摘要:
本文选取四川某地为研究区,配套采集了33套水稻土壤和水稻植株样本,分析测试了水稻籽实、茎、叶三部分以及对应土壤中Cd元素的含量;同时测试了土壤中Cd元素不同赋存形态的分量数据。通过对以上数据的分析处理,得出以下结论:该区域水稻中Cd元素超标率达到84.8%,最高达11.85 mg/kg,已经超过了国家食品卫生标准的59倍;从富集情况看,Cd从土壤迁移到水稻各部分迁移能力为籽实 > 茎 >叶;从土壤中Cd的相态来看,离子交换态和水溶态占全量的30.62%,碳酸盐结合态在弱酸性环境下容易释放出来被吸收,占比也达到了8.45%,对于水稻作物来讲,具有一定的安全威胁;从相态的变异系数来看,只有水溶态以及残渣态均超过了50%,尤其是水溶态,达到了152.5%,显示出这两种相态在土壤中分布不均匀;理论上,当样本数量增加到45个,籽实中Cd与土壤中水溶态相关性达到显著正相关;土壤中pH值与水稻茎、叶、籽实以及地上部分均呈负相关,与土壤中Cd含量显著正相关,结合土壤中Cd形态与pH和有机质的相关性分析,pH升高,碳酸盐结合态、腐殖酸结合态、铁锰结合态、强有机结合态均有较大程度的提高,水溶态降低;提高有机质含量有助于降低土壤中Cd活跃形态,同时降低地上部分中Cd含量。
Abstract:
33 sets of paddy soil and rice plants were sampled from a certain place of Sichuan province. Cadmium contents in these rice plant samples, including their rice seeds, stems, leaves, and their corresponding soil system have been analyzed and tested. Component data of cadmium elements in different forms have been screened as well. Based on the data mentioned above, the following conclusions can be drawn: 84.8% of cadmium contents in the rice plants samples were above the regulatory limits, and the maximum cadmium level reached 11.85 mg/kg, 59 times higher than the National Quality Standard for food. In terms of the enrichment, migration abilities of cadmium from soil to 3 parts of rice plants in descending order were: seeds, stem, and leaf. In terms of phase distribution, ion-exchangeable and water-soluble cadmium make up 30.62% of the total cadmium. Carbonate cadmium that was easily released and absorbed in weak acidic environment became security threats to the rice crops, accounting for 8.45%. The coefficient of variation of phase state showed that only the water-soluble and residua were more than 50% and cadmium in water soluble state was most impressive, up to 152.5%. It showed the two phases were not distributed uniformly in the soil. When the amount of samples increases to a certain extent, cadmium element in the rice seeds was directly proportional to the water-soluble. pH of soil was negatively correlated to rice stems, leaves, seeds and the aboveground and was positively correlated with cadmium content. A correlation analysis of cadmium phases, pH and organism showed that the carbonate, humate, iron-manganese and organic increased a lot as pH increased, while the water-soluble decreased as pH increased. The increase of organic matter content contributed to decrease active phases of cadmium in soil, and decreased cadmium content in the aboveground parts as well.
1. 引言
土壤是人类赖以生存、兴国安邦、生态文明建设的基础资源(赵其国等,2009)。世界面临的粮食、资源和环境问题均与土壤密切相关。国内外多项研究结果表明,超过一定数量Cd的吸收会对人体健康带来严重威胁 [1] - [12] 。Cd作为外缘可溶性重金属进入到水稻环境后,在水稻植株会发生一定程度的向上迁移直至进入人体,各地的“镉米事件”即可印证 [13] 。但是,Cd元素的存在形态决定了其在土壤环境中的稳定性、迁移性和生物有效性,因此对土壤–水稻系统中Cd的富集和分布研究可以对Cd的治理与人体健康风险规避提供科学依据。
2. 材料与分析
2.1. 研究区概况
研究区地处东经103˚45'~105˚15'、北纬30˚31'~31˚42'之间,地形地貌较为复杂,地表出露的第四系松散堆积物为全新统和更新统冲积层,北西部为龙门山中高山区,中部为成都盆地平原区,南东部为盆地丘陵区;该区属亚热带湿润气候,年均降水量1053 mm,年均气温15.7℃,大于
10 ℃
的年均积温为5300℃;土壤类型以紫色土和水稻土为主;植被类型以亚热带常绿阔叶林为主;农业种植以水稻、小麦、油菜、蔬菜为主;区内水系均属于沱江水系。
2.2. 样品采集
9月初,选择两个典型的区域,避开田边,按“S”形采样法采样。采样区内采取11个样点的样品组成一个混合样,每样点3株,共33株。连根拔起(注意茎、叶、穗部的完整性),用塑料纸包扎好。带回室内后从茎基部将根剪掉,样品自然干燥后取出籽粒,然后分别在65℃下烘干8小时,分别称量籽粒重量、茎叶与穗部剩余物的总重量,并将各处理的称重结果准确记录。称重后将它们单独包装,统一进行分析化验。
2.3. 测试方法
根据中国地质调查局《生态地球化学评价样品分析技术要求(DD2005-03)》的要求,测定了不同相态的Cd的含量,其中Cd全量和残渣态Cd采用原子荧光光谱法,其余相态均采用ICP-AES法。分析测试由国土资源部成都矿产资源监督检测中心完成。
2.4. 数据分析方法
采用Excel、Matlab、SPSS等数据分析软件对数据进行分析处理;制图采用原始校验后的分析数据,利用Mapgis对不同标准进行分级勾绘成图,然后进行各级含量参数的面积统计。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 水稻中Cd元素含量特征
根据我国水稻无公害食品标准、绿色食品标准和食品卫生标准(见表1),结合本次测试分析数据(见图1),Cd元素超标率达到84.8%,最高达11.85 mg/kg,已经超过了表1中限量标准的59倍;从水稻采样位置图上可以看出,水稻中超高Cd含量的点都分布在某镇最大污染企业某某集团的下风口处,受该企业排放的废气的影响很大。重金属Cd的超标已经严重影响到了当地大宗农作物水稻的安全。
3.2. 水稻各部分与土壤中Cd元素的富集特征及其相关性
为了了解水稻各部分与对应土壤中Cd含量的关系,本次调查研究了水稻土壤与水稻各部分的富集特征以及相关性(表2和表3)。
为了了解水稻对Cd元素的累积能力,本次研究采用生物富集系数BCF来表示。BCF是生物对某种污染物的累积能力,表征土壤–植物体系中元素迁移的难易程度,是反映植物将重金属吸收转移到体内的能力大小的评价指标。本次我们采用水稻中的元素含量与对应土壤中Cd全量之比计算土壤元素的生物富集系数(表2)。其生物富集系数大,则表明土壤中的重金属越容易被水稻吸收。
从表2可以看出,Cd从土壤迁移到水稻各部分迁移能力为籽实 > 茎 > 叶。具体如下:水稻土壤到水稻茎的富集系数中,最高达到1.969,从样本数量看,30%的样本富集系数超过1,属于高富通集状态,说明Cd从土壤到水稻茎的迁移能力较强;从水稻土壤到水稻叶的富集系数来看,所有样本均低于1,且仅有一个样本超过0.5,说明Cd从水稻土壤到水稻叶的迁移能力较弱;从水稻土壤与水稻籽实的富集情况看,有30%的样本超过1,另有30%的样本富集系数超过0.5,说明Cd从土壤到水稻籽实中迁移能力很强;从水稻土壤与地上部分(包括茎、叶和籽实)的富集情况来看,65%的样本富集系数超过1,最高达3.772,仅有一个样本低于0.5,表现出超强的迁移力,说明水稻植株具有较强的Cd富集能力。
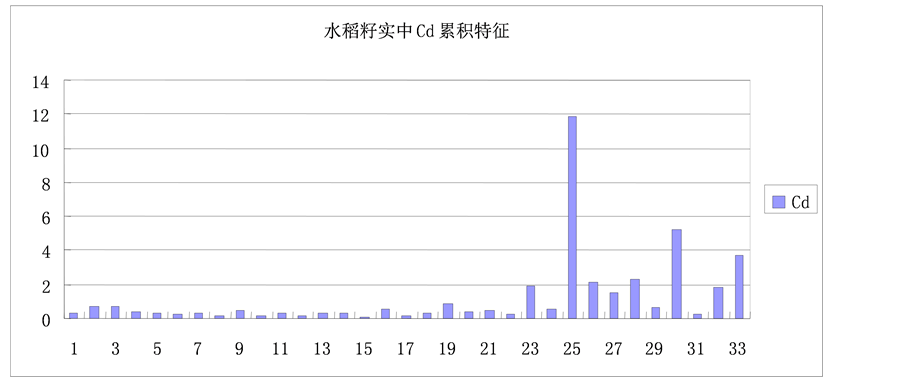
Figure 1. The characteristics of Cd content in rice seed
图1. 水稻籽实中Cd元素含量特征

Table 1. The standards of heavy metals and se content in rice seed (μg/g)
表1. 水稻籽实中重金属及硒含量相关标准(μg/g)
a《中华人民共和国农业行业标准NY 5115-2008无公害食品稻米》,b《中华人民共和国国家标准GB/T 22499-2008富硒稻谷》,c《中华人民共和国农业行业标准NY/T 419-2007绿色食品大米》,d《中华人民共和国国家标准GB 2715-2005粮食卫生标准》,其它数据来源:农业环境背景值协作组(1986)计算。

Table 2. The enrichment coefficient between Cd content indifferent parts of rice and Cd in soil (n = 33)
表2. 水稻各部位Cd含量以及与土壤中Cd含量的生物富集系数(样品数n = 33)

Table 3. The correlation between Cd content in different Parts of rice and pH and Org in soil
表3. 水稻各部分Cd含量与土壤中pH、Org的相关性
注:*表示在0.05水平上显著,**表示在0.01水平上显著,N = 33。
根据表3,土壤中Cd元素含量与土壤中pH值呈现显著正相关,与有机质Org较大正相关,但是却与水稻各个部分呈现较明显的负相关。要讨论这个数据产生的原因,就需要结合土壤中Cd元素的形态进行分析(见3.3节)。
3.3. 水稻及其对应土壤中Cd形态分析
3.3.1. 土壤中不同形态Cd的含量特征
研究区33件土壤样品不同形态的测试分析数据见表4。由表4可见,Cd全量的变化范围为0.362~0.779 μg/g,平均值为0.524 μg/g,超过国家土壤二级质量标准1.75倍,从Cd全量来看,该区域Cd含量严重超标。具体来看,最容易被水稻吸收的水溶态Cd仅占0.32%,在几个相态中含量最低;较为容易吸收的离子交换态Cd占30.30%,占比最多,这两种Cd较易吸收的相态占全量的30.62%,对于水稻作物来讲,具有一定的安全威胁。碳酸盐结合态在弱酸性环境下容易释放出来被吸收,占比也达到了8.45%,也会水稻形成潜在威胁。从变异系数来看,只有水溶态以及残渣态均超过了50%,尤其是水溶态,达到了152.5%,显示出这两种相态在土壤中分布不均匀。
3.3.2. 水稻籽实中Cd含量与其对应土壤中Cd各种相态的相关性讨论
鉴于Cd在土壤中的形态与土壤中pH值和有机质的关系,讨论水稻籽实中Cd含量与土壤中Cd形态含量的关系,引入pH和有机质两个指标,有利于研究表层土壤的改良以及当地产业结构调整,具体见表5至表8。
由表5至表8,可以看出,水稻籽实中Cd含量与对应土壤中水溶态呈现一定的正相关,与残渣态有一定的负相关。由于研究区土壤中形态数据有限,推断当形态样本数增加到45个左右,籽实中Cd与土壤中水溶态相关性达到显著正相关。
水稻籽实中Cd的生物富集系数与Cd腐植酸结合态呈现显著负相关,腐殖质含量越高,被吸附固定在土壤中的Cd越多;同时与水溶态也呈现一定程度的正相关。
结合pH与土壤中Cd除了水溶态有弱负相关外,其他相关性较好的原因,适当提高土壤的pH值,可以降低水溶态含量,同时降低Cd在水稻中富集的能力。
根据表3的分析结果,土壤中pH值与水稻茎、叶、籽实以及地上部分均呈负相关,但是却与土壤中Cd含量显著正相关,结合土壤中Cd形态与pH和有机质的相关性分析,pH升高,碳酸盐结合态、腐殖酸结合态、铁锰结合态、强有机结合态均有较大程度的提高,说明Cd增加部分以相对稳定的状态出现,水溶态的反而降低,这种状况也是我们想看到的,因为提高土壤的pH值,对于Cd地上部分Cd降低效

Table 4. The characteristics of Cd in different speciation of soil (n = 33)
表4. 土壤中不同形态Cd含量特征(n = 33)

Table 5. The relationship between Cd speciation in soil and Cd content in rice seed (n = 33)
表5. 土壤中Cd形态与水稻籽实中Cd含量的关系(n = 33)
注:*表示在0.05水平上显著,**表示在0.01水平上显著。

Table 6. The relationship between Cd speciation and pH and organic matter in soils (n = 33)
表6. 土壤中Cd形态与pH、有机质的关系(n = 33)
注:*表示在0.05水平上显著,**表示在0.01水平上显著。

Table 7. The relationship between Cd speciation in soil and enrichment coefficient of rice seed (n = 33)
表7. 土壤中Cd形态与水稻籽实生物富集系数的关系(n = 33)
注:*表示在0.05水平上显著,**表示在0.01水平上显著。

Table 8. The correlation between Cd speciation in soil and cd content in different parts of rice (n = 33)
表8. 土壤中Cd形态与水稻各部位Cd含量相关性(n = 33)
注:*表示在0.05水平上显著,**表示在0.01水平上显著。
果明显。同时,土壤中有机质与水稻地上部分中,除了叶以外均为弱负相关,加上叶子部位对水稻籽实贡献一般,同时有机质的提高对于Cd各种形态来说呈一定的弱正相关,尤其是几种较为稳定的Cd形态,所以提高有机质含量有助于降低土壤中Cd活跃形态,同时降低地上部分中Cd含量。
另外也可以看到,对水稻籽实中Cd含量相关最大的是水稻茎部分,同时水稻茎与地上部分整体相关度也很高,所以降低水稻茎中Cd含量就要适当提高pH和有机质含量,与上面描述无任何矛盾。
4. 结论
1) 该研究区土壤以Cd为主的污染区,样品中84.8%超过国家绿色食品标准,最高达11.85 mg/kg,已经超过了食品污染物限量标准的59倍,超高Cd含量的点都分布在某集团的下风口处,受其排放的废气的影响很大。该区大部分水稻都具有Cd累积的特性,33%的水稻籽实生物富集系数 > 1,这说明长期食用该地区水稻,对人体健康威胁较大。
2) 对土壤中Cd形态与水稻籽实中Cd含量以及Cd生物富集等方面进行了研究,同时对土壤中pH和有机质与水稻茎、叶、籽实以及地上部分进行相关性分析。结果表明提高该地区的pH值和有机质有助于降低水稻地上部分中Cd的含量,尤其是籽实中的Cd含量,增加土壤的固Cd能力。由于水稻茎部分对Cd的高度富集,故该地区秸秆还田需要控制,应进行集中处理。
基金项目
四川省国土资源厅基础研究项目。