1. 引言
突发事件因其爆发前兆不明显、破坏性强及存在潜在次生衍生危害等复杂性,社会公众对其真伪度、可靠度在短期内难以明辨,更多地趋于对突发事件表现为一定程度的负面性认定 [1] ,极易造成突发事件信息在毫无预期的情况下实现叠加、组合等多重耦合交互,直接影响经济社会安定和稳定,如:传染病疫情爆发导致的民众“逃城”、舆论和谣言扩散形成的百姓“打砸抢”、金融危机传导引起的股价“同涨共跌”等现象。因此,研究突发事件信息传播过程中的同步化内在机制,把握其内在演变规律,对预测预警突发事件信息扩散具有重要作用。
2. 研究现状综述
Daley和Kendall提出的谣言传播D-K系列模型 [2] [3] ,为定量研究谣言传播提供了理论基础。此后,Fiona和Linda [4] ,Kazuki等 [5] 对D-K模型进行了不同程度的拓展和创新。近年来,国内外学者重点围绕运用SIR、SIS和SIRS等传染病模型研究突发事件信息传播动力学特性,成果显著 [6] [7] [8] [9] 。针对突发事件信息传播过程中的同步化问题,学术界针同样进行了探索性研究。Prashant [10] 研究了小世界网络中基于SIRS模型的传染病疫情突发事件同步传播行为。Moreno等 [11] 基于无标度网络研究了交通系统堵塞容忍限度。Alessandro等 [12] 基于OCR模型研究社会舆论突发事件在全耦合网络上的同步传播现象。Li和Stewart [13] 基于40个国家在1990年到2001年间的股票收益数据,对股价股价“同涨共跌”现象进行了实证分析。卞曰瑭等 [14] 基于投资者行为策略的近邻择优视角构建投资者羊群行为演化模型。何敏华等 [15] 基于BA无标度网络研究公共突发事件舆论和网络结构耦合关联的自适应论演化模型。
然而,考虑到现实中信息传播主体间的耦合关联,无论在全局还是局部都极易呈现出不同程度的非均衡性 [1] ,其对突发事件信息传播过程具有显著影响。突发事件爆发后,信息传播主体因对外部信息难以有效获知和处理,必然存在着带有盲目或冲动心态下的行为集聚和跟从,形成复杂网络中的簇结构。Liu和Hu [16] 研究了带有簇结构的复杂网络上流行病传播问题。Yan等 [17] 分析了含有簇结构的无标度网络的群落结构强度对疾病扩散同步行为的影响。Chen等 [18] 基于SIS分析了流行病在具有簇结构网络上的传播过程,发现重叠的两个簇中共有节点在疾病的传播中有着桥梁作用。Liu等 [19] 基于社会公众依赖的互联网渠道,研究了2011~2014年间关于渤海湾漏油事件的信息扩散中带有模块化特征的网络结构与热点信息扩散趋同中的关联影响。程寅钊等 [20] 通过建立具有簇结构的舆论传播模型,分析了在不同簇公关能力和观点领袖作用下统一意见的演进趋势引导作用。
综上所示,国内外学者对突发事件信息传播过程中的同步化问题,尤其对具有簇结构网络的突发事件信息同步传播特征进行了大量研究,然而已有成果大多以外生性网络和传染病模型相结合进行研究,具有一定的局限性。考虑到社会公众间的耦合关联和面对特定突发事件信息认知、处理的异质性,本文以“H7N9”突发事件为研究对象,运用基于熵的簇结构发现算法,系统分析此类突发事件信息传播网络簇结构特征;其次,基于观点变化率(OCR)模型 [21] ,构建簇结构网络的突发事件信息同步传播演化模型,通过模拟仿真研判簇结构网络的突发事件信息同步传播演化机制和规律,为政府提升应对突发事件管理水平和增强社会综合治理能力提供理论支撑。
3. 突发事件信息传播簇结构网络
突发事件爆发后,社会公众根据各自的主观判断和意愿,进行信息传播和扩散,从而演变为信息传播网络。以“H7N9”事件信息传播网络为基础,运用基于熵的簇结构发现算法,理论分析突发事件信息传播簇结构网络拓扑特征。
定义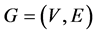 为突发事件信息传播网络,其中:V为网络节点集合,E为网络连边集合。假设网络有N个节点,其中:子簇数为M,记为
为突发事件信息传播网络,其中:V为网络节点集合,E为网络连边集合。假设网络有N个节点,其中:子簇数为M,记为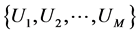 ;初始时刻每个簇内节点数为
;初始时刻每个簇内节点数为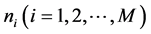 ,且有:
,且有:
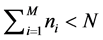
由此构建突发事件传播网络形成机制:(1) 簇内节点间以概率p连线,任意簇间节点以概率q连线,则簇i内的连边数为 ,簇i和簇j间的连边数是
,簇i和簇j间的连边数是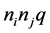 ,由此获得网络期初的总边数:
,由此获得网络期初的总边数:
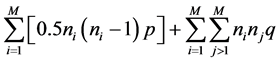
(2) 在网络形成中,每个时间步加入一个节点,假设其连接内部子簇节点个数为m,连接外部子簇节点个数为m’,且与每个簇内节点间以概率α增加连边,任意两个簇间的节点以概率β连边;(3) 经过t个时间步,当满足:
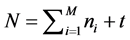
算法终止,生成带有簇结构的信息传播网络,输出网络邻接矩阵。同时,定义序参量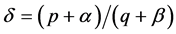 ,表示所生成传播网络的模块化程度。由此,对于具有簇结构的传播网络应满足
,表示所生成传播网络的模块化程度。由此,对于具有簇结构的传播网络应满足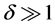 ;若
;若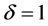 ,则所形成传络将演变为一般随机网络。
,则所形成传络将演变为一般随机网络。
基于上述网络形成机制,运用模拟仿真方法,理论构建具有簇结构的复杂网络,并分析其拓扑结构特征。实验参数设定为:网络规模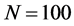 、初始网络中每个簇含有节点数
、初始网络中每个簇含有节点数 、网络簇个数
、网络簇个数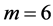 、随机连接概率
、随机连接概率 。模拟仿真实验形成的突发事件信息传播网络拓扑结构如图1所示,图中任意两节点之间若存在连边说明相互间存在信息交互。
。模拟仿真实验形成的突发事件信息传播网络拓扑结构如图1所示,图中任意两节点之间若存在连边说明相互间存在信息交互。
针对形成网络的邻接矩阵,计算网络平均路径长度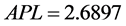 、聚类系数
、聚类系数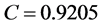 、平均度
、平均度

Figure 1. Cluster topology structure network
图1. 簇结构网络拓扑结构图
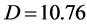 ,具体分布结构如图2和图3所示。由图可见,生成的簇结构网络在局部范围内呈现出度分布的幂律性,即突发事件信息传播网络结构具有显著的簇结构异质性特征。
,具体分布结构如图2和图3所示。由图可见,生成的簇结构网络在局部范围内呈现出度分布的幂律性,即突发事件信息传播网络结构具有显著的簇结构异质性特征。
基于上述分析,为更清晰识别簇结构网络的模块性采用Newman [22] 提出的算法对构建的网络进行聚类分析,通过不断合并网络节点来极大化网络模块评价Q函数,以获得网络簇结构的最佳划分。从单个节点组成的N组节点开始,在每一次迭代中合并存在连边的节点,而后能够让Q值增加最大或减少最小的两组节点,直至网络中仅剩单一子簇为止,最终输出网络簇的层次关系树状图,如图4。由图4可见,图中网络被分成6个子簇,这与网络构建期初设定的簇个数一致,表明理论构建的突发事件信簇结构息传播网络与实际传播网络结构基本一致,为后续研究奠定了理论基础。
4. 突发事件信息同步传播机理及演化模型
基于上述构建的突发事件信息传播簇结构网络和信息同步传播演化模型,为进一步分析信息传播过程中同步化现象的演变规律,采用模拟仿真的方法分析簇结构网络以及传播主体观点变化率等关键参数对信息同步传播过程的影响。
4.1. 网络耦合强度影响分析
现实中传播主体的观点倾向性难以把握,假设ω服从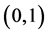 正态分布,即
正态分布,即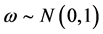 ,在模拟实验中随机产生,形成
,在模拟实验中随机产生,形成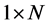 维矩阵。
维矩阵。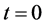 时刻,传播网络中任意个体观点
时刻,传播网络中任意个体观点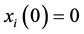 ,且假定传播主体观点是一个连续随机变量,服从
,且假定传播主体观点是一个连续随机变量,服从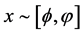 均匀分布。其他实验参数设置如下:网络规模
均匀分布。其他实验参数设置如下:网络规模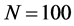 、节点连接外部簇概率
、节点连接外部簇概率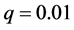 、耦合强度
、耦合强度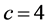 、有界信任水平
、有界信任水平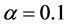 、仿真时间步
、仿真时间步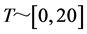 、实验次数为5次,最终根据实验结果取平均,具体实验结果如图5、图6和图7所示。
、实验次数为5次,最终根据实验结果取平均,具体实验结果如图5、图6和图7所示。
由图5(a),初始网络中传播主体观点较为接近,但随时间推移,网络中传播主体的观点逐渐分化成6类,与传播网络中的6个簇结构相对应;传播网络中簇内信息传播主体的行为趋于同步,而簇间却很难实现完全同步,即整体上表现为信息传播网络行为的局部同步。由图5(b),传播网络中传播主体的观点变化率经过一段时间波动后最终趋于各自的观点变化率(OCR),并没有趋于统一的观点变化率。可见,在上述参数下,突发事件信息传播网络很难实现完全同步。
图6对比分析了突发事件爆发始末两个时间段的信息传播主体观点分布情况。图6(a1)和图6(a2)显示了突发事件爆发后传播网络中各子簇的观点从开始的分散传播到最终实现各子簇内部的一致性趋同。图6(b1)和图6(b2)描述了传播主体的观点变化率会在一定概率范围内改变,但簇内主体观点变化率没有趋于

Figure 2. The size distribution of nodes in the network
图2. 网络中各节点度的大小分布图
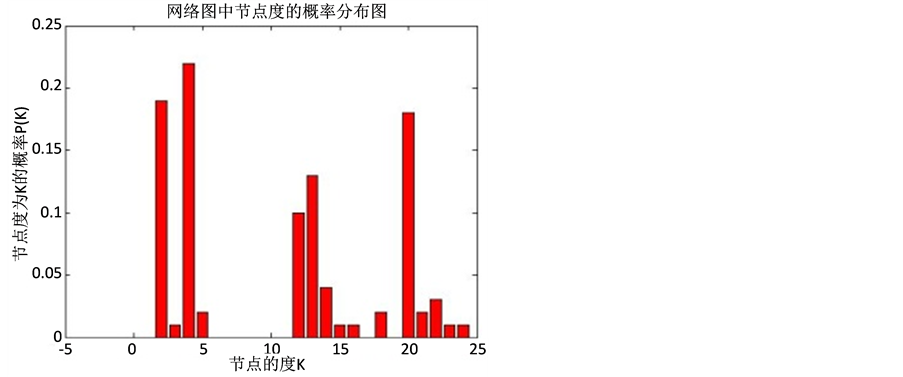
Figure 3. The probability distribution of nodes in the network
图3. 网络中节点度的概率分布

Figure 4. Cluster network structure partition tree diagram of emergency information dissemination
图4. 突发事件信息传播网络簇结构划分树状图

 (a) 传播主体观点随时间变化 (b) 传播主体观点变化率
(a) 传播主体观点随时间变化 (b) 传播主体观点变化率
Figure 5. The change rate of information communication subject's view with time
图5. 信息传播主体观点变化率随时间演变
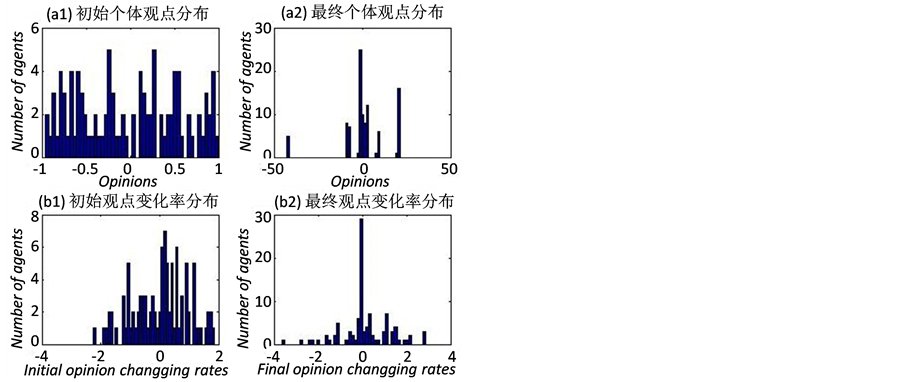
Figure 6. The distribution of information dissemination subjects before and after the outbreak
图6. 突发事件爆发前后信息传播主体观点分布
Figure 7. Emergency event information communication net- work synchronization order parameter change
图7. 突发事件信息传播网络同步序参量变化
完全同步。图7描述了簇结构网络下突发事件信息同步传播程度的序参量变化情况。由图可见,在突发事件爆发后的期初阶段,序参量迅速增加,之后立即处于波动状态;R值较小说明信息传播系统中各主体传播行为没有形成内在的一致性趋同。
在上述实验参数设定的基础上,分别研究 和
和 时传播主体观点变化特征以及传播网络同步行为演变过程,实验结果如图8和图9所示。
时传播主体观点变化特征以及传播网络同步行为演变过程,实验结果如图8和图9所示。
图8描述了网络耦合强度 时突发事件信息同步传播及演化过程。由图8(a)可见,随着网络耦合强度增加,网络节点相互作用力增大,传播主体的观点开始往同一方向聚集,但由于网络的簇结构特征使得网络很难达到完全一致性。但由图8(b)和图8(d)可见,传播主体的观点变化率在经过一段时间演变后最终趋于一致,即实现全局相位同步。由图8(c)所示,传播网络同步序参量R值比
时突发事件信息同步传播及演化过程。由图8(a)可见,随着网络耦合强度增加,网络节点相互作用力增大,传播主体的观点开始往同一方向聚集,但由于网络的簇结构特征使得网络很难达到完全一致性。但由图8(b)和图8(d)可见,传播主体的观点变化率在经过一段时间演变后最终趋于一致,即实现全局相位同步。由图8(c)所示,传播网络同步序参量R值比 时明显增大,说明此时传播网络中绝大部分节点都处于一致性状态,系统比较有序。
时明显增大,说明此时传播网络中绝大部分节点都处于一致性状态,系统比较有序。
图9描述了网络耦合强度 时的突发事件信息传播主体观点演变情况。由图可见,当进一步增强网络传播主体间的耦合作用时,各传播主体观点的改变速率极易趋同。图9(b)中的序参量R值迅速增加并趋于稳定,其稳态值明显大于网络耦合强度
时的突发事件信息传播主体观点演变情况。由图可见,当进一步增强网络传播主体间的耦合作用时,各传播主体观点的改变速率极易趋同。图9(b)中的序参量R值迅速增加并趋于稳定,其稳态值明显大于网络耦合强度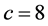 时的值,说明此时信息传播网络系统具有更高的同步化能力。
时的值,说明此时信息传播网络系统具有更高的同步化能力。
由上可见,具有簇结构的突发事件信息传播网络中传播主体的观点变化以及主体观点变化率的同步水平与网络耦合强度呈现出一定程度的正比关系。在网络规模、子簇个数、有界信任水平等参数不变条件下,增加网络耦合强度,有利于提高网络的同步能力;降低耦合强度,有利于降低网络同步能力。
4.2. 网络拓扑结构影响分析
具有簇结构信息传播网络对信息传播过程具有直接作用。因此,在上述研究的基础上,进一步研究信息传播网络的簇结构以及簇内和簇间连接数的差异性对信息传播同步化过程的影响。在其他参数不变的条件下,通过改变传播网络规模来比较信息同步传播过程特征。实验参数设置如下:网络规模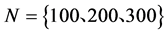 、节点连接外部簇概率
、节点连接外部簇概率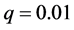 、耦合强度
、耦合强度 、子簇个数
、子簇个数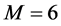 、有界信任水平
、有界信任水平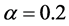 、仿真时间步
、仿真时间步 、试验次数5次,最终根据实验结果取平均,实验结果如图10、图11和图12所示。
、试验次数5次,最终根据实验结果取平均,实验结果如图10、图11和图12所示。
图10描述了三种不同网络规模水平下信息同步传播行为的演进过程。由图10,三种网络规模的序参量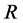 值在初始时间段的变化基本相同,随后网络规模
值在初始时间段的变化基本相同,随后网络规模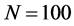 的序参量R值迅速上升,很快达到最高点并趋于稳定;网络规模
的序参量R值迅速上升,很快达到最高点并趋于稳定;网络规模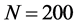 和
和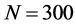 的网络也随后逐渐趋于稳定。整体上,三种不同网络规模下的序参量R值呈现
的网络也随后逐渐趋于稳定。整体上,三种不同网络规模下的序参量R值呈现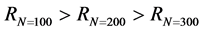 。由此可见,网络规模影响信息传播同步化过程;随着传播网络规模增大,网络不稳定性增强,任一节点对非邻居节点的间接影响力也逐渐减弱,导致信息传播网络的同步化水平趋弱。
。由此可见,网络规模影响信息传播同步化过程;随着传播网络规模增大,网络不稳定性增强,任一节点对非邻居节点的间接影响力也逐渐减弱,导致信息传播网络的同步化水平趋弱。
考虑到信息传播网络的簇结构特征,在上述分析的基础上,通过改变簇网络中子簇的数量和簇间节点连接概率,分别设定子簇个数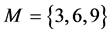 和簇间节点连接概率
和簇间节点连接概率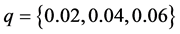 ,模拟仿真网络规模
,模拟仿真网络规模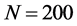 条件下上述两类因素对突发事件信息同步传播过程的影响,如图11和图12所示。
条件下上述两类因素对突发事件信息同步传播过程的影响,如图11和图12所示。
由图11可见,随着传播网络中子簇个数增加,信息传播同步能力逐渐减弱,即 。但当网络规模不变,子簇个数超过某一临界时,信息传播网络的整体同步能力反而有一定程度的提升,即
。但当网络规模不变,子簇个数超过某一临界时,信息传播网络的整体同步能力反而有一定程度的提升,即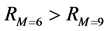 。究其原因在于,过多的细分子簇,使得网络模块性减弱,从而导致网络整体和簇内部的同步传播行为趋于一致。
。究其原因在于,过多的细分子簇,使得网络模块性减弱,从而导致网络整体和簇内部的同步传播行为趋于一致。
由图12,增加网络簇间连接概率可以提高网络的整体同步化水平,具有簇结构的突发事件信息传播网络的整体同步能力随着簇间连接数的增加而逐渐增大,即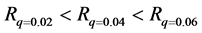 。
。

 (a) 传播主体观点变化演变 (b) 传播主体观点变化率
(a) 传播主体观点变化演变 (b) 传播主体观点变化率
 (c) 网络同步化序参量随时间变化 (d) 传播主体最终观点变化率分布
(c) 网络同步化序参量随时间变化 (d) 传播主体最终观点变化率分布
Figure 8. Evolution of information synchronous dissemination on emergency events (c = 8)
图8. 簇结构网络的突发事件信息同步传播及演化过程(c = 8)

 (a) 个体观点变化率 (b) 网络同步化序参量随时间变化
(a) 个体观点变化率 (b) 网络同步化序参量随时间变化
Figure 9. Evolution of information synchronous dissemination on emergency events (c = 10)
图9. 簇结构网络的突发事件信息同步传播及演化过程(c = 10)

Figure 10. Evolution of information synchronous dissemination in three different networks
图10. 三种不同网络规模下信息同步传播演化过程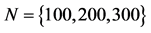
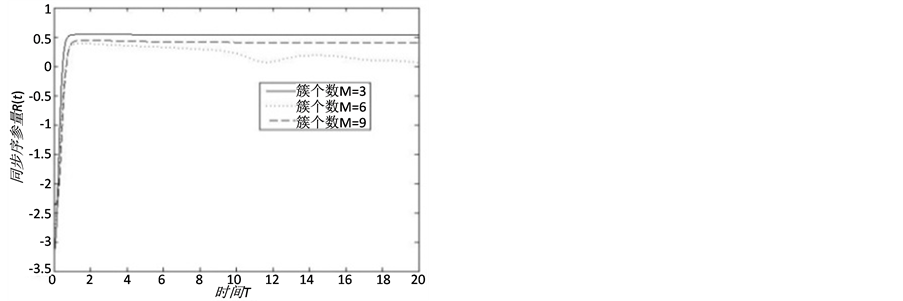
Figure 11. The effect from different sub cluster size
图11. 不同子簇规模的影响效应分析
Figure 12. The effect from the probability of different clusters
图12. 不同簇间连接概率的影响
4.3. 主体信任水平影响分析
传播主体间的信任水平一定程度上也反映了传播主体间的影响力,文中采用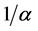 来衡量传播主体间的有界信任水平,分析其对信息传播同步行为的影响。实验参数设置如下:网络规模
来衡量传播主体间的有界信任水平,分析其对信息传播同步行为的影响。实验参数设置如下:网络规模 、连接外部簇的概率
、连接外部簇的概率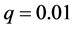 、耦合强度
、耦合强度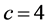 、仿真时间
、仿真时间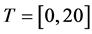 、分别取信任水平测度变量
、分别取信任水平测度变量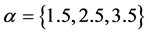 ,实验结果如图13所示。
,实验结果如图13所示。
由图13,不同信任水平下信息传播同步化过程呈现出一定程度的差异性。当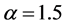 时,传播网络中各主体的信息传播状态波动性较小,传播网络的同步化能力较强;随着
时,传播网络中各主体的信息传播状态波动性较小,传播网络的同步化能力较强;随着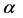 值增大,传播主体间的信任水平逐渐降低,网络的同步化能力逐渐减弱。实验结果表明,现实社会网络中个体信任水平较高时,网络中信息传播主体的观点容易趋于一致,网络同步化性也较强。这也说明,具有相同文化背景、从事相似职业或有着相近受教育程度主体间的信任水平较高,这导致对突发事件信息传播容易形成一致性意见,能够有效避免虚假信息在群体间的扩散。因而,针对具有簇结构网络特征的突发事件信息传播问题,同一簇内节点之间更加容易趋于同步,不同簇之间的同步化能力相对较弱。
值增大,传播主体间的信任水平逐渐降低,网络的同步化能力逐渐减弱。实验结果表明,现实社会网络中个体信任水平较高时,网络中信息传播主体的观点容易趋于一致,网络同步化性也较强。这也说明,具有相同文化背景、从事相似职业或有着相近受教育程度主体间的信任水平较高,这导致对突发事件信息传播容易形成一致性意见,能够有效避免虚假信息在群体间的扩散。因而,针对具有簇结构网络特征的突发事件信息传播问题,同一簇内节点之间更加容易趋于同步,不同簇之间的同步化能力相对较弱。
4.4. 主体初始观点影响分析
考虑到突发事件爆发初期各传播主体初始观点间的差异性,对信息传播过程必然产生不同程度的影响,为此研究簇结构网络中传播主体的初始观点分布对信息同步传播的影响。以上述构建的网络结构和
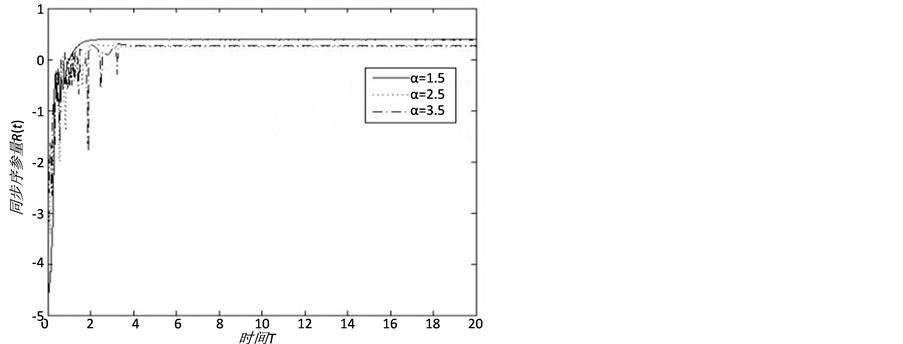
Figure 13. A comparative analysis of the level of synchronization of information transmission, when 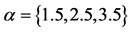
图13. 不同信任水平下突发事件信息传播同步化水平对比分析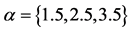
信息传播演化模型为基础,设置实验参数如下:网络规模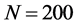 、连接外部簇的概率
、连接外部簇的概率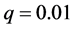 、子簇个数
、子簇个数 、耦合强度
、耦合强度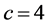 、个体信任水平
、个体信任水平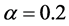 、仿真时间
、仿真时间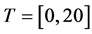 。实验初始随机选择3个子簇并设置其观点初始值为
。实验初始随机选择3个子簇并设置其观点初始值为 内的随机数,设置剩下3个子簇的观点初始值为
内的随机数,设置剩下3个子簇的观点初始值为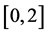 内的随机数。若传播主体的初始观点值被随机设定为−2或2,则假定该传播主体为所属簇中的观点领袖,则其在网络中的权重较为明显。实验结果如图14和图15所示。
内的随机数。若传播主体的初始观点值被随机设定为−2或2,则假定该传播主体为所属簇中的观点领袖,则其在网络中的权重较为明显。实验结果如图14和图15所示。
图14描述了传播主体初始观点不同分布条件下的信息传播演进过程。由图14,信息传播网络中主体观点演变过程呈现截然相反的趋势,信息传播网络中的簇结构逐渐合并成两个更大的簇结构分布,与信息传播同步化的稳态一致;整体上,簇间观点对立,簇内观点趋同,信息传播网络系统难以形成意见的完全一致性。
进一步,通过调节初始时刻个体观点认同差异的比例,信息传播网络的最终行为状态也呈现出极大的差异性,如图15所示。由图15(a),随着网络中持负面观点的主体数量增加,所有簇的主体观点最终朝着悲观方向发展,网络中负面信息蔓延,当舆论和谣言等信息传播同步化后,极易造成群体性社会事件发生。相反,如果在突发爆发的初始时刻,若能有效利用信息传播中的“首映效应”,引导传播主体积极面对事件的存在和发展,可以提高监管部门的应急管理能力,防止谣言的同步化传播,具体演变过程如图15(b)所示。
4. 结论与展望
针对社会网络中存在的簇结构特征,以OCR观点扩散模型为基础,构建突发事件信息同步化传播模型,研究了簇结构网络下突发事件信息同步传播演化过程,并分别探讨了簇结构网络拓扑、网络节点耦合强度、传播主体信任水平和传播主体的初始观点等因素对信息同步传播过程的影响。研究发现:(1) 突发事件信息传播网络中的簇结构直接影响网络同步化进程;网络中簇间和簇内的同步化过程存在差异;传播主体的观点变化率在一定条件下能够趋于同步。(2) 簇结构突发事件信息传播网络中个体观点变化及其同步化行为与网络耦合强度成正比例;网络耦合强度越大,网络同步能力越强。(3) 信息传播网络规模越大,其不稳定性也相应增强,信息传播个体对非邻居节点的间接影响力也逐渐减弱,传播主体观点同步化水平降低。(4) 网络同步性和网络簇内同步性之间的关联性受网络模块化程度影响。网络模块度较大,
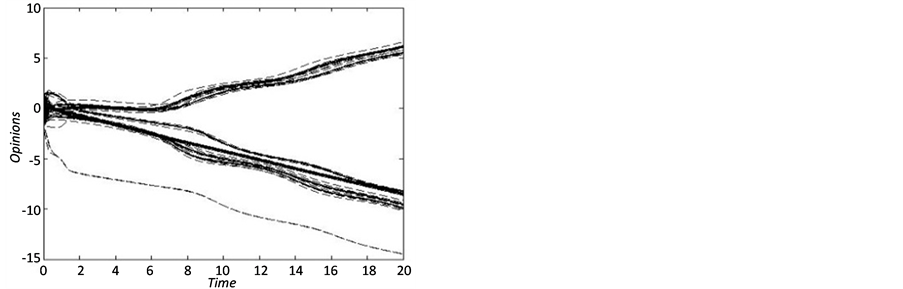
Figure 14. The evolution of communication under the different distribution of subject’s initial viewpoint
图14. 传播主体初始观点不同分布下的传播演进过程

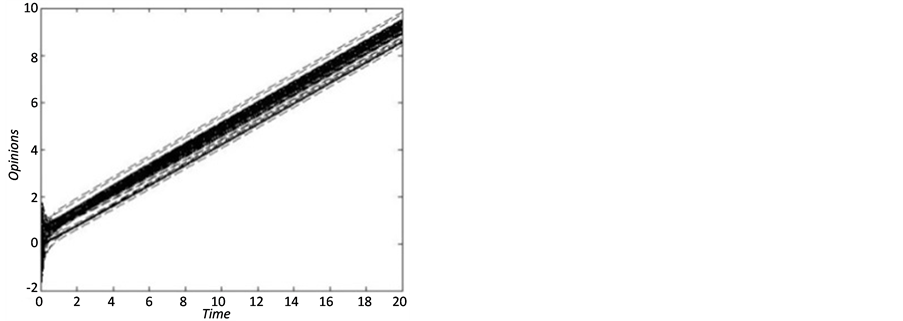 (a) 负面观点极化仿真 (b) 正面观点极化仿真
(a) 负面观点极化仿真 (b) 正面观点极化仿真
Figure 15. The evolution of spreading process from the monopole view
图15. 传播主体观点单极演进过程
网络同步性与簇内同步性之间不存在明显相关性;网络模块度较小,网络同步性与簇内同步性之间趋于一致。(5) 突发事件信息传播速度和同步化过程受初始传播者和观点领袖意见分布影响。基于上述研究结论,监管应急部门可以在避免突发事件爆发初期虚假消息扩散,调节信息传播网络中敏感群体结构,强化信息传播网络中规模较大簇中传播主体行为的引导等方面,进行相关对策和措施的制定,实现理论研究结论对管理实践的支撑作用。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(71502085;71301078)。