1. 引言
齿龈内阿米巴属于原生动物,主要寄生在人体口腔,原本被认为非致病性的共栖型阿米巴,然而流行病学调查显示,牙周病患者E.g.的感染率显著高于健康人群 [1] 。从进化医学角度考察寄生现象,是当前医学研究的新趋势。在现代口腔清洁技术出现以前,齿龈内阿米巴已经在人类口腔中长期存在,以食物残渣与细菌为食,与口腔细菌形成了一个微型生态圈 [2] 。从某种意义上说,可以把齿龈内阿米巴与人体之间看作共生关系,齿龈内阿米巴对于保持口腔健康事实上应该起到一定的促进作用。但这个生态圈存在微妙的平衡,齿龈内阿米巴在吞食口腔细菌的同时,对齿龈也有一定的攻击作用,一旦人体免疫力低下,就会引发齿龈内阿米巴相关的疾病。但齿龈内阿米巴在攻击齿龈的过程中,也会产生肿瘤抑制因子,可能对于人体抑制肿瘤产生具有一定的作用。牙龈癌发生率较低,可能与此不无关系。进一步挖掘齿龈内阿米巴与生物体共生过程中的行为,是值得研究的课题。
本文探讨齿龈阿米巴在小鼠腹腔内的吞噬能力与致病性,对于认识齿龈内阿米巴的寄生价值,具有一定的理论意义。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 菌种培养
菌种取自牙周病患者牙周袋内容物。
采用改良Locke-egg-serum (LES)培养基培养,配方如下:3个全蛋加2个蛋黄,加入琼脂1 g,Ringer液75 ml,蒸馏水50 ml,用KH2PO4调pH为6.4~6.7,80℃加热1小时 [3] 。改良的LES培养基,固体成分主要是鸡蛋,更易制备且虫体不悬浮于培养基中,有利于虫体收集。
齿龈阿米巴接种后培养3天,吸吸取管底培养物过滤,无菌生理盐水离心洗涤3次,调节齿龈阿米巴滋养体数,等量加入各管,每个样本各有2管。吸取10 μl培养物显微计数,计算各管虫体均数。然后置36℃连续培养,经不同时间取样计数 [4] 。以培养90 h为繁殖高峰,阿米巴数量达到1856个/μl。
2.2. 鸡红细胞悬液
取鸡静脉血,加入等量微孔过滤的Alsever’s液:葡萄糖2.46 g,柠檬酸钠0.96 g和氯化钠0.504 g,溶解在120 ml双蒸馏水中,调节pH至6.1,4℃贮存,加入肝素)。实验时,红细胞悬液2500 rpm离心5 min,洗涤三次,调节红细胞数至2 × 108/ml备用。
2.3. 动物分组
实验小鼠,昆明系,体重20~24 g,雄性,安徽科技学院实验动物中心提供。随机选择40只体重20~24 g的健康小鼠,分为4组,每组10只。
2.4. 吞噬功能测定 [5]
处理前禁食12小时,每只小鼠腹腔注射阿米巴液1.0 ml,低浓度组为1000个/μl,中浓度组为2000个/μl,高浓度组为3000个/μl,对照组注射等量生理盐水。两小时后,每只小鼠腹腔注射1%鸡红细胞悬液0.5 ml,轻轻揉腹部使外源细胞分散。0.5小时后颈椎脱臼处死小鼠,无菌打开腹腔,取腹腔液涂片,瑞氏染色,镜检,每片计数100个阿米巴细胞,计算吞噬百分率和吞噬指数。
吞噬百分率 = (吞噬鸡红细胞数的阿米巴/阿米巴总数) × 100%。
吞噬指数 = (被吞噬的鸡红细胞数/阿米巴总数) × 100%。
2.5. 数据处理
SPSS11.0统计软件进行t检验,数据以均数±标准差(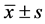 )表示。
)表示。
3. 结果
见表1。结果表明,随着阿米巴浓度上升,吞噬百分率和吞噬指数都同步上升,但与空白组相比,低浓度组的吞噬指数存在一定的降低现象。不同级别之间,差异达到显著水平。
鸡血细胞表面粘附着许多阿米巴,鸡血细胞明显减少,可以观察到阿米巴正在吞噬鸡血细胞。随着鸡血细胞的减少,阿米巴的数量不断增加,阿米巴呈现聚集的趋势。由于鸡血细胞大量减少。图1可以清楚地看出这种趋势(放大倍数:10 × 40)。

Table 1. The gum Amiba phagocytic function within the abdominal cavity in mice ()
表1. 齿龈阿米巴在小鼠腹腔内的吞噬功能( )
)
与空白组比较:*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01。

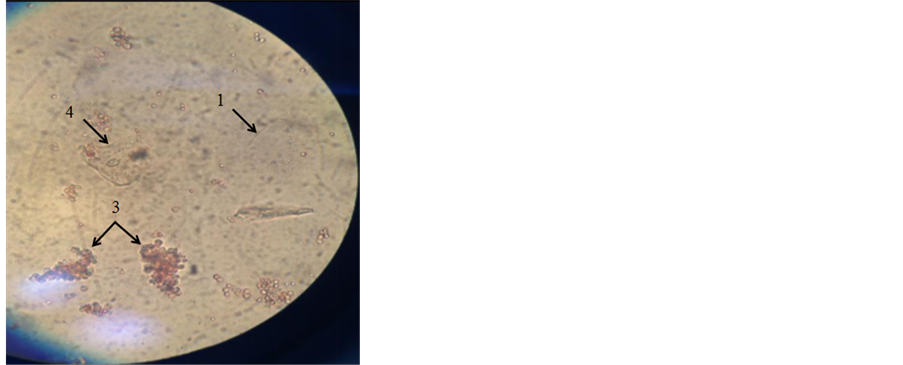 图注:1. 未吞噬鸡血红细胞的齿龈阿米巴。2. 齿龈阿米巴吞噬鸡血细胞的初级阶段。3. 吞噬了大量的鸡血细胞的齿龈阿米巴。4. 鸡血红细胞已被齿龈阿米巴逐渐消化。
图注:1. 未吞噬鸡血红细胞的齿龈阿米巴。2. 齿龈阿米巴吞噬鸡血细胞的初级阶段。3. 吞噬了大量的鸡血细胞的齿龈阿米巴。4. 鸡血红细胞已被齿龈阿米巴逐渐消化。
Figure 1. Entamoeba gingivalis phagocytosis of chicken red blood cells
图1. 齿龈阿米巴吞噬鸡血红细胞的情况
4. 讨论
自从Gannon等 [6] 成功在体外培养E.g.以来,对齿龈阿米巴的研究也得到了进一步提高。齿龈内阿米巴伪足内外质分明,活动迅速,形变能力发达,常呈现出球状、舌状及其他很不规则的形状。齿龈内阿米巴在小鼠腹腔内的速度各不相同,经历相同培养时间的阿米巴在视野中往往呈现出不同的吞噬状态。阿米巴的生存条件不是很高,它可以在低温度,偏碱等条件下生存。
导致齿龈内阿米巴处于不同吞噬状态的情况可能有两种:1、每个齿龈内阿米巴周围的鸡血红细胞浓度或酵母细胞浓度不同所导致;2、齿龈内阿米巴自身在培养基上的生长成都不同。在体表有损伤的情况下,E.g.可诱发自由基大量生成,引起病理性脂质过氧化反应,生成有细胞毒性的脂质自由基和MDA等,加速生物膜的破坏,促使细胞崩溃 [7] 。
溶组织内阿米巴具有某些表膜特性,拥有吞噬不同物质的能力 [8] 。早在100年前Lesh便证实在阿米巴痢疾患者粪便中分离的阿米巴滋养体含有红细胞 [9] ,认为其致病株可摄取和吞噬红细胞,并被公认为致病性虫株的最重要的鉴别特征。致病性虫株可在短时间内吞噬大量红细胞,吞噬过程远比非致病性虫株迅速而有效 [10] ,而较高的红细胞吞噬率又与其表面特性有关。
5. 结论
本研究表明,齿龈内阿米巴在小鼠腹腔中表现出高度吞噬红细胞作用,并出现了溶胶原作用,对小鼠腹腔有不同程度的攻击作用。
基金项目
本文受到安徽科技学院大学生创新创业训练计划项目资助,项目编号:108792015047。