.03%~0.11%;从变化上来看,2000~2015年间,草地和建筑用地面积明显增加,增加的面积分别为233.24 km2和146.73 km2,而湿地面积逐年减少,减少的面积为198.86 km2,耕地面积先增加34.34 km2,
然后减少215.40 km2,林地和其他土地类型变化不大。
3.1.2. 盘锦湿地退化影响因素
分别从气候因素和人为干扰两方面对盘锦湿地退化的主要影响因素进行分析。
1) 气候因素
气候因素主要包括气温和蒸发量。通过中国气象数据网的数据进行统计分析,得出盘锦湿地年平均气温、年平均最高气温和最低气温均不断上升,如图1所示,上升的速率分别达到每年0.03485℃,0.01212℃和0.04347℃。与全国气候变暖趋势一致,气温的升高,导致盘锦湿地水面和陆地蒸发量增加,进一步引起湿地土壤的盐碱化和沙化,对湿地的植物生长也产生多方面的不良影响。
2) 人为干扰
根据第六次人口普查数据报告,盘锦市人口达到139.2493万人,同第五次全国人口普查相比,10年间增加13.0740万人,增长10.36%,年平均增长率为0.99%。随着盘锦市的人口数量急剧增长,盘锦市民对各种湿地资源的需求也不断增加,表现为盘锦湿地区域的建筑用地不断增加,农业开发和石油开采程度不断加深,大量的盘锦自然湿地如天然水域和浅海的滩涂,逐渐转化为人工湿地如具有较大的经济效益的虾蟹田和水稻田,造成天然湿地面积锐减,耕地面积的不断扩大。
· 建筑用地的增加
根据2000~2015年期间的景观类型面积数据变化,可知草地和建筑用地面积明显增加,增加的面积分别为

Table 1. The changes in area of each type of landscape in Panjin wetland during the period 2000-2015
表1. 2000~2015年盘锦湿地景观类型面积变化/km2
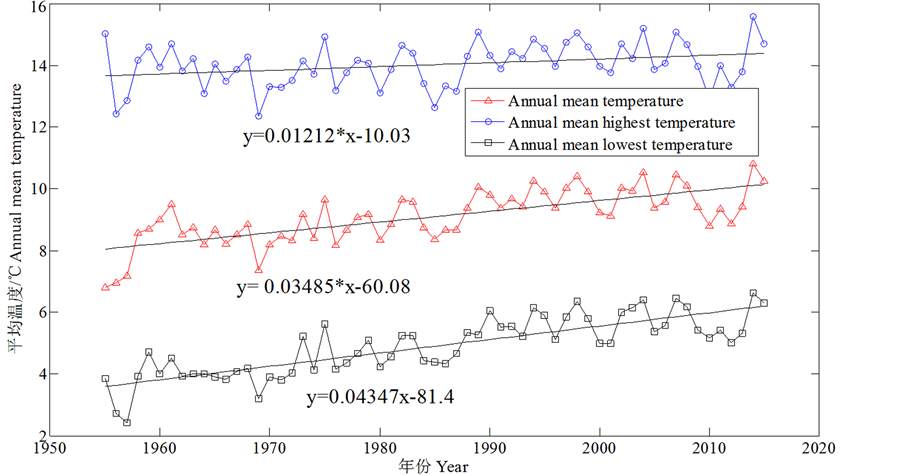
Figure 1. Annual mean temperature of Panjin wetland from 1955 to 2015
图1. 1955~2015年盘锦湿地年气温的变化
233.24 km2和146.73 km2。同时由盘锦市十三五计划可知,在十二五期间,盘锦市的第一、二、三产业均大幅度发展,相应的建设用地在不断增加,基础设施及公共设施不断完善,这些不断侵占原有的湿地面积,导致湿地退化。
· 农业开发与水产养殖业
在农业开发的过程中,过量的化肥和农药,在稻田排水的作用下,大量的积聚在了三角洲的河湖及沼泽湿地中,造成湿地水质污染严重。这不仅对湿地动植物生长和生存产生直接影响,而且对湿地的各种功能的呈现和发挥造成了严重的负面影响。同时由于区域内水产养殖业的快速发展,大量的滩涂被强制地修筑成为养殖场所,导致大量自然湿地转化为景观多样性较少的人工湿地。
· 石油资源开采
盘锦湿地地处辽河中下游冲积平原,是辽河油田的腹地,石油、天然气和井盐的储量非常丰富。油气资源的开发和开采,占用了大量的自然湿地面积,并且破坏了湿地的景观的完整性,如钻井和铺设油气运输管线等;与油田开采相应的人类活动,如钻井和各种井上和井下作业等,破坏了湿地地表的植被和湿地景观的完整性,同时,破坏了湿地中各种生物的栖息地。石油开采过程中泄露和散落在湿地周围的原油,会引起湿地土壤的理化性质变化。泄漏物质难以自身降解和消除,还会随着地表径流流入沼泽和河流等湿地的主要补给水源,从而不可避免地对湿地水质和生态环境造成了难以修复的污染和影响。
3.2. 蒲河湿地退化影响因素
3.2.1. 蒲河湿地概况及景观类型变化分析
蒲河发源于铁岭县横道河子乡想儿山,在辽中县黑鱼沟村南汇入浑河,全长共205 km,流域面积为2496 km²。蒲河在沈阳境内始于棋盘山水库,流经棋盘山开发区、沈北新区、于洪、新民市和辽中县,全长约168 km。沿途有多条支流河、棋盘山水库、仙子湖和团结水库,正常蓄水量近亿立方米。蒲河补充水源包括天然降水、上游水库弃水、支流河的补充水以及污水厂排水。此外,还包括未经处理的各类污水。蒲河水系水资源时空分布不均匀,径流年度变化主要受控于雨季、上游水库泄水和汛期降雨补水 [14] 。
蒲河受控于棋盘山水库和洋什水库的上游径流供水量非常有限,水库弃水时段不均,枯、平水期过水量较低。蒲河的主要水源来自南北干渠农灌余水,补水量大约占总水量的32%。以九龙河为代表的天然支流河补水作用非常有限,且主要受益于辽河的补水。此外,流域各类排水均占总水量的41%左右。即近一半天然水补给维持着蒲河的生态用水,而各类排水作为另一半补水资源,因污染严重对蒲河水生态环境造成严重破坏 [18] ,相应的蒲河湿地生态环境受到严重影响。近些年来,随着蒲河生态廊道建设成效显著,河流重污染状态得到一定程度上的控制,水质得到明显改善。但部分河段的水质仍无法达到既定的目标要求。目前蒲河受纳的污水包括城镇生活污水、农业面源污染、开发区工业废水和点源工业废水。蒲河水质污染较重,其周围的生态环境遭到较大的破坏,面对环境补给水少、污水汇入量大、生活垃圾污染严重等问题,蒲河湿地净化困难。
蒲河湿地景观格局类型面积如表2所示,总面积490.77 km2,其中耕地所占面积最大,占总面积的67.22%~62.59%,其次是湿地和建设用地,分别占总面积的12.88%~21.21%和11.45%~17.91%,然后是林地和草地;从变化上来看,2000~2015年间,草地和建筑用地面积明显增加,增加的面积分别为23.10 km2和31.73 km2,而湿地面积逐年减少,减少的面积为40.85 km2,耕地先增加后减少,变化幅度不大,林地先减少后明显增加,2015年面积为8.14 km2。
3.2.2. 蒲河湿地退化主要影响因素
由于受到自然因素和人为污染的影响,蒲河收纳的污水量大,严重超过自身的纳污能力和水环境容量 [14] ,为辽河流域内污染较为严重的河流湿地。目前,有机物污染为蒲河流域的水质的主要污染特征 [19] 。
1) 天然水源补给严重不足
蒲河湿地的天然水资源严重不足,水体自净能力差。其上游的棋盘山水库补给的水量较小,加上上游蓄水工程的拦截,天然水资源量的供给,不能满足蒲河水体自净对水资源量的基本需求。此外作为沈阳最重要的粮食产区,蒲河湿地年用水量极大,而自然降水量少,再加上主要的补给水来源于工业的污水,使得蒲河湿地难以保持生态平衡,进而导致湿地退化。
2) 蒲河水质的影响
目前,由于蒲河受纳的污水来源复杂,面源污染包括城镇生活污水和农业灌溉,以及工业废水的点源污染,蒲河流域的水质污染严重,主要为有机污染,污染指标为化学需氧量和悬浮物含量。尽管蒲河生态廊道的建设初见成效,蒲河水质恶化得到一定程度的控制,但仍无法达标。蒲河作为蒲河湿地的主要水源补给河流,其水质对蒲河湿地的生态环境造成了影响,是造成蒲河湿地退化的主要原因之一。
3) 生活垃圾及农村面源污染严重
蒲河沿岸的二十多个乡镇,都是分布在距离城区较远的地区,垃圾收集和处理的设施及条件严重不足,这导致乡镇的生活垃圾大量累积,并多数堆放在蒲河两岸;河流两岸的农业种植过程中,过量使用的化肥和农药中含有的大量营养物(N和P等元素)直接排入到河流中,导致河流富营养,水体发黑发臭。
3.3. 莲花湖湿地退化影响因素
3.3.1. 铁岭莲花湖概况及存在的问题
铁岭莲花湖湿地位于E123˚41'~123˚51',N42˚15'~42˚20',地处辽河与其支流柴河、凡河之间的洪泛平原区,属于辽河水系,海拔50.5~60.2 m,属于中温带大陆性季风气候区,气候主要特点是冬季寒冷干燥,夏季温热多雨,雨热同季,日照丰富,干湿季节分明。年平均气温为8.3℃,1月份最冷,平均气温为−11.9℃,7月份最热,平均气温为24.5℃。年平均降水量为630.4毫米。年日照时间为2801小时,平均每天7.7小时,春、夏两季日照时间较长,秋季次之,冬季最短 [20] 。
按湿地类型划分,莲花湖湿地是由人工库塘、河流、浅水型小型湖泊群及稻田组成的复合湿地类型,具有湖、泡相联的水网结构。其湿地生态系统结构基本完整,土壤结构、生物区系及其生态过程的湿地性质明显,

Table 2. The changes in area of each type of landscape in Puhe wetland during the period 2000-2015
表2. 2000~2015年蒲河湿地景观类型面积变化/km2
湿地景观特征显著。莲花湖湿地总面积为1500.3 km2,其中河流湿地42.0 km2,沼泽湿地82.0 km2,库塘湿地326.0 km2,水稻田1050.3 km2 [21] 。
莲花湖湿地景观格局类型面积如表3所示,总面积451.7 km2,其中耕地所占面积最大,占总面积的75.61%~40.80%,其次是建设用地,占总面积的10.30%~29.85%,然后是林地和湿地,草地面积最少;从变化上来看,2000~2015年间,草地和建筑用地面积明显增加,增加的面积分别为29.60 km2和88.40 km2,增加幅度分别为总面积的6.55%和19.55%,而耕地面积逐年减少,减少的面积为157.24 km2,减少幅度为总面积的34.81 %,湿地和林地均先减少后增加,近五年增幅均较大。莲花湖湿地所在的铁岭市主城区人口约40万人,生活污水为
城区主要污水类型,排放量约为14万m3/d。这些污水经过铁岭市城区污水处理厂处理后首先排入莲花湖湿地,经湿地生态系统净化后入凡河IV类水域,最终入辽河V类水域 [22] ,由于经过处理的污水不能完全净化,仍然有一定程度的污染,对莲花湖湿地的产生了负面影响。
3.3.2. 莲花湖湿地退化主要影响因素
1) 凡河水质的影响
作为莲花湖湿地的主要补给水源补给河流,凡河水质对莲花湖湿地的退化有着直接的影响。近年来辽河流域治理工作的逐步开展,初步取得了成效,使凡河水质恶化的趋势在一定程度上得到了控制,水质有所好转,但凡河水污染问题仍然存在。表4为2006~2010年凡河水质中主要污染物的年平均值。
由表4中可以看出,凡河水质在2007和2008年两年中的化学需氧量、氨氮和高锰酸盐指数的年均值均偏高,凡河水质污染严重。其余年份的三个指标均随时间增长逐渐降低,尤其是2009年到2010年,凡河水质中的化学需氧量、氨氮和高锰酸盐指数的年均值呈现明显下降的趋势,水质情况好转,但仍需进一步治理。
2) 经济的发展
通过查阅铁岭市统计年鉴,得到铁岭市1999~2011年的生产总值,如图2所示,生产总值飞速增加,12年间增加了7,552,941万元。从图3可以看出,各个产业均得到大幅度提升,尤其是第二产业中的工业,带动了总体经济发展,成为铁岭市发展重要支柱。工业发展的同时,产生大量工业废水,工业垃圾等,对铁岭市尤其是生态环境较为敏感的湿地造成很大影响,是引起莲花湖人工湿地退化的主要因素。
3) 铁岭市污水处理厂出水水质影响
铁岭市污水处理厂的出水,经泵站及一些铺设的管线,直接流进了莲花湖湿地,通过湿地中的人工湿地过滤系统后,处理的出水流入莲花湖中。来自老城区的污水处理厂的污水,经处理后排入莲花湖中,为莲花湖湿地提供水源。但由于污水处理厂的污水中污染物成分复杂,经处理后的出水水质不稳定,和水中的COD值偏高
等,这些均会对莲花湖湿地产生一定的影响,也是导致莲花湖湿地水质中COD值超过V类标准的主要原因。
4) 新城区建设的影响
铁岭市新城区建设规划位于莲花湖正南侧,与莲花湖湿地相邻。在新城区建设过程中,施工设施的搭建和人类的频繁活动都对湿地周围景观的连续性和植被的覆盖程度等产生不良影响;在施工过程中产生的固体废弃物以及污水等也对莲花湖湿地的生态环境造成影响。因此,新城区建设中的环境保护配套工程显得极为重要。

Table 3. The changes in area of each type of landscape in Lianhuahu wetland during the period 2000-2015
表3. 2000~2015年莲花湖湿地景观类型面积变化/km2

Table 4. Annual average values of main containments in Fanhe River during 2006 to 2010 (mg/L)
表4. 2006~2010年凡河水质中主要污染物年平均值(mg/L)
5) 政策法规
自十九世纪五十年代以来,莲花湖地区由于农业的开垦和渔业的养殖,开发了大量湿地湖滩,导致莲花湖天然湿地面积锐减,湿地功能逐渐衰退。铁岭市政府意识到湿地退化问题,并从2007年开始对铁岭市莲花湖湿地进行修复,实行“退耕还湖”策略,根据遥感解译数据可知,近5年,耕地面积大幅度减少,湿地面积明显增加,一定程度上恢复了莲花湖湿地。
4. 结论
1) 考虑湿地类型、湿地生态环境状况以及对辽河流域生态的影响程度等因素,在整个辽河流域范围内,确定了三个典型湿地,分别盘锦湿地、蒲河湿地以及铁岭莲花湖湿地:
盘锦湿地属于滨海湿地,湿地面积大,并具有很高的生态功能和经济功能,在整个辽河流域的湿地中具有代表性;蒲河湿地属于污染型湿地,该湿地的水资源匮乏,水体污染严重,河道形态不明显,且景观不完整,研究该湿地的景观格局分布并分析退化因子,对辽河流域同类湿地生态的修复具有指导意义;铁岭莲花湖湿地是辽宁省唯一的国家湿地公园,是以人工库塘、稻田、河流为主的复合湿地类型。这种复合结构在辽河流域湿地中具有一定代表性,对辽河流域生态恢复战略的实施具有非常重要意义。
2) 通过对典型湿地进行2000~2015年的TM遥感数据分析,得出景观格局类型面积及分析其变化特征,并从自然因素和人为干扰两个方面分析典型湿地的主要退化因素:
盘锦湿地总面积为3096.46 km2,2000~2015年间,草地和建筑用地面积明显增加,增加的面积分别为233.24 km2和146.73 km2,而湿地面积逐年减少,减少的面积为198.86 km2,耕地面积先增加减少,林地和其他土地类型变化不大。主要影响因素为气温升高和蒸发量增加的气候因子,及建筑用地的增加,农业水产养殖业的发展和原油开采的人工干扰;

Figure 2. Tieling City’s GDP from 1999 to 2011
图2. 1999~2011年铁岭市的生产总值
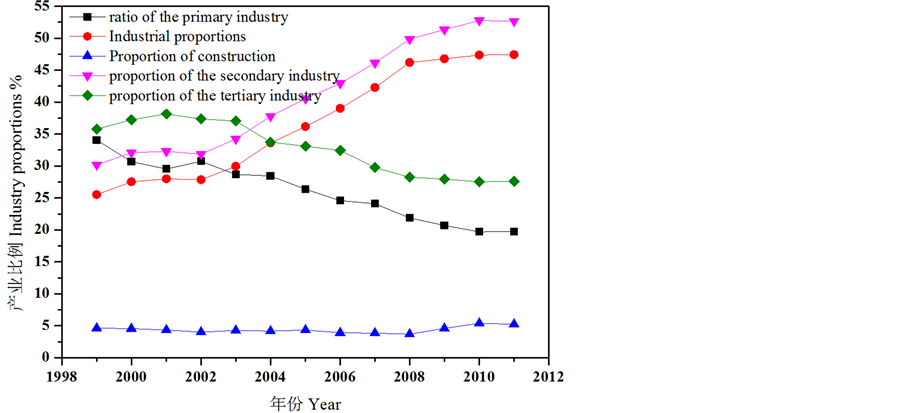
Figure 3. The proportion of GDP in various industries in Tieling City from 1999 to 2011
图3. 1999~2011年铁岭市各个产业生产总值比例关系
蒲河湿地总面积为490.77 km2,耕地所占面积最大,占总面积的67.22%~62.59%,2000~2015年间,草地和建筑用地面积明显增加,而湿地面积逐年减少,耕地先增加后减少,林地先减少后明显增加。其退化的自然因素为天然水资源严重不足,人为干扰主要包括蒲河流域点、面、源的污染,蒲河上游蓄水工程的建设以及蒲河两岸垃圾堆放等
莲花湖湿地总面积451.7 km2,其中耕地所占面积最大,占总面积的75.61%~40.80%,2000~2015年间,草地和建筑用地面积明显增加,而耕地面积逐年减少,湿地和林地均先减少后增加,近五年增幅均较大。其退化的主要影响因素为水源补给河流凡河等水质污染严重,经济的发展和铁岭新城区的建设。
基金项目
国家科技重大专项项目(2012ZX07505-001-004)。