1. 引言
传统的金属植入材料(例如:不锈钢、钛合金、钴铬合金和镍钛合金等),因物理化学性质非常稳定,抗腐蚀性能优异,使其不容易在生物体内发生生化反应而被腐蚀降解掉,将长期作为异物存在于生物体内 [1] ,甚至在病变组织愈合之后仍会残留在体内。这些植入物会持续地释放有毒的金属离子,引起生物体的排异反应从而诱发炎症等生理反应 [2] ,同时需要二次手术取出,会给病患带来二次创伤和经济损失。镁及其合金作为一种可降解的金属,可以在服役过程中逐步降解,且镁具有很好的生物相容性和力学性能 [3] ,有效避免了永久植入物带来的负面影响。然而,其过快的腐蚀降解速度引起的局部pH升高、氢气泡的聚集以及由局部腐蚀导致过快的丧失其力学性能等问题极大的限制了镁及镁合金在临床中的应用。目前已有多种技术方法来改善镁的腐蚀性能,其中有机涂覆技术是一种高效、便于操作的表面改性技术,它利用有机分子与基体材料通过物理吸附或化学键的形式结合,在基底的表面形成一层阻隔层,从而提高材料的耐腐蚀性能,达到保护基底材料的作用。同时,可以在有机分子表面构建具有治疗功能的其他药物分子实现涂层的功能化 [4] 。氨基三甲叉膦酸是一种含有三个膦酸基团的有机膦酸小分子,与镁离子有很强的螯合能力,形成的螯合产物对镁的腐蚀有很好的抑制效果。同时,它的化学结构类似于磷脂双分子层中的膦酸,具有较好的生物相容性 [4] 。
本实验采用液相沉积的方法在经过碱活化后的纯镁表面构建一层氨基三甲叉膦酸涂层。并讨论不同浓度ATMP溶液下沉积的涂层对镁腐蚀性能的影响以及涂层的沉积机理。
2. 实验
2.1. 样品制备
在本实验中采用液相沉积的方法在经过碱活化预处理过得纯镁表面上构建ATMP有机膦酸涂层。主要过程分为两个步骤,具体操作如下:
1) 采用直径:11 mm,厚度:1.8 mm的纯镁圆片。依次用600#、1000#、1500#和2000#的SiC的砂纸打磨纯镁表面。将制得的纯镁样品浸泡在3 M/L的NaOH的溶液中,并置于60℃的恒温水浴锅中保温24小时,然后用去离子水冲洗样品以除去残留的NaOH,然后用洗耳球将样品吹干保存备用。
2) ATMP涂层的沉积:将经过碱活化预处理的纯镁样品分别浸泡在pH = 7三种不同浓度的ATMP水溶液中(2.5 mM/L、5 mM/L和10 mM/L),并在60℃的恒温水浴锅中保温10小时。然后取出并用去离子水冲洗,以除去残留的ATMP溶液及其他吸附物。
2.2. 材料学表征
本实验中采用场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM;型号:JSM-7401F;日本JEOL公司)来表征样品的表面形貌;通过傅立叶红外(FTIR)和X射线能谱仪表征涂层成份和结构分析。红外检测参数为:检测方式为漫反射方式;扫描范围为500 cm−1到4000 cm−1;测试时扣除Au背底。在测试ATMP粉末时采用KBr压片的方式;
XPS的测试参数及规格如下:XPS型号为XSAM800型;阳极铝靶;X射线的入射动能hν为1486.6 eV;功率:12 kV × 15 mA;线宽0.7 eV;真空度:2 × 10−7 Pa,刻蚀时间为30 s。
2.3. 耐腐蚀性能评价
动电位极化测试(Potential dynamic Polarization, PDP)在三电极的IM6电化学工作站中进行。所用测试电解液为PBS (NaCl/8.1 g∙L−1,KCl/0.24 g∙L−1、Na2HPO4/2.89 g∙L−1、KH2PO4/0.2 g∙L−1)缓冲液(pH = 7.4 ± 0.2),测试温度为37.5℃。
pH值实验在50 ml的离心管中进行。样品通过环氧树脂密封,只暴露出一个表面。将密封好的样品放入离心管中并加入45 ml的PBS溶液。然后置于37.5℃ ± 0.5℃的恒温水浴锅中。体外浸泡析出氢气量在特制的装置中收集。氢气收集装置如图1所示:在每个氢气收集装置中放入4个由环氧树脂密封好的同一工艺的样品,然后加入450 ml的PBS溶液并置于37.5℃ ± 0.5℃的恒温水浴锅中。实验过程中,每隔24小时记录一次溶液的pH值和氢气的析出量,试样在溶液中浸泡21天(504小时)。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1. 材料学表征分析
3.1.1. 表面形貌
图2是样品表面形貌的扫描电镜图,从图中我们可以看出,相比于纯镁和经过碱活化预处理后的样品,经过沉积三种不同浓度的ATMP溶液后,在碱活化预处理后的表面形成了一层均匀的ATMP分子的涂层,在扫面电镜1000倍的放大倍数下可发现Mg-OH@ATMP-5和Mg-OH@ATMP-10的涂层相对于Mg-OH@ATMP-2.5更加的致密,这意味着在较高浓度的ATMP溶液中有足够的ATMP分子通过与Mg2+的螯合从而固定在纯镁的表面上。而Mg-OH@ATMP-10涂层的表面有明显的裂纹。在5000倍的放大倍数下在Mg-OH@ATMP-5也可以发现一些细小的裂纹,这是因为涂层在干燥后由于涂层各部分应力不匹配的原因引起涂层的开裂。

Figure 1. The scheme of hydrogen collection device
图1. 氢气收集装置示意图
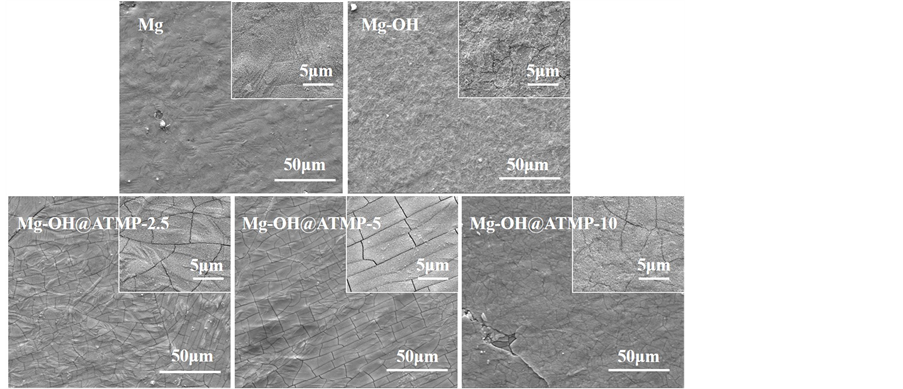
Figure 2. Surface morphology of ATMP coated Mg as compared with alkaline-treated Mg and untreated Mg
图2. 三种不同浓度ATMP涂层改性的镁与碱活化预处理的镁、纯镁表面形貌图
3.1.2. 涂层成分及结构分析
傅立叶红外光谱结果如图3,从图中可以发现经过碱活化处理的样品在3696 cm−1处出都现了羟基峰(OH),这说明经过碱活化预处理后在纯镁表面生成了Mg(OH)2,为后续接枝ATMP分子提供了大量的羟基(-OH)。经过液相沉积处理的样品和ATMP粉末相比于经过碱活化预处理的纯镁在1136 cm−1和976 cm−1分别出现了P=O的伸缩振动峰和P-OH的特征峰,这表明经过液相沉积后ATMP涂层成功地构建在预处理后的纯镁表面。
采用X射线能谱仪分析ATMP分子与碱活化预处理后的纯镁表面以及ATMP分子之间的结合方式。如图4所示,分别测试了Mg-OH@ATMP-5经过30 s刻蚀后的表面P2p、C1s、O1s和Mg1s四种元素的
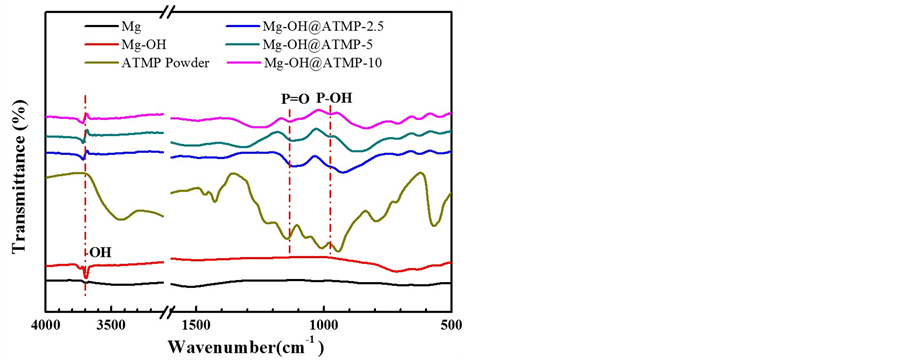
Figure 3. FT-IR spectra of the ATMP coated Mg samples as compared with the alkaline treated Mg, untreated Mg and ATMP powder
图3. 有ATMP涂层的镁、碱活化预处理的镁、纯镁和ATMP粉末的红外图谱

Figure 4. XPS spectra of the ATMP coated Mg samples as compared with alkaline treated Mg: (a), (b), (c) and (d) High-resolution XPS spectra (P 2p, C1s, O 1s and Mg 1s, respectively) of the samples surface and their deconvolutions
图4. ATMP涂层改性后的镁(Mg-OH@ATMP-5)与碱活化后的镁(Mg-OH)表面XPS高分辨图谱:(a) P 2p;(b) C1s;(c) O 1s和(d) Mg 1s
高分辨解析,并与碱活化预处理后的纯镁(Mg-OH)进行对比 [5] [6] [7] 。其中图4(a)为P2p的高分辨图谱,从图中可发现Mg-OH@ATMP-5在133.3 eV处出现了明显的P峰,而Mg-OH样品则没有,证明了ATMP涂层在纯镁表面的成功构建。对P2p的高分辨进一步分析,可以看到明显的ATMP分子上磷酸基团的峰以及一个肩峰,在133.7 eV处可分解为[R-PO3H2]的P2p1/2峰,在132.6 eV处可分解为[R-PO3H2]的P2p3/2峰;而在130.9 eV处出现的峰则可分解为P-O-Mg的峰,P-O-Mg峰的出现是因为在液相沉积过程中,基体发生轻微腐蚀而释放出的Mg2+与ATMP分子上的膦酸基团发生螯合反应 [8] 。从Mg-OH@ATMP-5的C1s高分辨图谱中可以看出在285.3 eV和286.1 eV分别出现了C-P和C-N的峰,C-P和C-N峰来自于涂层中ATMP分子的贡献,Mg-OH@ATMP-5与Mg-OH在284.6eV均出现了C-C/C-H的峰,两组样品出现的C-C峰的主要原因均来自于C污染 [9] ;在图4(c)中我们可以看出在533.1 eV处有P-O-Mg峰的出现,同时在图4(d) Mg1s的高分辨图中发现Mg-O-P的峰出现在1303.3 eV。因此,可以判断出Mg2+在沉积过程中与ATMP分子发生了螯合反应;从Mg1s图中可以发现Mg-OH@ATMP-5与Mg-OH相比也出现了Mg(OH)2、MgCO3和MgO的峰,这些峰的出现说明基体释放出的Mg2+未完全与ATMP分子螯合,而是部分Mg2+与溶液中的 、
、 等反应沉积。
等反应沉积。
3.2. 耐腐蚀性能评价
3.2.1. 电化学测试
图5所示为纯镁、碱活化预处理后的纯镁以及经过ATMP涂层改性后的纯镁的动电位极化曲线。
根据Tafel外推法计算出各样品的自腐蚀电流密度icorr、自腐蚀电位Ecorr、腐蚀保护效率η和击穿电压Ebd值,如表1所示。由于镁基材料在发生电化学腐蚀过程中,阴极发生析氢反应,阳极发生的反应主要为镁的溶解过程。由“限速步骤[rate-determining step (RDS)]”可知材料的腐蚀速率主要取决于反应慢的一方 [10] 。因为镁的活性较高,在阳极极化初始阶段就快速溶解,所以镁的腐蚀速率主要由阴极的析氢反应控制。因此,自腐蚀电流通过阴极Tafel斜率计算得到。
改性涂层对纯镁基体的保护效率η可以通过公式1 [10] 计算:
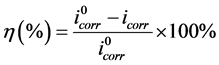 (1)
(1)
其中 、
、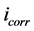 分别表示纯镁和经过ATMP涂层改性后的自腐蚀电流密度。从计算结果可知经过ATMP涂层改性后样品相比于纯镁的阴极自腐蚀电流明显减小,而且Mg-OH@ATMP-5样品具有最低的自腐蚀电流密度,对镁基体的保护效率高达到了92.06%。
分别表示纯镁和经过ATMP涂层改性后的自腐蚀电流密度。从计算结果可知经过ATMP涂层改性后样品相比于纯镁的阴极自腐蚀电流明显减小,而且Mg-OH@ATMP-5样品具有最低的自腐蚀电流密度,对镁基体的保护效率高达到了92.06%。
由于经过碱活化预处理后的纯镁由于表面具有Mg(OH)2转化层,因而阳极溶解过程被抑制,转化层对基体有一定的保护能力。从动电位阳极极化曲线图可以看出,经过ATMP涂层改性的样品的自腐蚀电位明显提高,在阳极极化过程中也出现了明显的钝化现象 [11] 。这是因为ATMP涂层不仅对电解液的侵入有物理阻隔的效果,而且随着阳极溶解释放出的Mg2+能够与涂层中的ATMP分子发生螯合作用形成的络合物能够阻碍镁的进一步溶解,达到类似“自修复”的效果。其中,Mg-OH@ATMP-5样品具有最高的击穿电位Ebd (常被用于表征有涂层的金属材料抵抗局部腐蚀的能力 [12] ),这也表明均匀致密的涂层对阻碍镁的溶解反应更为有效。
图6为样品经过极化测试后的表面形貌图。从图中可以看出Mg和Mg-OH发生了严重的局部腐蚀破坏,表面产生了大量的腐蚀产物。而经过ATMP涂层改性后的纯镁局部腐蚀明显减少,特别是Mg-OH@ATMP-5表面除有少量的腐蚀产物堆积以外,样品表面仍较为光滑平整。这表明具有ATMP涂层的样品对局部腐蚀的发生具有较好的抑制效果。
表1. 根据Tafel外推法计算出个样品在PBS中37℃ ± 0.5℃下的自腐蚀电流密度icorr、自腐蚀电位Ecorr、腐蚀保护效率η和击穿电压Ebd值
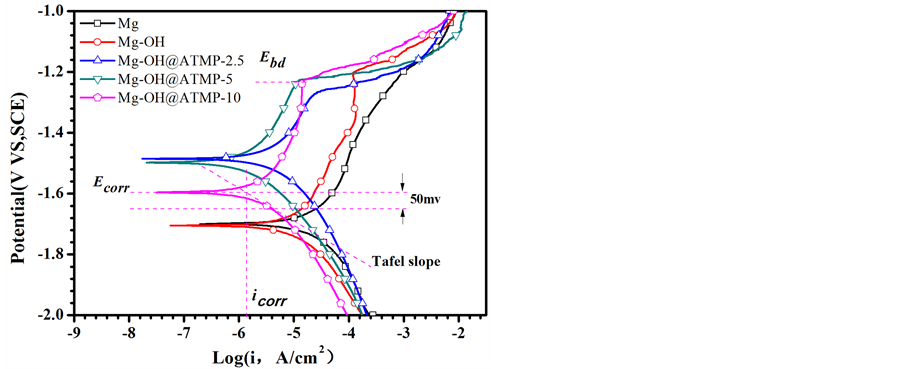
Figure 5. Potential dynamic polarization curves of the ATMP coated Mg samples in PBS solution at 37˚C ± 0.5˚C as compared to Mg-OH and untreated Mg
图5. Mg-OH@ATMP, Mg-OH和Mg在37℃ ± 0.5℃下的PBS溶液里PDP测试

Figure 6. Surface morphology of the ATMP coated Mg samples after PDP test in PBS solution at 37˚C ± 0.5˚C as compared to Mg-OH and untreated Mg
图6. Mg-OH@ATMP, Mg-OH和Mg在37℃ ± 0.5℃下PBS溶液里极化测试后样品表面形貌
3.2.2. 体外浸泡降解行为的研究
植入镁基材料在生物体内的降解是一个复杂的动态降解过程。根据镁在模拟体液中反应公式:
 (2)
(2)
由式(2)可知,要产生1 mol的H2则需要消耗1 mol的Mg,同时生成的OH−会使pH值升高。因此,我们可以通过收集浸泡过程中释放的H2和pH值的变化来简单评估经过ATMP涂层改性对纯镁腐蚀速率的影响。
从图7(a)中可以看出Mg和Mg-OH的pH值在整个浸泡过程中一直处于一个上升的过程,其中Mg-OH在200~350小时之间出现了pH上升减缓的趋势,这是因为形成的腐蚀产物覆盖在镁的表面,对基体产生了一定的保护作用,在350小时后由于腐蚀产物被破坏又出现了一个加速腐蚀的趋势;而经过ATMP涂层改性后的样品在0~200个小时之间处于一个上升过程,浸泡200小时后pH值达到一个稳定的状态。其中Mg-OH@ATMP-2.5的pH值甚至出现了小幅度的下降,这是因为在腐蚀的过程中产生的降解产物有ATMP小分子,ATMP分子与OH-发生了中和反应使pH值出现了下降的趋势。
从长期浸泡实验析氢的结果图7(b)中可以看出,在浸泡初期阶段(0~200 h) Mg和Mg-OH发生了快速的析氢反应,;在浸泡中期(200~400 h)仍有较多的H2析出只是速率有所减缓;在浸泡后期(400~500 h),H2的析出量基本达到稳定;这是因为在浸泡初期表面活性镁较多,随着浸泡时间的增加表面腐蚀产物的堆积使得活性镁的暴露减少因而H2的析出量有所减缓,直至没有活性镁的暴露H2的析出量达到一个稳定值。而经过ATMP涂层改性后的样品,在0~200 h之间由于涂层保护的作用因而前期的析氢速率相对的Mg和Mg-OH有明显的减缓;在200~500 h之间改性后的样品析氢量只有少量增加,基本保持稳定。

Figure 7. Immersion degradation behavior of the ATMP coated magnesium samples in PBS solution at 37˚C ± 0.5˚C for 500 hours as compared with alkaline treated Mg and untreated Mg: (a) pH value change as a function of time; (b) hydrogen evolution; (c) SEM micrographs of the samples surface after immersion degradation in PBS solution at 37˚C ± 0.5˚C for 500 hours
图7. 样品Mg-OH@ATMP,Mg-OH和Mg在37℃ ± 0.5℃下在PBS溶液中浸泡500 h结果:(a) pH值随时间变化图;(b) 析氢;(c) 浸泡后样品表面形貌图
经计算在整个浸泡过程中Mg和Mg-OH每平方厘米的析氢量分别为2.88和2.42 ml;而Mg-OH@ATMP-2.5" target="_self">Mg-OH@ATMP-2.5、Mg-OH@ATMP-5和Mg-OH@ATMP-10每平方厘米析氢量分别为1.65、1.32和1.63 ml。这表明经过ATMP涂层改性后样品的耐腐蚀性能明显提高,且Mg-OH@ATMP-5对基体的保护效果最佳,Mg-OH@ATMP-10次之,Mg-OH@ATMP-2.5" target="_self">Mg-OH@ATMP-2.5最差,这与之前电化学测试结果一致。
从图7(c)中我们可以发现Mg的表面发生了较为严重的局部腐蚀(其中亮白色部位),同时伴随着大量的腐蚀产物形成;Mg-OH的腐蚀降解发生在Mg(OH)2转化层下,经过长期浸泡后Mg(OH)2转化层发生严重的开裂,并有脱落的趋势;与之相比,经过ATMP涂层改性后的样品表面仍然保持着涂层的基本形状,特别是Mg-OH@ATMP-5只出现了少许的裂纹,涂层的均匀性和致密性保持较好。
4. 结论
通过对样品材料学的表征证明:采用液相沉积的方法,ATMP通过共价固定和螯合沉积的方式在纯镁表面成功地构建了一层均匀且致密的ATMP涂层。经过ATMP涂层改性后的样品在电化学测试和长期浸泡实验中表现出了优异的耐腐蚀性能。这是因为ATMP与镁离子形成的膦酸盐类螯合物具有很好的稳定性,且一层均匀且致密的ATMP涂层对电解液的侵入进而与镁基体接触起到了很好的物理阻隔效果,因而能够有效地降低镁在腐蚀介质中的腐蚀速率。这为镁基植入材料因腐蚀速率过快而限制了其在临床上的应用提供了一种有效的解决办法。同时,我们也将对ATMP涂层进行进一步的生物学评价,以验证ATMP涂层的生物学性能。
致谢
这项工作得到国家自然科学基金(No. 21473138)的支持。