1. 引言
植物组织培养技术是一门实用性非常强的现代生物技术,被广泛地应用于各个领域,在科研与生产上都具有广泛的应用价值 [1] [2] 。中国热带农业科学院橡胶研究所科技人员以此技术为基础,通过近30年的努力,成功建立起高效的工厂化繁育橡胶树自根幼态无性系培育体系,从而使橡胶树体培苗成为继实生苗和芽接苗后的新一代种植材料 [3] 。橡胶树体胚苗比实生苗的培育所需时间短,从2年缩短到8个月。从体培苗成长来的橡胶树抗风能力强,产量提高10%~30%,生长速度快 10%~20%,定植后5~6年即可割胶,而芽接苗需要种植7~8年才能割胶 [4] 。然而由于海南高温高湿的气候环境,真菌污染成为橡胶自根无性系体胚苗的生产成本偏高的因素之一 [5] 。通常在生产中污染材料处理所采用的方法有a) 污染的材料被挑拣出来,集中用各种农药处理后,再进行移栽等处理,但成活率降低了很多;b) 污染的材料被挑拣出来,高温灭菌后处理掉。如果能够了解污染源种类,做到有针对性地在培养基中添加抑菌剂或生防菌,不但能够降低污染率、提高成活率,而且简化操作流程,降低生产成本。
苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾具有低廉的价格和广谱的抑菌效果而成为食品、药品、化妆品的首选防腐剂 [6] 。据报道它们对霉菌、细菌等都有抑菌作用 [7] 。相比而言,山梨酸(钾)更能有效地抑制霉菌,其防腐效果是苯甲酸钠的5~10倍,而且苯甲酸钠的毒副作用较大,但是山梨酸钾的价格是苯甲酸钠的2~3倍,考虑到生产成本,胡春红等试用筛选这两种防腐剂的抑菌配比及抑菌浓度 [8] 。王丹和刘霞将山梨酸钾作为开放式组织培养红豆杉的抑菌剂,确定其最佳抑菌浓度为0.02 g/L [7] 。为了更有的放矢地解决橡胶组培苗生长过程中的污染问题,本文作者收集污染平板和污染的试管苗,根据表型及外观分类,将最常见污染源进行分离培养和ITS序列鉴定,并通过试验分析了苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾对这些菌的抑菌效果。
木霉菌(Trichoderma spp.)是一类重要的多功能益生真菌 [9] [10] 。它们不仅能通过多种机制来控制病原菌的侵染和病害的发生,而且还具有促进作物生长、提高作物抗生物和非生物胁迫的能力 [11] [12] [13] [14] ,是一种公认的环境友好型真菌 。根据我们前期对哈茨木霉菌株13-3-2的研究,发现木霉菌可有效抑制杂菌,可显著降低污染苗的死亡率,因此在本文研究中我们重点考察了哈茨木霉菌株13-3-2对黑曲霉的抑制作用。该研究结果将用于有效防除橡胶树组培生产中的杂菌污染,提升组织培养效率。
2. 试验材料和方法
2.1. 试验材料
苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾(国药集团化学试剂有限公司),化学纯。黑曲霉是我们从污染的平板上分离并进行形态和测序鉴定。哈茨木霉13-3-2 (保藏号为CGMCC No. 13163)和哈茨木霉5P-3 (保藏号为CGMCC No. 13164),本实验室鉴定并保藏于中国菌种保藏中心。污染平板及污染的热研7-33-97自根无性系的组培试管苗来自于中国热带农业科学院试验场九队,国家天然橡胶种植圃内组培苗大量生产工作室。
2.2. 试验方法
2.2.1. 真菌基因组DNA提取方法及ITS序列扩增
用孟加拉红培养基分离培养各个污染菌。用CTAB方法提取污染真菌的基因组DNA。用通用引物ITS5 (5’-GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG-3’)和ITS4 (5’-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3’)进行PCR扩增污染真菌的18S rDNA-ITS序列,PCR反应体系是25 µL:Taq酶0.20 µL、10 xbuffer 2.5 µL、dNTP 0.2 µL、10 µL的primer各0.3 µL,ddH2O 21.5 µL,DNA模板25 ng。扩增片段克隆后送由上海生物技术有限公司进行测序。
2.2.2. 菌液制备
取经28˚C培养4天的黑曲霉,加5 ml无菌水洗下霉菌孢子,依次10倍稀释为10−3, 使孢子数约为103个/ml。
2.2.3. 苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾抑菌培养基的制备
在配置1/2 PDA + 5 g酵母粉固体培养基时,分别加入苯甲酸钠或山梨酸钾,使其质量浓度分别为(3%、2%、1.0%、0.5%和0),高压蒸汽灭菌(121˚C,20分钟)备用。
2.2.4. 苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾不同配比培养基的配置方法
分别精确称取苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾各2.5 g混合即复合配伍为1:1,称取苯甲酸钠2.0 g、山梨酸钾3.0 g混合,即复合配伍为2:3;称取苯甲酸钠3.0 g、山梨酸钾2.0 g混合,即复合配伍为3:2。将3种配比的混合物加入培养基中,制备质量浓度为3.0、2.0、1.0、0.5、0 g/L的培养基用于分析它们对黑曲霉、炭疽菌等的抑制或杀菌效果。
2.2.5. 苯甲酸钠的抑菌作用
苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾对真菌抑菌效果的评价方法有两种:一是测量真菌菌丝生长速度受抑制率来判断;一是取0.1 ml稀释好的浓度为103个/ml分生孢子稀释液加入抑菌培养基平皿中,涂板,于28˚C培养,第2~3天观察和统计孢子萌发生长情况。
2.2.6. 哈茨木霉13-3-2孢子液的准备
哈茨木霉13-3-2在1/2玉米粉(CMA, corn meal agar) + PDA培养基上生长7天,将分生孢子用灭菌ddH2O洗下来,并用PDB + 1/2MS无机盐溶液稀释为浓度107个/ml备用。
2.2.7. 污染的组培橡胶苗接种方法
为了考察哈茨木霉13-3-2是否能够挽救被污染的橡胶组培苗,分别于2016年12月和2017年2月接种两次。我们选用生长势相对一致的被污染的热研7-33-97橡胶组培苗600株进行了接种试验。处理组每一个试管内接种哈茨木霉13-3-2分生孢子数量为107个/ml的营养液1 ml (用PDB + 1/2MS无机盐溶液配制),对照组的每一个试管内加入等量不添加哈茨木霉13-3-2分生孢子的PDB + 1/2MS无机盐溶液。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 分离及鉴定橡胶树组培的污染源
根据污染源出现的频率和污染源在培养基上的表型,挑取了6个进行分离接种,命名为R1-R6,又根据它们在孟加拉红培养基上的表型合并为四个,分别为R1,R3,R5和R6。它们的ITS扩增片段大小约分别为590 bp、607 bp、624 bp和644 bp,利用NCBI blast序列比较,发现它们与同源基因的rDNA-ITS区序列相似性为98%~100%。下载同源基因的fasta序列,利用软件ClustaX (1.81版本)进行序列比对分析,采用Neighbor-Joining方法进行聚类分析,进行1000次bootstrap统计学检验(图1),得到结果。R5与KY354579.1 Aspergillus niger黑曲霉归为一类,R3与KX961206.1 Penicillium青霉菌归为一类;R6与KT336515聚一起,属于哈茨木霉菌;R1与FJ878627.1、KJ082097.1、KJ527011.1聚为一组,属于Aspergillus versicolor杂色曲霉(又名采色曲霉和变色曲霉)。
KY354579.1 Aspergillusniger黑曲霉;KX961206.1 Penicillium青霉菌;FJ878627.1 Aspergillus versicolor采色曲霉,杂色曲霉,变色曲霉;KT336515 Trichoderma harzianum isolate
其中黑曲霉R5污染所占比例在50%以上是本研究的重点对象。
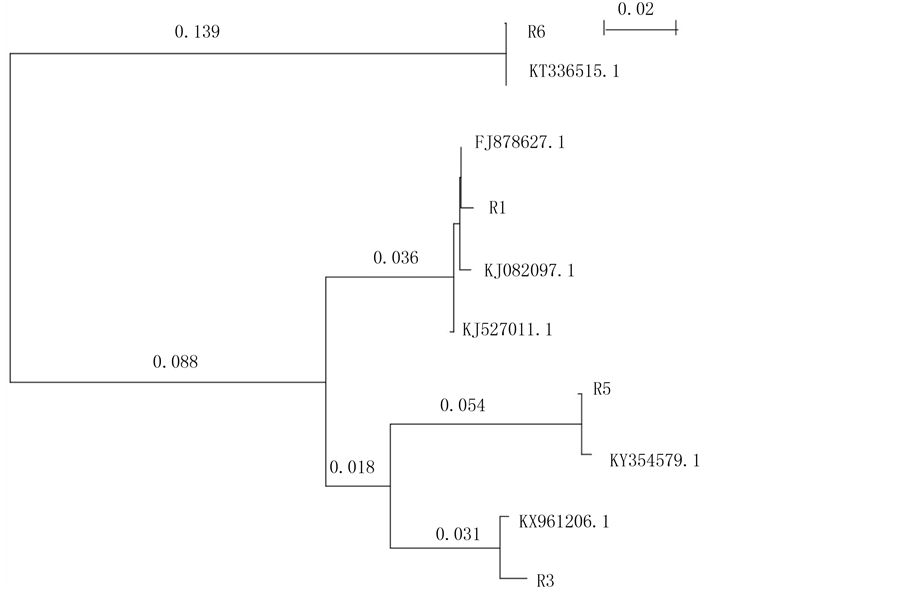
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of ITS sequences in several contaminated fungi and some homologous species
图1. 污染真菌ITS序列的进化分析
3.2. 黑曲霉分生孢子大小及pH适应特性
利用PDA固体培养基,用稀盐酸或氢氧化钾调节培养基的pH分别为3、5、7、9、11和12,接种黑曲霉菌块(菌块带有分生孢子),第三天观察观察黑曲霉的生长情况。结果表明在pH = 7~9的培养基上,黑曲霉生长最好,在pH < 5的培养基上,黑曲霉孢子的萌发率低于50%,在pH = 11~12培养基上,黑曲霉孢子也能生长(图2),可见黑曲霉对pH的适应性广,适应能力强。黑曲霉分生孢子大小在放大1000倍下,(Leica DMLB,油镜下拍摄)平均长度为在1~1.35微米。
3.3. 苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾对黑曲霉、杂色曲霉、青霉等生长的抑制作用
培养基中添加不同含量的苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾的试验结果表明1.0%的苯甲酸钠可以完全抑制黑曲霉菌丝的生长(图3(B));1.0%的苯甲酸钠可明显抑制黑曲霉分生孢子的萌发,2.0%~3.0%可以完全抑制其萌发(图3(C),表1)。同样质量浓度,且配比为1:1的苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾对黑曲霉生长的抑制效果不如单一的苯甲酸钠(图3(D),其它配比2:3,3:2的效果更差,略)。3.0%苯甲酸钠才能完全抑制青霉的菌丝生长和孢子的生长(图3(E))。哈茨木霉5P-3和13-3-2可以显著抑制黑曲霉的快速生长(图3(F)),在对峙生长中,黑曲霉及其分生孢子的生长被明显抑制,哈茨木霉5P-3的抑制率达75.0%,哈茨木霉13-3-2的抑制率为85.7% (图3(F))。
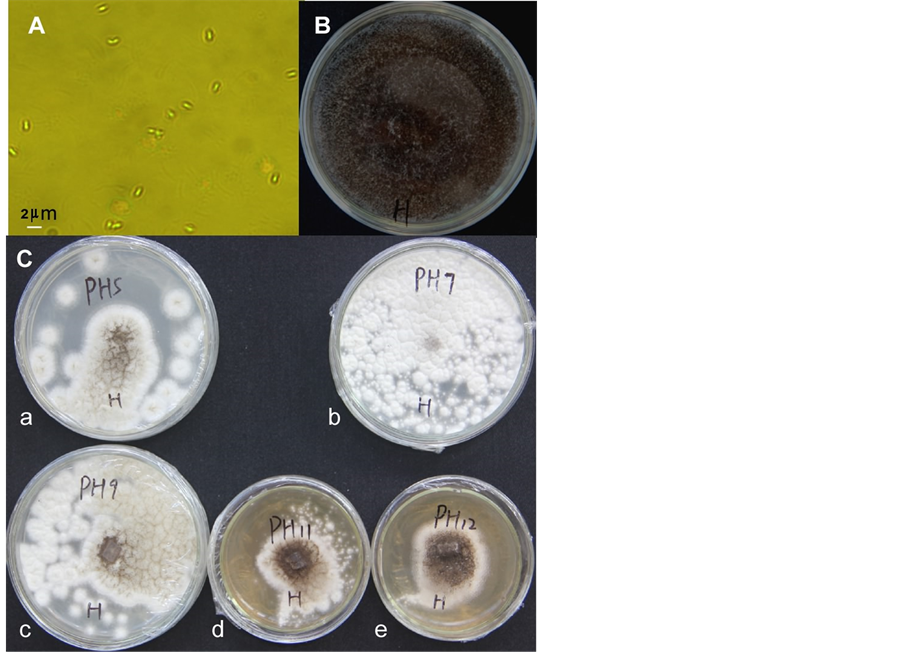 A、黑曲霉的分生孢子大小,放大1000倍,bar为2微米;B、黑曲霉产生大量的分生孢子;C、黑曲霉在不同pH平板上的生长情况(a~e,pH = 5、7、9、11和12)。
A、黑曲霉的分生孢子大小,放大1000倍,bar为2微米;B、黑曲霉产生大量的分生孢子;C、黑曲霉在不同pH平板上的生长情况(a~e,pH = 5、7、9、11和12)。
Figure 2. Spores of Aspergillus niger and its growth profiles on different pH media
图2. 黑曲霉的分生孢子及其在不同pH培养基上生长情况
表1. 苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾对黑曲霉、杂色曲霉和青霉生长的影响
注:表中数据为3次独立试验,数值结果为培养3天的平均值
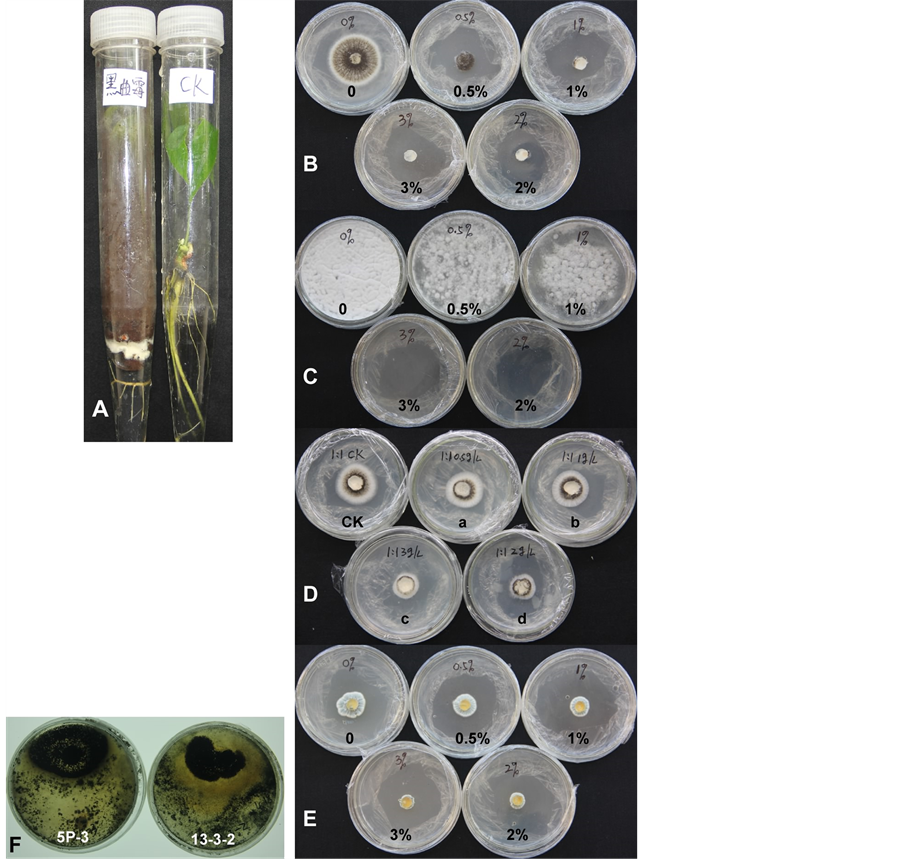 A、黑曲霉对橡胶苗的致死效果;B、不同浓度苯甲酸钠对黑曲霉菌丝及分生孢子生长的影响;C、不同浓度苯甲酸钠对黑曲霉分生孢子萌发的影响;D、不同质量百分比下配比为1:1的苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾对对黑曲霉菌丝及分生孢子生长,其中ck为0,a~d为质量百分比为0.05%~0.30%,配比为1:1苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾培养基;E、不同浓度苯甲酸钠对杂色曲霉菌丝及分生孢子生长的影响;F、木霉菌13-3-2和5P-3对黑曲霉生长的影响(8天对峙生长效果)。
A、黑曲霉对橡胶苗的致死效果;B、不同浓度苯甲酸钠对黑曲霉菌丝及分生孢子生长的影响;C、不同浓度苯甲酸钠对黑曲霉分生孢子萌发的影响;D、不同质量百分比下配比为1:1的苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾对对黑曲霉菌丝及分生孢子生长,其中ck为0,a~d为质量百分比为0.05%~0.30%,配比为1:1苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾培养基;E、不同浓度苯甲酸钠对杂色曲霉菌丝及分生孢子生长的影响;F、木霉菌13-3-2和5P-3对黑曲霉生长的影响(8天对峙生长效果)。
Figure 3. Growth of Aspergillus niger inhibited by sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate and Trichoderma harzianum
图3. 苯甲酸钠、山梨酸钾、哈茨木霉等对黑曲霉生长的影响

Table 2. Contaminated Reyan7-33-97 tissue cultured seedlings were dramatically saved by treatment with Trichoderma harzianum 13-3-2
表2. 污染的热研7-33-97组培苗用哈茨木霉13-3-2处理后成活率显著提高
注:表中数据为2次独立试验结果
3.4. 哈茨木霉13-3-2对热研7-33-97污染苗成活率的影响
选用污染的热研7-33-97组培试管苗于同一时间按照方法2.2.7所述,接种营养液或哈茨木霉菌孢子液,10天后移栽温室沙床,移栽10天后统计结果如表2所示。没有处理的污染苗死亡率达到47.0%,而处理后的达到95.9%,污染苗的成活率提高约43.0% (表2)。
4. 结论和讨论
通过单菌分离及分子鉴定结果表明:黑曲霉和杂色曲霉是热带地区橡胶树组织培养过程中最常见和最主要的污染源,青霉和哈茨木霉次之(图1)。研究发现黑曲霉最适温度是33˚C~37˚C (在45˚C下处理6小时的培养基上还能生长),最低相对湿度为88%,适应在高温、高湿环境下生长,而且生成黑曲霉的分生孢子小1.0~1.35 μm (图2),易扩散,生命力强,这些特性可能是该菌成为橡胶树组培中最主要的污染源的原因。由于降低成本和简化操作是植物组织培养科研工作者和大量商业繁育苗木时所追求的共同目标 [15] [16] ,为减少组培过程中的微生物污染,很多人已经做了不少的探索,比在培养基中添加抗生素 [17] 、苯甲酸钠和山梨酸钾以及利用植物益生菌 [13] 等。崔刚等探索并建立一种植物开放式组织培养模式,通过应用抑生素将污染率控制在10%以下的可接受范围内,从而使植物组织培养可以在自然、开放的有菌环境中进行操作,从根本上简化组培环节,降低组培成本 [18] 。在本文研究中,我们发现接种哈茨木霉菌株13-3-2对黑曲霉、杂色曲霉、青霉菌的孢子萌发和菌丝生长都有一定的抑制作用(图3)。此外,发现2%~3%的苯甲酸钠可以有效抑制黑曲霉。这些结果,有助于我们在明确污染源的情况下,通过有针对性地在培养基中添加适宜的抑菌剂和利用拮抗木霉,达到降低橡胶组培污染率,提高成活率,缩短培育时间,从而降低生产成本的目的 。至于在组织培养不同阶段的培养基中添加山梨酸钾和苯甲酸钠是否会影响橡胶胚状体的生长速度及苗子质量,还需要进一步研究。
基金项目
该研究得到海南省自然科学基金项目(20153213)的支持,国家橡胶树种质资源圃提供材料。
NOTES
*通讯作者。