1. 引言
从上世纪70年代改革开放至今将近40年的过程中,中国城市数量和面积都发生了翻天覆地的变化,城市化进程在全国甚至全球都在不断推进,近几年仍然有着愈演愈烈的趋势。及时、准确地获取城市区域空间信息可以对城市的发展进程进行宏观的控制,建成区作为城市区域的一个重要组成,是人类活动的主要载体,提取和监测城市中的建成区,对于进行合理的城市规划、提升城市生活品质有着重要意义。遥感技术是从20世纪60年代发展起来的一门新兴的技术,从1972年美国发射第一颗陆地卫星(Landsat系列卫星)开始快速融入人类社会发展的浪潮中,逐渐成为对地观测的主要方式之一,为人类提供宏观、大范围、持续的地表信息。其中Landsat系列影像具有较为丰富的空间、光谱信息,单景影像覆盖范围较大,易于获得,可以高效的监测城市尺度、区域尺度地表现状,具有实现大尺度城市区域实时监测和更新的潜力 [1] 。
利用Landsat影像进行城市中的建成区的提取,目前常见的方法包括监督分类 [2] 、混合像元分解 [3] 和指数方法 [4] [5] [6] 等。其中监督分类需要大量训练样本,而训练样本的采集是一个十分耗时耗力的过程;混合像元分解的方法需要经过端元提取,光谱解混的过程;指数方法利用了影像的波段运算,增强和识别目标地物,相对于前两种方法,指数方法具有简单易行的特点,适用于进行快速建成区提取。査勇 [4] 利用建成区在短波红外1波段和近红外波段的光谱差异,提出了一种归一化建成区指数(Normalized Difference Built-up Index, NDBI),NDBI可以用于建成区的快速提取,但其存在较严重的建成区和非建成区混分现象。针对建成区和水体、植被背景的混分,徐涵秋 [5] 在NDBI指数的基础上,加入水体和植被背景信息,提出了一种可以有效抑制水体和植被背景的建成区指数(Index Based Index, IBI)。针对建成区和植被的混分,何春阳 [7] 结合NDBI和归一化差分植被指数(Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, NDVI),提出了一种可以有效抑制植被背景的连续建成区指数(Built-Up Areas Continuous, BUc)。
针对建成区和裸土的混分问题,本文使用Landsat作为数据源,主要创新成果包括:
1) 在现有的建成区指数NDBI基础上,提出了一种修正的归一化差分建成区指数(Modified Normalized Difference Built-up Index, MNDBI),可以有效的抑制裸土背景,提高提取精度。
2) 针对指数提取的不确定性,提出两步后处理框架,包括聚类去裸土和形态学偏重建两步,进一步剔除建成区提取结果中可能混淆的裸土像素并降低漏检率。
2. 建成区提取方法
指数方法提取建成区具有便捷、快速的特点,可以进行快速城市建成区提取,为后续的应用分析提供基础。本文在归一化差分指数构造模式(Normalized Difference X Index, NDXI)下 [8] ,在现有的建成区指数基础上提出一种修正的归一化差分建成区指数(MNDBI),并提出一种对指数目标提取结果进行改进的提取后处理框架,总体流程如图1所示。
2.1. 修正的归一化差分建成区指数
由不同地物类型在Landsat不同波段上的光谱特征可知(图2),相对于其他几类地物类型,建成区在短波红外1波段(Swir1)反射率较强,近红外波段(Nir)反射率较低,在这两个波段上的差值相对其他几类地物类型较大,构造指数时可以通过这两个波段作差,增强建成区的响应。基于建成区在Swir1和Nir两个波段上的光谱特征,利用NDXI模型(公式(1)),查勇 [4] 提出了归一化差分建成区指数(NDBI) (公式(2))。

Figure 1. The flow chart of the built-up extraction
图1. 建成区提取流程图

Figure 2. Spectral characteristic curve of different objects (Landsat 8)
图2. 地物光谱特性曲线(Landsat 8)
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
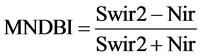 (3)
(3)
公式(1)中,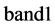 和
和 表示遥感影像中的两个波段,
表示遥感影像中的两个波段,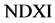 由
由 和
和 的差分运算构造得到。从图2中的光谱折线图可以看出,建成区和裸土两类地物在各个波段上的反射率特征相似,两者相对于其他地物在各个波段的反射率较高,且在近红外和短波红外波段反射率高于可见光波段。通过观察各类地物的光谱特性曲线我们可以发现,利用短波红外1波段和近红外波段之间的作差就可以很好的从建成区中区分出森林、耕地、水体。但是,由于裸土与建成区整体光谱特征相似,它们在短波红外1波段和近红外波段上的差值也十分相近,通过短波红外1波段和近红外波段的差值运算会同时增强建成区和裸土。现有的研究也表示NDBI指数提取结果中会出现建成区和裸土严重混淆的现象 [7] 。
的差分运算构造得到。从图2中的光谱折线图可以看出,建成区和裸土两类地物在各个波段上的反射率特征相似,两者相对于其他地物在各个波段的反射率较高,且在近红外和短波红外波段反射率高于可见光波段。通过观察各类地物的光谱特性曲线我们可以发现,利用短波红外1波段和近红外波段之间的作差就可以很好的从建成区中区分出森林、耕地、水体。但是,由于裸土与建成区整体光谱特征相似,它们在短波红外1波段和近红外波段上的差值也十分相近,通过短波红外1波段和近红外波段的差值运算会同时增强建成区和裸土。现有的研究也表示NDBI指数提取结果中会出现建成区和裸土严重混淆的现象 [7] 。
观察图2中建成区和裸土在Nir、Swir1、Swir2三个波段上的光谱特征,可以看出,相对于森林、耕地和水体,建成区和裸土在短波红外2波段(Swir2)和短波红外1波段都具有较高的反射率,Swir2与Nir的差值和Swir1与Nir差值都可以增强建成区和裸土的响应值,将这两类地物与其他地物类型区分开。而其中,建成区和裸土在Swir2与Nir两个波段上的差值的差异性要明显大于在Swir1与Nir两个波段上的差值的差异性。基于建成区和裸土的光谱特征,本文提出了一种修正的归一化差分建成区指数(MNDBI,公式(3)),在NDBI的基础上,将短波红外1波段替换成了短波红外2波段,更有效的抑制裸土背景对于建成区提取的影响。
2.2. 建成区提取后处理方法
2.2.1. 矿物指数影像聚类去裸土
裸土与建成区一样具有比较亮的亮度,且裸土没有形态多变,形状不统一,分布规律性较弱,在分类时往往会和建成区混淆,引起错分。实验发现,对于指数提取建成区来说,对提取精度影响最大的因素就是裸土的错分。
Ward [9] 在2000年使用了一组矿物指数,在建成区提取、地物分类中起到从建成区中剔除裸土的作用,减少建成区提取的错分现象。裸土的使用用途的不同决定了它有多种可能成分:城市中的裸土大部分即将用作建筑用地或排水场,它的成分多为黏土;耕地或农村中的裸土大多数为“砖红土”,铁含量比较多。将三种矿物指数影像组合起来进行非监督分类就可以将裸土分出。2002年,Phinn [10] 在VIS (Vegetation-Impervious surface-Soil)模型 [11] 的基础上也使用了这一组矿物指数,用于区分建成区和裸土,能够很好的提高分类精度。
这一组矿物指数包括:
1) 黏土矿物质指数:
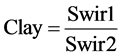 (4)
(4)
2) 氧化铁指数:
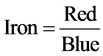 (5)
(5)
3) 铁类金属指数:
 (6)
(6)
本文将黏土矿物质指数、氧化铁指数、铁类金属指数三种矿物指数影像进行叠加,作为输入数据,利用K-means聚类,识别并剔除混淆在提取结果中的裸土。
2.2.2. 形态学偏重建
聚类去裸土可以降低建成区提取的虚警率,提高建成区提取的正确性。针对指数提取结果中可能存在的建成区漏分现象,如建成区中一些亮度较暗的建筑被漏分,我们对指数提取结果进行第二步的后处理,从保证建成区提取的完整性。
数学形态学已经被广泛应用于图像处理中 [12] ,它可以快速有效的抑制噪声、恢复与重建、填补空洞等,形态学基本运算主要包括腐蚀、膨胀、开运算、闭运算、形态学重建等,其中形态学重建相对于其他运算来说,能够更有效的保持目标地物边界信息的完整性,但是也存在一定问题,其中一点就是会导致一些不该消失的地物被不合理的滤去,如一些狭长目标,当结构元素的尺度大于狭长目标的最小宽度,目标就会被滤去,Bellens [13] 针对形态学重建这点不足提出了形态学偏重建算法,廖文志 [14] 将形态学偏重建运用到了高分影像分类当中。形态学偏重建是在形态学重构当中加入了一个距离约束对目标进行判定,在去除噪声点的同时,能够合理的保留一些目标地物,去噪速度慢于形态学重建。本论文采用形态学偏重建,对建成区的指数提取结果进行进一步优化。
3. 实验及分析
实验主要包括两个部分:第一部分是对本文提出的修正的归一化差分建成区指数的提取结果进行评价,并与现有的建成区指数方法进行对比;第二部分是比较经过后处理的建成区提取结果和指数提取结果,分析后处理各步骤对建成区提取效果产生的影响。本文对各个实验区域分别绘制了地面参考样本,在参考样本中随机抽取2000个像素点作为测试样本,其中包括:1000个建成区样本点、250个水体样本点、250个裸土样本点、250个草地样本点、250个森林样本点。利用混淆矩阵、总体精度OA、Kappa系数来衡量利用不同方法进行建成区提取的精度。
3.1. 实验数据及预处理
研究数据包括武汉市2014年Landsat-8 OLI数据、北京市1992年Landsat-5 TM数据、广州市2002年Landsat-7 ETM+数据,本文所使用的Landsat数据均为 L1T等级数据,可以从USGS上免费获取。L1T等级的Landsat数据已经经过了基本的地形数据参与的几何校正,一般情况下可以直接使用而不需要做几何校正。为了利用其丰富的波段光谱信息,获得地表反射率,我们对原始数据进行了辐射定标和FLAASH大气校正(ENVI 5.1)。本文对Landsat影像预处理步骤主要包括:
1) 统一坐标系;
2) 辐射定标;
3) 大气校正;
4) 拼接、裁剪。
统一所有数据的坐标系为WGS-84坐标系,使用UTM投影。辐射定标是将传感器直接获得的地表DN(Digital Number)值转换为辐射亮度值;大气校正则是将辐射亮度转换为地表真实反射率。本论文直接使用ENVI 5.1辐射定标和FLAASH大气校正相关工具对所有Landsat影像进行这两步处理。对于一个城市的多景影像,由于需要得到市级行政区域的Landsat影像,需要将多景影像进行拼接,再利用行政区矢量图(Database of Global Administrative Areas, GADM),对拼接得到的影像进行裁剪(这两步也可直接通过ENVI 5.1 Seamless Mosaic和Subset Data by ROIs两个工具实现),最终得到经过预处理的,武汉市、北京市、广州市的影像数据。
3.2. 指数提取实验
本节对比了归一化差分建成区指数NDBI、基于指数计算的建成区指数IBI,以及本文提出的修正的归一化差分建成区指数MNDBI在三个实验区域(武汉市、北京市、广州市)上的建成区提取结果及精度。
图3给出了各个指数提取建成区的结果图,图4给出广州市局部放大区域的提取细节。其中,IBI的提取结果在非主城区区域存在很多细碎点,经检查可知,这些细碎点大部分为土壤虚警,被错误的标记为建成区,NDBI的提取结果中同样存在一定的虚警。MNDBI提取结果中的虚警明显较少,同时建成区也被比较完整的提取出来。表1中的定量精度评定结果也展现出了类似的规律,总体上三个指数都可以较完整的提取实验区域的建成区,MNDBI在三个实验区域的建成区提取中获得了最高的精度,而IBI

Table 1. Accuracy assessment of the extraction results of different built-up indices
表1. 建成区指数提取精度评定

 广州局部放大影像 广州局部放大NDBI
广州局部放大影像 广州局部放大NDBI

 广州局部放大IBI 广州局部放大MNDBI
广州局部放大IBI 广州局部放大MNDBI
Figure 4. Zoned-in extraction results of Guangzhou
图4. 广州市局部放大区域提取结果
和NDBI的精度相对略低。尤其是在广州市,MNDBI的提取精度(总体精度:94.00%;Kappa系数:0.8800)显著高于IBI(总体精度:86.10%;Kappa系数:0.7220),略高于NDBI(总体精度:92.55%;Kappa系数:0.8510)。以上的实验结果验证了MNDBI的有效性和优越性。
3.3. 建成区提取后处理
根据本文提出的建成区指数提取后处理框架,我们需要对MNDWI指数提取出的建成区进行两步后处理:
1) K-means聚类去除裸土;
2) 形态学偏重建减少漏分、去噪。
需要注意的是,为了提高效率,本文对于指数提取错分率小于10/1000的影像省略了后处理步骤1),直接进行后处理步骤2)。在本实验中,广州2002年的影像符合这一条件,只进行了第二步后处理。
分别对武汉、北京、广州三个城市的指数提取结果进行后处理,每一步的城市提取实验结果见图5,精度评定结果见表2。从各个步骤的处理结果看,聚类去裸土后非中心城市区域离散点显著减少,裸土区域被进一步去除,而经过形态学偏重建,建成区提取结果变得更加聚集,内部空洞被适当填补,中心城市区域建成区漏分被缓解。从每一步的精度评定混淆矩阵中也可以看出,经过聚类去裸土,被分到建成区的非建成区样本点显著减少,虚警率显著降低。经过形态学偏重建,被分到非建成区的建成区样本点数量明显减少,建成区提取的漏检率降低,建成区提取的更加正确和完整。随着每一步的后处理,总体精度和Kappa系数也在逐渐升高,三个实验区域的建成区提取精度在后处理之后均在90%以上,Kappa系数均在0.86以上,武汉市的总体精度达到了97.25% (Kappa: 0.9450),总体精度比指数提取结果提高了10.5% (Kappa系数提高了0.21)。在三个实验区域的建成区提取结果说明了指数提取后处理方法的有效性。
4. 结论
本文针对Landsat影像建成区提取问题,首先基于建成区的光谱特征提出了一种修正的归一化差分建成区指数MNDBI。MNDBI在NDBI基础上,将Swir1波段替换为Swir2,从而拉开建成区与裸土的光谱差异,抑制裸土背景,提高建成区提取的正确性。指数目标提取具有计算简便、易于实施的特点,但

Table 2. Accuracy assessment of the built-up extraction results after post processing
表2. 建成区提取后处理精度评定

Figure 5. Built-up extraction results after post processing
图5. 建成区提取后处理结果
对于建成区这样具有很高光谱多样性和复杂性的地物类型,指数提取结果往往依然存在很多的不确定性。针对建成区指数提取结果的不确定性,本文提出了一个建成区指数提取后处理框架,包括聚类去裸土和形态学偏重建两步。聚类去裸土可以有效剔除建成区提取结果中可能混淆的裸土像素,形态学偏重建可以填补提取结果中的空洞,降低漏检率,去除噪声点,使提取结果更加连续和完整。在三个实验区的建成区提取中,MNDBI可以获得最高的建成区提取精度,且建成区的提取精度随着后处理逐渐提高,提取结果中的虚警减少,漏检降低。实验结果验证了MNDBI进行建成区提取的优越性,同时验证了本文所提出的后处理框架对于提高建成区提取精度的有效性。