1. 引言
深水型湖泊(包括水库)由于水体温差大、持续时间长,因此引起水体季节分层,这种现象是深水型湖泊一个重要的特征 [1] 。相对于浅水湖泊而言,深水湖泊一方面受风力影响小,垂直温差大,易形成稳定的分层现象 [2] ,其次深水湖泊的热分层阻碍上下层水体的对流交换,影响氮、磷营养盐及光照在水体中的分布,从而对水体溶解氧浓度和水生生物的垂直分布产生影响,引起水环境质量的变化 [3] [4] [5] 。
我们在长期观测分析过程中发现,深水湖泊下层水温与当地年平均气温存在某种关系,因此,研究湖泊温度变化、叶绿素浓度、溶解氧和pH值等水化学参数的变化不仅对湖泊富营养化预防及水质保护具有现实意义,而且对局部气候变化研究,甚至全球气候变化研究具有很重要的参考意义。
程海作为重要的淡水资源载体,一直承担着湖区周边民众的生产生活用水,湖中动植物资源丰富,更为重要的是作为世界上三大螺旋藻自然生长地之一,以出产高质量螺旋藻而闻名 [6] [7] [8] [9] 。然而,随着湖周边人口日益增多,工农业逐渐发展,程海水质每况日下,尤其是螺旋藻人工养殖以来,其水体富营养化日益严重,一年中水华多次爆发 [7] [8] ,对湖泊生态环境产生重要影响。以往的研究大多从水生植物和浮游动物角度对程海的富营养化进行分析,很少有针对水质参数长期定点监测数据的发表或评述,未见有公开发表数据或有效监测数据,同时数据获得困难,更不用讲获得测点位置及其它相关信息。为弥补上述不足、系统了解现今程海水质状况,我们从2015年10月起对程海开展了监测工作,以期得到第一手的现场资料,从水质参数方面分析程海水质变化及差异性特征。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 研究区概况
程海地处青藏高原与云贵高原的衔接部位,东经100˚33'至100˚45',北纬26˚25'至26˚40',行政区划上属于云南省丽江市永胜县。湖面海拔高程1502.0 m,流域面积318.3 km 2,湖面积75.971 km2,湖体呈南北向椭圆形展布,南北轴线长19.154 km,东西最大宽度5.205 km,最大水深35.87 m,平均水深24.98 m,湖水容量19.794亿m3,是典型的高原深水湖泊。程海大约形成于新生代第三纪中期(距今1.2 Ma以前),是喜马拉雅期造山运动形成断裂地堑,中陷低凹之处聚水成湖,湖区气候属中亚热带类型,平均温度18.7℃,全年无霜。程海曾经是一个外流湖,湖水通过程河向南30 km流入金沙江,现在为封闭湖泊,主要靠东西两山的地下水和降水补给,由于地处金沙江干热河谷地带,蒸发量大约是流域降水量的3倍,致使湖泊水位持续下降。
2.2. 数据采集
由于程海湖盆底部西侧深度更大,水质应当更具有代表性,所以本研究沿湖泊深水轴自北向南分别设置四个采样点,标记为A、B、C、D (图1),其中A、B点深度大,南部的C、D点较浅。
本文利用2015年10月23日、2016年3月20日、2016年5月20和2016年7月20日监测数据进行解剖分析。监测过程为从表层开始以1 m为间隔进行水质现场监测,并以2 m为间隔,使用钢化玻璃采水器进行水样采集,用1 L塑料瓶装2瓶放进加冰保温箱保存带回实验室分析。
本研究中温度、叶绿素、pH和溶解氧指标采用美国YSI公司的YSI6600型多参数仪现场连续监测所得数据。测量过程中利用两台仪器进行平行测量以保证数据的准确性和可靠性。
2.3. 统计分析
本研究所有数据均采用Excel、Grapher和SPSS软件完成计算、分析与成图。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 温度的垂直分层及季节变化
程海地处金沙江干热河谷地带,流域内年均气温较高,从监测数据可以清楚的看到湖泊水温季节变化(图2)。就所监测季节来看,10月的湖水整体温度较高,水平方向上南部湖区温度高于北部湖区,垂向上北部湖水深度较大的A点在20~26 m深度范围内出现了明显的温跃层,温度跃变在4℃左右。B点在23~27 m深度范围内出现了明显温跃层,温度跃变也在4℃,南部湖水较浅的C、D点未出现明显的温跃层;次年3月的湖水温度是所监测月份中最低的,水平方向上北部湖区温度高于南部,可能为湖水较深区具有更大的热焓有关。垂向上自北向南四个采样点均未出现明显的分层现象,温度只随深度增加而缓慢降低;5的月湖水温度在水平方向上分布比较均匀,南北湖区水温比较一致,垂向上在四个采样点均出现了温度跃变,北部深水湖区的A点在21~24 m深度范围内出现了温跃层,温度跃变3℃,同样处于
深水区的B点在16~24 m深度范围内出现了温跃层,温度跃变2.4℃,温跃层厚度达8 m,南部湖区的C点在17~24 m深度范围内出现了温跃层,温度跃变2.4℃,D点在8~14 m深度范围内出现了温跃层,温度跃变1.2℃,温度跃变梯度明显小于其他三个点。7月的湖水平均温度是四次监测中最高的,特别是上部水层,其最大值25.5℃,水平方向上表层水温北部湖区高于南部湖区,垂向上四个采样点均出现了明显温度跃变,A点在13~22 m深度范围内出现了温跃层,温度跃变6.8℃,22 m以下温度随深度增加缓慢降低,B点在7~23 m深度范围内出现温跃层,温度跃变7.1℃,23 m以下温度随深度增加缓慢降低,C点在0~11 m深度范围内温度几乎不变,11~15 m深度范围内出现了一次小的温度跃变,在15~23 m深度范围内出现了明显的温跃层,温度跃变5.5℃,23 m以下温度随深度增加缓慢降低,D点温度在0~10 m
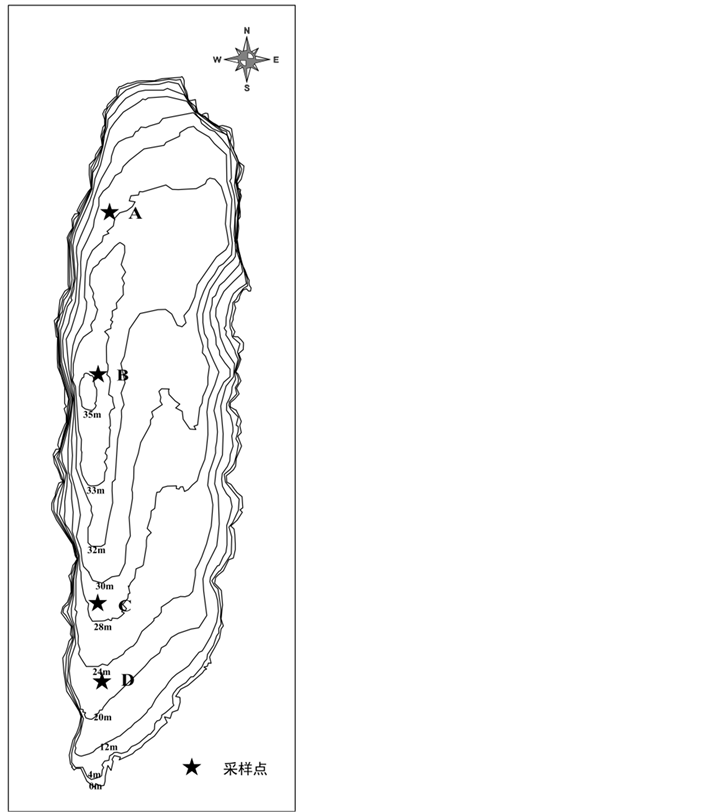
Figure 1. Meuring and sampling sites of water quality in Lake Chenghai
图1. 程海水质采样点分布

Figure 2. Vertical profile of water temperature in Lake Chenghai
图2. 程海水温垂直剖面变化
深度范围内几乎不变,从水深10 m开始到湖底(18 m)随深度增加温度急剧降低。
3.2. 叶绿素垂直分层及季节变化
叶绿素含量是反映湖泊浮游植物生物量的重要指标。据研究认为,程海藻类植物种类175种,其组成结构特点以硅藻、绿藻、蓝藻为主,数量结构特点则是蓝藻占绝对优势,表现出典型的富营养化蓝藻型特征 [7] [8] 。我们的检测结果显示,程海水体中叶绿素含量在时间和空间上存在很大差异,如图3所示。
监测结果显示,10月份程海的湖水中叶绿素含量相对较高,垂向上北部深水湖区的A点0~7 m深度范围内自上而下先升高后急剧降低,最大值出现在水深1 m处,含量高达15.4 ug/L,7~26 m深度范围内叶绿素含量随深度增加缓慢降低,在水深26 m以下则表现出稍有增加趋势,这主要可能是因为部分藻类死亡沉降所致。B点0~6 m深度范围内先升高后急剧降低,最大值出现在水深3 m处,含量11.4 ug/L,6~16 m深度范围内叶绿素含量稳定在8 ug/L左右,16~19 m深度范围内再次出现降低,19~24 m深度范围内叶绿素含量基本稳定在5.5 ug/L,深度24 m至湖底再次出现降低,总共29.5 m深的B点叶绿素含量发生了三次明显变化,说明该区域藻类植物种类相对比较丰富且种群规模相对较大。C点在0~6 m深度范围内先升高后急剧降低,在水深2~3 m处达到最大值9.5 ug/L,6 m以下随深度增加缓慢降低,D点0~3m范围内叶绿素含量逐渐升高,水深3 m之后随深度增加缓慢降低,最大值出现在水深3 m处,含量为5.6 ug/L。水平方向上叶绿素含量自北向南逐渐降低,0~12 m深度范围内的叶绿素平均含量A点为9.4 ug/L,B点为8.4 ug/L,C点为7.3 ug/L,D点为4.9 ug/L。
次年3月的湖水中叶绿素含量相对较低,垂向上北部深水湖区的A点表层含量低,在0~3 m深度范

Figure 3. Vertical profile of Chlorophyll in Lake Chenghai
图3. 程海叶绿素垂直剖面变化
围内迅速升高,之后变化比较微弱,3~16 m深度范围内叶绿素含量随深度缓慢升高,16 m~26 m深度范围内叶绿素含量随深度增加有所降低,最大值出现在水深16 m处,含量为7 ug/L,B、C两点叶绿素含量表层到底层整体变化不大,分布较为均匀,D点叶绿素含量明显低于其他几个点,0~12 m深度范围内随深度增加其含量先降低后升高,最低值出现在水深1 m处,含量为0.3 ug/L。水平方向上叶绿素含量自北向南逐渐降低,0~12 m深度范围内的叶绿素平均含量A点为5.4 ug/L,B点为4.4 ug/L,C点为3.2 ug/L,D点为1.8 ug/L。
5月的叶绿素含量在垂向上变化比较大,A点水深0~2 m叶绿素含量从3.1 ug/L迅速升至8.3 ug/L,2~20 m深度范围内叶绿素含量基本维持在8 ug/L左右,20 m以下随深度增加叶绿素含量逐渐降低,最终低至3 ug/L。B点0~4 m深度范围内叶绿素含量先降低后迅速升高,之后在4~13 m深度范围内维持在7 ug/L左右,13~24 m深度范围内叶绿素含量随深度增加持续降低,24~28 m深度范围内又缓慢升高,最低值2.2 ug/L。C点在0~12 m深度范围内叶绿素含量随深度增加持续升高,其中0~4 m上升幅度较大,在12~22 m深度范围内叶绿素含量随深度增加持续降低,22 m以下叶绿素含量基本稳定在2.8 ug/L左右。到南部D点,0~2 m之间叶绿素含量随深度增加快速升高,2~6 m随深度增加又快速下降,6 m以下持续稳定下降。0~12 m深度范围内叶绿素平均含量A点为7.9 ug/L,B点为6.6 ug/L,C点为5.4 ug/L,D点为5.3 ug/L。
7月的叶绿素含量在垂向上变化最为显著,例如A点0~2 m叶绿素含量从9.9 ug/L急剧升高到17.4 ug/L,2~4 m叶绿素含量又降到13.7 ug/L,4~12 m叶绿素含量随深度增加缓慢降低,12~17 m叶绿素含量从10.2 ug/L降低到2.2 ug/L,17 m以下基本维持在1.7 ug/L左右。B点0~4 m叶绿素含量为所测到的最大值,达19.9 ug/L,4~6 m基本维持稳定在16 ug/L,6~15 m叶绿素含量随深度增加急剧降低至1.9 ug/L,15 m以下随深度增加缓慢降低,之后稳定在1.8 ug/L左右。C点0~5 m叶绿素含量表现为先升高后降低,在1~3 m叶绿素含量维持在17 ug/L以上的高水平,在5~10 m叶绿素含量随深度增加波动降低,10~17 m叶绿素含量随深度增加从12.7 ug/L急剧降低到2.2 ug/L,17 m以下维持在2 ug/L左右的低水平状态。D点表层叶绿素含量为4.1 ug/L,在1 m水深处跃升到12.5 ug/L,1~10 m叶绿素含量维持在12 ug/L左右,但到15 m水深处叶绿素含量增加到15 ug/L,10~15 m叶绿素含量随深度增加从15 ug/L急剧降低到2 ug/L,15 m到湖底(18 m)稳定在1.7 ug/L。水平方向上叶绿素含量中南部湖区的C点最高,其次是北部湖区的A点和B点,南部湖区的D点最低,表现出强烈的空间异质性。
3.3. pH值垂直分层及季节变动
程海水体pH值受地理位置、气候条件、区域地质地貌、地球化学背景、湖泊形态特征、封闭状况等因素综合影响导致碱度高 [10] ,从我们的监测数据来看具有非常明显的季节变化(图4)。同时,对于一般湖泊来讲,存在由于表层湖水藻类光合作用强烈,消耗大量CO2,pH值较高,而深层藻类光合作用弱,藻类的大量死亡使CO2大量积累,加之有机质分解产生酸,使pH逐渐降低的现象 [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] 。
10月湖水pH值整体较高,垂向上在北部深水湖区的A、B两点温跃层附近出现明显的下降,跃变梯度0.4左右,南部浅水湖区的C、D两点则在垂向上变化不大,水平方向上呈现出南部湖区高于北部湖区的趋势。3月湖水pH值相对稳定,垂向几乎没有变化,水平方向上呈现出北部湖区高于南部湖区的趋势。5月湖水pH值垂向上在北部湖区的A、B两点温跃层附近有明显降低,跃变梯度0.4左右,C点呈

Figure 4. Vertical profile of pH in Lake Chenghai
图4. 程海pH垂直剖面变化
现稳定减小趋势,南部最浅的D点0~4 m急剧减小,之后稳定减小,水平方向上呈现出南部湖区高于北部湖区的趋势。7月pH值垂向上A点从表层到3 m深急剧减小,跃变幅度0.6。3~17 m pH值先小幅度增大后又缓慢减小,之后基本稳定,B点pH值在0~14 m深度范围内随深度增加缓慢减小,之后趋于稳定,C点pH值在0~17 m深度范围内随深度增加缓慢减小,之后随深度增加缓慢增大,D点pH值在0~11 m深度范围内随深度增加缓慢减小,11~12 m跳跃式减小,减小幅度0.2,之后随深度增加pH值缓慢增大,水平方向上,北部湖区pH值高于南部湖区。总体来讲,程海pH变化幅度不是很大。
3.4. 溶解氧垂直分层及季节变化
溶解氧是湖泊初级生产力及水动力条件的综合反映 [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] ,程海水体溶解氧季节变化明显,不同月份各自特征鲜明(图5)。
监测数据显示,程海10月湖水中溶解氧含量整体不高,垂向上北部深水湖区的A点在0~7 m深度范围内先略升后降低,在1 m深处达到最大值9.6 mg/L,7~16 m深度范围内溶解氧含量缓慢降低,保持在5.3~4.6 mg/L,16~21 m深度范围内溶解氧含量迅速下降,最终保持在0.3 mg/L左右,B点也是在0~7 m深度范围内有先升高后降低的趋势,之后保持在5 mg/L直到22 m深,在22~25 m深度范围内溶解氧含量急剧下降,最终保持在0.3 mg/L左右,南部湖区的C、D两点溶解氧含量随深度增加缓慢降低,但并未表现出跃变。水平方向上,北部湖区的溶解氧含量远高于南部湖区,0~12 m深度范围内的溶解氧平均含量A点为6.5 mg/L,B点为6.1 mg/L,C点为5.7 mg/L,D点只有4.5 mg/L,表现为有北向南逐渐降低的总趋势。
次年3月的湖水中溶解氧含量相对较高,垂向上北部湖区的A点溶解氧含量只随深度增加缓慢降低,

Figure 5. Vertical profile of ODO in Lake Chenghai
图5. 程海溶解氧垂直剖面变化
最大值为7.58 mg/L,出现在表层,最小值为6.92 mg/L,出现在底层;B点0~19 m深度范围内溶解氧同样也只随深度增加而缓慢降低,但在19 m之后出现迅速降低。最大值出现在表层,为7.43 mg/L,最小值出现在底层,为4.23 mg/L;C点0~20 m深度范围内溶解氧随深度增加缓慢降低,之后快速降低,最大值出现在表层,为7.47 mg/L,最小值出现在底层,为3.12 mg/L;D点由于深度较小,溶解氧含量随深度增加缓慢降低,最大值出现在表层,为6.96 mg/L,最小值出现在底层,为6.07 mg/L。水平方向上北部湖区的溶解氧含量远高于南部湖区,0~12 m深度范围内的溶解氧平均含量A点为7.3 mg/L,B点为7.3 mg/L,C点为6.9 mg/L,D点仅为6.3 mg/L。
5月的湖水中溶解氧含量最高,垂向上北部湖区的A点溶解氧含量上层水体高于下层水体,0~6 m深度范围内先升高后降低,并在2 m深处达到最大值9.71 mg/L,6~19 m深度范围内溶解氧随深度增加缓慢降低,19 m往下溶解氧含量急剧变化,最低到0.3 mg/L;B点溶解氧含量在0~4 m深度范围内下降较快,7~13 m深度范围内稳定降低,在13 m之后跳跃式连续下降,并在22 m以下形成了稳定的低氧环境;C点0~11 m深度范围内溶解氧含量随深度增加逐渐降低,在11~14 m深度范围内溶解氧含量急剧降低,14~19 m深度范围内溶解氧含量保持稳定降低,19 m以下急剧降低,并在27 m以下形成稳定的低氧环境,南部湖区的D点0~10 m深度范围内溶解氧含量随深度增加稳定下降,10 m以下溶解氧含量急剧下降。水平方向上北部湖区的溶解氧含量远高于南部湖区,0~12 m深度范围内的溶解氧平均含量A点为8.8 mg/L,B点为8.7 mg/L,C点为8.4 mg/L,D点只有6.9 mg/L。
程海7月的湖水中的溶解氧含量较低,垂向上北部湖区的A点0~3 m深度范围内溶解氧含量较高,3~11 m深度范围内几乎不变,11~16 m深度范围内溶解氧含量急剧降低,16 m以下稳定在0.3 mg/L以下的低氧水平;B点0~6 m深度范围内溶解氧含量基本维持在7 mg/L以上,6~11 m深度范围内溶解氧含量急剧降低,11 m以下稳定在0.3 mg/L以下的低氧水平;C点0~11 m深度范围内溶解氧含量随深度增加缓慢降低,11~17 m深度范围内溶解氧含量急剧降低,17 m以下稳定在0.3 mg/L以下的低氧水平;南部浅水湖区的D点0~9 m深度范围内溶解氧含量基本稳定在7 mg/L左右,9~12 m深度范围内溶解氧含量急剧降低,12 m以下溶解氧含量随深度增加缓慢降低。水平方向上溶解氧含量A、D点相对较高,B、C点相对较低。
4. 讨论与结论
从以上数据分析和变化可以得出,程海水质参数空间和季节性变化十分明显,出现这种情况的原因并非单个水质参数的变化所引起,在对温度、pH值、叶绿素和溶解氧等水质参数做了相关性分析(表1)后可以看出,各个水质参数之间呈明显的显著正相关,尤其pH值和溶解氧之间的相关系数为0.546、温度和叶绿素之间的相关系数为0.391、pH值和叶绿素之间的相关系数为0.391,很好的验证了温度高低影响叶绿素含量多少,以及温度与叶绿素共同作用影响pH值和溶解氧含量 [15] 。
从监测数据和永胜县气象数据(图6)分析来看,大型水体对气温的反馈敏感度较低,水体温度变化总是滞后于气温变化,而降水量则对气温影响较大,2015年10月和2016年10月相比较,前者由于阴雨天数大于后者,所以月平均气温较后者低2.3℃。从整年来看,程海夏秋季南部湖区平均温度高于北部湖区,但在冬春季北部湖区平均温度高于南部湖区,湖泊表层水全年均表现出北部湖区温度高于南部的现状,这主要是由于程海流域常年盛行南风,受风力扰动影响南部浅水区湖水混合较均匀,热力交换频繁,而北部深水湖区较为稳定。由于程海北部深水湖区在夏秋季节出现明显的温度分层,阻碍了上下层水体间的对流交换,影响了N、P等营养盐及光照在水体中的分布,从而对水体溶解氧浓度和水生生物的垂直分布产生影响 [7] - [18] ,继而影响pH值变化,引起水环境质量变化 [14] - [24] 。
程海水体中叶绿素含量与温度呈显著正相关关系,随着温度的升高,水中浮游植物量增加,并且在不同深度范围内出现多次峰值,表现出水生植物种类的多样性与复杂性。水体pH值的变化主要受到

Table 1. The correlation among water temperature, pH, Chlorophyll and ODO in Lake Chenghai
表1. 程海水三体温度、pH值、叶绿素和溶解氧之间的相关性
**在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关。

Figure 6. Weekly mean temperature and precipitation of Yongsheng County in October 2015 - December 2016
图6. 2015年10月~2016年12月永胜县逐周降水量和温度变化
和 含量变化的影响,所以当春季温度升高浮游植物大量生长后,pH值随之升高,但是程海的情况有其特殊性,5月和7月的温度明显高于3月,但pH值却低于3月,这可能是由于这一时期多次水华爆发结束,卷曲鱼腥藻等藻类大量死亡分解所致 [7] [9] 。
含量变化的影响,所以当春季温度升高浮游植物大量生长后,pH值随之升高,但是程海的情况有其特殊性,5月和7月的温度明显高于3月,但pH值却低于3月,这可能是由于这一时期多次水华爆发结束,卷曲鱼腥藻等藻类大量死亡分解所致 [7] [9] 。
冬季程海处于混合时期,良好的水体对流交换使底层水体始终保持较高的溶解氧水平。夏秋季发生的热分层现象,直接阻碍了变温层和滞水层的物质交换,使溶解氧形成分层,湖水温度越高,溶解氧分层越靠近水面,即缺氧水体厚度越大,再加上底泥中硫化物、亚硝酸根、亚铁离子等还原性物质和微生物的长期作用,底泥附近形成厌氧区域,而厌氧条件会加速沉积物中氮磷的释放进而恶化底层水质。伴随着程海热分层的季节性形成和消失,沉积物中不同形态的氮、磷会在强还原条件下释放和扩散不断促进整个湖泊的富营养化,因此在程海保护方面应做好夏秋季节的水质监测工作,提前制定快速应急机制 [3] [14] - [24] 。
基金项目
云南省领军人才项目“云贵高原湖泊演化与水安全”(2015HA024)和高端人才引进项目“云南(云贵高原)湖泊记录与生态环境及可持续发展研究”(2010CI111)资助。