摘要:
本文以江西省转移人口市民化意愿调查数据为基础,采用logistic二元回归模型,研究了江西省转移人口市民化意愿问题,并分析了该意愿的影响因素。文章首先对转移人口的概念及内涵进行了新的界定,并通过描述统计分析初步确定了性别、年龄、文化程度、月收入、子女情况、岗位类型、住房情况以及福利体系满意情况对市民化均有影响,并得到在调查者中有81.7%的人表示愿意留在城市生活,18.3%的调查者不愿意留在城市生活,可得到大多数人愿意生活在城市。然后通过logistic二元回归模型进行实证分析发现性别、婚姻状况、文化程度、对福利体系的满意度是影响转移人口市民化意愿的主要显著性因素,针对该结果本文提出了相关制度供给侧改革的相关建议。
Abstract:
This paper bases on the survey data of the transfer population urbanization of Jiangxi Province, the paper studies the willing of the population of Jiangxi province and analyses factors of the willing by the two classification logistic regression model. This paper gives a new definition for the concept and connotation of population transfer, and through the descriptive statistical analysis finding the gender, age, education level, monthly income, family situation, types of work, housing and welfare satisfaction having impact on urbanization, and 81.7% of the participants said they are willing to stay in the city life, 18.3% of respondents are not willing to stay in the city life, however, most people are willing to live in the city. Then by the two classification logistic regression model for the empirical analysis finding gender, marital status, education level, satisfaction of the welfare system are the main factors effecting transfer population urbanization willingness, according to the results, this paper puts forward relevant suggestions related to the supply side system reform.
1. 引言
随着改革开放的进程不断加速,城镇化进程也在加快。城镇化是改革开放的产物,是其发展的必然趋势。城镇化包括几个核心内涵,即转移人口由农村户口转为城镇户口、社会福利提高、子女教育较以往有进步、农村发展紧跟国家步伐 [1] 。而随着城镇化的发展,在十八届三中全会中,又提出来新型城镇化,其内涵较以往的城镇化有了新一层的加深,即在城镇化的基础上表示不仅农村户口改变就是城镇化,而是需要让转移人口真正的同城里人一样享受到相同的福利待遇,子女教育问题得到全面的解决,转移人口的思想行为能够适应城市的习惯,这就要求城市的公共服务要同时跟上步伐。转移人口是指由第一产业转向其他产业的人口。广义上是指户籍由农村户籍转为城镇户籍的人口,实际上应该是在户口为城市的基础上,自身所享受的社会福利也跟上了国家一般城市水平以及子女教育问题得到解决的人 [2] 。而正是基于此,很多人们对城市的环境有追求、有向往,但是基于这些水平不足或者一系列其他公共与心理上的问题而止步。所以对转移人口的意愿问题进行分析是很必要的。本文的调查对象是江西省较大市的转移人口,包括户口已经转为城市户口的人群以及有居住在城市的意向但是尚未转移户口的人群。
本文所研究的主旨是调查研究江西省转移人口市民化问题,所以调查地点与对象均在江西省范围内。本调查的调查对象不再受限于以往文献中的农民工,而是还包括高校学生、私企、国企以及个体工作者,共五类人群,职业包含领域较其他学者较为广泛。从实证调查的角度,通过描述分析以及二分类逻辑回归的方法,揭示了转移人口的转移意愿影响因素以及已转移人群的现有状况的一些问题,并综合分析了推进转移人口市民化的进程中各机制多存在的需要努力问题,并提出相关的对策与建议。
2. 转移人口概念的界定与内涵
转移人口是指离开出生户籍所在地,并向其他城市转移且有意在城市定居的人口。农业转移人口则是从农业转移至其他产业的人口,包含了只在城市工作但未在城市落户的人群和虽在城市落户,但是未适应城市习惯且没有完全享受到城市公共服务的人群。
内涵:转移人口是指由第一产业转向其他产业的人口,不应该是指狭义的从事建筑类体力劳动的农民工,广义上是指户籍由农村户籍转为城镇户籍的人口,实际上应该是在户口为城市的基础上,自身所享受的社会福利也跟上了国家一般城市水平以及子女教育问题得到解决的人 [3] 。学术界不同学者对转移人口内涵判断标准存在不同界定,且对转移人口市民化概念也就存在理解上的缺乏,部分学者对市民化的内涵标准界定如表1。
在城镇化过程中的转移人口的最终确定按照相关学者的研究表示,应该包括农村退出、城市进入、城市融合三个阶段。 [4] 第一阶段,农村退出指不再拥有农村户籍,并且不再享受农村人的相关政策待遇,在农村的土地和一些资产也同时放弃,失去先前所拥有的土地使用权。第二阶段,城市进入是指进入了以非农业经济为主的城市生活或者工作,且有了城市户籍,户籍制度是进入的首要制度保障。第三阶段,城市融入是指在自身拥有城市户籍的基础上,其自身和家人享受到城市人同等的社会福利以及公共服务,并深入适应城市生活,包括能与城市人进行相等的对话,思想习惯上适应节奏。这三个阶段的完整实现,需要国家、社会、个人的共同作用 [5] 。
3. 数据来源及处理
本数据采集于2016年江西省上饶、九江、抚州、南昌等较大市的农民工、高校学生、国企人员、个体经营户、私企职工这五大人群,采用现场填写问卷以及网上问卷同步的方式发放问卷,共发放问卷230份,有效问卷230份。问卷内容包括个人基本情况、薪资收入、居住情况、负担情况、享受福利、意愿调查、对公共服务满意度八大内容,分为个人、家庭、社会三大因素进行统计分析。
4. 模型选择和描述统计
4.1. 模型的选择
针对问卷调查的最终目的,最终转移人口市民化的愿意分为愿意和不愿意两种情况,是典型的二元变量,将“愿意”和“不愿意”分别赋值“1”和“0”,即“1 = 愿意”、“0 = 不愿意”,所以本文选择逻辑二元回归模型进行实证分析 [6] 。问卷中自变量的符号定义见表2。
4.2. 描述性统计
1)个人方面
男性125人,占比54.3%,女性105人,占比45.7%。年龄22岁及以下有15人,占比6.5%,23 - 30岁有115人,占比50%;31-40岁有42人,占比18.3%;41岁以上58人,占比25.2%;未婚91人,占比39.6%;已婚139人,占比60.4%。小学及以下学历10人,占比4.3%;初中学历46人,占比20%;高中学历40人,占比17.4%;中专学历26人,占比11.3%;大专学历38人,占比16.5%。本科学历46人,占比20%;硕士及以上学历24人,占比10.4%。工资在2000及以下有50人,占比21.7%;2000 - 3500

Table 1. The connotation standard of the urbanization
表1. 市民化内涵标准 [7]

Table 2. The sign definition of independent
表2. 自变量的符号定义
元90人,占比39.1%;3500以上90人,占比39.1%。农村户籍133人,占比57.8%;城市户籍97人,占比42.2%。
从上面的个人情况可以看出在外出人群中男性比例高于女性,符合中国国情,转移人口年龄最多的是23 - 30岁的人群,因为此年龄段属于青年时期,且由于本研究包含了学生群,所以符合现实情况。已婚者较未婚者比例更高,说明该研究具有真实性。本科人数最多,其次是初中和高中,说明接受更高教育的人越希望出来务工,且工资普遍分布在2000 - 3500元之间,该调查中的城市户籍和农村户籍人数相当,该调查的城市户籍均为由农村转为城市户籍的人群,设置这种对比,可以通过后面的交叉分析将已经为城镇户口的人对现在享受的社会福利的满意度和还未转为城镇户口的人群满意度进行对比分析,发现问题 [8] 。
2)家庭方面
目前无子女的有96人,占比41.7%;1个子女的有98人,占比42.6%;2个子女的有31人,占比13.5%;3个及以上子女的有5人,占比2.2%。家中有老人的有165人,占比71.7%;无老人65人,占比28.3%。
由于以前实行的计划生育政策,所以独生子女的人群比例最高,而且可以看出目前无子女的人群排在第二,且有老人需要赡养的比例为71.7%,属于比例很高,所以推进转移人口市民化的建议制定应该对子女教育以及老人社会福利着重进行考虑。
3)社会方面
职业类型管理者有27人,占比11.7%;高级技工有22人,占比9.6%;普通职工有108人,占比47%;其他73人,占比31.7%。住房租房者有79人,占比34.3%;企业提供宿舍有47人,占比20.4%;经济适用房有19人,占比8.3%;自购商品房的有76人,占比33%;寄宿在亲戚朋友家的有9人,占比3.9%。未参加任何医疗保险有37人,占比16.1%;城镇职工医疗保险有89人,占比38.7%;城镇居民医疗保险16人,占比7%;新型农村合作医疗保险81人,占比35.2%;商业医疗保险7人,占比3%。未参加任何养老保险的有99人,占比43%;城镇职工养老保险91人,占比39.6%;城镇居民养老保险有9人,占比3.9%;新型农村社会养老保险有23人,占比10%;商业养老保险8人,占比3.5%。
由于转移人口年龄普遍偏小,并且未受到太多职业培训,所以在职业等级占比最高的是普通职工,当然这也是本文调查的重点对象。在住房情况中自购商品房的人群最多,其次就是租房,因为40岁以上的人口都可以自购房子,在年轻人中也有部分在家庭的帮助下购房,但是中国的房价问题还是急需处理的。在医疗保险和养老保险方面,大多数人都有医疗保险和养老保险,所以可以看出,中国医疗保险和养老保险覆盖面正在扩大,但是未参加任何保险的人占比也不小,因此,我国在医疗保险和养老保险方面还需再接再厉。对各种社会福利制度体系的满意情况如表3。
转移人口对社会福利体系满意度分值还是较低,尤其住房制度和失业保险制度方面,其和通货膨胀有关且成反比,所以难免会顾此失彼。愿意居住在城市的有188人,不愿意的有42人,分别占比81.7%、18.3%,可以看出大多数人都愿意居住在城镇,但大多数人还表示影响进城的困难因素按大到小的分别是“住房”、“就业不稳定”、“社会地位低”以及其他原因 [9] ,所以社会应该重视这些障碍因素,从其入手,积极引导转移人口市民化。
对性别、年龄、文化程度、子女个数、赡养老人情况、职业类型、住房情况、医保类型、养老保险类型、对福利体系满意情况与城镇化意愿做交叉分析。发现72.8%的男性愿意市民化,而女性愿意人数则更高,达到了92.4%,P值为0;23 - 30岁的人口转移意愿最高,82.6%的人都愿意,P值为0.06;而未婚与已婚的人口转移意愿基本持平,P值为0.829;文化程度中本科以及硕士以上学习的人群转移意愿较高,P值为0.006;对于月收入在2000 - 3500元之间的人群90%的人更倾向于转移,P值为0.024;对无子女或者有一个子女的个人的转移意愿比例分别达到了84.4%和81.6%,其他群体也达到了75%左右,P值为0.549;有无老人赡养的人群转移意愿比接近,均为81%,P值为1;除高级技工以外,其他岗位的人群转移意愿均达到了80%以上,P值为0.07;租房与购买了经济适用房和商品房的人群转移率最高,P值为0.131;参加城镇职工以及城镇居民医保者转移意愿率达到了81%以上,P值为0.056;对福利体系满意人群转移意愿率逐步提高,P值为0.003。
将置信区间设为90%,通过上一步可以初步认为性别、年龄、文化程度、月收入、子女情况、岗位类型、住房情况以及福利体系满意情况均对市民化有显著影响。本文接下来将进一步用实证分析对市民化意愿有显著影响的因素。
5. 实证分析
通过对调查数据进行了预处理,即将变量编码以后均定义为数值类型之后,运用SPSS17.0软件的二

Table 3. The satisfaction of the welfare system
表3. 社会福利满意度表
分类Logistic模型以转移人口的转移意愿概率为因变量,以转移人口的年龄、性别、文化程度、婚姻状况、个人收入水平、家庭子女与老人情况、职业类型、住房情况、社会保险情况、社会福利体系满意度几个方面为自变量指标进行实证分析。二分类逻辑回归函数一般形式如式子(1):
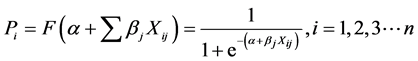 (1)
(1)
其中Pi是第i个受访者的转移意愿概率,bj表示第j个自变量的参数,Xij是自变量,表示第j个自变量对第i个受访者的影响,a为截距,利用式(1)以及表1中自变量的编码进行二分类回归,得到结果见表4和表5。
从表4和表5结果可以得到,模型检验卡方为37.635,P值为0,模型具有显著性,有统计意义。参数估计与检验可看出性别、婚姻状况、文化程度、福利体系满意情况P值均在0.1以内,所以这是显著影响因素,模型拟合度比较好,与预期影响方式符合。通过表5还可以看出影响方向,以上4个因素转移意愿均是正向影响方向,且女性较于男性更容易流动 [10] 。

Table 4. The assembly testing of the model coefficient
表4. 模型系数的综合检验

Table 5. The result of the two classification logistic regression model
表5. 二分类逻辑回归结果
6. 结论与建议
结合目前江西省转移人口的个人、家庭、社会三方面现状以及问卷分析结果,可以看出该结论符合英国的E.Ravenstien的七大转移理论 [11] ,已婚者更倾向于转移,为家人提供更好生活环境,文化程度越高,对福利体系满意度越好,也就越倾向于转移。故提升教育力度、制定好福利体系、政策制度对女性稍有偏向可以让农村家庭整体转移意愿更加强烈。
针对以上结果本文将对制度的改革合并为供给侧改革:对于转移人口市民化问题,其实是一个制度供求有不平衡状态向最优状态移动的过程。 [12] 户籍制度、福利体系制度、土地制度等一系列制度是影响市民化的重要因素,而将转移过程视作一场交易则是转移人口希望通过最小的费用赢得在城市居住的权利,而政府是供给者,所以可以从供给侧改革出发。通过降低转移户籍门栏,现在虽然2016年12月进行了新的户籍改革,统一登记为居民,但还是要进一步明确成为真正的城市居民需要哪些程序与条件,尽量削减不必要的手续。此外,对于转出农村的人口的土地可采用暂时保留使用权的方法,等五年之后若是土地未利用,则可以按比例有偿转让,这样可以缓解转移人口对土地的一时离不开的心理 [13] 。对于福利体系中的养老保险制度则是应该加强养老保险的宣传以及组织人员带领有条件的人员缴纳。对于外出就业的人员进行基本的培训,从而提高效率,并在产业结构中偏向服务业培训,加快第三产业发展。对于外出创业的人群,则应该在经济政策上给予制定优惠政策,提升信贷服务系统功能。