摘要:
新型二维层状材料Mxenes (过渡金属碳化物或氮化物)因其具有与石墨烯类似的结构和丰富的物理化学性质,在储能、催化、光电、生物等领域具有巨大的潜在应用价值。但至今为止,关于MXenes的制备方法并不成熟。本文分别采用HF腐蚀液选择性刻蚀的方法制备了MXenes,通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、X射线衍射仪(XRD)等表征手段研究了HF的浓度、反应时间、反应温度等工艺因素对MXenes形貌和结构的影响。研究结果表明,用浓度50 wt%的HF在50℃下反应24 h,得到的层状MXenes最佳,将有助于进一步拓宽MXenes在多领域的应用。
Abstract:
The novel two dimensional material MXenes (early transition metal carbides and nitrides) exhibit rich physical and chemical properties like graphene, thus show a wide application in energy storage, catalyst, photoelectricity, biology, etc. But until now, the method fabricating MXenes is not mature. In this paper, we used HF to selectively etch out a layer in MAX phase for synthesizing MXene. Then with the help of the scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD), it is found that the HF concentration and system temperature can severely influence the morphology and structure of the obtained MXene. The results show that the perfect layered MXene can be synthesized used 50 wt% HF under 50℃ for 24 h, which will broaden the potential application of MXenes.
1. 引言
近年来,石墨烯和其他二维材料因其特殊的结构和优异的物理化学性质,在储能、光电、传感和催化等领域获得了广泛的应用,成为了研究热点 [1] [2] [3] 。其中类石墨二维层状材料具有较大的比表面积、较多的活性位点以及原子层厚度等特性,成了近十年的研究热点。2011年,Gogotsi和Barsoum发现一种新型二维层状材料MXenes,为二维层状材料增添了很多新成员 [4] 。MXenes的合成主要是通过选择性刻蚀三元层状化合物材料MAX中A层而得到。MAX化学式为Mn + 1AXn,其中M代表前过渡金属元素(Sc,Ti,Zr,Hf,V,Nb,Ta,Cr,Mo等),A代表主族元素(第三或四主族元素),X代表碳或氮元素,n = 1,2或3 [5] 。根据n值的不同,可以将MAX相分为211、312和413相。目前合成出来的MAX有70多种。MAX相为六方层状结构,其晶体结构中X原子填充于M原子形成的八面体空隙中,MX层和A原子层交替排列 [6] [7] 。在MAX相中,M与X之间是较强的共价键,M与A之间是相对较弱的金属键。合成MXenes的机制就是利用A层反应活性高,键能低,易从MAX相中移除等特点。为了强调其与石墨烯类似的性能,用同样的后缀(ene)来命名。
与石墨烯、硫化钼等典型的二维材料相比,MXenes不仅具有比表面积大、活性位点多以及原子层厚度等特性,还拥有良好的亲水性,金属导电性(可达437 Ωsq−1),化学组成可调等优势 [8] 。理论预测这类材料具有高弹性模量及高载流子迁移率,在导电材料及功能增强复合材料等方面有良好的应用前景 [4] 。尽量MXenes在光学、电学、生物学和化学领域表现了潜在的应用价值 [9] [10] [11] ,然而成功合成、剥离单层MXenes纳米片仍然存在很多挑战,阻碍它的大量生产研究。目前已知MXene的合成方法主要有三种,溶液法(HF和HCl+LiF刻蚀法) [12] 、高温氟化物熔融法 [13] 、自下而上合成法 [14] 。高温氟化物熔融法是将MAX相与含氟的金属盐混合后,通入惰性气体,高温加热反应生成MXenes。自下而上合成法主要是利用化学气相沉积(CVD)来生成大面积的连续的MXenes薄膜。这两种方法与HF刻蚀MAX相比,都有一定的缺陷,如成本高、实用性低以及合成工艺不成熟等。本文将重点阐述HF选择性腐蚀Ti3AlC2相这种方法,借用扫描透射电子显微镜(SEM)和X射线衍射(XRD)具体讨论分析其合成Ti3C2Tx (Ti3C2Tx是合成技术较成熟、应用最广泛的一种MXenes机制以及影响因素。
2. 实验
2.1. 试剂
40 wt%和49 wt%氢氟酸(HF)购买于上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。Ti3AlC2粉末购买于北京智慧有限公司。
2.2. 实验过程
2.2.1. 预处理Ti3AlC2粉末
将直接买来的Ti3AlC2粉末球磨18 h,后将混合好的粉料装入氧化铝坩埚中,然后将坩埚放在管式炉中抽真空后,通入氩气作为保护气氛,以10 ℃/min的速率升到1400℃,保温2 h,自然冷却到室温。
2.2.2. Ti3C2Tx的合成过程
1) 将处理Ti3AlC2粉末经研磨后过300目筛子。取1.0 g研磨好的Ti3AlC2粉末慢慢加入到12.5 ml 40%的HF溶液,在室温下磁力搅拌下反应。注意为保证实验的安全性,整个反应需要在通风橱中进行。分别在20 h,40 h,60 h取反应液,进行离心清洗至pH到达中性后,放入真空干燥箱中在60℃下干燥24 h,取出备用。
2) 取1.0 g筛好的Ti3AlC2 (商业获取)粉末慢慢加入到10 ml 50%的HF溶液,在50℃下磁力搅拌下反应24 h。然后将得到的混合液进行离心清洗5~6次至pH到达中性后,放入真空干燥箱中在60℃下干燥24 h,取出备用。
2.3. 分析表征
扫描电子显微镜(Nova NanoSEM 450)、球差校正透射电子显微(Tecnai G2 20 U-TWIN)和X射线衍射仪(PAN alytical B.V.X’Pert PRO)来表征材料的形貌和结构。
3. 结果和讨论
将Ti3AlC2加入到HF溶液中的过程中,会有大量的气泡产生,发生的化学反应如下:
 (1)
(1)
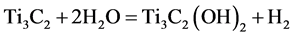 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
利用Hummer方法制备石墨烯,只需要克服石墨层与层之间的范德华力,然而HF腐蚀MAX要克服M-A之间的较强的化学作用力。反应开始时,HF电离的H+和F+进攻Ti3AlC2分子边缘的Ti原子。当H+和F+连接到Ti原子表面后,Ti-Al键的键长分别会增加约2%和0.6%,Ti-Al键的强度相应地会减小。随着越来越多的H+和F+与Ti3AlC2分子发生化学作用后,Ti-Al键的键长会进一步增加到原长的147%,易于HF反应生成AlF3分子,从而成功刻蚀掉Al原子 [15] 。在整个反应的过程中,H+也起着关键的作用,H+与Ti原子反应生成的中间产物提供活性位点,加速整个反应的进行。
接下来,我们将从HF的浓度、反应时间、反应温度等宏观方面详细讨论Ti3C2Tx的合成。图1(A)为Ti3AlC2粉末的扫描电子显微镜照片,从中可以明显看到其自然分层特性。在室温条件下,我们将40% HF溶液加入到Ti3AlC2粉末,随着反应的进行,它的分层效果越来越显著,图1(B)-(D)所示。当Ti3AlC2与HF反应20 h时,与母体MAX相比层状结构越来越明显,但是层与层之间并没有分开;反应40 h时,层与层之间的距离渐渐变大了,到60 h时,层与层之间才彻底分开。事实上,在室温下继续增加40% HF与Ti3AlC2的反应时间,层与层之间的距离并没有继续变大,反而出现堆叠,并且片层的面积也显著减小了,如图2所示。这可能是因为随着反应时间的增加,过多的氧气进入到反应物中,一方面影响了HF的腐蚀反应,另一方面使层与层之间发生了堆叠。
研究发现,当使用50% HF在稍微加热的条件下(50℃)腐蚀Ti3AlC2,反应进行到24 h时,已经出现

Figure 1. (A) SEM image for Ti3AlC2; (B)-(D) SEM image for Ti3AlC2 reacting with 40% HF for different time under room temperature, (B) 20 h, (C) 40 h, (D) 60 h
图1. (A) 为Ti3AlC2扫描电子显微镜的照片;(B)-(D)为Ti3AlC2与40% HF反应不同时间的扫描电子显微镜的照片,(B) 反应20 h,(C) 反应40 h,(D) 反应60 h

Figure 2. (A) SEM images for Ti3AlC2, (B) magnified SEM images reacting with 40% HF for 80 h under room temperature
图2. Ti3AlC2与40% HF反应80 h的扫描电子显微镜的照片
了明显的层状结构,且层与层之间是基本分开的,如图3(A)-(B)所示。与40% HF腐蚀的MAX相比,用50% HF腐蚀的不仅时间更短,并且合成的MXenes层与层之间的距离更大,更有利于在实际应用中发挥其层状结构的优势。因为在使用40% HF腐蚀的过程中,HF浓度低、反应温度低,不能充分刻蚀掉Al层,还有反应时间过长,层与层之间自然会堆叠。我们还利用透射电子显微镜表征Ti
3C
2Tx的结构特性,如图3C-D所示,Ti3C2Tx层与层分开的结构清晰可见。另外,通过高分辨透射电子显微镜图可以观察到其晶格条纹,还可由衍射花样图(图3(D)右插图)来确定Ti3C2Tx的六方晶型。
图4展示了Ti3AlC2和不同方法制备的Ti3C2Tx XRD图。由图4(A)可知,无论用40% HF在室温下腐蚀的Ti3AlC2反应60 h,还是用50% HF在的50℃下腐蚀24 h,属于Ti3AlC2的(104)晶面的衍射峰都消失了,标志着成功合成Ti3C2Tx。从图中还可以看出用50% HF制备的Ti3C2Tx的衍射峰(≈ 9.6度)比40% HF制备的更向低角度偏移,这是因为用50% HF制备的Ti3C2Tx层与层之间的距离大,晶面间距也大。从图4(B)中同样可以看出,继续增加40% HF与Ti3AlC2的反应时间到80 h,得到的样品并不是纯Ti3C2Tx,会

Figure 3. (A)-(B) SEM images for Ti3AlC2reacting with 50% HF for 24 h under 50˚C, (A) low-magnification SEM image, (B) high-magnification SEM image; (C)-(D) TEM images for Ti3AlC2reacting with 50% HF for 24 h under 50˚C, (C) low-magnification TEM image, (D) high-magnification TEM image, the corresponding electron diffraction patterns are shown in inset of the figures
图3. (A)-(B)为用50% HF制备的Ti3AlC2扫描电子显微镜的照片,(A) 为低倍率图,(B) 为高倍率图;(C)-(D) 为Ti3C2Tx的透射电子显微镜的照片,(C) 为低倍率图,(D) 为高倍率图,右上角插图分别为其对应的衍射花样图

Figure 4. XRD patterns for Ti3AlC2 and Ti3C2Tx, in figure of (A) a for Ti3AlC2, b for Ti3C2Tx obtained by reacting with 40% HF, c for Ti3C2Tx obtained by reacting with 50% HF; in figure of (B) a for Ti3C2Tx obtained by reacting with 40% HF for 60 h, b for 80 h
图4. Ti3AlC2和不同方法制备的Ti3C2Tx XRD图,(A) 图中a为Ti3AlC2,b为用40% HF制备的Ti3C2Tx,c为50% HF制备的Ti3C2Tx;(B) 图中的a为40% HF反应60 h制备的Ti3C2Tx,b为40% HF反应80 h制备的
有副反应发生生成其他的物质。
4. 结论
本文主要报道了通过HF腐蚀液选择性刻蚀MAX来制备Mxenes,通过SEM、TEM、XRD等手段表征详细地分析了HF浓度,反应温度等对于整个制备过程的影响。研究发现用浓度50 wt%的HF在50℃下反应24 h得到的层状MXenes最佳,与一般文献报道在室温下反应2 h有所不同。
基金项目
这项工作是由湖北省自然科学基金项目(2014CFB631),湖北省教育厅科研计划(Q20141802)、(Q20111801)支持。