1. 引言
水污染问题对于中国经济的影响相对来说比较严重,而重金属废水污染是最大的污染之一 [1] [2] 。重金属废水是工业生产过程中排放的废水,主要在电镀行业产生的较多,而且重金属废水中的重金属一般很难被分解去除,因此重金属废水对水资源的污染和对人类的危害非常大 [3] [4] 。针对水体重金属污染所采取的处理方法包括:加入化学药剂进行沉淀以及通电电解和膜分离法,利用硫酸盐还原菌对水体净化,利用部分生物的吸附作用进行吸附。这些方法由于耗能大、成本高,在工业生产时效果也并不好 [5] 。
近年来,电絮凝法处理含重金属废水已成为研究热点之一,该方法集氧化还原、絮凝、气浮为一体,其操作简单,处理效率高,节省电能,可同时除去多种污染物及多种重金属离子,具有很好的推广应用价值。F. Akbal等 [6] 研究对比了电絮凝法和化学混凝法对重金属废水的去除效率的影响。结果显示,电絮凝处理重金属废水的效率高、成本低。I. Kabdash等 [7] 以不锈钢作电极处理Zn和Ni电镀电解过程中产生的大量混合重金属废水。结果显示,电絮凝可在相对简单的条件下将Zn和Ni去除率均达到100%。I. Heidmann等 [8] 以穿孔铝板为阳极材料,处理含有Zn、Cu、Ni、Ag和Cr (ΓI)等离子的重金属废水。实验发现Zn、Cu、Ag和Cr可以通过阴极与氢氧根的共同沉淀同时被去除。因此,越来越多低成本、高回报的处理方法受到了追捧和研究。用还原性铁粉进行处理就是一种价廉高效回收方便的方法 [9] [10] 。铁是活泼金属,有较强的还原性,可以将活性排在它后面的重金属置换出来,因此可以用于对重金属废水的处理。近年来国内外的研究发现,还原性铁粉对处理电镀废水中的重金属离子具有较高的去除率,所以其去除重金属离子的适合条件以及影响去除率的因素是研究关键。
对电镀污泥的回收,目前存在很多方法,包括酸浸、氨浸等,但这些技术,不是成本高就是会有很多残渣出现。考虑到这些因素,本文的污泥回收采取的是铁氧体化磁回收处理工艺。铁氧体的干湿法工艺,这种污泥处理方法具有的优点是:在完成了污泥处理后,残渣可以合成性能优异的磁粉检验,这对于工业生产是非常有用的。况且相对于其他的工艺,这个更为简单,效率也高,处理成本也低,对于一些污水处理厂是个很不错的选择。
2. 试验
2.1. 主要试剂和仪器
本实验采用的废水是某公司的电镀废水,该电镀废水只含有锌,镉,浓度均为20 mg/L,不含有其他的金属离子和氰化物。还原性铁粉(Fe,A. R广东台山化工厂),双硫腙(C13H12N4S,A. R上海展云化工有限公司),柠檬酸钠(C6H5O7Na2∙2H2O,A. R北京化工厂),酒石酸钾钠(KNaC4H4O6∙4H2O,A. R广东台山化工厂),丁二酮肟(C4H8N2O2,A.R北京化工厂),锌、镉粒(Zn、Cd,A. R广东台山化工厂),硫代硫酸钠(Na2S2O3∙5H2O,上海荧光材料厂),乙酸钠(CH3COONa∙3H2O,上海化学试剂总厂),乙醇(C2H5OH,95%,上海久亿化学试剂有限公司),四氯化碳、氯仿(CCl4,CHCl3,A. R国药集团化学试剂有限公司),氨水、HCl、HNO3 (A.R上海久亿化学试剂有限公司),乙酸(CH3COOH,A.R上海化学试剂总厂),去离子水(实验室自制)。
仪器:紫外可见光分光光度计(UΓ 5100B,上海元析仪器有限公司),离心机(TDZ4-WS,湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司),pH计(990江苏江环分析仪器),电子天平(TD-2002,上海路达实验仪器有限公司),超纯水机(AKDL-II-16型,成都康宁实验专用纯水设备厂)。烧杯(若干)、玻璃棒、量筒、试管刷、比色皿、容量瓶(若干)、移液管(若干)、注射器1支、分液漏斗(若干)、棕色玻璃瓶(若干)、pH试纸、胶头滴管等等。
2.2. 试验过程
试验采用正交试验法,选用L9(34)正交表,其中分别代表的是A (pH),浓度(B),反应时间(C)和投加量(D),因素与水平如表1,Zn和Cd的测定采用双硫腙分光光度法,测定条件及标准曲线见表2。
根据正交表的试验设计,取9只烧杯依次编号1~9号,根据反应所需的浓度向每支烧杯中加入一定量的电镀废水,最后用去离子水稀释到200 mL,向每组试验加入其所需的投加量,并且调节pH,反应至所需的时间后,用注射器吸取一定量的溶液,通过0.45 um滤膜过滤后,测其滤液的吸光度,对照标准曲线,得出反应后的浓度,根据公式 ,式中:C0为Zn2+和Cd2+的初始质量
,式中:C0为Zn2+和Cd2+的初始质量

Table 1. Factors and levels of orthogonal test
表1. 正交试验因素与水平表

Table 2. Conditions for the determination of Zn and Cd
表2. Zn和Cd的测定条件
浓度,mg/L;Ce为反应平衡结束溶液剩余Zn2+和Cd2+的质量浓度,mg/L,分别计算Zn2+和Cd2+去除率,最佳组合用极差R分析法确定。
2.3. 反应动力学研究
本文研究的反应动力学的反应过程可以用Langmuir-Hinshelwood [11] 动力学模型来描述:
 (1)
(1)
式中:K——固体表面的反应速率常数;b——与固体的吸附热和温度有关的常数。
当反应物浓度很低时 ,(1)式可写成:
,(1)式可写成:
 (2)
(2)
式中,k = Kb,此时,反应简化为一级反应。对(2)式积分得:
 (3)
(3)
即ln(C/C0)与时间t成线性关系,斜率kobs即为表观速率常数。
试验过程:在投加量为75 mg/L,初始浓度为20 mg/L时,在不同的pH的条件下,对于锌,镉分别是在pH为9和5时,初始浓度为20 mg/L时,在不同的投加量的条件下,对于Zn2+,Cd2+分别是在pH为9和pH为5时,投加量为75 mg/L,在不同初始浓度的条件下,分别测其在不同时间下的反应后的吸光度,通过标准曲线得到反应后的浓度,最后根据公式计算斜率kobs,绘制分析图。
3. 结果分析与讨论
3.1. 正交试验结果分析
分析采用极差分析法,正交试验结果分析见表3。
从表3看出,对锌和镉离子的去除率的影响的主次关系是,溶液的pH、还原性铁粉的投加量、金属离子浓度和反应时间。对于镉来说,当pH为5的时候去除率明显较高,当pH逐渐增大的时候,去除率越来越低,而废水的浓度和反应时间影响并不明显,尤其在碱性的时候,去除率最低。由表3中去除锌的最佳组合条件为A1B3C3D2,具体条件为镉去除率的最佳组合是,pH为5,浓度20 mg/L,反应时间1.5 h以上,投加量为50 mg/L,在这种条件下的验证试验,镉的去除率为98.2%,大于第3组试验条件下的96.8%;对于去除锌来说,当pH为9的时候去除率明显较高,当pH逐渐增大的时候,去除率越来较高,尤其在碱性的时候,去除率普遍都很高,由表3中去除锌的最佳组合条件为A3B3C1D3,具体条件为pH为9,浓度20 mg/L,反应时间0.5 h以上,投加量为75 mg/L,经过在这种条件下的验证试验,锌去除率为95.4%,大于第8组试验条件下的93.4%,均可以达到排放标准。为了操作方便可行,最后采用的条件为在锌镉离子浓度为20 mg/L,反应时间1.0 h以上,铁粉投加量为75 mg/L,先在pH = 5除去镉后,再在pH = 9下去除锌,都可以达到排放标准。
3.2. pH对锌、镉去除率的影响
为了更好的研究pH对锌、镉去除率的影响,控制废水的初始浓度为20 mg/L,投加量为75 mg/L,反应时间1 h,pH的调节范围为5,7,9。pH对锌,镉去除率的影响如图1所示,从图1中可以很明显地看出,随着pH的增大,锌的去除率逐渐增大,而镉的去除率逐减小。其中在pH为5时,镉的去除率

Figure 1. Effect of pH on removal rate of zinc and cadmium
图1. pH对锌,镉去除率的影响

Table 3. Result of orthogonal experiment
表3. 正交试验结果
达到了90%以上,而在碱性时,就只有50%左右了。与之相反的是其中在pH为9时,锌的去除率达到了90%以上,而在酸性时,就只有50%多了。实验表明酸性条件更有利于还原性铁粉对镉的去除,这是因为,增大H+浓度将使得反应向有利于镉还原的方向进行,促进了镉的还原。而在碱性条件下,铁表面易氧化生成氢氧化铁或碳酸铁钝化层,使铁的反应活性降低。但是在碱性的条件下更有利于锌的去除,这是因为混凝,OH−的涌入使Fe3+与Zn2+变成絮凝物,而Fe(OH)3,有吸附的功能,对锌的去除更有利。
当Zn2+和Cd2+的初始浓度均为20 mg/L,还原性铁粉的投加量为75 mg/L,对于不同的pH值,还原性铁粉与Zn2+和Cd2+反应动力学拟合曲线如图2所示,表观反应速率常数见表4。
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 2. Reaction kinetics of reduction of zinc and cadmium with reduced iron powder at different initial pH
图2. 不同初始pH下还原性铁粉去除锌(a)和镉(b)的反应动力学曲线

Table 4. Apparent reaction rate constants of iron powder with Zn2+ and Cd2+ reduction reaction under different pH
表4. 不同pH下还原性铁粉与Zn2+和Cd2+反应的表观反应速率常数
从表4可以看出R2的值为别为0.91757,0.91114和0.98481,说明ln(C/C0)与t呈现出良好的线性相关性,因此在不同pH条件下,还原性铁粉对废水中Zn的还原过程均符合准一级反应动力学。
另外,反应速率常数在pH为5时,是0.915,pH为7时是1.063,而在pH为9时是1.246。说明反应速率随着pH的增大而增大,因此酸性条件并不有利于锌离子的去除,碱性条件对锌离子的去除效果最好。原因在于Fe的活泼锌并没有Zn的好,所以Fe不可能把Zn从溶液中还原出来。在酸性条件下,虽然产生了产生的[H],但它并不会还原锌,所以在酸性条件下的反应速率是最低的。对于锌的去除最好的是在碱性的条件下,因为碱性时可以提供OH−,从而产生混凝,产生Fe(OH)3絮凝物,对锌有吸附作用,从而达到去除。综上所述:在弱碱性条件用还原性铁粉对于锌的去除是最好的。
从表4可以看出R2的值为别为0.98026,0.97596和0.90956,说明ln(C/C0)与t呈现出良好的线性相关性,因此在不同pH条件下,还原性铁粉对废水中Cd的还原过程均符合准一级反应动力学。反应过程中,当将铁投进溶液中后,因为在酸性条件下,所以,部分铁会和H+反应从而会生成[H],这种[H]的产生会对反应有促进效果,也就是会加快镉的还原。然后,大部分的铁粉是会和溶液中的镉离子反应的,铁将镉离子还原。所以在这种双重的还原的作用下,溶液中的镉离子得到大量的去除。随着pH的增加,溶液中有大量的OH−涌入,虽然可以使部分镉变成沉淀,但是并没有[H]的还原,所以去除效率并没有在酸性时候的好。
3.3. 投加量对Zn2+ 和Cd2+ 去除率的影响
为了更好的研究投加量对Zn2+和Cd2+去除率的影响。控制废水的初始浓度为20 mg/L,Zn2+的pH为9,Cd2+的pH为5,反应时间都为1h,投加量的调节范围为25 mg/L,50 mg/L,75 mg/L。投加量对Zn2+和Cd2+去除率的影响如图3所示,从图3中可以看出,随着样品投加量的增加,Zn2+和Cd2+的去除率逐渐的增加,因为,在投加量为0.025 mg/L时,反应还没有达到饱和,再继续增加投加量有更多的离子被去除。在投加量为0.025 g/L时,Zn2+和Cd2+去除率都较低。投加量为0.05 g/L时,Zn2+和Cd2+的去除率下相比与0.025 g/L有明显的增加。继续增加投加量到0.075 g/L时,去除率达到了最大。所以,投加量对去除率的影响也是比较显著的 。
当Zn2+的初始浓度为20 mg/L,反应pH为9的时候,对于不同的投加量,其动力学拟合曲线如图4(a)所示。当Cd2+的初始浓度为20 mg/L,反应pH为5的时候,对于不同的投加量,其动力学拟合曲线如图4(b)所示,不同投加量下还原性铁粉与Zn2+和Cd2+反应的表观反应速率常数见表5。
从表5可以看出,随着还原性铁粉投加剂量的增加,Zn的表观反应速率常数提高,二者的变化呈现较好的线性关系。当还原性铁粉投加量为25 mg/L、50 mg/L和75 mg/L,Zn的kobs值分别为1.805,1.314和1.246,R2值分别为0.9211,0.90157和0.98481;Cd的kobs值分别为0.739,1.448和2.1,R2值分别为0.98206,0.98025和0.98781。影响Zn2+和Cd2+去除反应动力学的另一重要因素为还原性铁粉的投加量,溶液中还原性铁粉剂量的增加增大了其总的比表面积以及相应的反应位点,从而为Zn2+和Cd2+提供了更多的接触机会。因此,去除时间因素的影响,当还原性铁粉的投加量越大,反应速率越快。

Figure 3. Effect on the removal rate of zinc and cadmium of dosage
图3. 投加量对锌,镉去除率的影响
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 4. Reaction kinetics curves of iron powder with Zn and Cd reduction reaction in different dosage
图4. 不同投加量下还原性铁粉与(a) Zn2+和(b) Cd2+的反应动力学曲线

Table 5. Apparent reaction rate constants of iron powder with Zn2+ andCd2+reductionreaction under different dosage
表5. 不同投加量下还原性铁粉与Zn2+和Cd2+反应的表观反应速率常数
3.4. 初始浓度对锌、镉去除率的影响
为了更好地研究废水初始浓度对锌,镉去除率的影响,先控制镉的pH为5,再调节到锌的pH为9,反应时间都为1 h,投加量为75 mg/L,初始浓度范围为5 mg/L,10 mg/L,20 mg/L。初始浓度对锌,镉去除率的影响如图5所示,从图5中可以看出不同初始浓度的废水也会对反应物之间的接触产生影响,从而使反应效果受到影响。随着初始浓度的不断增加,锌,镉的去除率在不断的增大。其中,初始浓度为5 mg/L时,去除率只有70%左右,浓度为10 mg/L,去除率增加到了80%多,浓度为20 mg/L,去除率最大,达到了90%多。
当还原性铁粉的投加量为75 mg/L,反应pH为9的时候,对于不同的Zn2+溶液的浓度,其动力学拟合曲线如图6(a)所示。当还原性铁粉的投加量为25 mg/L,反应pH为5的时候,对于不同的Cd2+溶液的浓度,其动力学拟合曲线如图6(b)所示。还原性铁粉与不同Zn2+和Cd2+浓度下反应的表观反应速率常数见表6。
从表6中的数据可以看出R2的大小分别是0.91009,0.90476和0.98481。说明在不同的Zn2+初始浓度下还原性铁粉对Zn2+和Cd2+的去除有较好的相关性。当Zn2+和Cd2+均浓度为5 mg/L时,Zn2+和Cd2+的kobs分别为0.833和1.542;最大的是在Zn2+和Cd2+均10 mg/L时,分别达到了1.251和2.852,而在Zn2+和Cd2+浓度为20 mg/L时,Zn2+和Cd2+的kobs分别只有1.246和0.739,从表3可以看出Zn2+的初始浓度在10 mg/L和20 mg/L时,它的kobs相差不大,说明初始浓度并不是影响还原性铁粉去除的关键因素,而对于Cd2+在浓度由10 mg/L变成20 mg/L时,kobs的变化较大,反应了Cd2+初始浓度是影响还原性铁粉去除Cd2+的较重要因素。
3.5. 反应机理分析
在弱酸性的条件下,向废水中加入铁粉,部分的铁粉会与溶液中的H+生成氢气,但是反应过程较慢,且产生的氢气量并不多。而其中大部分的铁粉会和废水中的Cd2+等重金属离子反应,铁将其还原。而对于锌来说,铁并不能将其还原,只能是混凝,所以,在酸性条件下去除锌的效果没有在碱性的条件好。在中性的条件下,并不会有氢气产生,而是所有的铁都用于还原废水中的重金属离子。反应机理表示如下:
 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
在碱性的条件下,向废水中加入铁粉,Fe先和废水中的重金属离子反应,生成Fe2+,Fe3+。碱溶液提供的OH−,其中有一些OH−与废水中的重金属离子反应生成对应的沉淀,例如:Zn(OH)2,Cd(OH)2等。还有一些OH−与Fe2+,Fe3+生成Fe(OH)2或Fe(OH)3絮凝物,其中Fe(OH)3具有一定的吸附能力。可以看到是砖红色的沉淀,说明一定存在Fe(OH)3,其他的铁的(氢)氧化物也可能存在。而可以被磁铁吸引说明

Figure 5. Effect on zinc and cadmium removal rate of initial concentration
图5. 初始浓度对锌、镉去除率的影响
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 6. Reaction kinetics curves of Zn removal at different initial concentrations of Zn
图6. 不同初始浓度下去除Zn2+和Cd2+的反应动力学曲线

Table 6. Apparent reaction rate constants of iron powder with different initial concentrations of Zn2+ and Cd2+ reduction reaction
表6. 还原性铁粉与不同Zn2+ + Cd2+浓度下反应的表观反应速率常数
产物中含有磁性物质,可能还有没有反应完的铁存在。铁氧化物的磁化顺序:磁铁(Fe3O4,σ = 90~92) > 赤铁(γ-Fe2O3,σ = ~80) > 纤铁矿(γ-FeOOH,σ < 10) > 针铁矿(α-FeOOH,σ < 1) > 赤铁矿(α-Fe2O3,σ = 0.4) > 六方纤铁矿(δ-FeOOH) [12] 。如表7所示,是铁的部分氢氧化物和氧化物 [13] 。反应机理表示如下:
 (6)
(6)
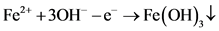 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
 (9)
(9)
 (10)
(10)
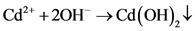 (11)
(11)
3.6. 反应产物回收
如图7所示,向溶液中滴加适量的氨水,再用玻璃棒搅拌一会,一段时间后,溶液变成了棕黄色,继而有絮凝物产生。由图7所示,絮凝物逐渐沉积到烧杯底部,并用磁铁吸引,可以看到所有的沉淀物都聚于被吸引的地方,而溶液的其他地方是澄清的。
对于反应后产物的猜想,表7是铁的氢氧化物和氧化物。试验最后的产物是会被磁性吸附的但又不是很强,所以铁的氢氧化物可能带有弱磁性。现在对铁的氢氧化物和氧化物之间的关系进行分析,不同的条件下铁的氢氧化物和氧化物之间也会发生转化像在弱碱性的条件下,含有Fe3+溶液水解都生成二线水铁矿(Fe5HO8∙4H2O);如果碱性增强,Fe5HO8∙4H2O就会转化为α-FeOOH相;这里所提到的Fe3+溶液,其中包含FeCl3和Fe(NO3)3溶液。但是Cl−离子更有利于β-FeOOH的形成、而NO3−离子有利于α-FeOOH的形成,但是 会阻碍Fe5HO8∙4H2O向α-FeOOH相转化。加热陈化可促进Fe5HO8·4H2O转化为α-FeOOH,且有利于良好结晶α-FeOOH的形成;在酸性条件下,含有Cl−的铁盐溶液加热水解有利于β-FeOOH的生成。
会阻碍Fe5HO8∙4H2O向α-FeOOH相转化。加热陈化可促进Fe5HO8·4H2O转化为α-FeOOH,且有利于良好结晶α-FeOOH的形成;在酸性条件下,含有Cl−的铁盐溶液加热水解有利于β-FeOOH的生成。
4. 结论
1) 还原性铁粉去除锌、镉的主要影响因素有:初始pH值,样品的投加量和锌、镉的初始浓度。镉的最佳组合是pH为5,浓度为20 mg/L,铁的投加量为50 mg/L,反应时间达到1.5 h以上时,此条件下镉的去除率最高达到98.2%;锌的最佳组合是pH为9,浓度为20 mg/L,铁的投加量为75 mg/L,反应时间达到0.5 h以上时,此条件下锌的去除率最高达到95.4%。为了操作方便可行,最后采用的条件为在锌镉离子浓度为20 mg/L,反应时间1.0 h以上,铁粉投加量为75 mg/L,先在pH = 5除去镉后,再在pH = 9时去除锌,都可以达到排放标准。

Figure 7. Produces yellow precipitate (a) at the end of the reaction and magnetic recovery (b)
图7. 反应结束产生黄色沉淀(a)和磁力回收(b)
表7. 铁的氢氧化物和氧化物
2) 还原性铁粉还原去除锌、镉的体系符合准一级反应动力学。影响锌、镉去除反应速率的主要因素有:初始pH值,锌、镉的初始浓度,样品的投加量。实验结果表明,反应速率随着锌的初始浓度、pH值和投加量的增加而升高,随着镉的初始浓度和pH值的升高而降低,随着还原性铁粉投加量的增加而升高。
3) 在不同条件的下反应产物是不同的,酸性中性条件下,铁把废水中的重金属还原,自己变成离子状态。而在碱性条件下,发生化学反应产生沉淀,有絮凝物产生,这些絮凝物可能是众多反应物的沉淀,并且可以磁性分离和回收,进一步得到应用。
基金项目
国家自然基金项目(56218018)。
NOTES
*通讯作者。