1. 引言
加氢工艺是一种广泛用于化学工业的技术,对整个化学工业的发展具有重要意义。加氢工艺主要分为两大类:第一类是直接加氢,例如一氧化碳与氢气生成甲醇的过程;另一类在反应过程中同时伴随着化学键的断裂,又称之为氢解反应,加氢裂化、加氢脱硫就是这类过程的典型代表。加氢工艺在原油氢化裂化 [1] ,渣油加氢脱碳 [2] ,芳烃加氢还原 [3] ,以及氰化物、叠氮化物加氢还原 [4] [5] 等方面有着广泛的运用。在加氢工艺中,起到关键作用的就是加氢催化剂的性能。然而,随着高硫原油产量的增加,环境保护的要求日益严格,以及某些需要加氢的物质本身就含有硫原子等,使得传统的加氢催化剂在这些过程中极易发生硫中毒,造成了催化剂的失活。因此对于这些加氢过程,寻找到合适的耐硫催化剂一直是近年来人们关注的热点之一。
所以,本文对目前耐硫加氢催化剂的最新研究进展进行了相关综述,首先综述了不同形态的硫元素造成加氢催化剂失活的机理,包括H2S、硫酸盐以及有机硫化物 [1] ;然后阐述了最近几年国内外的耐硫加氢催化剂的相关进展,并对未来进行了展望。
2. 硫使催化剂失活的机理
使催化剂失活的硫主要分为三类,包括H2S、硫酸盐以及相关的有机硫化合物 [1] 。
2.1. 硫化氢使催化剂中毒机理
当反应气中存在H2S时,固体催化剂表面会吸附上大量的H2S,这些H2S会覆盖甚至破坏催化剂的活性中心,阻碍在催化剂表面上的反应,使得催化剂活性降低甚至完全失活 [2] 。
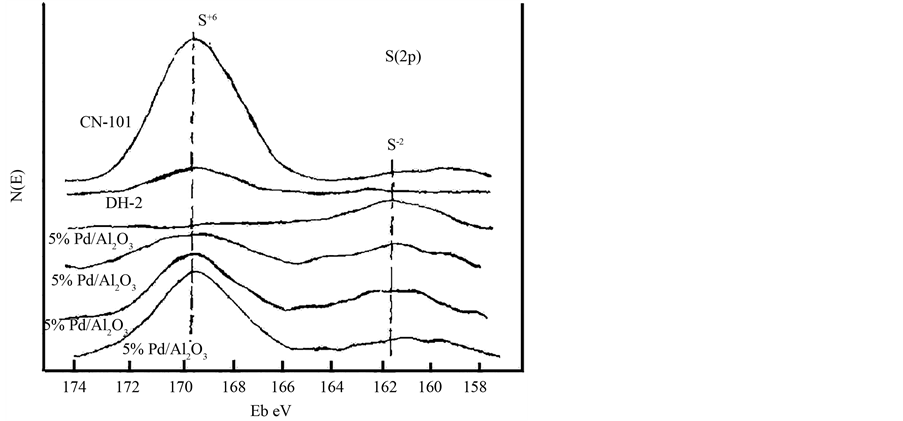
邓友权等 [3] 在H2与O2生成H2O的反应中,以H2S为毒物,模拟了Pd/Al2O3催化剂在不同氢氧比的条件下该反应的硫中毒情况,并对其失活机理做出了分析。发现在氢气浓度较高时,催化剂完全失活,并且不可逆,对使用后的催化剂进行电子能谱与XPS分析后(图1、图2、图3),推测催化剂表面的Pd与S2−形成了Pd-Sx (1 < x < 2)的化合状态,说明催化剂表面被严重硫化,提出失活机理如下:
 Reaction condition: 180˚C, 13% H2 in the feed gas, volume space velocity = 1 × 104. 1. H2 conversion (O2/H2 = 2), 2. H2 conversion (O2/H2 = 0.55), 3. H2 conversion (change O2/H2 = 0.55 to 2), 4. H2S in the feed gas (O2/H2 = 0.55), 5. H2S in the feed gas (O2/H2 = 2).
Reaction condition: 180˚C, 13% H2 in the feed gas, volume space velocity = 1 × 104. 1. H2 conversion (O2/H2 = 2), 2. H2 conversion (O2/H2 = 0.55), 3. H2 conversion (change O2/H2 = 0.55 to 2), 4. H2S in the feed gas (O2/H2 = 0.55), 5. H2S in the feed gas (O2/H2 = 2).
Figure 1. Transient H2-O2 reaction activity and H2S concentration profiles for 5% Pd/Al2O3
图1. 5% Pd/Al2O3催化剂H2-O2反应硫中毒活性随时间的变化
 1. Fresh, reductive, 2. Operated in O2/H2 = 0.55 at 180˚C for 18 h, 3. Sample in 2 treated in pure N2 at 300˚C, 4. Operated in O2/H2 = 2 at 180˚C for 34 h, 5. Fresh, oxidative state.
1. Fresh, reductive, 2. Operated in O2/H2 = 0.55 at 180˚C for 18 h, 3. Sample in 2 treated in pure N2 at 300˚C, 4. Operated in O2/H2 = 2 at 180˚C for 34 h, 5. Fresh, oxidative state.
Figure 2. XPS spectra of Pd(3d5/2) for 5% Pd/Al2O3 catalysts
图2. 5% Pd/Al2O3催化剂的Pd(3d5/2) XPS图

同时邓也发现,当氧气浓度较高时,催化剂的活性虽然有所下降,但不会完全失活,并且可用H2恢复活性,提出的失活与再生机理如下:


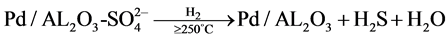 在温度超过250˚C时,H2S大量逸出,催化剂Pd-S/Al2O3再生。Pt系催化剂在H2S下的失活机理与Pd类似 [4] ,H2S会与Pt生成PtS、PtS2、Pt2S等,造成催化剂中毒。
在温度超过250˚C时,H2S大量逸出,催化剂Pd-S/Al2O3再生。Pt系催化剂在H2S下的失活机理与Pd类似 [4] ,H2S会与Pt生成PtS、PtS2、Pt2S等,造成催化剂中毒。
 1. Operated in O2/H2 = 2 at 180˚C for 34 h, 2. Operated in O2/H2 = 2 at 80˚C for 32 h, 3. Operated in O2/H2 = 0.55 at 180˚C for 20 h, 4. Operated in O2/H2 = 0.55 at 80˚C for 18 h, 5. Operated in industrial device for 2000 h, 6. Operated in industrial device for 7300 h.
1. Operated in O2/H2 = 2 at 180˚C for 34 h, 2. Operated in O2/H2 = 2 at 80˚C for 32 h, 3. Operated in O2/H2 = 0.55 at 180˚C for 20 h, 4. Operated in O2/H2 = 0.55 at 80˚C for 18 h, 5. Operated in industrial device for 2000 h, 6. Operated in industrial device for 7300 h.
Figure 3. XPS spectra of S(2p) for 5% Pd/Al2O3, DH-2 and CN-101 catalysts
图3. 5% Pd/Al2O3,DH-2,CN-101催化剂的S(2p) XPS波谱图
2.2. 硫酸盐使催化剂中毒机理
SO2的存在也会使催化剂中毒,其过程为SO2先步氧化生成SO3,再形成硫酸盐沉积于催化剂表面,破坏了催化剂的结构,导致催化剂失活。Weng等 [5] 制备了一种用于氧化煤灰的催化剂Cu-K/CeO2,在通入1 L/min的含400 ppm的SO2的实验条件下测定CO2的产率来测定催化剂的活性。研究发现,在温度为313˚C~359˚C时催化剂具有较好的活性;当温度高于359˚C时,K盐会与SO2生成K2SO4,覆盖于催化剂表面,造成失活。李小定等 [6] 通过XPS和XRD法测定了Co-Mo/γ-Al2O3、Ni-Mo/γ-Al2O3、Co-Mo-K/γ-Al2O3等催化剂与硫酸盐的反应,发现金属离子的种类对硫酸盐化反应有直接的影响,当Co-Mo系催化剂中不含Ni、K等低价离子时,硫酸盐化反应较难发生;而含K催化剂的硫酸盐化反应十分明显,主要生成K2SO4,含Ni的次之,不含K、Ni的Co-Mo/γ-Al2O3催化剂硫酸盐化反应甚微。含K过程的其机理如下:

硫酸盐形成后,会破坏催化剂的活性中心,降低表面酸性和催化剂的比表面积,从而使催化剂失活。
2.3. 有机硫和硫化物使催化剂中毒机理
有机硫的物质主要包括硫醇、噻吩及其衍生物以及其他硫化物诸如CS2、COS等 [1] 。在高温下,有机硫和硫化物会与氢气反应生成H2S,从而使催化剂中毒 [7] [8] 。Liu等 [7] 发现在费托合成过程中COS会与H2反应生成H2S,从而造成铁系催化剂的失活。而Mellor等 [8] 认为高温下在水煤气变换过程中也会发生如下反应,造成催化剂失活:
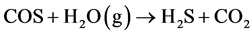
但黄星亮等 [9] 认为在低温下有机硫使催化剂的失活与之不同,认为有机硫对Pd/树脂催化剂中毒的规律是:随着硫化物的分子量的提高,其毒性减弱。分析其可能的失活机理为:有机硫化物初始以分子形式在催化剂金属活性中心上发生化学吸附,其吸附强度符合电子给体-受体机理,硫受电子能力随供电子基团(如烷基)供电子能力的减弱而增强,导致硫-金属键增强,至一定程度时就会使硫化合物中硫价键断裂,以及形成带烷基基团的S-Pd键,从而使Pd失去解离吸附H2的作用。例如二甲基二硫醚使催化剂中毒的机理见图4。
总之,H2S和有机硫使催化剂失活的机理主要是由于毒物与活性中心结合,造成了催化剂的失活。而硫酸盐主要是通过覆盖于活性中心,降低催化剂的比表面而使得催化剂失活。
3. 耐硫加氢催化剂研究进展
根据硫使催化剂失活的机理,可以将耐硫催化剂分为三大类:耐硫化氢的催化剂、耐有机硫的催化剂和耐硫酸盐的催化剂。但加氢条件下是还原性的环境,因此不会出现SO2氧化为SO3再成为硫酸盐覆盖催化剂的情况,因此根据机理可以将耐硫加氢催化剂分为耐硫化氢的加氢催化剂和耐有机硫的加氢催化剂两大类。
3.1. 耐硫化氢类加氢催化剂
耐硫化氢类加氢催化剂主要分为两种,最主要的一种在对燃料油进行加氢脱硫(HDS)的精制工艺中所使用的催化剂,另一种是对含有少量硫化氢的加氢过程,例如炼化企业中常见的烷基化工艺中所使用的催化剂。所不同的是,HDS工艺中是通过加氢的方式将燃料油中的有机硫等变为H2S除去,即“脱硫”;而对含有少量硫的加氢过程更侧重于催化剂本身的对硫中毒的耐受能力,即“抗硫”。
3.1.1. 燃料油HDS过程中的加氢催化剂
石油是以碳和氢为主要成分,同时含有硫、氮和重金属等组分的有机物,这造成了以石油为原料加工生成的汽油和柴油等燃料油在燃烧过程中产生大量硫化物、氮化物等污染物 [10] 。而随着石油开采已逾百年,低硫轻质原油的产量已经越来越少。而随着对保护环境的要求越来越迫切,对燃料油中的硫含量的要求也越来越严格。因此开发出更高效的HDS催化剂是当务之急。
HDS催化剂的反应机理主要是将燃料油中的有机硫加氢为H2S除去,表1 [11] 展示了几种有机硫在加氢过程中所发生的反应:

Figure 4. The mechanism of the poisoning of the catalyst by dimethyl disulfide
图4. 二甲基二硫醚使催化剂中毒的机理

Table 1. Some typical hydrodesulfurization reactions
表1. 一些典型的加氢脱硫反应
以噻吩为例,噻吩经β-消除、C-S键断裂之后生成丁二炔或丁二烯,即噻吩加氢脱硫中间产物并非四氢噻吩。有学者认为使用二硫化钼催化反应,得到噻吩HDS初级产物只有丁二烯 [12] ;还有学者认为噻吩HDS初级产物包括丁二烯和丁烯 [13] ,猜测噻吩HDS的途径为:一是双键加氢饱和后开环脱硫;二是直接开环脱硫。相关机理见图5。大多数学者认同前种理论。
一般加氢精制催化剂多为第ⅦB族过渡金属,多以Mo和W为活性组分,而助催化剂多用Ⅷ族的过渡金属如Co、Ni等,助剂和与不同的活性组分的组合后会有不同的HDS效果,目前在工业生产中,直馏柴油脱硫一般使用Co-Mo的硫化物作催化剂,加工含有较多的裂化馏的裂化柴油馏分常使用Ni-Mo的硫化物作催化剂 [14] 。也有一些用Pd作为活性中心的催化剂。孙淑玲 [15] 等采用氧化铝负载的Co-Mo-S催化剂对模拟的硫化油进行加氢处理,硫源采用4,6-二甲基苯并噻吩。通过TEM表征证明,随着催化剂上Mo原子数量的增多,催化剂的效果越好,两者呈现线性关系。同时,经过化学处理的催化剂比未处理的活性要高近30%。李哲哲 [16] 等在固定床中研究了不同温度下噻吩的转化率与Ni-Mo催化剂中Ni与Mo含量的关系,得出较高温度下(280˚C~320˚C)最佳Ni/Mo为0.68 (mol),较低温度下(160˚C~240˚C)最佳Ni/Mo为0.27 (mol)。鲁勋等 [17] 采用浸渍法制备了CeO2改性的Pd/A12O3加氢脱硫催化剂,结果表明,CeO2的改性导致还原态Pd/A12O3催化剂的初始活性提高26%。鲁认为CeO2的改性机理在于Pd与Ce发生了强相互作用,生成的Ce3+成为新的不同于B酸的噻吩吸附活性中心。
除了传统的过渡金属,过渡金属碳化物、氮化物和磷化物在催化学科中作为一类新的催化材料也引起了人们的极大关注。徐坤 [18] 等制备的Ni-Mo2-N催化剂在360˚C,3 MPa的条件下进行噻吩加氢,转化率达95%;同样催化剂用于苯加氢,转化率高达97.5%;而用于含有0.01%的噻吩的苯加氢,转化率为81%,且保持了长时间的活性,说明催化剂具有较好的加氢脱硫能力与芳烃加氢能力。而过渡金属磷化物由于比碳化物和氮化物具有更好的抗硫能力,运用的更加广泛。李丽娜等 [19] 研制了一种MoP/TiO2-ZrO2催化剂,在n(Ti)/n(Zr)为2、Mo负载量为20%时,MoP/TiO2-ZrO2催化剂的加氢脱硫效果最佳,脱硫率可达99.34%。
载体在催化剂中起负载活性组分、提高活性组分和助剂分散度的作用,在一定程度上参与某些反应。因此载体的选择对催化剂的效果也有着非常重要的作用。Al2O3作为一种常见的加氢催化剂载体 [20] ,却由于Co、Ni、Mo均可以与Al2O3相互作用而使得催化剂的加氢脱硫效果较低。SiO2和TiO2也是常见的催化剂载体。研究表明 [21] ,由于存在相互作用,Al2O3无法负载含磷化物的活性中心,而SiO2却是一种非常好的载体,在HDS反应中催化剂有着较高的活性与选择性。Tanaka [22] 等合成的以TiO2-Al2O3为载
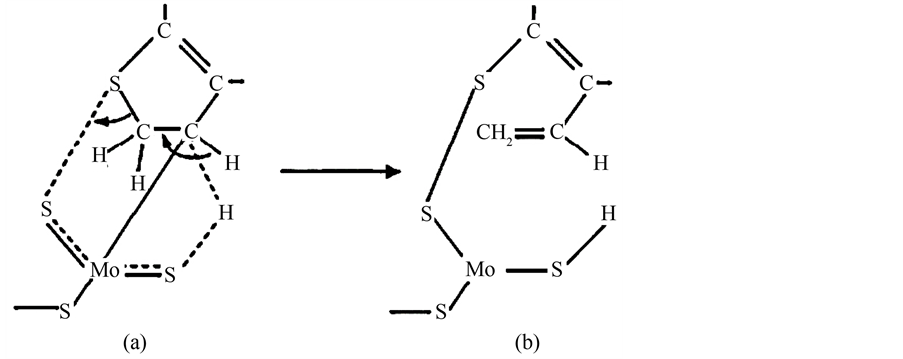
Figure 5. Mechanism of C-S bond cleavage in thiophene over sulfided CoMo/ Al2O3 and related catalysts
图5. CoMo/Al2O3及类似催化剂下噻吩的C-S键断键机理
体的Co-Mo催化剂相比于只以Al2O3为载体的催化剂具有更好地低温活性、高选择性以及抗中毒能力。最近Zhang [23] 等以MgO的纳米颗粒作为Co-MoS2的载体进行HDS反应,当以二苯并噻吩(DBT)为硫源时,DBT的转化率达94.2%,远高于以γ-Al2O3为载体的64.1%。
除了传统的氧化物可以作为载体外,由于介孔分子筛的诸多优点,目前也有其作为活性中心载体的催化剂。Reddy [24] [25] 等将介孔MCM-41分子筛作为Co-Mo、Ni-Mo和Ni-W催化剂的载体,由于其具有较大的孔径结构[(1.5~10) nm]、较高的比表面积,可以使负载的金属能高度分散,并且让多环噻吩容易扩散到活性中心,同时具有适度的酸性,铝改性的MCM-41负载的催化剂能获得较高的活性,特别是当MCM-41有着合适的Si/Al比和金属负载量时,Co-Mo/MCM-41在二苯并噻吩、二甲基苯并噻吩上的HDS活性均比Al2O3负载的Co-Mo活性高。温钦武等 [26] 以介孔分子筛SBA-15为载体,负载Co-Mo双金属活性组分制备了一种深度加氢脱硫的催化剂。经过XRD和BET表征,负载金属后的SBA-15分子筛仍然保持二维晶相结构,但比表面积略有下降。用0.5%二苯并噻吩的环己烷溶液为模型化合物,考察了在固定床反应器上金属负载量的影响及最佳反应条件。并用高硫催化裂化柴油为原料评价了催化剂的脱硫反应活性。结果表明,当催化剂含5% CoO和25% MoO3的Co-Mo/SBA-15催化剂具有最高的加氢脱硫活性,硫质量分数由490 μg/g降至11 μg/g,二苯并噻吩脱硫率可达97.75%。
3.1.2. 其他含有少量硫的加氢过程的催化剂枚举
其他的加氢过程主要是指给诸如某种或某类烯烃,某种或某类芳烃等的加氢过程,因为原料来源等的一些问题,原料中含有少量的硫化氢。因此需要使用具有耐硫能力的催化剂来催化加氢过程。下面仅枚举一些具有代表性的催化剂。
在煤制乙二醇工艺中,草酸二甲酯(DMO)加氢是非常关键的一步,然而由于原料来源的限制,DMO中往往含有少量H2S,张博 [27] 等合成了Cu/SiO2作为DMO加氢的催化剂,发现该催化剂在硫存在的条件下很快失活,提出可以参考合成甲醇的催化剂Cu/ZnO/Al2O3中加入ZnO来避免Cu的失活,因为ZnO与硫化物更易结合可以有效防止铜催化剂的中毒。
Liu [28] 等采用两步结晶的方法合成封装Pt的方钠石Pt/SOD,并用其测试了在苯加氢过程中的耐硫特性。样品在硫化氢的毒化前后表现了良好的加氢活性。Liu通过H2-TPD表征的方法证实了是氢溢流效应才保护了催化剂的活性。
3.2. 耐有机硫类加氢催化剂
有机硫作为毒物在加氢条件下影响催化剂活性的情况可以分为低浓度条件下与高浓度条件下两部分。
低浓度有机硫的条件下,一部分有机硫被氢气还原成了硫化氢,相关反应式可参照表1,另一部分常作为实验室测定催化剂性能的硫源:由于反应条件的限制,这部分有机硫(硫化物)很少会形成H2S,而主要还是以原来的形态存在的。譬如,Baldyga [29] 等通过胶体技术合成了一种以SiO2为骨架的单分散Pt纳米颗粒催化剂,并以噻吩为硫源,用其对乙烯进行加氢反应。Baldyga通过实验发现,当Pt的纳米粒径为6 nm时,催化效果最佳。粒径过小时,氢气无法接触到Pt形成氢原子,粒径过大时,Pt易于与硫接触从而导致活性降低。Baldyga最后提出,采用胶体化学的方法来合成制备催化剂,并适当调整活性中心的粒径大小,可以有效地应对催化剂的失活。Kim [30] 等将Pd分别负载于两种沸石A和Y上来作催化剂,在低温条件下对芳烃进行加氢反应。其中A沸石的粒径大于6 Å,Y沸石的粒径小于5 Å。在以苯并噻吩(BT)为硫源的条件下,负载于A沸石上的Pd无催化活性,负载于Y沸石上的Pd催化活性较低,但将两种催化剂混合后,发现混合的催化剂活性要高于负载于Y上的催化剂。Kim等认为这是因为产生的H2S更多的吸附于A沸石上,从而使得混合催化剂的活性要高于单一沸石载体的催化剂。同时Kim等利用SiO2对Pd/A催化剂进行表面气相沉淀,使得Pd/A催化剂也有了加氢活性,认为也是氢溢流效应保护了Pd/A的活性中心。
高浓度有机硫的条件一般是指需要加氢的物质为诸如含有噻吩环的物质,这些反应的催化剂可以在高浓度硫的条件下依然保持有较高的活性。不同于HDS过程的加氢催化剂,此类催化剂是要对噻吩环上的链的不饱和键加氢,或者是生成四氢噻吩等衍生物,而不像HDS是完全破坏掉噻吩环生成了H2S。
日本的Okamoto [31] 等制备了一种将四(三苯基膦)钯镶嵌于聚合物上的一种加氢催化剂,并通过调整聚合物中的各组分的成分,提高了催化剂的抗硫能力,可以在更加苛刻的条件下对更多的不饱和键进行加氢的能力。实验证明,在以乙醇/乙酸 = 6:1为溶剂,140˚C,100 atm的条件下,反应24 h后,苯并噻吩的加氢转化率达到了92%,催化剂依然具有良好的活性。Okamoto等认为催化剂的高活性是因为Pd的高度分散,耐硫性是因为四(三苯基膦)钯的苯环保护了活性中心,避免了催化剂的失活,而调整载体中几种聚合物的组分可以提高催化剂的活性与适用度。Urban [32] 等制备了一种钌-N-杂环卡宾催化剂,可以在室温,H2压力为90 bar下对取代的噻吩和苯并噻吩加氢生成相应的四氢噻吩衍生物。其相关反应方程式见图6和图7。
Malanga [33] 等制备了一种可以广泛用于叠氮化合物还原成伯胺的催化剂。通过将三丁基氢化锡(Bu3SnH)与1,2-双(二苯基膦)乙烷氯化镍按2:1混合制成的催化剂,可以在非常温和的条件下对各类叠氮化合物进行加氢,并且对含噻吩环的叠氮化合物有很好加氢效果,收率可达95%。Lange [34] 等研制了一种铁螯合物的催化剂,也可对广泛的叠氮化合物进行加氢,其催化剂制备方法见图8。
其中,通过实验发现2的催化效果较1与3更好。以2为催化剂(1 mol%),在30 bar H2,100˚C下对2-氰基噻吩进行加氢还原为伯胺的反应,反应3 h收率达90%,催化剂未见失活。
4. 结论与展望
随着石油资源的逐渐枯竭,工业上的主要原料渐渐被低品质的原油代替了,同时市场上对一些有机硫化合物诸如苯并噻吩的加氢还原产物的迫切需要,急需开发出合适的新型耐硫加氢催化剂,来满足环境法的要求与市场的需求。对于HDS过程,人们通过尝试采用过渡金属碳化物、氮化物和磷化物等作为新的活性中心,SiO2、TiO2、MgO的纳米颗粒和介孔分子筛等作为新的载体来制备新的加氢催化剂,较
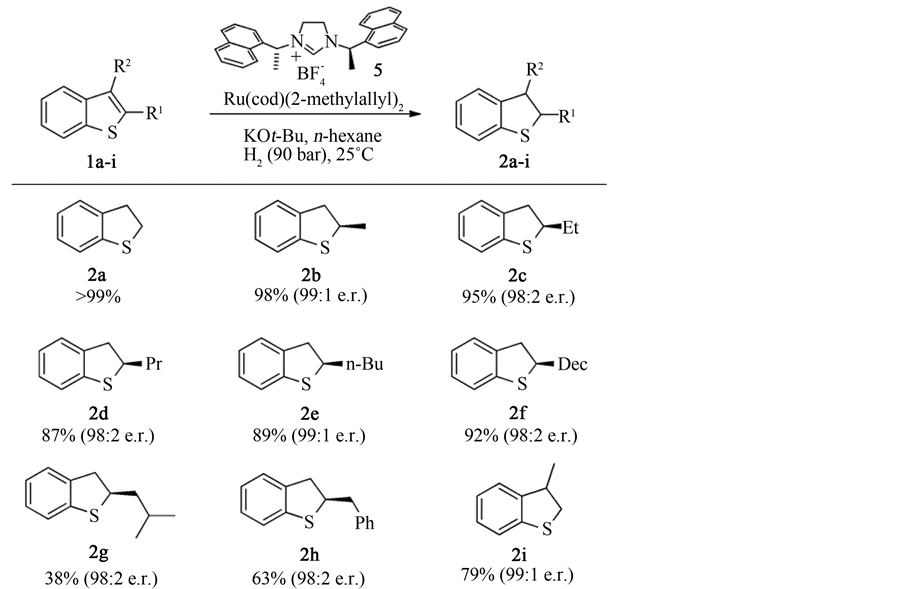
Figure 6. Scope of the asymmetric hydrogenation of thiophenes
图6. 噻吩及其衍生物的不对称氢化反应

Figure 7. Scope of the asymmetric hydrogenation of benzothiophenes
图7. 苯并噻吩及其衍生物的不对称氢化反应

Figure 8. Structure of different Fe (PNP) catalysts 1-3 and synthesis of complex 2
图8. 催化剂Fe (PNP) 1-3的不同的结构以及对复合物2的合成
传统的过渡金属催化剂在活性、选择性与抗毒能力上均有明显提高。而对于有机硫加氢过程,开发的新型催化剂使得绝大部分反应过程都可以在温和的条件下进行,而且催化剂几乎都没有失活,收率与选择性也非常令人满意。但是,这些新型的耐硫加氢催化剂在制作成本上都比较高昂,制作工艺也较为复杂,限制了它们在工业上的大规模运用。
因此,从工业角度来看,开发出成本低廉、制作工艺简单,同时又能在反应条件、活性、选择性与抗毒能力上比传统催化剂更好的耐硫加氢催化剂,将是未来的加氢催化剂的发展方向。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(21376213) (the National Natural Science Foundation of China)陈新志;国家自然科学基金(21476194,基于量子化学效应的超临界氨体系溶解性能研究及其在氨解反应中的应用)钱超;国家重点研发计划项目(The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFB0301800,低价煤高值转化中的产物综合利用和能量回收技术))。
NOTES
*通讯作者。