.
1. 引言
近年来,拓扑超导态因其新奇的物理特性受到了凝聚态物理学界的广泛关注,其中石墨烯中可能存
在的手征性d + id (具体形式为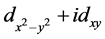 )超导态更是目前的一个研究热点。理论研究发现手征性d + id
)超导态更是目前的一个研究热点。理论研究发现手征性d + id
超导态同时缺了时间反演和宇称对称性,而且表现出非平庸的拓扑特性,例如量子化自旋霍尔电导和热霍尔电导、超导涡旋中的马约拉纳态,以及边界上的无能隙态。Pathak等人运用变分蒙特卡罗方法模拟哈伯德模型的结果表明在低掺杂的石墨烯中存在手征性d + id超导态 [1] ,随后Nandkishore等人的重正化群结果显示在1/4掺杂的石墨烯中存在手征性d + id超导态 [2] 。Black-Schaffer 等人运用重正化平均场以及量子蒙特卡罗方法的计算结果进一步证实在电子半填充附近存在手征性d + id超导态 [3] 。
手征性d + id超导态的实部即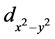 超导态对应于铜氧化物高温超导体的超导状态。为了解释高温超导机理,人们对均匀 [4] [5] [6] [7] 和非均匀 [8] [9] [10] [11] 四方晶格中的
超导态对应于铜氧化物高温超导体的超导状态。为了解释高温超导机理,人们对均匀 [4] [5] [6] [7] 和非均匀 [8] [9] [10] [11] 四方晶格中的 超导态开展了大量的研究工作,其中非均匀主要包括棋盘状和条纹状两种形式。Kivelson 等人采用微扰法和数值精确对角化的计算结果表明一定的棋盘状非均匀有助于掺杂空穴形成
超导态开展了大量的研究工作,其中非均匀主要包括棋盘状和条纹状两种形式。Kivelson 等人采用微扰法和数值精确对角化的计算结果表明一定的棋盘状非均匀有助于掺杂空穴形成 配对状态 [8] [9] 。Baruch等人运用contractor重正化群方法的计算结果同样显示适当的棋盘状非均匀有助于增强
配对状态 [8] [9] 。Baruch等人运用contractor重正化群方法的计算结果同样显示适当的棋盘状非均匀有助于增强 超导态 [10] 。最近,有限温度行列式量子蒙特卡罗方法的模拟结果显示在四方晶格中存在最优化的棋盘状非均匀度使得
超导态 [10] 。最近,有限温度行列式量子蒙特卡罗方法的模拟结果显示在四方晶格中存在最优化的棋盘状非均匀度使得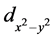 电子配对关联函数取得最大值,并且最优化的非均匀度随着在位电子库仑相互作用的增大而增加 [11] 。
电子配对关联函数取得最大值,并且最优化的非均匀度随着在位电子库仑相互作用的增大而增加 [11] 。
受Kivelson等人工作的启发,我们构造了非均匀二维蜂巢晶格并采用约束路径量子蒙特卡罗方法 [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] 探究了非均匀性对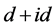 超导态的物理影响。我们的计算结果表明在弱电子关联区域,适当的非均匀有助于增强
超导态的物理影响。我们的计算结果表明在弱电子关联区域,适当的非均匀有助于增强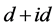 超导态,而随着电子关联的增强,非均匀对超导难以产生增强作用。我们的研究工作一方面可以扩展对二维蜂巢晶格中关联电子物理特性的理解,另一方面为探寻更强的非常规超导态提供了重要的理论思路。
超导态,而随着电子关联的增强,非均匀对超导难以产生增强作用。我们的研究工作一方面可以扩展对二维蜂巢晶格中关联电子物理特性的理解,另一方面为探寻更强的非常规超导态提供了重要的理论思路。
2. 模型结构和哈密顿量
参照棋盘状非均匀四方晶格 [8] [9] ,我们构造了非均匀二维蜂巢晶格,如图1所示。
图1(a)表示尺寸为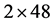 的晶格结构示意图,它由两套相互嵌套的三角晶格组成。图中黑色实心表示A类子格点,黑色空心表示B类子格点。我们将碳原子由黑色实线连接形成六边形的蜂巢,然后用红色点线将蜂巢连接起来。通过定义蜂巢内近邻碳原子之间电子的跃迁积分为t1,蜂巢间近邻碳原子之间电子的跃迁积分为t2,我们可以改变t1和t2的比值来调控二维蜂巢晶格的非均匀性。图1(a)中以a1和a2为基矢构成的平行四边形代表非均匀情况下的晶格原胞,内含六个碳原子。当只考虑在位库仑相互作用时,系统的哈密顿量表示为下面的形式:
的晶格结构示意图,它由两套相互嵌套的三角晶格组成。图中黑色实心表示A类子格点,黑色空心表示B类子格点。我们将碳原子由黑色实线连接形成六边形的蜂巢,然后用红色点线将蜂巢连接起来。通过定义蜂巢内近邻碳原子之间电子的跃迁积分为t1,蜂巢间近邻碳原子之间电子的跃迁积分为t2,我们可以改变t1和t2的比值来调控二维蜂巢晶格的非均匀性。图1(a)中以a1和a2为基矢构成的平行四边形代表非均匀情况下的晶格原胞,内含六个碳原子。当只考虑在位库仑相互作用时,系统的哈密顿量表示为下面的形式:
 (1)
(1)
上式中三角括号表示二维系统中的近邻格点, 分别表示原胞中A类子格点和B类子格点。
分别表示原胞中A类子格点和B类子格点。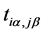 表示近邻格点间的跃迁积分,
表示近邻格点间的跃迁积分, 分别表示原胞中A类子格点上的产生(湮灭)算符,
分别表示原胞中A类子格点上的产生(湮灭)算符, 分别表示原胞中B类子格点上的产生(湮灭)算符,
分别表示原胞中B类子格点上的产生(湮灭)算符, 表示自旋,
表示自旋,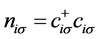 表示自旋为
表示自旋为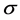 的电子密度算符,U表示在位库仑相互作用。本文中我们取近邻格点之间的距离为a,在结果部分所给出的t1,t2,U等均以近邻格点间的最大跃迁积分作为能量单位,原胞中的基矢可以写为:
的电子密度算符,U表示在位库仑相互作用。本文中我们取近邻格点之间的距离为a,在结果部分所给出的t1,t2,U等均以近邻格点间的最大跃迁积分作为能量单位,原胞中的基矢可以写为:
 (2)
(2)
由(2)式可以方便地得到倒格子基矢为:
 (3)
(3)
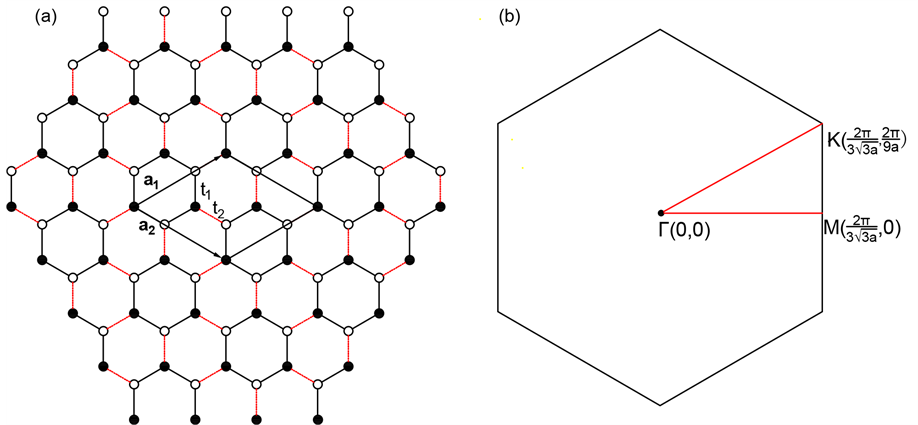
Figure 1. (a) Schematic diagram of the inhomogeneous honeycomb lattice with double-48 sites; (b) Sketch of the first Brillouin zone. In the left panel, filled and open circles represent the A and B sub-lattice sites, a1 and a2 denote the basis vectors of the unit cell, and t1 and t2 stand for the hopping integrals within and between honeycombs
图1. (a) 晶格大小为2 × 48的非均匀二维蜂巢晶格结构示意图;(b) 第一布里渊区示意图。图(a)中黑色实心和空心圆圈代表A和B两套子格子,a1和a2代表原胞基矢,t1和t2代表蜂巢内和蜂巢间的跃迁积分
体系的第一布里渊区由图1(b)表示。运用傅里叶变换我们将电子算符变换到波矢空间
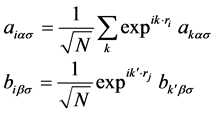 (4)
(4)
这里N为有限晶格上的原胞数。采用紧束缚近似系统的哈密顿量在波矢空间可以描述为:
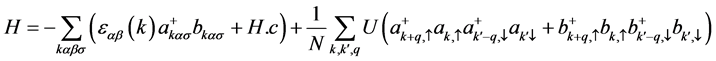 (5)
(5)
上式中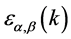 可以写成以下矩阵形式:
可以写成以下矩阵形式:
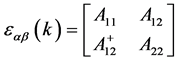 (6)
(6)
其中矩阵中的元素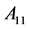 与
与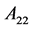 为0矩阵,
为0矩阵,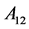 可以描述为:
可以描述为:
 (7)
(7)
在本文的计算中,我们采用了约束路径量子蒙特卡罗方法。它的总体思路是一个多粒子体系的基态波函数可以通过不断投影得到,即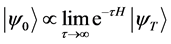 其中
其中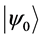 表示体系的基态波函数,
表示体系的基态波函数,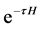 为投影算符,
为投影算符,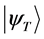 为试探波函数。在以下计算中,试探波函数选取为自由电子对应的波函数,即U=0时哈密顿量给出的单个Slater行列式。为了克服费米子符号问题,我们要求任意一个投影后的Slater行列式
为试探波函数。在以下计算中,试探波函数选取为自由电子对应的波函数,即U=0时哈密顿量给出的单个Slater行列式。为了克服费米子符号问题,我们要求任意一个投影后的Slater行列式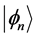 与试探波函数都有正的交叠积分,即
与试探波函数都有正的交叠积分,即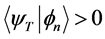 。
。
为了探究非均匀二维蜂巢晶格体中的手征性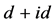 超导特性和磁性特征,我们计算了体系的电子配对关联函数和自旋关联函数
超导特性和磁性特征,我们计算了体系的电子配对关联函数和自旋关联函数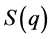 。前者由以下公式定义:
。前者由以下公式定义:
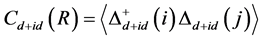 (8)
(8)
其中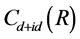 表示相距R的格点
表示相距R的格点 和格点
和格点 之间的电子配对关联函数。电子对算符
之间的电子配对关联函数。电子对算符 写为:
写为:
 (9)
(9)
式子中 表示近邻格点之间的连接,
表示近邻格点之间的连接, 表示手征性
表示手征性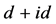 超导态的形状因子,其表达方式如下:
超导态的形状因子,其表达方式如下:
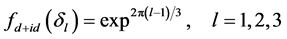 (10)
(10)
超导态的特征可由长程电子配对关联函数的平均值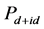 来加以刻画,其定义如下:
来加以刻画,其定义如下:
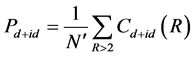 (11)
(11)
这里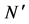 为距离大于2的R数目。系统的磁性可以根据动量空间的自旋关联函数来描述,其计算公式如下:
为距离大于2的R数目。系统的磁性可以根据动量空间的自旋关联函数来描述,其计算公式如下:
 (12)
(12)
其中
 (13)
(13)
3. 计算结果与讨论
在以下的讨论中,我们固定t1和t2其中一个跃迁积分为1.0,并通过改变另一个跃迁积分来调节体系的非均匀性。
图2(a)和图2(c)、图2(b)和图2(d)分别表示在U = 0.2, 0.5,和1.0时对于固定t1 = 1.0或者固定t2 = 1.0,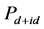 随跃迁积分t2或者t1变化的曲线。图2(a)和图2(b)对应的是晶格大小为
随跃迁积分t2或者t1变化的曲线。图2(a)和图2(b)对应的是晶格大小为 ,电子填充浓度
,电子填充浓度 时得到的计算结果。图2(c)和2(d)对应的是晶格大小为
时得到的计算结果。图2(c)和2(d)对应的是晶格大小为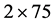 ,电子填充浓度
,电子填充浓度 时得到的计算结果。从图中可以发现,随着跃迁积分t2或t1的减小,
时得到的计算结果。从图中可以发现,随着跃迁积分t2或t1的减小,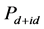 均表现出先增大后减小的规律,图中箭头表示
均表现出先增大后减小的规律,图中箭头表示 取得最大值的位置。同时从图2中还可以发现在位库仑相互作用
取得最大值的位置。同时从图2中还可以发现在位库仑相互作用 的大小对
的大小对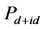 随t2或者t1的变化有很大影响。随着在位库仑相互作用
随t2或者t1的变化有很大影响。随着在位库仑相互作用 的增大,非均匀性对
的增大,非均匀性对 超导态的增强效应被显著抑制。比较图2(a)和图2(b)以及图2(c)和图2(d),可以发现
超导态的增强效应被显著抑制。比较图2(a)和图2(b)以及图2(c)和图2(d),可以发现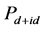 取得最大值对应的t2值均小于相同U值条件下
取得最大值对应的t2值均小于相同U值条件下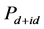 取得最大值对应的t1值。这说明t1和t2引起的非均匀性具有不对称性,而且t2对
取得最大值对应的t1值。这说明t1和t2引起的非均匀性具有不对称性,而且t2对 超导态具有更大的可调控范围。
超导态具有更大的可调控范围。
我们的计算结果说明通过调节二维蜂巢晶格的非均匀性可以增强手征性 超导态,并且弱的在位库仑相互作用更有利于增强手征性
超导态,并且弱的在位库仑相互作用更有利于增强手征性 超导态。在图2中,随着在位库仑相互作用的增加最优化的t2或者t1在逐渐增加,这与T. Ying等人采用有限温度行列式蒙特卡罗方法研究四方晶格得到的计算结果一致 [11] 。同时在不同尺寸的晶格上,
超导态。在图2中,随着在位库仑相互作用的增加最优化的t2或者t1在逐渐增加,这与T. Ying等人采用有限温度行列式蒙特卡罗方法研究四方晶格得到的计算结果一致 [11] 。同时在不同尺寸的晶格上,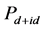 随跃迁积分的变化以及在位库仑相互作用对它的影响都存在相同的规律。该结果说明了我们的计算结果反映了非均匀性引起的内在物理效应。
随跃迁积分的变化以及在位库仑相互作用对它的影响都存在相同的规律。该结果说明了我们的计算结果反映了非均匀性引起的内在物理效应。
为了进一步考察晶格大小引起的有限尺寸效应,我们将晶格尺度进一步扩大,计算了晶格大小为 ,电子填充浓度
,电子填充浓度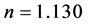 时
时 电子配对关联函数
电子配对关联函数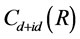 与格点距离
与格点距离 之间的函数关系。图3(a)、图3(c)、图3(e)对应固定t1 = 1.0,U分别取0.2,0.5,以及1.0时,
之间的函数关系。图3(a)、图3(c)、图3(e)对应固定t1 = 1.0,U分别取0.2,0.5,以及1.0时,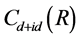 随跃迁积分t2的变化情况。在较小的在位库仑相互作用下,即U = 0.2和U = 0.5时不同格点距离处手征性
随跃迁积分t2的变化情况。在较小的在位库仑相互作用下,即U = 0.2和U = 0.5时不同格点距离处手征性 电子配对关联函数随t2的减小而增加。当在位库仑相互作用增加到U = 1.0时,电子配对关联函数在较远的格点距离
电子配对关联函数随t2的减小而增加。当在位库仑相互作用增加到U = 1.0时,电子配对关联函数在较远的格点距离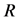 上的数值随跃迁积分t2的减小而减小。这与图2中观察到的不同U值时
上的数值随跃迁积分t2的减小而减小。这与图2中观察到的不同U值时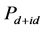 随跃迁积分t2的变化特征相一致。图3(b)、图3(d)、图3(f)对应固定跃迁积分t2 = 1.0,U分别取0.2,0.5,以及1.0时,不同格点距离R处手征性
随跃迁积分t2的变化特征相一致。图3(b)、图3(d)、图3(f)对应固定跃迁积分t2 = 1.0,U分别取0.2,0.5,以及1.0时,不同格点距离R处手征性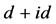 超导态的电子配对关联函数值随t1的变化情况。同样我们发现t1引起的改变与图2所得到的结果相一致。
超导态的电子配对关联函数值随t1的变化情况。同样我们发现t1引起的改变与图2所得到的结果相一致。
综合图2和图3的计算结果表明在弱的在位库仑相互作用下,调节跃迁积分引起的非均匀性可以增强手征性 超导态。为了能够清楚地理解在非均匀二维蜂巢晶格中手征性
超导态。为了能够清楚地理解在非均匀二维蜂巢晶格中手征性 超导态随跃迁积分的变化所表现出的行为,我们将从磁性、态密度以及费米能附近的带宽三个方面进行详细的理论分析。
超导态随跃迁积分的变化所表现出的行为,我们将从磁性、态密度以及费米能附近的带宽三个方面进行详细的理论分析。
在关联电子体系中,磁性对超导配对往往具有重要的影响。我们计算了晶格大小为 ,电子填充浓度n = 1.167,在位库仑相互作用U = 0.2时非均匀蜂巢晶格中的自旋关联函数S(q)。图4(a)和图4(b)分别为固定跃迁积分
,电子填充浓度n = 1.167,在位库仑相互作用U = 0.2时非均匀蜂巢晶格中的自旋关联函数S(q)。图4(a)和图4(b)分别为固定跃迁积分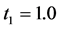 或者
或者 时自旋关联函数S(q)随t2或者t1的变化情况。我们可以发现,自旋关联函数在不同的跃迁积分t2或者t1下沿着第一布里渊区中高对称线的数值几乎没有变化。为了便于对
时自旋关联函数S(q)随t2或者t1的变化情况。我们可以发现,自旋关联函数在不同的跃迁积分t2或者t1下沿着第一布里渊区中高对称线的数值几乎没有变化。为了便于对
比分析,图4中M’和K’分别对应均匀蜂巢晶格中第一布里渊区的边界点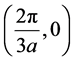 和
和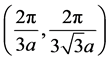 。图4的
。图4的

Figure 2. 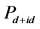 as a function of the inhomogeneity for different lattice sites and on-site Hubbard interactions. (a) The size of lattice is 2 × 48, n = 1.167and t1 = 1.0; (b) The size of lattice is 2 × 48, n = 1.167 and t2 = 1.0; (c) The size of lattice is 2 × 75, n = 1.107 and t1 = 1.0; (d) The size of lattice is 2 × 75, n = 1.107 and t2 = 1.0
as a function of the inhomogeneity for different lattice sites and on-site Hubbard interactions. (a) The size of lattice is 2 × 48, n = 1.167and t1 = 1.0; (b) The size of lattice is 2 × 48, n = 1.167 and t2 = 1.0; (c) The size of lattice is 2 × 75, n = 1.107 and t1 = 1.0; (d) The size of lattice is 2 × 75, n = 1.107 and t2 = 1.0
图2. 不同晶格尺度和不同在位库仑相互作用下 随非均匀度的变化关系。(a) 晶格大小为2 × 48,n = 1.167以及 t1 = 1.0;(b) 晶格大小为2 × 48,n = 1.167以及t2 = 1.0;(c) 晶格大小为2 × 75,n = 1.107以及t1 = 1.0;(d) 晶格大小为2 × 75,n = 1.107以及t2 = 1.0
随非均匀度的变化关系。(a) 晶格大小为2 × 48,n = 1.167以及 t1 = 1.0;(b) 晶格大小为2 × 48,n = 1.167以及t2 = 1.0;(c) 晶格大小为2 × 75,n = 1.107以及t1 = 1.0;(d) 晶格大小为2 × 75,n = 1.107以及t2 = 1.0

Figure 3. Pairng correlation function Cd + id(R) of the chiral d + id superconducting state as a function of distance for different hopping integral t2 or t1 on the 2 × 108 lattice and n = 1.130. (a) t1 = 1.0, U = 0.2; (b) t2 = 1.0, U = 0.2; (c) t1 = 1.0, U = 0.5; (d) t2 = 1.0, U = 0.5; (e) t1 = 1.0, U = 1.0; (f) t2 = 1.0, U = 1.0
图3. 晶格尺度为2 × 108,电子填充浓度n = 1.130时不同的跃迁积分t2或者 t1下手征性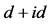 超导态的配对关联函数随格点距离的变化关系。(a) t1 = 1.0,U = 0.2;(b) t2 = 1.0,U = 0.2;(c) t1 = 1.0,U = 0.5;(d) t2 = 1.0,U = 0.5;(e) t1 = 1.0,U = 1.0;(f) t2 = 1.0,U = 1.0
超导态的配对关联函数随格点距离的变化关系。(a) t1 = 1.0,U = 0.2;(b) t2 = 1.0,U = 0.2;(c) t1 = 1.0,U = 0.5;(d) t2 = 1.0,U = 0.5;(e) t1 = 1.0,U = 1.0;(f) t2 = 1.0,U = 1.0
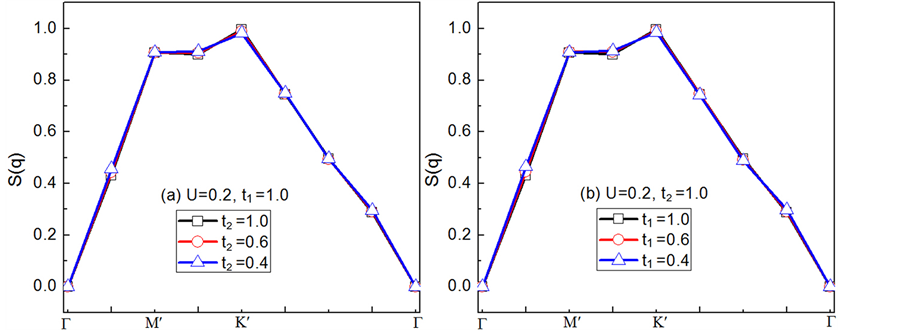
Figure 4. Spin correlation S(q) on the 2 × 48 lattice along the high symmetric lines in the first Brillouin zone at n = 1.167 and U = 0.2. (a) t1 = 1.0; (b) t2 = 1.0
图4. 晶格大小为2 × 48,电子填充浓度n = 1.167以及在位库仑相互作用i = 0.2时自旋关联函数在第一布里渊区高对称线上随t2或者t1的数值变化。(a) t1 = 1.0;(b) t2 = 1.0
结果说明了跃迁积分的改变几乎不会影响体系的磁性,因而在非均匀蜂巢晶格中磁性并不是影响手征性 超导态的主要因素。其它参数情况下的磁性变化特征与图4的情况完全一致。
超导态的主要因素。其它参数情况下的磁性变化特征与图4的情况完全一致。
鉴于费米能附近的电子状态数对超导态的强弱有着重要的影响,我们计算了非均匀蜂巢晶格体系的态密度。图5(a)~图5(d)表示固定跃迁积分t1 = 1.0,t2分别为1.0、0.8、0.4、以及0.2时的电子态密度分布图。图中箭头表示电子填充浓度 时相应费米能的位置,DOS代表费米能处的电子状态数。我们从图5中可以发现随着跃迁积分t2的减小,费米能附近的电子状态数不断增加,t2 = 0.2时对应的电子状态数比t2 = 1.0时的值增加了4.6倍。这一变化趋势与图2和图3中观察到的
时相应费米能的位置,DOS代表费米能处的电子状态数。我们从图5中可以发现随着跃迁积分t2的减小,费米能附近的电子状态数不断增加,t2 = 0.2时对应的电子状态数比t2 = 1.0时的值增加了4.6倍。这一变化趋势与图2和图3中观察到的 电子配对关联函数随t2的减小而增加这一行为相一致。这个结果说明,费米能附近电子状态数的增加有利于增强手征性
电子配对关联函数随t2的减小而增加这一行为相一致。这个结果说明,费米能附近电子状态数的增加有利于增强手征性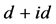 超导态。
超导态。
同样,我们也计算了固定t2 = 1.0,t1分别为1.0、0.8、0.4、以及0.2时的电子态密度分布图,如图6所示。我们同样发现,随着跃迁积分t1的减小,费米能附近的电子状态数不断增加。在t1 = 0.2时对应的电子状态数比t1 = 1.0时的值增加了15倍。对比图5中的计算结果,理论上减小跃迁积分t1更有利于增强手征性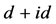 超导态,因为减小t1时费米能附近的电子状态数相比于减小t2时费米能附近的电子状态数增加更快。然而这与我们在图2中观察到的结果并不一致,说明还有其它因素对
超导态,因为减小t1时费米能附近的电子状态数相比于减小t2时费米能附近的电子状态数增加更快。然而这与我们在图2中观察到的结果并不一致,说明还有其它因素对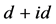 超导态具有重要的影响。从图5和图6中可以发现在费米能处的带宽随跃迁积分的减小表现出逐渐减小的趋势。这说明电子的有效在位库仑相互作用Ueff (由U和带宽之间的比值来表征)在逐渐增大,从而会抑制手征性
超导态具有重要的影响。从图5和图6中可以发现在费米能处的带宽随跃迁积分的减小表现出逐渐减小的趋势。这说明电子的有效在位库仑相互作用Ueff (由U和带宽之间的比值来表征)在逐渐增大,从而会抑制手征性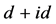 超导态。在位库仑相互作用对
超导态。在位库仑相互作用对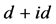 超导的抑制效应已经在我们的前期工作 [16] 中明显表现出来。为了说明我们的结果,下面我们对带宽进行了更详细的定量分析。
超导的抑制效应已经在我们的前期工作 [16] 中明显表现出来。为了说明我们的结果,下面我们对带宽进行了更详细的定量分析。
图7(a)~图7(d)表示是t1 = 1.0, t2,分别为1.0,0.8,0.4,0.2时,蜂巢晶格体系的电子能带结构图。图中绿色线对应 的费米能所在位置。费米能处的带宽可以通过计算靠近费米能附近的能带底和能带顶之间的距离获得,其值由图中W给出。可以看到,随着跃迁积分t2的减小费米能位置的带宽不断减小。相似的结果也在固定t2 = 1.0而改变t1时被观察到,如图8所示。对比图7和图8,我们发现图8(d)中带宽降低为0.3135,它小于图7(d)中的带宽0.4,说明改变跃迁积分t1对带宽的影响更为剧烈。窄的带宽将使得体系有效在位库仑相互作用Ueff大幅度增加,从而强烈抑制了手征性
的费米能所在位置。费米能处的带宽可以通过计算靠近费米能附近的能带底和能带顶之间的距离获得,其值由图中W给出。可以看到,随着跃迁积分t2的减小费米能位置的带宽不断减小。相似的结果也在固定t2 = 1.0而改变t1时被观察到,如图8所示。对比图7和图8,我们发现图8(d)中带宽降低为0.3135,它小于图7(d)中的带宽0.4,说明改变跃迁积分t1对带宽的影响更为剧烈。窄的带宽将使得体系有效在位库仑相互作用Ueff大幅度增加,从而强烈抑制了手征性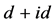 超导态。这个结果为解释图2中观察到的电子配对关联函数
超导态。这个结果为解释图2中观察到的电子配对关联函数 在非均匀度较大时反而降低的行为提供了理论依据。
在非均匀度较大时反而降低的行为提供了理论依据。
考虑到费米能位置的电子状态数和带宽对手征性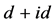 超导态的影响随蜂巢晶格非均匀度变化时的
超导态的影响随蜂巢晶格非均匀度变化时的
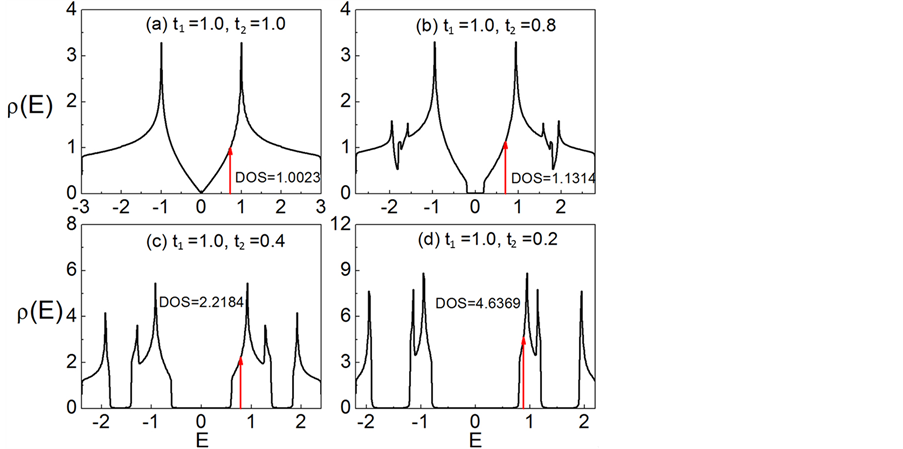
Figure 5. Density of states for different t2 at the fixed t1 = 1.0. (a)-(d) correspond to t2 = 1.0, 0.8, 0.4, and 0.2, respectively
图5. 固定t1 = 1.0时不用的跃迁积分t2下的态密度。(a)~(d)分别对应t2 = 1.0,0.8,0.4,以及0.2
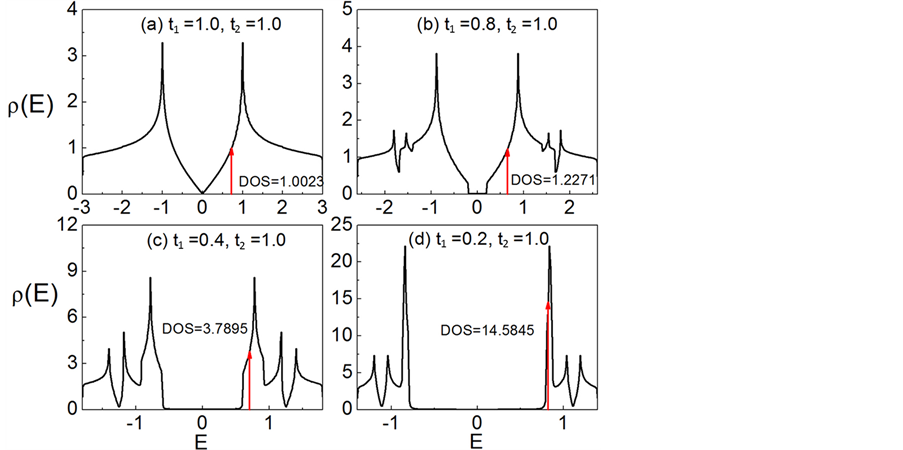
Figure 6. Density of states for different t1 at the fixed t2 = 1.0. (a)-(d) correspond to t1 = 1.0, 0.8, 0.4, and 0.2, respectively
图6. 固定t2 = 1.0时不用的跃迁积分t1下的态密度。(a)~(d)分别对应t1 = 1.0,0.8,0.4,以及0.2
相互竞争关系,我们在图9中详细比较了费米能位置的电子状态数与有效在位库仑相互作用随跃迁积分的变化趋势。图9(a)和图9(b)表示电子填充浓度n = 1.107时,分别固定t1 = 1.0或t2 = 1.0得到的费米能位置的电子状态数和有效在位库仑相互作用Ueff随跃迁积分t2或t1的变化行为。黑色点线代表Ueff = 0.5,对应于中等关联强度;黑色虚线表示Ueff = 1.0,反映体系处进入强关联状态。图9显示随着跃迁积分t2或t1的减小,费米能位置的电子状态数不断增加,从而有利于增强手征性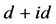 超导态。另一方面,有
超导态。另一方面,有
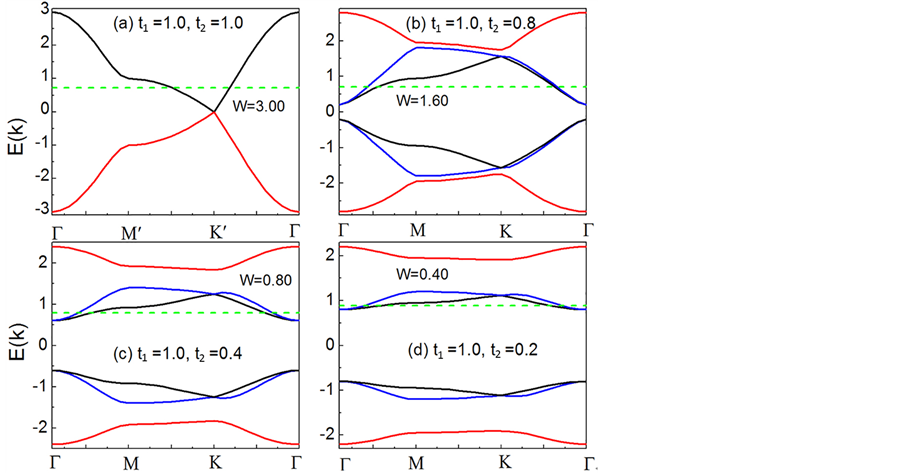
Figure 7. Energy dispersion along the high symmetric lines for different t2 at the fixed t1 = 1.0. (a)-(d) t2 = 1.0, 0.8, 0.4, and 0.2, respectively
图7. 固定t1 = 1.0时不同的跃迁积分t2下沿着高对称性线的能量色散关系。(a)~(d)分别对应t2 = 1.0,0.8,0.4,以及0.2

Figure 8. Energy dispersion along the high symmetric lines for different t1 at the fixed t2 = 1.0. (a)-(d) t1 = 1.0, 0.8, 0.4, and 0.2, respectively
图8. 固定t2 = 1.0时不同的跃迁积分t1下沿着高对称性线的能量色散关系。(a)~(d)分别对应t1 = 1.0,0.8,0.4,以及0.2
效在位库仑相互作用也在逐渐增加,表现为抑制手征性 超导态的增强效应。两者之间的相互竞争对手征性
超导态的增强效应。两者之间的相互竞争对手征性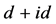 超导态随非均匀度的演化行为起着关键作用。
超导态随非均匀度的演化行为起着关键作用。
由图9中还可以看出,在较小的在位库仑相互作用下U = 0.2下随着跃迁积分的减小体系存在从弱关联过渡到中等关联的转变,在较大的在位库仑相互作用U = 0.5以及U = 1.0下随着跃迁积分的减小体系
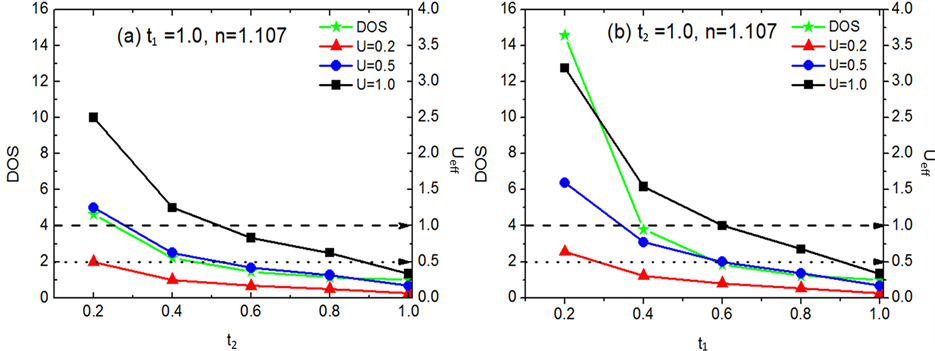
Figure 9. Density of states at the Fermi level and effective on site Hubbard interaction Ueff as a function of t1 or t2 at n = 1.107. (a) and (b) correspond to t1 = 1.0 and t2 = 1.0, respectively
图9. 电子填充浓度n = 1.107时费米能位置的电子状态数与有效库仑相互作用Ueff随跃迁积分的变化关系。(a)和(b)分别对应t1 = 1.0和t2 = 1.0
存在从弱关联过渡到中等关联再过渡到强关联的转变。对比图9(a)和图9(b),我们发现费米能位置的电子状态数以及有效在位库仑相互作用的数值随跃迁积分t1 (固定t2 = 1.0)的减小而增加的幅度比随跃迁积分t2 (固定t1 = 1.0)的减小而增加的幅度更加显著,然而相应的手征性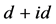 超导态的增强效应却并不显著。这个结果说明了有效在位库仑相互作用对手征性
超导态的增强效应却并不显著。这个结果说明了有效在位库仑相互作用对手征性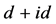 超导态的抑制行为比费米能位置电子状态数的增加引起的增强行为更加显著。结合图2和图9的结果可以发现,当Ueff处于弱关联和中等关联区时,手征性
超导态的抑制行为比费米能位置电子状态数的增加引起的增强行为更加显著。结合图2和图9的结果可以发现,当Ueff处于弱关联和中等关联区时,手征性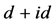 超导态受非均匀性的增强,而当接近或进入强关联区,手征性
超导态受非均匀性的增强,而当接近或进入强关联区,手征性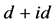 超导态反而被抑制。
超导态反而被抑制。
4. 结论
在本文中,基于哈伯德模型并采用约束路径量子蒙特卡罗方法,我们系统地研究了手征性 超导态随二维蜂巢晶格中非均匀度的变化特性。非均匀度由蜂巢内和蜂巢间的跃迁积分来加以调控。我们的研究结果表明当在位库仑相互作用U很小时,
超导态随二维蜂巢晶格中非均匀度的变化特性。非均匀度由蜂巢内和蜂巢间的跃迁积分来加以调控。我们的研究结果表明当在位库仑相互作用U很小时, 电子配对关联函数随着非均匀度的增加先明显增大而后逐渐减弱。即当取合适的
电子配对关联函数随着非均匀度的增加先明显增大而后逐渐减弱。即当取合适的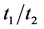 (或者
(或者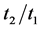 )比值时,
)比值时,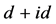 电子配对关联函数存在最大值,该结果表明在较小U的情况下存在一个最佳的非均匀度,使得体系具有最强的手征性
电子配对关联函数存在最大值,该结果表明在较小U的情况下存在一个最佳的非均匀度,使得体系具有最强的手征性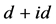 超导态。我们还发现在非均匀的蜂巢晶格中,电子状态数与有效在位库仑相互作用均随非均匀度的增加而逐渐增大,但两者对
超导态。我们还发现在非均匀的蜂巢晶格中,电子状态数与有效在位库仑相互作用均随非均匀度的增加而逐渐增大,但两者对 超导的影响却存在竞争关系:费米能位置电子状态数的增加将会有利于增强
超导的影响却存在竞争关系:费米能位置电子状态数的增加将会有利于增强 超导态,而有效在位库仑相互作用的增加将会抑制
超导态,而有效在位库仑相互作用的增加将会抑制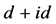 超导态。具体表现在费米面位置电子状态数的增加有利于准粒子浓度的增加,有效在位库伦相互作用的增加抑制了准粒子浓度的增加。因此两者之间的竞争关系合理地解释了
超导态。具体表现在费米面位置电子状态数的增加有利于准粒子浓度的增加,有效在位库伦相互作用的增加抑制了准粒子浓度的增加。因此两者之间的竞争关系合理地解释了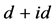 超导态随非均匀度的演化特征。本文的研究结果对量子调控二维蜂巢晶格中的超导态提供了重要的理论思路。
超导态随非均匀度的演化特征。本文的研究结果对量子调控二维蜂巢晶格中的超导态提供了重要的理论思路。
致谢
感谢湖北大学物理与电子科学院杨辉博士的深入交流与讨论。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(批准号:11674087,11574076)资助的课题。