1. 引言
旋花科(Convolvulaceae)菟丝子属(Cuscuta)植物具有全寄生特性,无根与叶的组织器官,以茎上特化的吸器刺入寄主中吸取光合产物。其寄主范围广泛,豆科、菊科、旋花科等植物均可作为菟丝子的寄主 [1] 。菟丝子生长范围也较广,在我国许多省市均有分布,以北方地区为主。菟丝子入药历史悠久,早在《神农本草》中就有记载,是常见的一味重要中药材。根据中国药典2015版记载,菟丝子为旋花科植物南方菟丝子(Cuscuta australis R. Br.)或菟丝子(Cuscuta chinensis Lam.)的干燥成熟种子,呈类球形,直径1~2 mm。表面灰棕色至棕褐色,粗糙,种脐线形或扁圆形(图1)。质坚实,不易以指甲压碎。具有补益肝肾,固精缩尿,安胎,明目,止泻等重要功效,外用亦可以消风祛斑。然而目前菟丝子用药缺乏系统的理论指导体系,究其原因主要是菟丝子的药用活性成分尚未充分解析,进而导致其药理机制研究受限,难以深入开展,这也是诸多中药研发中面临的共同难题。
2. 菟丝子的药用活性成分
中药菟丝子含有多种化学成分,包括黄酮类、酚酸类、多糖类、木质素类、以及甾体类、化合物,此外还有生物碱、蒽醌、香豆素类、皂苷类、鞣质、卵磷脂和脑磷脂等成分 [3] 。研究人员借助多种物化分析技术,使菟丝子中越来越多的化学物质得以鉴定。林倩等通过色谱法分离纯化出菟丝子中的多种化学成分,分析了其理化性质与相应波谱数据,鉴定出两种新的黄酮类物质即紫云英苷-6″-O-没食子酸酯、槲皮素-3-O-(6″-没食子酰基)-β-D-葡萄糖苷 [4] 。He等通过HPLC-DAD-MS和HPLC-UV的技术手段对两种菟丝子中的化学成分进行了定量与分析 [5] ,鉴定出分属黄酮类、木质素类和奎宁酸衍生物等36种化合物。目前多数研究认为菟丝子的药用活性成分主要为黄酮类物质,例如金丝桃苷、紫云英苷、槲皮素、山奈酚等(图2)。中国药典2015版中也明确规定干燥品菟丝子中金丝桃苷的含量不得少于0.10%。
根据图2所示化学结构,黄酮类化合物中碳基与芳香环形成较强的两个共轭体系,分别对应紫外吸收光谱的两个主要吸收带(溶剂乙醇):其中一个出现在240~280 nm范围,为A环的苯甲酰结构的吸收峰区;另一个出现在300~380 nm范围,为B环肉桂酰的吸收峰区 [6] 。这个特征也可作为黄酮类物质粗
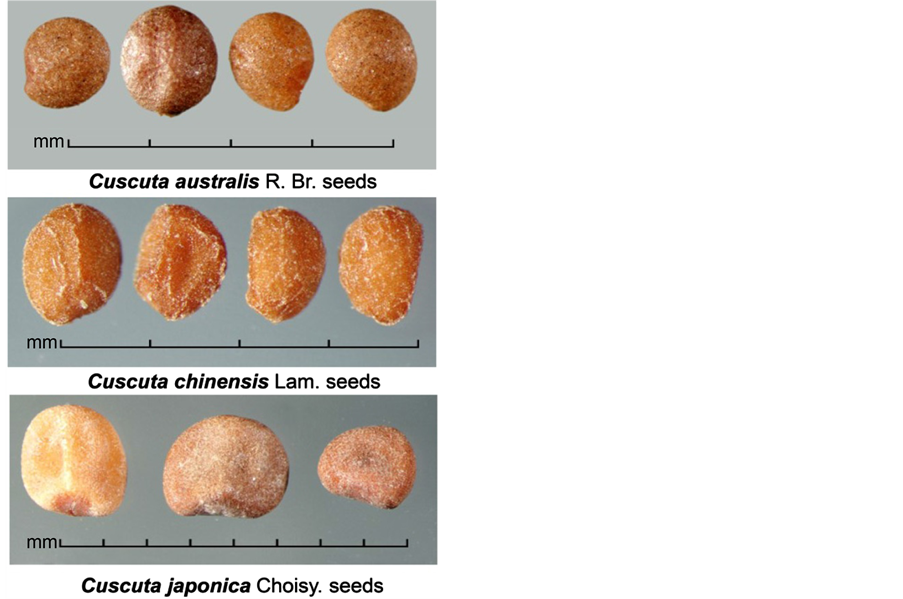

Figure 1. Seed morphology of several common dodders in China. Seeds are Cuscuta australis R. Br., Cuscuta chinensis, Lam., and Cuscuta japonica Choisy (from top to bottom), adapted from Gilligan et al. [2]
图1. 国内常见几种菟丝子的种子形态,依上而下分别为南方菟丝子(Cuscuta australis R. Br.)、菟丝子(Cuscuta chinensis Lam.)、和金灯藤(或称日本菟丝子、大菟丝子Cuscuta japonica Choisy)、修改自Gilligan等 [2]
提物的初步鉴别方法。
多糖也是菟丝子中的重要化学成分,然而有关多糖组分与结构分析的研究还较少。王展等通过纯化菟丝子水提物和碱提物,先后得到酸性杂多糖H2、H3、CHC-1 [7] [8] [9] ,中性杂多糖H6、H8 [10] ,结构分析发现它们多由阿拉伯糖、鼠李糖、木糖和半乳糖等组成,并具有免疫增强与抗氧化活性。
不同来源的菟丝子药用成分存在差异。以黄酮类成分为例,南方菟丝子(Cuscuta australis R. Br.)与菟丝子(Cuscuta chinensis Lam.)相比,含有更多黄酮类化合物,并且山奈酚和紫云英苷的含量明显更高 [5] 。除此以外,寄主差异也会对菟丝子药用成分造成影响。林慧彬发现菟丝子因寄主植物不同,黄酮类含量差异明显,例如南方菟丝子因寄主差异,总黄酮含量可在0.84% (寄主:葎草,Humulus scandens (Lour.) Merr.)-1.64% (寄主:大豆,Glycine max (L). Merr)范围内浮动 [1] 。
菟丝子中影响治疗效果的化合物种类仍不明确,制约了菟丝子药用潜力的进一步开发。随着基因组学、转录组学和代谢组学的不断发展,将该类技术应用在植物学、药理学研究中,或可找到突破口解决菟丝子以及其他类似中草药开发中面临的共同难题。
3. 菟丝子的品质鉴定与质量控制
中药菟丝子的传统鉴定法以形态学为主。检疫鉴定中常对菟丝子属种子的大小、花纹、晕轮和种脐
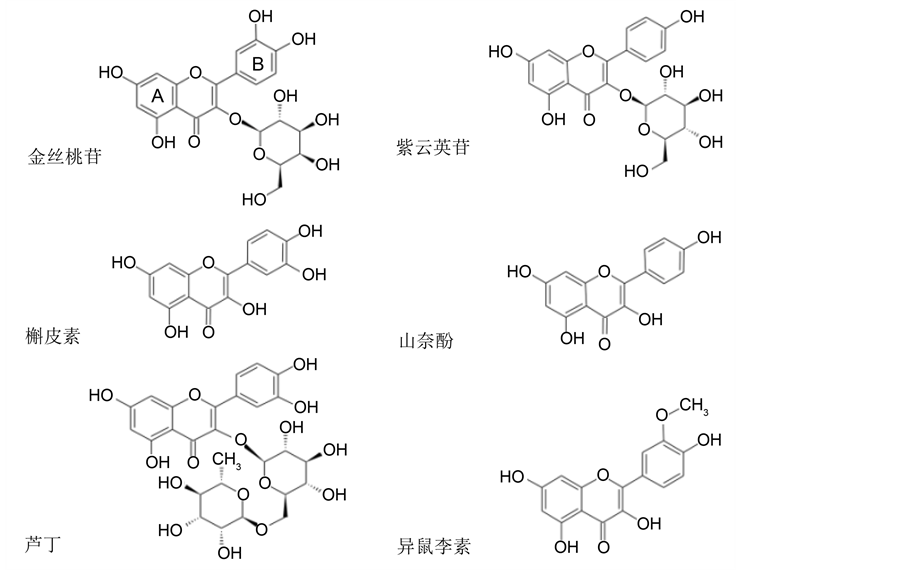
Figure 2. Several important flavonoids from Dodders
图2. 菟丝子中常见的几种黄酮类物质
等方面做系统比较 [11] ,例如南方菟丝子与金灯藤在种子大小上差异明显,较易检出。通过扫描电镜可观察到更多种子的细微特征 [12] 。但因菟丝子属植物种类众多,种间存在较多相似特征,而药效差异大,仅以形态鉴定具有很大的局限性。
借助于先进的物理化学分析技术,中药鉴定也发展出了多种检测方法。其中,指纹图谱法是目前国际公认的中草药鉴定与质控技术手段。中药指纹图谱的概念是依照DNA指纹图谱定义衍生而来,指利用特定分离分析技术采集数据信息,绘制图谱用以反映中药及其制剂的整体化学特征。指纹图谱法可定性或定量分析药材特性,并且不受其中未知化学成分信息的制约。按照建立图谱所用的技术手段,常见的指纹图谱法可分为紫外光谱法(ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, UV-Vis)、红外光谱法(infrared radiation IR)、薄层色谱法(thin layer chromatography, TLC)、气相色谱法(gas chromatography, GC)、高效液相色谱法(high performance liquid chromatography, HPLC)、高速逆流色谱法(high-speed countercurrent chromatography, HSCCC)、毛细管电泳法(capillary electrophoresis, CE)、质谱法((mass spectrometry, MS)、X射线衍射法(X-ray diffraction, XRD)、核磁共振法(nuclear magnetic resonance, NMR)等。
目前菟丝子指纹图谱研究以高效液相色谱HPLC法居多。肖岚等以绿原酸、金丝桃苷、槲皮素、山奈酚、异鼠李素标准品作为对照,针对五种不同炮制方法的菟丝子建立了HPLC指纹图谱,标示出20个共有峰,并发现菟丝子及其炮制品的化学成分含量差异较大,可能是造成其药效不同的重要原因 [13] 。高新开等以金丝桃苷、异槲皮苷、紫云英苷、山奈酚为标准品,针对不同供货单位提供的10个批次的菟丝子样品建立了黄酮类与酚酸类成分的HPLC指纹图谱,找出13个共有峰,相似度0.949~0.946 [14] 。谭喜莹等以香豆酸、绿原酸、槲皮素、山奈酚为标准品,对来自全国15个不同产地的菟丝子建立HPLC指纹图谱,找出18个特征峰,多数特征峰相似度高,但少数如槲皮素的特征峰则差异较大,为不同产地来源的菟丝子质量控制与分级提供了依据。该法可区分菟丝子(Cuscuta chinensis Lam.)、南方菟丝子(Cuscuta australis R. Br.)和金灯藤(Cuscuta japonica Choisy.) [15] 。孟蔚等以金丝桃苷、槲皮素、山奈酚、异鼠李素为标准品,对来自11个不同寄主的菟丝子检出10个共有峰,相似度大多大于0.9。该研究发现不同寄主的主要成分组成相近,但含量差异大,尤其是槲皮素的色谱峰差异显著。经过相似度分析与聚类分析可部分区分不同寄主来源的菟丝子 [16] 。此外,孙蓉梅等通过近红外光谱法对菟丝子药材整体扫描鉴定,可区分菟丝子、南方菟丝子和金灯藤,鉴别率达93% [17] 。
菟丝子指纹图谱的相关研究逐渐增多,但仍在起步阶段,存在许多问题。由于菟丝子中药用活性成分鉴定不完全,标准品难以统一;测定中采用的仪器设备、试剂等也需要统一,便于数据对比,实现标准化、稳定的图谱构建流程;菟丝子样品受品种、产地、种植环境、采收期、炮制加工方法等因素影响,绘制的指纹图谱存在较大差异,需建立特定因素相关的数据库,完善指纹图谱的技术体系;建立图谱峰与药效的相关性,以更好的控制中药菟丝子的质量。
4. 菟丝子化学成分的提取纯化与合成
菟丝子黄酮类化合物的提纯研究较多,其提取方法主要有浸提法、回流法、索氏法、闪式法、微波辅助法、超声辅助法和半仿生提取法等。彭金年等比较回流法、索氏法、微波辅助法、闪氏法的优劣,发现微波辅助法提取的总黄酮含量较高,且省时高效,更适合菟丝子总黄酮的提取 [18] 。不同提取方法除了可造成黄酮类化合物含量差异之外,还能同时影响黄酮类化合物结合物质如金属离子锌、铜的含量 [19] 。这也可能是造成药效差异的因素之一。
菟丝子多糖具有抗氧化等作用。其提取方法主要有热水浸提法、酶法、微波法、超声法等 [18] [20] 。由于菟丝子多糖常与黄酮类物质共同行使抗氧化功能,戴永强等因此也尝试利用超声波方法同时提取总黄酮与多糖,为菟丝子的综合利用、批量生产黄酮与多糖提取物提供了参考 [21] 。
由于中药原材料中药用成分含量普遍较低,或存在提取分离难度大,溶解度差、毒副作用大等问题,部分化学成分可采用化学人工合成或生物转化的方式解决。如菟丝子中黄酮类成分槲皮素,通过化学合成法得到槲皮素磺酸酯类衍生物可改善槲皮素的溶解性,并进一步提高其生理活性 [22] 。而采用更温和的生物转化法可避免化学合成中出现的氧化、环化、聚合等副反应,例如,黄酮类化合物葛根素可被嗜热脂肪芽孢杆菌(Bacillus stearothermophilus)中的麦芽糖淀粉酶转化得到两种主要糖基化产物,分别为α-D-葡萄糖基-(1→6)-葛根素和α-D-麦芽糖基-(1→6)-葛根素,溶解度分别是葛根素的14倍和168倍 [23] 。
5. 菟丝子药理学研究
5.1. 调节与保护生殖系统
传统中医常用菟丝子治疗脾肾虚泻、胎动不安、目昏耳鸣、腰膝酸软、白癜风等症状。近年来,药理学研究也从细胞学和分子生物学层面找到菟丝子作用的基础,发现其对动物生殖系统具有调节与保护的功效。
以菟丝子水提物定量喂食卵巢过度刺激综合症(OHSS, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome)型大鼠,发现其可降低OHSS型大鼠在血清和卵巢中过度升高的白介素IL-1、IL-6水平,回复过低的IL-10至正常水平。除此以外,OHSS型大鼠增重的卵巢质量也有所减轻。说明菟丝子水提物可通过调节细胞因子的分泌,有效改善OHSS病症 [24] 。
雷公藤多苷会对雄性幼鼠造成生殖损伤,造成精管腔内上皮变薄,细胞层次紊乱,精原细胞、精母细胞与精子数量减少等症状 [25] 。在此过程中,表皮生长因子(epidermal growth factor, EGF)的mRNA与蛋白水平明显降低(与空白组差异P < 0.05),细胞凋亡相关蛋白BcL-2表达明显减少(与空白组差异P < 0.05)而Bax显著增高(与空白组差异P < 0.05)。菟丝子总黄酮则可以调节这两类分子的表达水平,干预雷公藤多苷的作用通路,并且使睾丸组织形态部分修复,用药12周后与空白组相比无显著性差异(P > 0.05),达到保护幼鼠生殖系统的效果 [25] [26] [27] 。
研究人员还发现了菟丝子安胎功效的作用基础。刘华等 [28] 发现菟丝子总黄酮可提高溴隐亭致流产模型SD大鼠的妊娠率,降低流产率,还可促进其胎盘绒毛、毛细血管内皮发育,改善蜕膜及腺体分布。在考察了菟丝子总黄酮对细胞凋亡因子CD95分子及其配体(Fas/FasL)、增殖细胞核抗原(proliferating cell nuclear antigen, PCNA)、人肝素结合性表皮生长因子(human heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor, HB-EGF)及妊娠免疫调节因子孕激素受体(progesterone receptor, PR)、催乳素(Prolactin, PRL)、孕酮(progesterone, P)、辅助性T细胞Th1/Th2 变化的影响之后,他们认为菟丝子助孕安胎的机理可能是通过调节母胎界面的内分泌—免疫网络分子水平的平衡,使其恢复到正常妊娠状态而起到安胎的作用。
5.2. 增强免疫力
除了对动物生殖系统有调节与保护的功效,菟丝子还可增强动物免疫力。菟丝子生药提取液可使小鼠免疫器官脾脏、胸腺增重,提高巨噬细胞的吞噬能力,诱导白介素IL-1、IL-2、IL-3的释放,促进T淋巴细胞增殖反应 [29] 。在肾阳虚模型大鼠中菟丝子乙醇提取物也有类似的作用,并且可调节其T细胞CD3+CD4+、CD3+CD8+的数量,平衡CD3+CD4+/CD3+CD8+比值,恢复免疫球蛋白IgG、IgM到正常水平。菟丝子对动物免疫力的调节具有剂量效应,以50 mg/kg剂量的菟丝子金丝桃苷中药制剂腹腔注射小鼠7 d后,发现其脾脏T细胞和B细胞都有增殖反应,而增大剂量后则出现相反的抑制效果。体外实验也证明金丝桃苷对T细胞、B细胞的增殖以及巨噬细胞的吞噬能力等具有剂量效应 [30] 。
5.3. 调节血糖与血脂
菟丝子还具有调节血糖血脂的作用。李道中等发现菟丝子多糖具有明显的降糖作用,可显著提高实验性糖尿病小鼠肝糖原含量,改善糖尿病小鼠的体重、耐力、免疫器官重量等指标。并可调节血脂代谢,对影响胰岛素分泌与传导的游离脂肪酸(free fat acid, FFA)含量有明显抑制作用,同时可降低血清中甘油三酯、胆固醇的含量 [31] [32] [33] 。但菟丝子多糖对胰岛素水平并无明显影响,目前其对糖尿病治疗的机理仍需更多研究。
5.4. 抗氧化作用及其他
菟丝子多糖可通过提高小鼠体内超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase, SOD)与谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase, GSH-PX)的水平,清除多余的自由基,达到抗氧化的作用 [34] 。除多糖的抗氧化活性外,体外实验发现,同等浓度条件下,菟丝子黄酮提取物对羟基自由基的清除能力优于维生素C,对DPPH (1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼)活性自由基、超氧阴离子自由基O2−的清除能力也优于人工抗氧化剂BHT (2,6-二叔丁基-4-甲基苯酚) [35] 。此外还发现菟丝子乙酸乙酯提取物、正丁醇提取物、90%醇沉多糖对DPPH与O2−均有较强的清除能力 [36] 。这些都说明菟丝子具有较高的抗氧化能力。
上述菟丝子具有调节血脂的代谢以及抗氧化的能力,因此也可对心脑血管、肝脏等器官形成良好的保护作用。此外,菟丝子还可促进骨修复、抑制肿瘤细胞分裂与增殖,达到延缓肿瘤,降低癌症发生率的功效 [37] [38] 。
6. 系统生物学在中草药研究中的应用
菟丝子等中草药中含有的活性成分多数为复杂的次生代谢产物,其代谢通路的研究较为困难。近年来新兴的系统生物学(Systems Biology)通过基因组学、转录组学与代谢组学等技术手段为解析植物中各类化学成分的代谢途径提供了全新的解决方法。越来越多的中草药研究借助于系统生物学获得了重要的发现。
铁皮石斛 [39] 、丹参 [40] 、赤芝 [41] 、黑丑 [42] 等物种已完成基因组测序,部分物种完成精细图谱的绘制。铁皮石斛的研究中发现其基因组大小为1.11 Gb,预测有28,910个蛋白编码基因,其中存在大量的抗性基因,暗示其可能具有强大的免疫系统,从而能适应不同的复杂环境。另外研究中也发现与葡甘聚糖合成酶活性有关的大规模基因扩增,相关基因可能参与药用多糖的合成代谢。除此以外还发现了许多与生长发育调节相关的MADS-box转录因子可能参与植物形态建成等,这些基因组学的研究结果对推动石斛属的相关植物研究具有十分重要的意义。赤芝的研究显示基因组大小约为43.3 MB,编码16,113个基因,其中有大量与其体内次生代谢相关的编码基因,主要类别包括细胞色素P450 (Cytochrome P450, CYP)、转运蛋白、调节蛋白等。研究还发现有78个CYP基因与羊毛固醇合酶协同表达,暗示CYP在三萜类化合物的合成代谢中有重要作用。
还有许多重要的中药材如人参 [43] 、西洋参 [44] 、甘草 [45] 、金银花 [46] 等通过转录组测序与分析,发现大量参与药用成分化合物代谢的重要基因。例如,西洋参转录组研究发现了从乙酰CoA开始通过类异戊二烯途径合成人参皂苷骨架的各种已知酶类。此外还发现了150个CYP基因和235个糖基转移酶基因,其中部分基因可能参与从骨架向各类人参皂苷转化的过程。随后结合甲基茉莉酸诱导实验和组织特异性表达检测,确定了一个细胞色素P450和4个UDP-糖基转移酶基因作为负责人参皂苷合成的最佳候选基因。
近年来合成生物学(Synthetic Biology)发展速度突飞猛进。2003年E. Kool重新定义“合成生物学”为基于系统生物学的遗传工程,将工程学原理与方法应用于遗传工程与细胞工程等生物技术领域。根据生物学规律,设计创建以人工合成DNA为基础的元件、器件或模块,用以改造和优化现有自然生物体系,或从头合成具有预定功能的全新人工生物体系,从而突破自然体系的限制,实现合成生物体系的规模化应用。2006年美国加州大学伯克利分校的Jay Keasling实验室在大肠杆菌中引入异源甲羟戊酸途径,并表达来自于黄花蒿(Artemisia annua L.)的紫穗槐-4,11-二烯合酶(amorpha-4, 11-diene synthase, ADS)基因,成功实现了青蒿素合成前体紫穗槐-4,11-二烯(amorpha-4, 11-diene, AD)的生物合成 [47] ,进而通过优化改造生物合成元件与发酵工艺等,使AD的产量呈数量级增长,达到了规模化生产的水平。这是合成生物学的标志性研究成果。此后在医药、环境保护、生物能源、化学材料与制品等领域,合成生物学都展现出了巨大的应用潜力。
系统生物学与合成生物学等现代生物学技术方法也将对菟丝子药用价值开发产生强大的推动力。例如,通过转录组学可预测分析菟丝子体内黄酮类化合物的生物合成代谢途径,发现其中关键酶或转录因子的编码基因。也可发掘其他药用成分的合成基因,深化对菟丝子的生物活性成分的认识,通过进一步结合相关药理学研究资料,可预测影响药效的功能基因,也为下游工业化提纯与人工合成活性成分的研究提供了基础数据。鉴于造成菟丝子样品之间化学成分差异的因素众多,可依据种属、产地、寄主以及栽培环境差异等因素,通过代谢组学建立菟丝子中各类化合物成分与结构信息数据库,分析化合物与药效相关性,发展稳定高效的化学指纹图谱,方便对中药菟丝子的质量控制。结合菟丝子系统生物学的分析研究,获悉金丝桃苷、槲皮素等活性化学成分的生物合成代谢途径关键基因,并据此通过合成生物学技术,设计优化相应生物调控元件、模块,实现药用成分高效的体外生物合成。如图3所示,基因组学、转录组学与代谢组学的整合分析可快速获得菟丝子基因背景与化学成分的信息,与新兴的合成生物学以及传统的药理学有机结合,共同推动菟丝子等中药的研究进程,为基于其活性成分的新药开发提供新的发展思路。
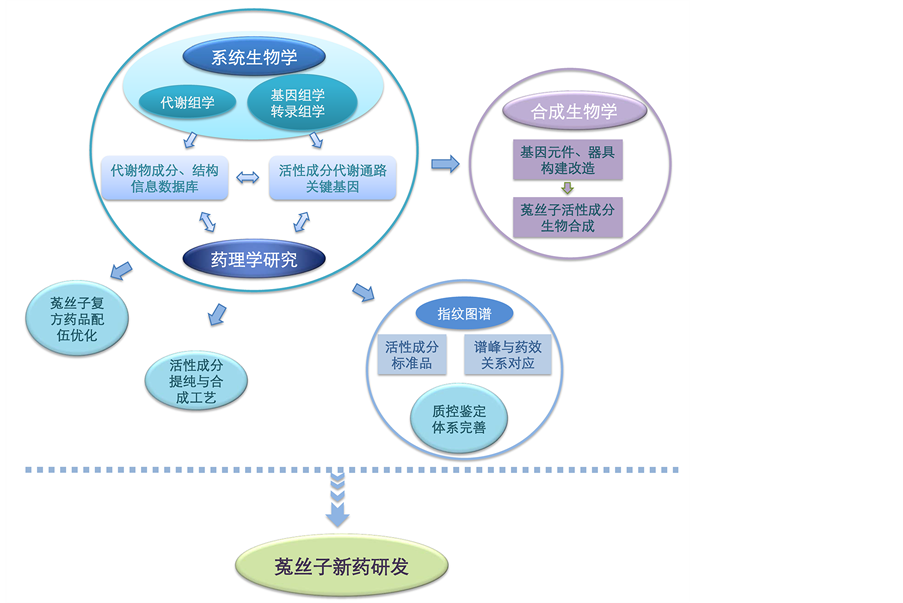
Figure 3. Systems biology in promoting research and development of dodder
图3. 开展系统生物学研究推动中药菟丝子的研发
7. 问题与展望
目前菟丝子药理学研究中多以水提物、药煎剂等为研究对象,多数研究以其中主要活性成分是总黄酮为前提假设探讨菟丝子的药效及作用机制。而以明确的化合物成分如金丝桃苷 [30] 开展的药理研究还非常少。然而菟丝子中化学成分复杂多样,有效成分尚难以确定。既可能为一种或几种黄酮类物质,更可能是几种不同类别化合物如黄酮类、酚酸类物质共同发挥作用。这些复杂的情况制约着菟丝子药理学研究的深入开展。
将蓬勃发展的系统生物学引入中药菟丝子的研究,分析由种属、寄主、环境等因素造成的药效差异与菟丝子体内代谢物变化、基因表达变化等之间的关联关系,可预测菟丝子中主要药效成分及可能的作用机制,并通过药理学进行验证。这些研究将揭示在众多富含黄酮类物质的植物中菟丝子具有独特功用的原因,还可分析药效成分差异提供临床用药参考,根据病情优化配伍。菟丝子新药开发、质控体系、提纯与合成工艺、保健品研发等众多相关领域的研究进程也将大大加快。
目前菟丝子的研究面临团队人员不足,系统生物学研究的基础薄弱,相关领域研究团队合作较少等问题,还需要投入大量的人力、物力才能加快研究进展,推进菟丝子等重要中草药资源的开发进程。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(31501353);上海市自然科学基金项目(14ZR1414100)。
NOTES
*通讯作者。