1. 引言
我国稀土资源不仅储量丰富,而且分布广泛,元素齐全,有氟碳铈矿等多种稀土矿 [1] ,其储量约占世界80%,产量约占世界90%以上,储量和产量均居世界首位 [2] 。而攀西地区是我国第二大稀土矿产地,其主要工业矿物为氟碳铈矿 [3] 。1965年美国钼公司提出氧化焙烧–盐酸浸取法分解氟碳铈矿的经典方法 [4] [5] ,其提取的稀土产品为氯化稀土,是目前工业生产中采用分解精矿工艺之一 [6] ,该方法也是目前研究回收稀土的主要工艺 [7] 。池汝安等证明盐酸的浸取能力要比硫酸强 [8] ,故用盐酸来进行浸取可以提高稀土中铁等非稀土杂质的分离效果,使稀土回收率得到有效提高。目前除铁的研究方法可以分为沉淀法和萃取法两大类 [9] ,溶剂萃取法已经成稀土提取分离技术重要方向。
N235萃取法 [10] (胺类萃取剂),具有较强的萃取铁的能力,田军,池汝安等做过用N235有机萃取分离了氯化稀土浸液中的铁 [11] ,证实了水相酸度对铁的萃取效果有重要的影响,而中性磷类如TBP主要适用于盐酸、硝酸体系 [12] 。
N235的物理化学性质:N235属碱性萃取剂,平均分子量387,闪点189℃,在25℃下密度为0.8159 cm4,燃点226℃,在水中的溶解度低于0.01 g/L (25℃),毒性(LD50) 442 mg·kg [13] 。
N235为三烷基胺,与一次浸液中的铁反应机理:
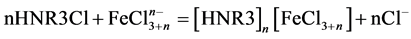 (1)
(1)
TBP的物理化学性质:TBP又称磷酸三丁酯,分子式:(C4H9O)PO,无色、无臭液体,易燃。相对密度0.976(25/4℃)。熔点<−80℃。沸点289℃,在沸点温度下有分解;177℃~178℃ (3.6 kPa)。闪点146℃。折射率nD(25℃) = 1.425,汽化热230.7 J/g。
TBP与一次浸液中铁的反应机理:
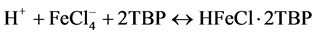 [14] (2)
[14] (2)
故本试验采用N235和TBP两种不同的萃取剂来分离稀土中的铁等非稀土杂质元素。
2. 实验
2.1. 试验材料
2.1.1. 试验仪器
pH试纸、温度计、玻璃杯、烧杯、分液漏斗(125 ml)、碱式滴定管、铁架台、烧瓶、量筒(100 ml)、比色管(25 ml)、容量瓶(100 ml)、移液管(1 ml, 10 ml)、电炉、氟度计(PFS-80,上海康仪仪器有限公司)、ICP (HK-8100,北京华科易通分析仪器有限公司)、原子吸收分光光度计(AA320N,上海仪电分析仪器有限公司)。
2.1.2. 试验原料、试剂
一次浸液(德昌智能稀土)、N235、TBP、煤油、蒸馏水、抗坏血酸、溴甲酚绿、氨水(1:1)、盐酸(1:1)、六次甲基四胺、二甲酚橙、EDTA标准溶液(0.03468 mol/L)、NaOH (0.2537 mol/L和20%)、乙酸钠、铁的标准溶液(2 ug/L)、铅的标准溶液(5 ug/L)。
2.1.3. 主要分析方法
稀土采用EDTA容量法分析 [15] ,铁采用原子吸收分光光度计分析。
2.2. 试验设计
2.2.1. 原浸液中成分分析
1) REO总量的测定(注:REO为氧化稀土)
用1 ml的移液管取0.5 ml一次浸液于烧瓶中,加入适量的水稀释,加入少量的抗坏血酸,然后滴入2~3滴溴甲酚绿溶液变成黄色,加入氨水溶液变成蓝色,之后加入盐酸使溶液恢复黄色,再加入10 ml六次甲基四胺和3滴二甲酚橙溶液变成紫色,用EDTA标准溶液滴定,直到溶液瞬间变成亮绿色为止。
2) 酸度的测定
用1 ml的移液管取1 ml的一次浸液于烧瓶中,加入适量的水稀释,滴入3滴溴甲酚绿,然后用NaOH标准溶液滴定直到溶液颜色完全变化为止。
3) F-的测定
用20%的NaOH溶液溶解出一次浸液中的F−,并对其进行适当稀释,最后用氟度计测定F−的浓度。
4) Fe的测定
取一次浸液1 ml于100 ml的容量瓶中并定容,从容量瓶中取1 ml溶液于25 ml的比色管中,加入5 ml盐酸(1:1)并定容。用原子吸收分光光度计测定铁的吸光度。
5) Al2O3的测定
取10 ml一次浸液于100 ml容量瓶中并定容,然后用ICP测定Al2O3在REO中的百分含量。
2.2.2. 相同酸度条件下不同浓度的TBP对浸液中铁的分离效果
1) 配制CH+ = 2.0803 mol/L的一次浸液和20%、25%、30%、35%、40%五组不同浓度的TBP–煤油萃取剂。
2) 用量筒量取一次浸液和第一组TBP萃取剂各30 ml (O/A = 1:1)于125 ml的分液漏斗中,摇晃分液漏斗5 min,再静置3 min,放出萃余液。再量取30 ml蒸馏水倒入分液漏斗中,摇晃5 min,再静置3 min,放出反萃液,并量出萃余液、反萃液的体积。
3) 用EDTA标准溶液滴定萃余液和反萃液中REO的含量,用原子吸收分光光度计测定萃余液和反萃液中铁的吸光度并计算其浓度。
4) 后四组都采用2)和3)相同的操作方式。
2.2.3. 不同浓度的N235萃取剂对浸液中铁的分离效果
1) 用煤油作为稀释剂,配制体积百分比为20%、25%、30%、35%、40%的不同浓度N235–煤油萃取剂。
2) 用量筒量取一次浸液和第一组N235萃取剂各50 ml (O/A = 1:1)于125 ml的分液漏斗中,摇晃分液漏斗5 min,再静置3 min,放出萃余液。再量取50 ml蒸馏水倒入分液漏斗中,摇晃5 min,再静置3 min,放出反萃液,并量出萃余液、反萃液的体积。
3) 用EDTA标准溶液滴定萃余液和反萃液中REO的含量,用原子吸收分光光度计测定萃余液和反萃液中铁的吸光度并计算其浓度。
4) 后四组都采用第2)和第3)步相同的操作方式。
2.2.4. 不同酸度条件下N235对浸液中铁的分离效果
1) 将2.2.3中萃取后的N235有机相用盐酸洗涤3次,用分液漏斗分离出N235有机相。
2) 配制H+浓度为0.5074 mol/L、1.0655 mol/L、1.5197 mol/L、2.1184 mol/L、2.5116 mol/L五组不同的一次浸液。
3) 用量筒量取第一组一次浸液和N235萃取剂各30 ml (O/A = 1:1)于125 ml的分液漏斗中,摇晃分液漏斗5 min,再静置3 min,放出萃余液。再量取30 ml蒸馏水倒入分液漏斗中,摇晃5 min,再静置3 min,放出反萃液,并量出萃余液、反萃液的体积。
4) 用EDTA标准溶液滴定萃余液和反萃液中REO的含量,用原子吸收分光光度计测定萃余液和反萃液中铁的吸光度并计算其浓度。
5) 后四组都采用第3)和第4)步相同的操作方式。
2.2.5. 计算方法
REO浓度计算:
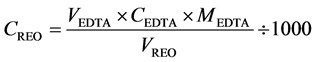
其中:VEDTA表示滴定所消耗的EDTA标准溶液体积,单位:ml;CEDTA表示EDTA标准溶液浓度,单位:mol/L;MEDTA表示EDTA的摩尔质量,单位:g/mol;VREO表示移取REO的体积,单位:mL。
铁浓度计算:
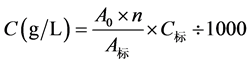
其中:A0表示试样的吸光度,n表示稀释的倍数,A标表示标准溶液的吸光度,C标表示标准溶液的浓度,单位:ug/L。
H+的测定
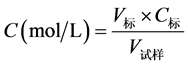
其中:V标表示滴定所消耗NaOH标准溶液的体积,单位:ml;C标表示NaOH标准溶液的浓度,单位:mol/L;V试样表示移取试样的体积,单位:mL。
F−浓度计算:
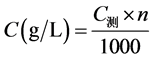
其中:C测表示测定的F−浓度,单位:mg/L;n表示稀释的倍数。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 原浸液中各主要成分浓度(见表1)
在萃取前对原一次浸液的主要成分进行分析,主要成分及其浓度如下表1所示。
3.2. 在相同的酸度不同浓度的TBP条件下试验结果(注:V试样 = V萃取剂 = V蒸馏水 = 30 ml)
(注:浸液中CREO = 224.60 g/L,CFe = 5.8432 g/L)
3.2.1. 配制不同浓度的TBP (见表2)
在工业上常用TBP来萃取稀土中的铁等杂质,为了探究TBP浓度对铁萃取效果的影响,该实验中配制了五种不同浓度TBP萃取剂,如下表2所示。
3.2.2. 萃余液中REO和铁的含量(见表3)
用五种不同浓度的TBP萃取剂,以1:1的水相比进行萃取,采用EDTA容量法分析和原子吸收分光光度计来测定REO和Fe的含量,其结果如表3所示。
3.2.3. 反萃液中REO和铁的含量及铁的萃取率(见表4)
用相同体积的蒸馏水反萃,测定出反萃液中铁的浓度,根据表3所测定的数据可以算出铁的萃取率,其结果如下表4所示。
3.2.4. 铁的萃取率随萃取剂TBP浓度变化曲线(见图1)
根据表2和表4中的数据可以绘制出铁的萃取率随TBP浓度变化曲线,如图1所示。
结合图1的函数图像可以看出:铁的萃取率随着TBP的浓度增加而增加,浓度增加到40%时,增加趋于平稳。

Table 1. The original extracts of major constituents in concentration
表1. 原浸液中各主要成分浓度

Table 2. Extracts of different concentrations of TBP
表2. 不同浓度TBP萃取剂

Table 3. The content of REO and Fe in the extract
表3. 萃余液中REO和铁的含量

Table 4. The content of REO and iron in the liquid and the extraction rate of iron
表4. 反萃液中REO和铁的含量及铁的萃取率
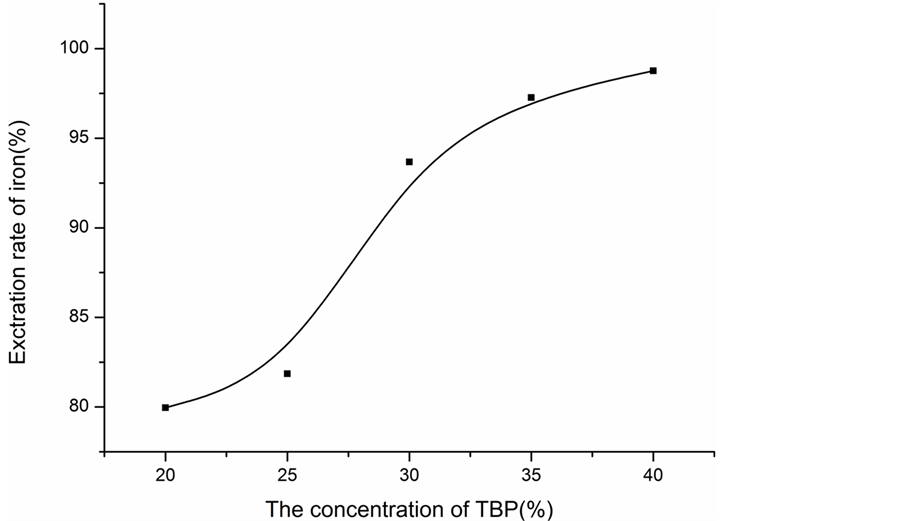
Figure 1. The change curve of the extraction rate of iron with the TBP concentration of the extract
图1. 铁的萃取率随萃取剂TBP浓度变化曲线
3.3. 不同浓度的N235条件下试验结果(注:V试样 = V萃取剂 = V蒸馏水 = 50 ml)
3.3.1. 配制不同浓度的N235 (见表5)
为了探究N235萃取剂浓度对铁的萃取效果,故配制了五种不同浓度的N235的萃取剂,其结果如表5所示。
3.3.2. 萃余液中REO和铁的含量(见表6)
用五种不同浓度的N235萃取剂,以1:1的水相比进行萃取,采用EDTA容量法分析和原子吸收分光光度计来测定REO和Fe的含量,其结果如下表6所示。
3.3.3. 反萃液中REO和铁的含量及铁的萃取率(见表7)
用相同体积的蒸馏水反萃,测定出反萃液中REO和铁的浓度,根据表6所测定的数据可以算出铁的萃取率,其结果如表7所示。
3.3.4. 铁的萃取率随萃取剂N235浓度变化曲线(见图2)
根据表5和表7中的数据可以绘制出铁的萃取率随N235浓度变化曲线,如图2所示。
结合图2的函数图像可以看出:铁的萃取率先升高然后下降,在N235浓度为35%时,铁的萃取效果最好,此时的浓度为萃取铁的最佳浓度。
3.4. 不同酸度用相同浓度N235条件下试验结果(注:V试样 = V萃取剂 = V蒸馏水 = 30 ml)
3.4.1. 不同酸度的浸液中REO和铁的含量(见表8)
根据图2可以看出在N235的浓度在35%时,铁的萃取效果最好,在此浓度条件下进一步探究一次浸液的酸度对铁的萃取效果的影响,故配制了五种不同酸度的一次浸液,并对各一次浸液中的REO和Fe的浓度液进行了测定,其结果如表8所示。
3.4.2. 反萃液中REO和铁的含量(见表9)
用35%的N235来萃取五种不同酸度的一次浸液,并测定了反萃液中REO和Fe的浓度,其结果如表9所示。
3.4.3. 萃余液中REO和铁的含量及铁的萃取率(见表10)
用相同体积的蒸馏水反萃,测定出反萃液中REO和铁的浓度,根据表9所测定的数据可以算出铁的

Table 5. Extracts of different concentrations of N235
表5. 不同浓度N235萃取剂

Table 6. The content of REO and Fe in the extract
表6. 萃余液中REO和铁的含量

Table 7. The content of REO and iron in the liquid and the extraction rate of iron
表7. 反萃液中REO和铁的含量及铁的萃取率
萃取率,其结果如表10所示。
3.4.4. 铁的萃取率随酸度的变化曲线
根据表8和表10中的数据可以绘制出铁的萃取率随H+浓度变化曲线,如图3所示。

Figure 2. The change of the extraction rate of iron with the concentration of the extract N235
图2. 铁的萃取率随萃取剂N 235浓度变化曲线

Table 8. The content of REO and extracts of different acidity in iron
表8. 不同酸度的浸液中REO和铁的含量

Table 9. The content of REO and Fe in the solution
表9. 反萃液中REO和铁的含量

Table 10. The content of REO and Fe in the extract and the extraction of iron
表10. 萃余液中REO和铁的含量及铁的萃取
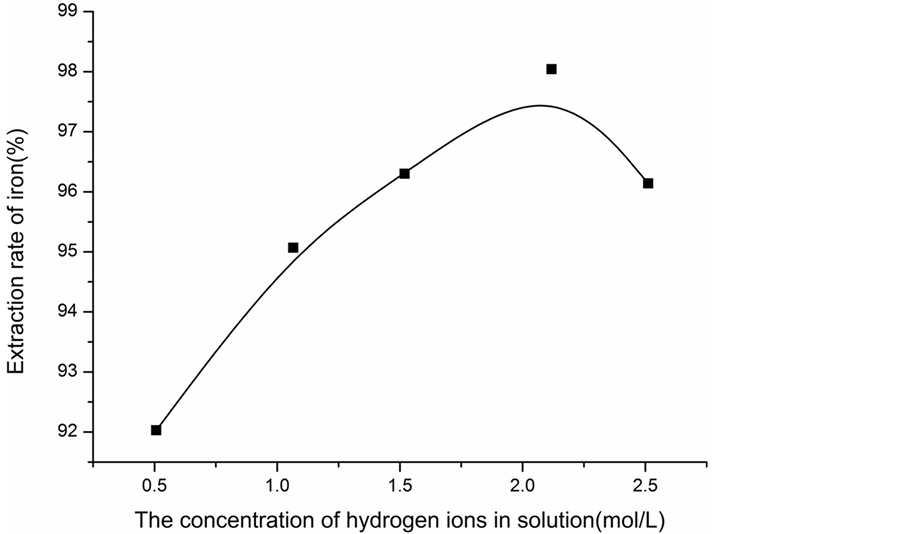
Figure 3. The change of the extraction rate of iron with acidity
图3. 铁的萃取率随酸度的变化曲线
结合图3的函数图像可以看出:随着H+的浓度增加,铁的萃取率先升高然后下降,一次浸液中在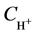 = 2.0 mol/L左右铁的萃取效果最好,此时为萃取铁的最佳酸度。
= 2.0 mol/L左右铁的萃取效果最好,此时为萃取铁的最佳酸度。
4. 讨论与结果
本试验是以氟碳铈矿经氧化焙烧后用盐酸浸后的一次浸液为原料,在N235、TBP和不同酸度的三种条件下,研究对稀土中铁的分离效果,探索最佳分离工艺条件。采用原子吸收分光光度计测定萃余液、反萃液中铁的吸光度,计算得出铁的萃取率。
从而得到以下结论:
1) N235萃取剂对稀土中铁的分离效果要比TBP的分离效果好,可达90%以上,故N235是比较理想的萃取剂。
2) N235萃取剂对稀土中铁的分离效果受其浓度的影响较小,而TBP受其浓度的影响比较大,随其浓度的增加而增加,最佳萃取浓度为40%,最佳萃取率为98.76%。
3) N235的最佳萃取浓度为35%,最佳酸度为CH+ = 2.0 mol/L左右。
从经济角度考虑,N235的成本要比TBP高,并且在工业上TBP要比N235应用更为广泛,故分离铁的最佳工艺,应该选用浓度为40%的TBP来萃取酸度为2.0 mol/L左右的浸液中的铁。
基金项目
四川省教育厅重点课题“轻稀土叶面复合肥的研制及其对凉山烟叶生理性状影响研究”(16ZA0271);凉山州产学研合作项目“稀土尾矿固体废弃物综合利用研究”(15cxy0017)。