1. 研究背景
潜流带是河流河床内水分饱和的沉积物层,是河流和地下水相互作用的区域,也是河床中能与河流存在物质和能量交换的区域 [1] [2] 。前人在潜流带研究方面也有一定进展,如李佳选等人利用温度梯度法在北洛河进行的水交换研究,发现同一断面上的5个测试点温度分布廓线表现出相同的趋势 [3] 。研究潜流带的水文特性与气象特性的关系,可以深入了解气象变化对地表水地下水相互作用的影响。当前,应国家建设生态城市,整修河道相关政策,河道的综合治理相关工程较多。有关潜流通量动态特征研究可预测气候变化情况下潜流带的时空变异 [3] 。能够为河道综合治理工程提供一定的参考依据,同时,为水环境污染的防治奠定基础。
与常规研究潜流带的方法(如同位素示踪 [4] 、水化学 [5] [6] 等)相比,温度示踪法因其独特的优势逐渐被人们广泛应用 [7] [8] [9] 。如李英玉, 赵坚等人利用温度示踪法探测温度场和流场分布特性 [10] [11] [12] 。杨国强等人以大克泊湖(西侧)为例进行的潜流带水动力交换量计算研究 [13] [14] [15] 。但目前的研究大多集中在规模较小、未曾经过治理的原始河流 [16] [17] [18] 。而规模较大的河流,水位深、流速快,仪器安放与数据采集有一定困难,这方面的研究相对较少。渭河户县段近期要进行全线整治,大规模修建防护林,而改造后的河道对潜流带有较大的影响,迫切需要进行深入研究。
本文旨在通过对渭河陕西户县段横断面的温度监测,通过温度示踪法来探索潜流通量的动态变化特征 [19] ,得到温度数据后,利用MATLAB插入VFLUX垂直流体热传导求解器求潜流通量。同时,通过远程气象监测站对气象指标进行检测并进行数据统计分析。结合气象特征和潜流通量变化特征,分析其时空动态变化特性,这将从高时空分辨率角度,提高对潜流交换时空异质性的认识,揭示气象变化对河流与地下水相互作用的影响。
2. 潜流通量计算的方法
地下水与地表水的运动及相互作用伴随这能量的传递,热是能量的一种表现方式。因此在多种因素作用下,地质体温度具有一定的时空差异性,此差异性表现水的运动。因地下水与地表水对流,随着对流深度增加,发生温度波动振幅衰减和相位延迟现象,能够反映地表水与地下水的相互交换,从而为计算潜流带垂向潜流通量提供了理论基础。
本研究利用MATLAB插入VFLUX垂直流体热传导求解器,VFLUX分布是在MATLAB环境下编写MATLAB计算语言设计运行的一个工具箱。该程序通过饱和多孔介质计算一维垂直流(流量),利用热传导方程,它使用温度时间序列数据测量由多个温度传感器在一个垂直的配置文件中,以计算在特定时间深度的潜流通量。VFLUX运行过程中将温度时间序列的第一重采样数据降到一个较低的采样率,以减少与过采样滤波问题该程序将温度传感器所测的原始数据进行处理,然后过滤采用动态谐波回归时间序列(DHR)的工具箱项目,通过它的操作系统(一个典型的昼夜振荡信号)隔离一个基本的温度信号,使杂乱无序的温度序列变为存在周期性变化的谐波回归时间序列,将用于下一步温度传感器使用额振幅以及潜流通量的计算中。最后,该程序计算出的温度传感器使用的振幅和相位,以及相应的垂直通量。
利用VFLUX在MATLAB工作空间中运行的计算语言编写的程序,专门用于处理获取的浅层沉积物温度时序数据。该程序将原始数据进行处理,然后过滤采用动态谐波回归时间序列(DHR)的工具箱项目,通过它的操作系统(一个典型的昼夜振荡信号)隔离一个基本的温度信号。最后,该程序计算出的温度传感器使用的振幅和相位,其过滤的温度信号计算出相应的垂直通量。VFLUX分布作为一个工具箱,是在MATLAB环境下编写MATLAB计算语言设计运行的功能。
该程序针对不同深度的温度时序数据进行同步处理、重取样、信息分离及波动振幅、相位提取的基础上,利用Keery和Hatch提出的一维热运移模型解法进行垂向潜流通量计算。其中一维热运移模型是在以下四个假设条件下建立:1) 水流垂向运动;2) 介质和水流的热特征在时空上同时稳定不变;3) 热量在垂直方向上进行传导;4) 水的温度与潜流带沉积物的温度保持相同。针对河道内地下水和地表水以垂向运动为主,对潜流交换中的热量运移采用饱和多孔介质的一维稳态热量运移控制方程 [8] 来描述,如式(1):
 (1)
(1)
式中: 为河床内深度z处的温度(℃);t为时间(s);
为河床内深度z处的温度(℃);t为时间(s); 为垂向达西流速(m/s);
为垂向达西流速(m/s); 为固液系统的综合体积热容(J/m3∙K);
为固液系统的综合体积热容(J/m3∙K);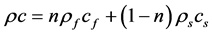 ,
, 为液体体积热容,
为液体体积热容, 为固体体积热容;
为固体体积热容;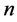 为孔隙度;
为孔隙度; 为饱和沉积物导热系数(J/(s∙m))。一般来说,潜流通量越大,表明地表水与地下水的连通性越好,该处河床温度越接近地下水温度。潜流通量越大,温度相对稳定的位置距河床表面越近,即潜流带深度越小。式(1)揭示了潜流带深度和地下水温度的关系,可用来进行潜流通量的数值计算并对潜流带垂向潜流通量动态变化特征进行研究,分析地表水与地下水的补给关系,了解水流方向变化。
为饱和沉积物导热系数(J/(s∙m))。一般来说,潜流通量越大,表明地表水与地下水的连通性越好,该处河床温度越接近地下水温度。潜流通量越大,温度相对稳定的位置距河床表面越近,即潜流带深度越小。式(1)揭示了潜流带深度和地下水温度的关系,可用来进行潜流通量的数值计算并对潜流带垂向潜流通量动态变化特征进行研究,分析地表水与地下水的补给关系,了解水流方向变化。
3. 研究区域和野外试验
3.1. 研究区域
渭河,古称渭水,是黄河的最大支流。发源于甘肃省定西市渭源县鸟鼠山,主要流经今甘肃天水、陕西省关中平原的宝鸡、咸阳、西安、渭南等地,至渭南市潼关县汇入黄河。本次研究区域为陕西西安户县境内渭河流域,观测点的地理位置为34˚13'48N,180˚33'25E,海拔370米。
渭河流域地形特点为西高东低,自西向东,地势逐渐变缓,河谷变宽,地貌为经黄土沉积和渭河干支流冲积而成的河谷冲积平原区—关中盆地(盆地海拔为370米),本研究观测点在渭河下游,植被良好。
3.2. 野外试验
本试验于2016年5月1日到4日在研究区选取1个垂直于河道的剖面,选取左岸一处为观测点,在河主干道布设温记录仪。记录仪为直径2.5 cm木棍,由裸露在空气的一个传感器(测量环境温度)和在断面垂直河流方向排列的1组温度传感器组成(5个传感器和一个记录仪,传感器分别在河床15、25、50、85、110 cm以下)。
将温度记录仪用液体蜡密封,套上真空袋抽成真空防水,再套入金属保护套,利用橡胶锤将固定了温度传感器的木棒打入河床并用与水色相近的塑料薄片掩护,连续记录2016/5/1-2016/5/4河床浅层沉积物的温度变化(图1,图2)。
4. 结果与分析
4.1. 气象因素
通过远程气候监测站观测研究区域温度、湿度压强及降雨量等指标,具体观测值如图3:
1) 温度指标
如图3所示,观察期内每天温度变化趋势大致相同,早上6时左右温度开始上升,在下午2点左右达到峰值。5月2日当天有降雨,室外温度明显降低。
2) 湿度指标
如图4,湿度在凌晨0点到6点湿度较高,观察期内5月2日因有降雨湿度出现反常。在上午10点左右达到峰值。
3) 气压指标
气压变化趋势与湿度变化趋势呈正相关,但变化幅度小于湿度变化幅度(见图5)。气压在5月2日变化幅度大,下午3点开始基本稳定,一直到5月3日中午,随后开始下降。
4.2. 河床温度时空变化特征
图6为传感器在原始时间序列下的温度分布图;图7为传感器在过滤时间序列下的温度分布图。
把获取的浅层沉积物温度时序数据用VFLUX在MATLAB工作空间中运行的计算语言编写的程序进行处理。过滤采用动态谐波回归时间序列(DHR)的工具箱项目,隔离一个基本的温度信号,使杂乱无序的温度序列变为存在周期性变化的谐波回归时间序列,用于下一步温度传感器使用额振幅以及潜流通量的计算中。由图7可以得出,随着深度增加,温度变化振幅逐渐减小。河床深达到1.1 m时变化曲线接近水平。
图8显示,0.25 m处的温度传感器数值变化比较明显。0.15 m处振幅缓慢减小。由图9可见,0.5 m处相位变化大,0.25 m相位为负。
4.3. 不同深度的瞬时潜流通量
本次研究过程中使用Keery振幅方法求解潜流通量,计算结果如下:
研究区在监测时间段内,河床下不同深度平均潜流通量如下:0.2 m处为9.7 × 10−7 m/s,0.375 m处为2.6 × 10−6 m/s,0.675 m处为1.8 × 10−6 m/s,0.975 m处为2.9 × 10−6 m/s,0.325 m处为2.0 × 10−6 m/s,0.55 m处为2.1 × 10−6 m/s,0.8 m处为2.2 × 10−6 m/s。可知,地表水和地下水的补给关系为地表水补给地下水。
图10显示,0.2 m处潜流通量在5月1日6:00左右开始增加,20:00开始趋于平稳直至5月2日12:00,随后垂向潜流通量持续下降,并在5月3日9:00左右垂向潜流通量出现负值,其余均为正值;0.375 m处潜流通量在5月1~2号维持稳定,5月3日有所增长。0.975处潜流通量几乎维持不变。随着潜流带深度增加,其潜流通量随时间的波动振幅减小。垂向潜流通量随时空变化不具规侓性。
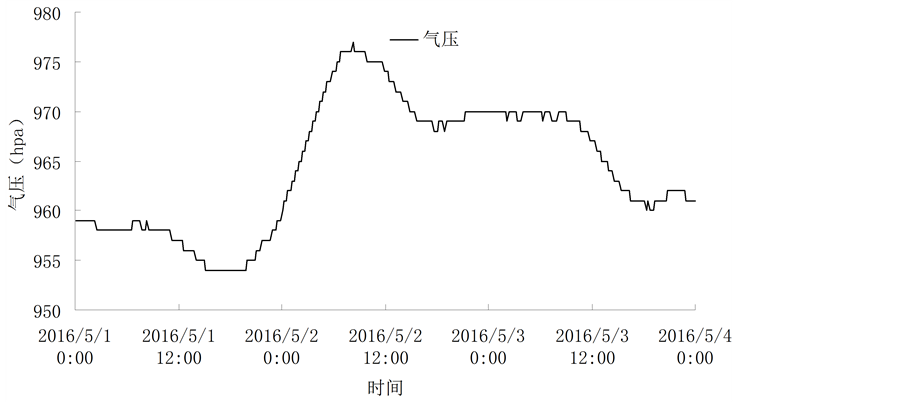
Figure 5. Daily pressure change chart
图5. 5月1~3日气压变化图

Figure 6. Temperature distribution in the original time series
图6. 传感器在原始时间序列下的温度分布图
Figure 7. The temperature distribution graph of the sensor under the filter time series
图7. 传感器在过滤时间序列下的温度分布图

Figure 8. The amplitude distribution graph of the sensor under the filtered time series
图8. 传感器在过滤时间序列下的振幅分布图
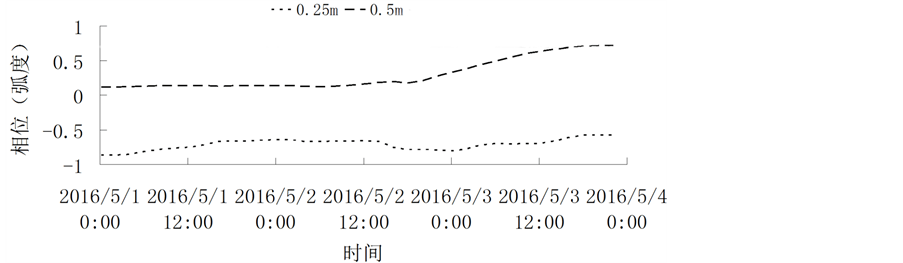
Figure 9. Phase angle distribution graph of the sensor in the filtered time series
图9. 传感器对在过滤时间序列下的相位角分布图

Figure 10. Daily hyporheic flux change chart
图10. 5月1~3日瞬时潜流通量变化图
4.4. 河流地下水补给关系
潜流通量为正值,表示地表水补给地下水;潜流通量为负值,表示地下水补给地表水。由图10显示,在5月1日0:09:01~5月2日22:09:01时间段内潜流带垂向潜流通量数值为正值,地表水(河流)补给地下水。在5月3日0:09:01~22:09:01时间段内河床下0.15 m与0.25 m传感器对的潜流带垂向潜流通量数值为负值,其余6组传感器对的潜流带垂向潜流通量数值为正值,计算得出0.15~0.25 m处的平均潜流通量为9.7 × 10−7 m/s,即水流方向向下其补给关系仍为地表水(河流)补给地下水。第一组传感器为负值原因可能是5月2日上午有降雨,导致地下水位上升,出现局部区域地下水补给地表水。
5. 结论
1) 流通量为正值,表示地表水补给地下水;潜流通量为负值,表示地下水补给地表水。由图10显示,在5月1日0:09:01~5月2日22:09:01时间段内潜流带垂向潜流通量数值为正值,地表水(河流)补给地下水。本次研究中温度数据检测的精度为0.0625℃,数据采集较精准。
2) 5月2日上午有降雨,而潜流通量数据在5月3日出现负值。可知,降雨对潜流影响有一定延缓作用。
3) 潜流通量随潜流带深度增大,潜流通量数值随时间波动幅度减小。垂向分布上随时空变化具有差异性。
本研究揭示了潜流带深度和地下水温度的关系,进行了潜流通量的计算并对潜流带垂向潜流通量动态变化特征进行了分析,分析了地表水与地下水的补给关系。分析水流方向变化能够为河道综合治理工程提供一定的参考依据,同时,为水环境污染的防治奠定基础。
基金项目
长安大学2017年大学生创新创业训练计划项目(201710710161)。
致谢
感谢马瑞同学在原位温度测试方面大力支持,在此表示衷心感谢!